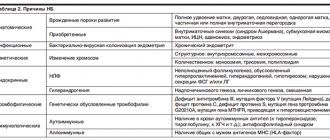
About 16% of women face the disappointing news of a missed pregnancy every year. The fetus dies, but remains in the uterus, and the patient’s ability to have children later depends on how skillfully and carefully it is removed. We will tell you in the article how to clean after a frozen pregnancy.
Ultrasound is now recognized as the most informative and reliable method for detecting pathology in the early and late stages of pregnancy. Unfortunately, it is impossible to resuscitate and save the fetus, so by treating the pathology, doctors mean promptly ridding the patient of pregnancy.
How is curettage performed and what happens to the uterus?
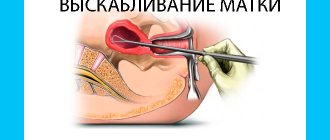
Curettage is performed blindly using gynecological instruments. In some cases, special equipment is used - a hysteroscope, with which the doctor can control the manipulations. This allows you to determine the exact location of the tumors and carry out cleaning carefully and without complications. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Scraping lasts about 15–30 minutes. At the initial stage, using a special instrument, the doctor opens the cervix. Next, he inserts a curette (a miniature spoon-like instrument) and removes the top layer of epithelium lining the inner walls of the uterus. The material is sent for histological analysis, based on the results of which treatment is prescribed.
How is curettage done?
Anesthesia ensures a complete absence of unpleasant sensations. If there are contraindications, local anesthesia is used.
After the anesthesia begins to take effect, the doctor’s actions are as follows:
- genitals are disinfected;
- a gynecological speculum is inserted;
- the vagina and cervix are treated;
- a special substance is introduced that stimulates uterine contractions and endometrial rejection, which greatly simplifies the procedure;
- a curette is inserted into the uterus - a surgical spoon for curettage, with the help of which the organ is cleansed from the fertilized egg and the upper layer of the endometrium;
- instruments are removed from the vagina.
After the operation, the woman is taken to the ward.
The uterine curettage procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
Why does pain occur after brushing?
Cleaning done professionally and in compliance with all antiseptic rules rarely causes complications. However, in the first days after it, many patients are interested in why their lower abdomen hurts. If the pain is not severe, this is normal. At the site of the removed mucous membrane, a wound surface remains that bleeds. Gradually it tightens, the endometrial layer is completely restored within 2 weeks.
In order for healing to proceed without complications, it is recommended to avoid constipation, sexual intercourse, and excessive stress on the abdominal area. Bleeding does not differ from menstrual bleeding, it gradually decreases and stops after 3–5 days.
Pathological pain in the lower abdomen and ovarian area due to cleaning and curettage of a frozen pregnancy causes:
- perforation (puncture) of the uterine body;
- tear of the neck of a muscular organ;
- endometritis (inflammatory process);
- accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity;
- traumatization of the mucous membrane due to ineptly performed manipulations.
Doctors attribute the fact that the back or lower back hurts after curettage not only to physiological reasons. How long can the pain normally last? When recovery is normal, the pain goes away within 2-3 days. If a woman does not observe a rest regime or experiences physical exertion, the pain may intensify. When pain is accompanied by bleeding, painful spasms, fever and other symptoms, endometritis should be excluded, in which pain and disturbances in the discharge pattern are often observed.
Curettage after abortion
The reasons for removing the endometrial layer are spontaneous miscarriage and complications after abortion. Such manipulations are necessary in cases where embryo particles remain in the organ.
After cleaning the uterus, a woman notes that she has pain in her lower back, as well as her lower abdomen, and spotting appears. They will be observed until the process of restoration of the cervix and the reproductive organ itself is completely completed. Sometimes the temperature rises after curettage. With such changes, doctors prescribe antibiotics. With their help, it is possible to prevent the development of inflammation.
How to relieve pain and when should you see a doctor?
To prevent pain and hematometra (accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity), it is recommended to take No-Shpa tablet 2-3 times a day for 3 days. To prevent complications, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, which should also be taken according to the schedule for 5 days. Pain after curettage is relieved with Nalgesin and Ibuprofen. In this case, it is important for a woman to carefully monitor her condition and consult a doctor if she has the following symptoms:
- heavy bleeding;
- the stomach hurts and cramps are observed after curettage of a frozen pregnancy;
- chills;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- heat.
Pain after curettage can persist for up to 5 days - this is considered a normal reaction of the body to the intervention. To avoid postoperative complications, it is important to carefully choose a clinic and trust an experienced gynecologist to perform the procedure.
Painful sensations after getting rid of a non-developing pregnancy with adequate pain relief during the procedure are quite tolerable. Not comparable to those that occur after abdominal surgery. However, you can get rid of them too.
Pain after curettage of the uterine cavity, performed for a missed pregnancy or miscarriage, is a common occurrence. But nevertheless, some women manage to avoid it. This difference in well-being is due to several reasons:
- pain threshold;
- pain relief during the procedure;
- individual characteristics (uterine contractions).
The downside of any strong painkillers is their negative impact on the stomach and intestines - nausea, vomiting, bloating are common side effects. But with a single use everything should be fine, the main thing is not to take painkillers repeatedly over a short period of time.
It happens that the stomach does not hurt and there is no discharge after curettage of a non-developing (frozen) or interrupted pregnancy. But this is often not a positive symptom, but indicates a probable spasm of the cervical canal (cervix) and accumulation of blood in the uterus. A doctor can diagnose this symptom by palpating the abdomen. An enlarged uterus is detected. Well, the diagnosis is confirmed by ultrasound, which must be done before discharge from the gynecological department. If you do not do an ultrasound and vacuum aspiration or repeated cleaning of the uterus, after 2 weeks or a month, or maybe even a few days after the procedure, severe uterine bleeding will begin, the body temperature will rise, and pain in the lower abdomen will appear. These are all signs of acute endometritis, requiring urgent medical attention and active treatment with antibiotics.
How long do you have to stay in the hospital to avoid such complications after cleaning? Much depends on the probable cause of what happened. If it is an acute bacterial or viral infection, there is a high risk of ascending infection - at least 5-7 days.
If for some reason the fetus freezes inside the mother’s womb, then it is important to do everything necessary to maintain the woman’s health. Curettage during a frozen pregnancy is a vital procedure. It is carried out in order to remove the fetus and its membranes from the body. However, cleaning is far from being a harmless operation, as some might think. After all, it can provoke pain and the development of some complications (infection, bleeding).
How is cleaning done during a frozen pregnancy?
If the fetus has no signs of life, the doctor determines how to remove it:
- through spontaneous abortion in the first weeks after conception, when the reproductive system itself gets rid of the clot of cells that has lost its viability and brings it out;
- with medical assistance. If the pregnancy is frozen at a long term, you cannot hesitate - soon after the death of the fetus, decomposition products affect the mother’s body in the most destructive way.
Cleaning during a frozen pregnancy through miscarriage
If the fetus stops developing at the very beginning of pregnancy (before the 12th week), then doctors prefer to do nothing and monitor the woman for 2 to 4 weeks. During this time, the amount of hCG drops, as a result of which the muscles of the uterus, under the influence of tone, push out unnecessary contents.
After this, the woman is given an examination to determine the degree of cleansing of the uterine cavity. Timely removal of remnants of dead biomaterial using curettage prevents the development of an inflammatory reaction and infection. Self-cleaning of the uterus during early frozen pregnancy is the most favorable outcome for a woman’s health.
Cleaning during a frozen pregnancy using medical abortion
If the fertilized egg died before the 8th week of its existence, drug cleansing of the frozen pregnancy will help speed up the cleansing of the uterus from dying tissue. For this purpose, the drugs Mifepristone and Misoprostol are used. The activity of the active components of these drugs is aimed at stimulating the contractility of the uterus and the development of miscarriage. As in the case of expectant management of pregnancy, the remains of the fetus (if any) after medical abortion are removed by curettage.
Cleaning during a frozen pregnancy using curettage
Very often, the consequences of a frozen pregnancy are eliminated with the help of curettage, or curettage. However, it cannot be said that this procedure is completely safe: during the operation there is a high probability of tissue trauma and, accordingly, the development of complications.
Mechanical cleaning during a frozen pregnancy takes place under general anesthesia: the uterus is opened with the help of dilators and a special instrument is inserted into its cavity through the cervical canal, which is used to clean off the functional upper mucous layer from the inner surface of the organ. After the surgical abortion is completed, the patient is administered Oxytocin to speed up the process of returning the uterus to its previous shape and condition.
The woman is recommended to spend the next few days in a hospital under the supervision of specialists. The curettage operation does not guarantee the absence of bleeding or the development of extensive inflammation.
Cleaning during frozen pregnancy using vacuum aspiration
Vacuum aspiration is performed under both general and local anesthesia. The fertilized egg is removed from the uterus using vacuum suction. The operation can be performed “blindly” or accompanied by ultrasound. In the second case, the procedure is more effective. After completing vacuum aspiration, the patient rests for 1 hour lying on her stomach under the supervision of a doctor.
Among the advantages of this cleaning method are the low trauma to the internal genital organs and the ability to avoid general anesthesia. However, the procedure also has disadvantages in the form of incomplete abortion and a number of complications:
- penetrating damage to the cervix or body of the uterus;
- inflammatory reaction;
- hormonal disbalance;
- significant disorder of the monthly cycle;
- secondary infertility.
Cleaning during frozen pregnancy through childbirth
Most cases of frozen pregnancy are recorded in the early stages, but it also happens that the fetus dies in the second and even third trimester. Terminating a late pregnancy that is frozen is a serious psychological test for a woman.
Doctors mostly refuse to remove the fetus by caesarean section due to the fact that dead tissue can become infected. In addition, a woman may subsequently have problems with pregnancy and natural delivery. To terminate a non-developing pregnancy at a long term, artificial stimulation of labor is performed.
The woman goes to the hospital the day before the procedure. To carry out an emergency birth, doctors act as follows:
- 24 hours before delivery, kelp sticks are inserted into the pregnant woman’s cervical canal. The substance swells and thus gradually and gently expands the cervical canal;
- To stimulate uterine contractions, the patient is given an injection of Oxytocin or prostaglandins are injected in one of the available ways: intravaginally, into the uterus or into the amniotic fluid. Labor will gradually gain momentum, since the woman’s body was simply not ready for it. Sometimes this process lasts for several days;
- when the time comes, the woman gives birth to a fetus;
- If during the examination remains of dead tissue are found in the uterus, the organ cavity is finally cleaned out by curettage or vacuum aspiration.
Artificial birth during a frozen pregnancy is associated with several difficult moments for the woman in labor:
- the procedure can take up to several days;
- dilation of the uterus causes severe pain, which is not eliminated with painkillers so as not to reduce the intensity of contractions;
- For the same reason, the woman in labor is not given anesthesia, and she is forced to give birth to the dead child on her own.
Complications after curettage
Most women who have been prescribed uterine cleansing after a confirmed frozen pregnancy are afraid not of the procedure itself, but of its consequences. They are worried about how curettage will affect the ability to bear a child during subsequent conceptions, how painful the procedure is, and what complications there may be.
Just 30 years ago, the curettage procedure was considered deadly. As a result of unskilled manipulations, the mortality rate among women reached 9%, complications were diagnosed in 20%. That is, every fifth woman who decided to have an abortion became infertile.
The qualifications and experience of the gynecologist play a fundamental role. After all, a woman’s well-being, as well as her chances of carrying a new pregnancy, depend on the professionalism of the doctor. Today, the statistics of dangerous consequences are not so frightening, but it is worth knowing in advance about the occurrence of possible complications.
New pregnancy
Pregnancy after a frozen pregnancy must be approached with all responsibility! Necessary:
- fully recover after the procedure;
- find out the cause
of the pathology; - undergo a course of treatment;
- prepare the body for a new conception.
The first question that arises in a woman after curettage is whether it is possible to get pregnant after a frozen one? The answer is yes, but there are conditions:
- curettage must be carried out on time so that suppuration does not have time to affect the uterus and all reproductive organs remain healthy;
- establish and eliminate the cause of the fading;
- hormonal levels must correspond to standards;
- endure the rehabilitation course and not become pregnant until its completion;
- undergo a course of recovery from psychological trauma, if necessary. Morale is very important and can cause miscarriage or death.
An important point - when can you get pregnant after a frozen pregnancy? The recommended period is to withstand from one to two years,
depending on individual characteristics.
During this period, the body will probably recover, you will be able to get rid of all bad habits, your diet will improve, and your hormonal levels will return to normal.
The second important aspect is how long before you can prepare for re-fertilization? After half a year - not earlier.
In 6 months, most pathologies leading to freezing are cured, or most of the course of their treatment is completed. The overlap of courses of therapeutic and preparatory therapy can lead to undesirable consequences.
Preparing for pregnancy
after frozen suggests:
- quit bad habits;
- get out of depression;
- take vitamins;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- watch your diet.
Abdominal pain after cleansing
Soreness in the groin or umbilical area of the abdomen immediately after curettage is normal.
Evacuation of pregnancy remains is carried out using a special metal mirror, which provides access to the cervix. After opening the cervix (not softened), a manipulation is performed to clean out the inside of the uterus (cavity) using a curette. The procedure itself is very traumatic for the delicate tissue of the organ, and therefore there is a risk of complications.
Most complications after cleansing a frozen pregnancy occur due to damage to the cervix. This occurs because an unprepared organ is forcibly expanded with special instruments.
Dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen is considered normal if the woman can tolerate the pain and the abdomen is soft to palpation. And also if there are no signs of complications: fever, chills, spasms with sharp increasing pain in the groin.
After cleaning a frozen pregnancy, the medical staff applies a cold compress to the lower abdomen to increase the intensity of contractions of the uterine body. If after surgery or during the first 24 hours the temperature rises and pain increases, then all this may indicate the development of complications in the postoperative period.
Increasing abdominal pain against a background of high temperature indicates a number of disorders:
- The presence of a focus of infection in the reproductive organs. As a rule, mucous membranes are susceptible to the development of pathogenic flora: vagina, cervix, endometrium.
- Incomplete cleansing of the uterine body from possible accumulations of remnants of the fertilized egg or embryo.
- Tear or damage to the cervical canal of the cervix.
- Hematometra, formed as a result of the accumulation of blood in any quantity. For the development of the inflammatory process, even one small clot that does not come out is enough. The first symptoms, as a rule, appear a little later: on the second - third day after cleansing.
- Inflammation of the uterus. Occurs in case of excessive pressure on the tissue during the cleaning process (insufficient opening of the cervix, the doctor makes more effort).
In fact, all of these complications, provided that the woman in labor did not have any obvious symptoms before curettage, are the result of medical negligence.
Moreover, before cleaning, a woman undergoes a series of studies and tests that show the presence of pathologies and foci of infection. Trauma to the cervix (tear, crack) in 85% of cases occurs as a result of the forceps coming off or excessive pressure on the tissue during the cleaning period.
An increase in temperature is the body’s reaction to developing inflammation. The uterine cavity after surgery is a continuous bleeding wound, susceptible to any infection. Therefore, a woman should pay close attention to her health after curettage.
Vacuum antiseptic filling of the uterine cavity is a mandatory procedure that prevents the formation of pathogenic flora after curettage.
It is not necessary to use non-sterile instruments (which is impossible); even specially treated instruments do not guarantee that pathogenic flora will not grow. Here the woman’s body and her immune defense play a primary role.
The listed complications can be easily avoided if the surgical cleaning of a frozen pregnancy was carried out correctly, in compliance with all requirements. The natural process is bleeding immediately after curettage, which is observed for two weeks.
The duration of abdominal pain is also justified by the presence or absence of a pathological process. If all manipulations were carried out carefully, and the woman complies with the rules of the postoperative period, then the pain should go away within five days. You may be concerned about:
- prolonged abdominal pain of any nature (more than a week);
- discharge of varying intensity;
- purulent discharge, large amounts of blood;
- temperature;
- headache, migraine;
- swelling of the limbs;
- pain on palpation of the abdomen, slight bloating.
The most dangerous complication after curettage is removal of the uterus. This complication is observed only in 2% of women with pathologies of pregnancy.
If pathogenic flora is present, the doctor will prescribe an additional course of antiseptics and antibiotics or intravenous administration of drugs that block the spread of infection.
Abdominal pain, blood and fatigue after curettage are normal. Symptoms such as purulent discharge, high fever, spasms with acute intolerable pain should alert you. Any complications cause anxiety in women, but fortunately they are treated. If after cleaning there are no negative signs, then after two weeks the uterus contracts and the mucous membrane returns to normal.
Possible complications
The development of complications can be suspected if the bleeding does not stop for more than a week and a half and does not decrease in volume. Also, undesirable consequences are indicated by weakness, pain in the lower abdomen and fever after hysteroscopy.
Bleeding from the uterus
During the treatment of gynecological pathology, bleeding may begin after cleaning. During surgery, the cervix and organ cavity are injured, due to which they cannot fully function. Among the main signs of the development of this complication are the following:
- no brown discharge;
- the blood is scarlet in color, does not look like normal menstruation, there are a lot of clots in it;
- hygiene items have to be changed every hour;
- moderate or severe pain in the abdominal area;
- pale skin;
- severe dizziness, and in some cases loss of consciousness.
If these symptoms appear, urgent hospitalization is required. This condition poses a threat not only to a woman’s health, but also to her life.
Inflammation in the endometrium
After curettage of the cervix and reproductive organ, an endometrial disease such as endometritis may develop. This is due to the fact that during the recovery process after surgery, the uterus becomes more susceptible to various diseases. Pathogenic microorganisms can easily enter it and provoke the development of inflammation.
The main clinical manifestations of the pathology are the following:
- hyperthermia;
- feeling of chills;
- abdominal pain;
- general malaise and weakness;
- the appearance of uncharacteristic secretion.
In the treatment of this disease, antibiotics are prescribed.
Hematometer
If, during the process of restoration of the uterus, the discharge completely stopped or sharply decreased in volume, the development of this pathological condition can be suspected. Hematometra occurs after curettage due to spasm of the cervical canal and the creation of an obstacle to the normal outflow of blood. In this case, the discharge may acquire an unnatural color and an unpleasant odor, and if infection occurs, chills and severe pain in the lower abdomen are observed.
With the development of this pathological condition, urgent hospitalization is required. During the therapy, Longidaza suppositories, antimicrobial and antispasmodic medications are used. Repeated cleaning is also carried out.
Comments
Take painkillers, nothing bad will happen if everything is fine on the ultrasound.
I had an ultrasound. You are right, all these are features of the body) painkillers and that’s it)))
That's good) Good luck next time!
Did you have it cleaned by curettage or vacuum? They offered me pills. It's called Medical Termination of Pregnancy.
Vacuum. Doctors need cytogenetics
Were you prescribed any pills? I had a cleanse 3 weeks ago. For a week after it I took antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The discharge, very scanty, lasted exactly 14 days, my stomach was tight periodically for the first week... the doctor said that all this was within the normal range... if you're worried, go for an ultrasound. I haven't been yet, I'll go next week, I'm a little worried myself.
I drink everything. And antibiotics and anti-inflammatory. But I have such pain in my stomach that I can’t get up ((
Well, yes, you obviously need an ultrasound. Just don’t worry, because everyone has different symptoms in the first 2 weeks. The uterus may be contracting strongly to get rid of the remnants. Please write what they tell you on the ultrasound.
Metroendometritis
Metroendometritis is a combined inflammation of the mucous and muscular layers of the uterus. After cleaning, pathology is formed relatively rarely. The cause of metroendometritis is the penetration of opportunistic microflora into the uterine cavity from the vagina or fallopian tubes, as well as pathogenic microorganisms and the patient’s failure to comply with the antibiotic regimen.
With metroendometritis, both the endometrium and myometrium are involved in the pathological process.
After infection penetrates into the uterine cavity, the endometrium is involved in the pathological process and only later, as a result of the penetration of infectious agents into the deeper layers, does the muscle layer (myometrium) become inflamed. In most cases, metroendometritis is formed precisely after curettage (cleaning), since it is during the procedure that severe damage to the endometrium occurs.
Symptoms
Metroendometritis occurs differently in all women, but certain symptoms still exist. It is worth including these.
- Pain in the projection of the uterus. In acute endometritis, pain is eliminated with the help of painkillers, but after the myometrium is involved in the pathological process, the pain becomes unbearable. They radiate to the lumbar region, groin or rectum.
- Serous-purulent discharge, which is determined during a gynecological examination.
- Vaginal discharge that looks like meat slop.
- Soreness of the uterus on palpation. An attempt to palpate the uterus is accompanied by severe pain.
Symptoms of acute metroendometritis can develop three to four days after completion of uterine cleansing.
In order to prevent inflammation, after cleaning the uterus, a woman must take medications from the category of antibiotics. An increase in temperature after curettage is an unfavorable symptom that requires qualified medical advice.
Inflammation of the uterus can lead to the spread of microorganisms to the ovaries and tubes, which can lead to the development of adhesions and infertility. Serious complications such as peritonitis and sepsis pose a danger to a woman’s life, therefore, if the temperature rises after curettage, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help.
After a frozen pregnancy
Gradually the body should return to a normal state. For example, menstruation should begin on time, although a delay of up to one and a half months is within the normal range.
It can be triggered by stress.
If deviations from the usual timing occur, internal inflammation may be to blame.
Can the temperature rise after a frozen pregnancy?
However, a number of deviations from the norm are also possible, which should be paid attention to. One of these indicators is temperature, which in many cases can be a signal of the development of a pathological process.
In some cases, particles of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus, and then internal inflammation may develop. Here they usually play it safe and undergo a control ultrasound examination a week and a half after curettage.
Signs of inflammation after a frozen pregnancy
However, inflammation is still possible. It has a number of characteristic symptoms. This is, in particular, brown discharge that begins later than the second week after curettage. When inflamed, these discharges are accompanied by pain and an increase in temperature. This condition requires immediate medical attention. A symptom of inflammation that requires medical treatment is yellow discharge. The reaction to injury during curettage may be abdominal pain, but it may also be short-term pain in the form of contractions.
There may be no discharge, but there will be pain in the lower abdomen, indicating blood retention in the uterine cavity. The combined manifestation of pain with bleeding can signal perforation of the uterine wall and retention of fragments of the fertilized egg. All these complications can be accompanied by an increase in temperature.
Possible consequences after curettage
The consequence of curettage after a frozen pregnancy can be, which is an inflammation of the lining of the uterus. If the results of curettage are not corrected, this is fraught with blood poisoning; naturally, all these conditions are accompanied by an increase in temperature. The risk of developing endometritis is reduced much lower in the early stages of fetal extraction, which is carried out using a vacuum.
Additional symptoms of endometritis are weakness and pain in the lower abdomen, and the diagnosis can be confirmed using an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. In such a situation, broad-spectrum antibiotics, physiotherapy and sedatives are prescribed.
After a frozen pregnancy, your period may be delayed by two months. If the onset of menstruation is too heavy and with clots, you should undergo an ultrasound examination to determine whether there are any fetal fragments left in the uterus. This condition often ends in intoxication and the development of sepsis, which does not occur without an increase in temperature.
After a frozen pregnancy, it may also occur, in which fluid accumulates. Although four out of five cysts go away on their own, it is possible for the cyst to twist and compress due to physical activity. As a result, suppuration develops. When torsion occurs, weakness occurs and the woman may lose consciousness.
If, after cleaning, the remains of the fertilized egg are determined, repeated curettage is prescribed, but you should not wait for these studies if such alarming symptoms appear as fever, fainting, heavy discharge with clots, sharp pain in the lower abdomen not associated with menstruation.
After curettage of the uterus
Curettage of the uterus or gynecological cleansing (curettage) is a procedure during which the top layer of the uterine mucosa is removed using a vacuum system or a special instrument. In this case, the cervix is dilated with special instruments or with the help of medications. Curettage of the uterus is performed for the treatment and diagnosis of a variety of gynecological diseases.
Curettage, as a rule, is carried out several days before the start of the menstrual cycle, which helps the uterus to quickly recover after curettage and reduces blood loss.
After the anesthesia used during curettage wears off, most women experience pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, reminiscent of the pain that occurs during menstruation. The duration of these pains can be several hours or several days, and, as a rule, special treatment is not required. An ibuprofen tablet will help relieve the painful condition.
After the curettage procedure, blood clots and heavy bleeding may come out of the vagina for several hours. There is no need to be alarmed, this is normal - the amount of discharge will decrease after a few hours. For ten days after curettage, small bloody or spotting yellowish or brown discharge persists. Their rapid disappearance may indicate cervical spasm and the presence of blood clots in the uterus.
After curettage, the first period may appear with a slight delay, which is no more than four to five weeks. There is no need to worry about a missed period after curettage, but if it lasts more than three months, then you should consult a doctor.
After the curettage procedure, you must not be sexually active for one to two weeks. This is due to the fact that after gynecological cleansing, the cervix remains open for some time. At the same time, there is erosion on the mucous membrane inside the uterus, which is a consequence of curettage. Because of this, during sexual intercourse, an infection can enter the uterus, which will lead to undesirable consequences.
It is possible that for some time a woman will experience pain during intercourse; after curettage this is a normal phenomenon, but if the pain does not stop for several months, then it is necessary to consult a specialist.
After the curettage procedure, a woman can usually become pregnant within two to three weeks, and the birth, in most cases, proceeds normally.
But if pregnancy has not occurred within six to nine months after gynecological cleansing, then in this case you should consult a doctor. Curettage can disrupt a woman’s ability to conceive a child only in rare cases.
Planning a pregnancy after gynecological cleansing largely depends on the reason that necessitated the procedure. If you plan to conceive a child after curettage, you should definitely consult a gynecologist about this. A specialist will correctly assess the situation and advise you on the best time to conceive a child.
Premature placental abruption during pregnancy
Hepatitis and pregnancy can occur together
Abdominal pain at the beginning of pregnancy
Recovery period
Curettage is a simple surgical procedure. Despite this, in the first days after cleansing the patient may experience pain of varying intensity in the lower abdomen. For some women, the pain is dull. While other representatives experience cramping severe pain spreading to the lower abdomen and back. If such pain is the only symptom, the woman is advised to use painkillers. As a rule, she is prescribed drugs that relieve spasms. The duration of pain varies from several days to seven to ten days.
After cleansing, the woman experiences bloody and bloody discharge for several days. Normally, discharge mixed with blood can last up to ten days. Some patients experience mild pain in the lower abdomen, which does not affect their quality of life.
After appropriate diagnosis, the patient will be prescribed treatment.
Curettage may be accompanied by a weakening of the body's defenses. This leads to the activation of opportunistic microflora, which can cause bleeding, cramps and pain in the lower abdomen. A rise in temperature and a deterioration in general condition cannot be ruled out.
The nature of bloody discharge after curettage may also indicate restoration of the uterine cavity. The most intense discharge is observed during the first days after curettage. After a few days they become bloody and gradually disappear. In the presence of increasing dark-colored discharge with clots, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, the development of complications can be suspected.
Curettage often affects the cycle. As a rule, the first menstruation after cleansing occurs later, which is associated with the complete removal of the functional layer.
Within two weeks after curettage, the woman is recommended to have sexual rest. This is due to the fact that the cervix remains open due to surgery. Injured tissues and bloody discharge can trigger the development of an inflammatory process. Thus, sexual rest eliminates possible infection and injury to damaged tissues.
During sexual intercourse, for the first time after cleaning, a woman experiences minor pain and discomfort, which is normal. If pain persists for a long time, you should consult a doctor to rule out a gynecological disease.
Who survived the curettage? What kind of discharge and pain were there?
4 days ago we had a curettage done because of a stylus, the baby froze at 8.5 weeks, was cleaned at 10.5 weeks, the first 2 days there was moderate discharge, yesterday (day 3) there was nothing all day, today again there is not much smearing, but This is not what worries me, what worries me is the pain in my back, all these days my back hurts when I walk or sit for a long time, the next day after the curettage they did an ultrasound, they said that everything was clear, my stomach sometimes hurt, now it doesn’t anymore, but why does my back hurt? Now The treatment is: oxytocin injection once a day, metronidazole 1 tablet 3 times a day, flucostat 1 t per day, vilprafen 1 t 2 times a day, Terzhinan suppositories at night, plus today when the doctor looked at me in the chair, I was in a lot of pain And I was also prescribed an Ortrofen injection once a day. What kind of pain did you have after this procedure? And why does your back hurt? The temperature sometimes only rises to 37.2. Mostly 36.8.
My friend had it done and her back, lower back and lower abdomen hurt very badly, painkillers helped a little, she continued to have these pains for two weeks, then everything went away.
I’m familiar with this situation, endure it and everything will pass! In general, they cleaned me 2 times, after 1 cleaning my stomach hurt terribly, after an ultrasound it turned out that there were still clots. and again. then it became easier! They also injected a bunch of things and gave me IVs! And my back hurt too, it will go away with time! don't worry, don't get sick! good luck to you =)
4 days ago we had a curettage done because of a stylus, the baby froze at 8.5 weeks, was cleaned at 10.5 weeks, the first 2 days there was moderate discharge, yesterday (day 3) there was nothing all day, today again there is not much smearing, but This is not what worries me, what worries me is the pain in my back, all these days my back hurts when I walk or sit for a long time, the next day after the curettage they did an ultrasound, they said that everything was clear, my stomach sometimes hurt, now it doesn’t anymore, but why does my back hurt? Now The treatment is: oxytocin injection once a day, metronidazole 1 tablet 3 times a day, flucostat 1 t per day, vilprafen 1 t 2 times a day, Terzhinan suppositories at night, plus today when the doctor looked at me in the chair, I was in a lot of pain And I was also prescribed an Ortrofen injection once a day. What kind of pain did you have after this procedure? And why does your back hurt? The temperature sometimes only rises to 37.2. Mostly 36.8.
Every day you will feel better after such a procedure, and this mini operation takes time for the pain to stop.
Today it’s been exactly a week since the curettage, and I feel much better. I was discharged from the hospital and I’ve already stopped taking the pills, two more days and that’s it! Next week I’ll go to another one (as everyone says to a VERY good gynecologist) I hope everything will be fine!)))
after the sting, they gave antibiotic injections plus hemostatics, in total 5-7 injections a day for 5 days, I didn’t take contraceptives, my stomach didn’t hurt, my lower back hurt, the discharge has been smearing for a week now, I’m waiting for the test to be done for hormones, they did an ultrasound and they said it was clean, but I want to do it again.
After the cleaning, I was discharged from the hospital two days later. There was no discharge at all and I felt as if nothing had happened. I took metronidazole and Marvelon. They didn't do an ultrasound.
4 days ago we had a curettage done because of a stylus, the baby froze at 8.5 weeks, was cleaned at 10.5 weeks, the first 2 days there was moderate discharge, yesterday (day 3) there was nothing all day, today again there is not much smearing, but This is not what worries me, what worries me is the pain in my back, all these days my back hurts when I walk or sit for a long time, the next day after the curettage they did an ultrasound, they said that everything was clear, my stomach sometimes hurt, now it doesn’t anymore, but why does my back hurt? Now The treatment is: oxytocin injection once a day, metronidazole 1 tablet 3 times a day, flucostat 1 t per day, vilprafen 1 t 2 times a day, Terzhinan suppositories at night, plus today when the doctor looked at me in the chair, I was in a lot of pain And I was also prescribed an Ortrofen injection once a day. What kind of pain did you have after this procedure? And why does your back hurt? The temperature sometimes only rises to 37.2. Mostly 36.8.
You are currently taking treatment and you need a couple of days for these medications to give results, get treated and everything will go away for you.
Endometritis
Endometritis is the next reason why the temperature may rise after curettage of the uterine cavity. The inflammation that develops in this case covers the inner surface of the organ - the endometrial layer.
Endometritis that forms after cleansing the uterus can be caused by various factors. The cause of illness and fever can be:
- particles of fertilized egg or placental tissue left in the uterine cavity during curettage;
- accumulation of blood caused by cervical spasms is one of the relatively uncommon complications of cleansing;
- penetration into the organ cavity while cleaning pathogenic bacteria, etc.
Pathology with an increase in temperature can be caused by various pathogens, which are usually divided into specific and nonspecific. The first category of endometritis includes infectious inflammation of the uterine cavity initiated by STIs. With nonspecific formats, pathogenic microflora is not detected. The cause of endometritis can be bacterial vaginosis, vaginal dysbiosis, but an increase in body temperature occurs in any case.
Symptoms
The acute form of endometritis develops approximately on the third or fourth day after completion of curettage of the uterine cavity. Its typical signs are:
- increased body temperature accompanied by chills;
- the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- tachycardia;
- pain when urinating.
If the temperature rises after curettage (cleaning) of the uterus and typical symptoms develop, it is necessary to obtain urgent medical advice.
In addition to high temperature, during a gynecological examination the patient reveals typical signs of endometritis:
- the uterus is moderately enlarged and painful on palpation;
- visible serous-purulent discharge from the cervical canal.
The acute form of the disease lasts approximately 10 days, during which elevated body temperature may persist. Then, in the absence of treatment, endometritis becomes chronic, and with low body resistance it can lead to inflammation of the entire uterus, peritonitis and sepsis.
Treatment
Since the acute form of endometritis, which develops after curettage (cleaning) of the uterus, is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, the woman will be recommended bed rest.
Treatment of pathology is carried out in a hospital setting.
Drug therapy for acute forms of endometritis is carried out with drugs from the antibiotic category. The choice of drug depends on the sensitivity of the pathogen. This may be Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lycomycin. Gentamicin and other drugs.
When diagnosing a mixed microbial form, treatment is carried out with several drugs at once. In almost every case, in addition to antibiotics, Metronidazole is prescribed. Temperature - sometimes very high - is accompanied by intoxication of the body. To alleviate the condition, intravenous infusion of saline and protein solutions is indicated.
Pain after curettage in the lower abdomen, pulling and radiating to the lower back
This will help you avoid complications and pain after curettage.
On the 5th day after curettage, the lower abdomen began to hurt and cramps appeared. After curettage, you may have spotting and spotting for several days (from 3 to 10). Today is the third day after cleansing.pain and blood on the third day is normal. I was discharged from the hospital after 19 in the morning. After discharge on the 19th day, she began to smear and have pain in the lower abdomen. Curettage of the uterine cavity is used in gynecological practice for various purposes. Most often, this operation is performed to terminate a pregnancy. But there are also other types of these manipulations. Therefore, it is important to understand what curettage is and why it can be carried out. A hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus, which allows you to see the area of treatment and the manipulations being performed. This is the safest method for diagnosing and removing polyps and tumors.
Indications for curettage of the uterine cavity may be abnormal bleeding, which is caused by pathologically altered areas of the mucous membrane. You may feel a burning sensation in the lower abdomen and nagging pain.
With the modern level of medical equipment, complications after gynecological intervention are a relatively rare occurrence. Although everything depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the level of immune protection of the woman being operated on. Trauma to the uterine wall with penetration of the curette into the muscle layer is accompanied by extensive bleeding and general weakness.
Pain can be caused by ruptures in the cervix, which appear as a result of improper application of expansion forceps. Inflammatory diseases and accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity can be treated quite successfully with conservative treatment - which is why it is necessary to consult a specialist in a timely manner. The main advice for women who need curettage is to carefully choose a doctor and clinic.
ZB at 7 weeks #8212; I went until 12. 2 hours after cleaning I went home. I didn’t experience any particular pain, the discharge was like menstruation, and had already begun to stop. The pain has been going on for days. The hospital prescribed antibiotics #8212; ofloxacin, tincture of water pepper, and the doctor prescribed birth control in the LCD.
And pain #8212; This is how the uterus contracts, the discharge can last up to 10 days, the main thing is that there are no clots. No-spa helped me with pain. After the noshpa I began to bleed, but not much. My stomach still hurts. Colitis is like an open wound. And there is blood, but not much. I had a glaucoma at 6 weeks and had a curettage done. I spent 3 days in the hospital, received injections of Imunofan and Oxytocin, and went to diodynamic procedures.
They did an ultrasound and said that the uterus had not yet closed and there was a small accumulation of blood, and that there would still be discharge. They told me to do squats to prevent the blood from stagnating. They also prescribed Cyclodinone for 1 month. 1 tab. in a day. And from the first days of menstruation Jazz, course for 6 months.
In general, I stocked up on pills and eat them. In 4 days I’ll go to the doctor again, let’s see what he says. For the first three days there was almost no discharge, but then it appeared and now there is (a week has already passed), not abundant, but dark. Tomorrow I'll go to the doctor #8212; I hope everything will be fine. Hang in there, girls, we will definitely succeed.
The miscarriage occurred on September 17. years at 23:15. I did an ultrasound and they said everything was clear. prescribed propyl tablets #171;Zitmak 500#8243; and #171;Kandazol#187;. 4. Could this have something to do with cleaning? Most women in their lives are faced with a situation where the gynecologist, after an examination, prescribes curettage. Not all patients are told in an accessible form what this operation is, and this ignorance gives rise to unfounded worries.
RDV+ GS – separate diagnostic curettage under hysteroscopy control – is a modern modification of curettage. Conventional curettage is performed virtually blindly. Hysteroscopy allows you to evaluate how well the curettage was performed and whether there are any pathological formations left.
A day later (yesterday) my stomach started to hurt. I went to the doctor, they did a vaginal ultrasound and they said that there was a delay in discharge in the uterus. We found some clots there. For many women, pain after gynecological surgery may appear several days later.
Pyometra
Pyometra, which is also accompanied by an increase in temperature, is a purulent endometritis. The development of pathology is preceded by the formation of hematometra. In addition to high temperature, the condition is characterized by the accumulation of purulent liquid contents in the uterine cavity. Most often, pyometra develops against the background of complications after curettage (cleaning).
The main reason for the formation of pyometra is the closure of the cervix, which prevents the natural outflow of blood and the subsequent addition of a secondary bacterial infection. As a result, the accumulated liquid contents transform into pus.
Obstruction of the cervical canal can be caused by various reasons. In particular, the free flow of blood from the uterine cavity can be prevented by:
- polypous formations in the lumen of the cervical canal;
- fragments of the fertilized egg, if the cleaning was carried out for the purpose of abortion, etc.
The development of pyometra can be facilitated by cervical stenosis, which can also occur against the background of curettage of the organ.
Symptoms
The disease has an acute onset and is accompanied by characteristic clinical signs:
- the presence of severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- voluminous purulent discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant putrefactive odor;
- high body temperature, chills and deterioration in general condition - symptoms indicate purulent intoxication of the body.
When palpating the lower abdomen, the gynecologist determines an enlarged, painful uterus. One of the signs of pyometra, in addition to an increase in body temperature, is a sudden cessation of discharge after curettage (cleaning) of the uterus.
In diagnosing pyometra that has developed after cleaning, in addition to the presence of high temperature, an important role is played by a gynecological examination.
The doctor identifies the following signs of pyometra:
- the presence of purulent discharge from the cervical canal of the uterus;
- increase in organ size;
- doughy consistency of the uterus.
During diagnostic probing, the doctor observes the discharge of pus, which confirms suppuration.
Treatment
Detection of pyometra becomes an absolute indication for hospitalization. First of all, doctors relieve spasm of the cervical canal and evacuate the contents of the uterus. In some cases, repeated cleaning may be prescribed.
After removing the purulent contents, in order to stabilize the condition, drug therapy is prescribed, including intravenous administration of drugs from the category of broad-spectrum antibiotics. The elevated temperature decreases after evacuation of the contents and initiation of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Post navigation
No comments yet!
If for some reason the fetus freezes inside the mother’s womb, then it is important to do everything necessary to maintain the woman’s health. Curettage during a frozen pregnancy is a vital procedure. It is carried out in order to remove the fetus and its membranes from the body. However, cleaning is far from being a harmless operation, as some might think. After all, it can provoke pain and the development of some complications (infection, bleeding).
Consequences
In the early stages, curettage is replaced by vacuum cleaning
. A tube is inserted into the uterus, which, like a vacuum cleaner, sucks the embryo into itself. The method is safe up to 11 weeks of pregnancy.
After 11 weeks, curettage is used - the entire layer of the endometrium, with the attached fetus, is torn off from the wall of the uterus.
After curettage during a frozen pregnancy, a woman will experience a number of characteristic symptoms:
- vaginal bleeding;
- discharge;
- lower abdominal pain;
- pain in the mammary glands;
- temperature increase;
- depression.
Curettage is a wound in the uterine cavity. As long as the top layer does not heal, blood discharge does not cause suspicion. Normally, bleeding is not too heavy, without additional aggravating symptoms, and lasts up to 4 days.
Vaginal discharge can be brown or yellow. Brown spots up to 2 weeks after curettage are considered normal. This could be clotted blood coming out of the healing uterus.
After 14 days, such discharge is not considered normal. Yellow discharge is a sign of an inflammatory process.
Pain in the lower abdomen is caused by a wound and contraction of the uterus to its natural size.
Contraction is painful because hormonal levels are disrupted and the process does not go as smoothly as after childbirth.
Hormonal changes also affect the condition of the breast. The process of preparing for feeding has already begun, and a sharp reverse motion causes natural pain in the tissues.
Temperature increase
normal in the first days, but its growth must be monitored and the appearance of additional symptoms monitored. Inflammation could occur.
Complications after curettage
Most women who have been prescribed uterine cleansing after a confirmed frozen pregnancy are afraid not of the procedure itself, but of its consequences. They are worried about how curettage will affect the ability to bear a child during subsequent conceptions, how painful the procedure is, and what complications there may be.
Just 30 years ago, the curettage procedure was considered deadly. As a result of unskilled manipulations, the mortality rate among women reached 9%, complications were diagnosed in 20%. That is, every fifth woman who decided to have an abortion became infertile.
The qualifications and experience of the gynecologist play a fundamental role. After all, a woman’s well-being, as well as her chances of carrying a new pregnancy, depend on the professionalism of the doctor. Today, the statistics of dangerous consequences are not so frightening, but it is worth knowing in advance about the occurrence of possible complications.
Planning a baby after cleansing a frozen pregnancy
If we turn to the experience of foreign medicine, then we can “work” towards the next pregnancy after cleansing immediately after the restoration and stabilization of the monthly cycle. At the same time, doctors recommend drinking folic acid every day.
Domestic experts are less radical on this issue and advise the woman to rest for at least six months after the incident. A patient who has experienced a frozen pregnancy is certainly prescribed COCs.
Curettage of the uterine cavity is in some cases not only a necessary operation, but also the only way out of a serious condition when it comes, for example, to a frozen pregnancy. During this surgical procedure, the doctor removes the surface epithelium of the uterine cavity, cleaning it using special instruments. This is a very difficult operation, which quite seriously injures the surface layer of the mucous membrane, so the patient may feel unwell for quite a long time after it.
Abdominal pain after cleansing
Soreness in the groin or umbilical area of the abdomen immediately after curettage is normal.
Evacuation of pregnancy remains is carried out using a special metal mirror, which provides access to the cervix. After opening the cervix (not softened), a manipulation is performed to clean out the inside of the uterus (cavity) using a curette. The procedure itself is very traumatic for the delicate tissue of the organ, and therefore there is a risk of complications.
Most complications after cleansing a frozen pregnancy occur due to damage to the cervix. This occurs because an unprepared organ is forcibly expanded with special instruments.
Dull or aching pain in the lower abdomen is considered normal if the woman can tolerate the pain and the abdomen is soft to palpation. And also if there are no signs of complications: fever, chills, spasms with sharp increasing pain in the groin.
After cleaning a frozen pregnancy, the medical staff applies a cold compress to the lower abdomen to increase the intensity of contractions of the uterine body. If after surgery or during the first 24 hours the temperature rises and pain increases, then all this may indicate the development of complications in the postoperative period.
Increasing abdominal pain against a background of high temperature indicates a number of disorders:
- The presence of a focus of infection in the reproductive organs. As a rule, mucous membranes are susceptible to the development of pathogenic flora: vagina, cervix, endometrium.
- Incomplete cleansing of the uterine body from possible accumulations of remnants of the fertilized egg or embryo.
- Tear or damage to the cervical canal of the cervix.
- Hematometra, formed as a result of the accumulation of blood in any quantity. For the development of the inflammatory process, even one small clot that does not come out is enough. The first symptoms, as a rule, appear a little later: on the second - third day after cleansing.
- Inflammation of the uterus. Occurs in case of excessive pressure on the tissue during the cleaning process (insufficient opening of the cervix, the doctor makes more effort).
In fact, all of these complications, provided that the woman in labor did not have any obvious symptoms before curettage, are the result of medical negligence.
Moreover, before cleaning, a woman undergoes a series of studies and tests that show the presence of pathologies and foci of infection. Trauma to the cervix (tear, crack) in 85% of cases occurs as a result of the forceps coming off or excessive pressure on the tissue during the cleaning period.
An increase in temperature is the body’s reaction to developing inflammation. The uterine cavity after surgery is a continuous bleeding wound, susceptible to any infection. Therefore, a woman should pay close attention to her health after curettage.
Vacuum antiseptic filling of the uterine cavity is a mandatory procedure that prevents the formation of pathogenic flora after curettage.
It is not necessary to use non-sterile instruments (which is impossible); even specially treated instruments do not guarantee that pathogenic flora will not grow. Here the woman’s body and her immune defense play a primary role.
The listed complications can be easily avoided if the surgical cleaning of a frozen pregnancy was carried out correctly, in compliance with all requirements. The natural process is bleeding immediately after curettage, which is observed for two weeks.
The duration of abdominal pain is also justified by the presence or absence of a pathological process. If all manipulations were carried out carefully, and the woman complies with the rules of the postoperative period, then the pain should go away within five days. You may be concerned about:
- prolonged abdominal pain of any nature (more than a week);
- discharge of varying intensity;
- purulent discharge, large amounts of blood;
- temperature;
- headache, migraine;
- swelling of the limbs;
- pain on palpation of the abdomen, slight bloating.
The most dangerous complication after curettage is removal of the uterus. This complication is observed only in 2% of women with pathologies of pregnancy.
If pathogenic flora is present, the doctor will prescribe an additional course of antiseptics and antibiotics or intravenous administration of drugs that block the spread of infection.
Abdominal pain, blood and fatigue after curettage are normal. Symptoms such as purulent discharge, high fever, spasms with acute intolerable pain should alert you. Any complications cause anxiety in women, but fortunately they are treated. If after cleaning there are no negative signs, then after two weeks the uterus contracts and the mucous membrane returns to normal.
Cervicitis
The reason for the increase in temperature - sometimes to very significant levels - after cleaning (curettage) of the uterine cavity is inflammation of the vaginal segment of the cervical canal.
In addition to high fever, the disease is characterized by the appearance of vaginal discharge. They can be either mucous or contain purulent impurities. In addition, the pathology is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, as well as significant discomfort accompanying the process of urination.
There are two forms of cervicitis. The gradation depends on which tissues of the cervical canal were involved in the pathological process.
- When the vaginal part of the cervical canal becomes inflamed after curettage of the uterus, a woman develops exocervicitis.
- If, after cleaning, inflammation of the inner surface of the cervical canal of the uterus begins, then we are talking about endocervicitis.
The main cause of the disease is tissue damage during uterine curettage, which is subsequently joined by nonspecific infectious agents. The development of inflammation after cleansing and the accompanying rise in body temperature can be provoked by:
- staphylococci;
- coli;
- streptococci, etc.
After cleaning (scraping) the uterine cavity, the female body becomes more vulnerable to various types of infections as a result of decreased immune defense.
In addition to its own opportunistic flora, inflammation and fever are caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Pathogens such as chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, viruses can provoke cervicitis when open sexual activity begins after cleansing earlier than recommended by the doctor. The disease also becomes more active if the infection has progressed before the cleansing. Failure to comply with the principles of rational antibiotic therapy leads to cervicitis and a rise in temperature after cleaning.
Symptoms
As a rule, after injury to the cervix during curettage and the addition of a secondary infection, a woman develops acute cervicitis. In addition to the increase in temperature, the following symptoms appear:
- copious mucous and even mucopurulent discharge;
- presence of dull pain in the lower abdomen.
During a gynecological examination - a few days after curettage - swelling and redness of the cervix are noted.
In addition, the gynecologist notes protrusion of the mucous membrane, as well as pinpoint hemorrhages and ulcerations.
If an increase in temperature is typical for all types of cervicitis, then the accompanying symptoms depend on the pathogen and the current state of immune defense.
- For the gonorrheal form, an acute course is typical - high body temperature, significant purulent discharge with a pungent odor.
- With chlamydial cervicitis, the symptoms are somewhat blurred, but the temperature still rises.
- When a herpetic infection forms, the cervix becomes loose, covered with ulcers and becomes very red.
- Trichomonas cervicitis is characterized by the appearance of small hemorrhages on the surface of the mucosa.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease becomes chronic, which is fraught with the development of serious consequences. An ascending infection can penetrate the tubes and ovaries, leading to an inflammatory reaction, which is quite difficult to treat and causes infertility.