How is the fruit receptacle normally located?
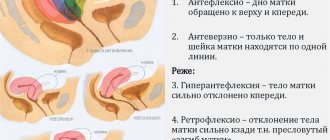
The typical (classical) position of the fetal receptacle in the small pelvis is as follows: the uterus, against the background of an unfilled intestine and bladder, is localized in the middle of the small pelvis, and the bottom of the organ does not protrude beyond the plane of the entrance to the pelvis, the cervix lies on the line of intersection of the ischial spines (the plane of the narrow part of the pelvis). The bottom of the organ is facing anteriorly and upward, the visible part of the cervix “looks” downward and posteriorly due to the obtuse angle formed by the length of the uterus and the cervix, open anteriorly. This position is called anteversio and anteflexio of the uterus (anteversio - anteflexio uteri). The vagina is located at the outlet of the small pelvis, its direction is outward and somewhat anteriorly upward, but posteriorly to the cervix.
Factors that determine the normal location of the fetal sac in the pelvis:
- tone of the organs of the reproductive system (depends on the content of sex hormones, the state of the nervous system, blood supply);
- coordinated work of the diaphragm, abdominal wall, and pelvic floor muscles, maintaining normal intra-abdominal pressure;
- ligamentous apparatus of the uterus (supporting, securing, fixing ligaments)
note
In girls, the uterus is much higher; in old age, due to atrophy of the pelvic muscles, it descends compared to women of childbearing age.
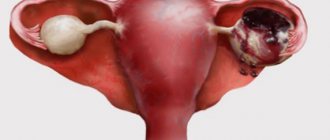
Ovaries in women
Normally, each ovary is located on the side of the uterus. When viewed from the abdomen, these organs are located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity, directly under the inguinal folds. They are attached to the surface of the small pelvis by a ligament of nerves and blood vessels. This area is called the ovarian fossa.
From there the fallopian tubes go to the uterus. The reproductive organs in question have their own peculiarity of location, namely that they are located asymmetrically in relation to each other - one is located slightly higher than the other. Also, the size of the organs is slightly different. Usually the right ovary is larger and heavier than the one on the left. In shape and color they are absolutely identical.
Normally, the reproductive organ is equal to the following dimensions: length - 20-50 mm, width, thickness - 15-30 mm. If there are minor discrepancies, within a few millimeters, then most likely this indicates the individual characteristics of the woman. If the size is much higher than normal, then there is a reason to visit a doctor.
Classification
Systematize the displacement of the organ in relation to the horizontal, vertical planes and around the longitudinal axis:
- Offset relative to the horizontal plane:
- the organ is displaced anteriorly (anteposition);
- the fruit receptacle is displaced posteriorly (retroposition);
- the organ is deviated to the right (dextraposition);
- the organ is deviated to the left (synistroposition).
- Changing position around the longitudinal axis:
- rotation (rotation) of the organ;
- torsion;
- eversion
- Offset relative to the vertical plane:
- the uterus is elevated;
- the fruit receptacle is lowered to the line combining the ischial spines and below;
- organ prolapse (protrudes from the genital opening).
- Inflection of the uterus:
- anteriorly, the angle created by the body and neck becomes acute (hyperanteflexion);
- posteriorly, the uterus is deviated towards the large intestine, the angle formed by the body and cervix opens towards the rectum (retroflexion);
- the organ is deviated to the right or left side, the angle formed by the body and neck looks sideways, towards the ovary (lateral flexion is right or left).
Important
Congenital organ retroflexion is diagnosed in 5% of cases, is caused by heredity and is not a pathology.
Also, the curvature of the uterus is systematized into mobile and fixed. Mobile retroflexion does not require treatment.
The most suitable positions for conception
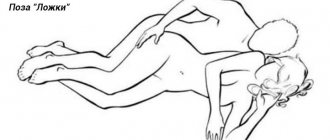
Knee-elbow. It is the best position for retroflexion. It is the most natural and popular among animals. This position minimizes the path of the sperm to the egg, as it allows deep penetration.
The man is behind. A large number of women with pathology of a bent uterus have a chance of becoming pregnant only when their partner is behind them. This position is also called “doggy style”. A woman can lie on her side. With retroflexion in this position, the uterus will tilt forward, making it easier for sperm to penetrate it.
Missionary position and its variations. If, when performing the classic pose, a woman slightly raises her hips with the help of a pad, then the likelihood of fertilization will increase. In general, any position is suitable for fertilization, under one condition - during ejaculation, the partner is below, under the man. With this position, the penis and uterus are located most closely, and this increases the likelihood of conception.
Many women who were diagnosed with retroflexion were able to become pregnant, carry them to term safely, and give birth to a healthy baby. They say that it was not so much certain positions that contributed to conception, but special actions after intercourse. A very effective exercise for increasing the likelihood of conception is the “birch” exercise after sex. It is necessary to raise your legs up and keep them in this position for up to 20 minutes. If you find it difficult, you can prop your feet up against a wall or ask a man to help you.
You can also just lie down with a pillow under your buttocks. Lying on your stomach for half an hour can also increase your chance of pregnancy. Some women with a bent uterus take the following position: lie on their back, press their knees to their chest and rock from side to side for 10-20 minutes.
Causes of uterine bending
The position of the fetus receptacle in the pelvic cavity is determined by the following conditions:
- gestation;
- intra-abdominal pressure drop;
- empty or full bladder and intestines.
If there is a persistent deviation from the normal location of the fetal receptacle in the small pelvis, which leads to a disorder in the relationships between the female reproductive organs, they speak of an abnormal position of the genitals.
The leading cause of retroflexion of an organ or its bending anteriorly is inflammatory diseases, often chronic, of the uterus and appendages (endometritis, adnexitis). Chronic inflammation of the genital area spreads into the abdominal cavity and provokes the formation of connective tissue cords or adhesions. It is the adhesions that modify the location of the fetal sac, ovaries, tubes and cause infertility in women. Adhesions are also caused by operations on the abdominal organs, inflammatory bowel diseases, abdominal injuries accompanied by rupture of the muscles and ligaments that keep the organ in a normal position, and endometriosis. In addition, the abnormal position of the organ can be caused by tumors of significant size (fibroids, ovarian cyst/neoplasm, tumors of the intestinal tube, bladder). Retroflexion of the uterus is one of the symptoms of genital infantilism due to underdevelopment of the ligamentous apparatus of the organ.
Predisposing factors for uterine retroflexion/hyperanteflexion include:
- sudden loss of body weight (cancer intoxication, anorexia);
- hormonal imbalance leading to changes in uterine tone;
- numerous births;
- miscarriages, abortions (provoke inflammation);
- complicated childbirth with obstetric aids (sprained ligaments in the pelvis);
- intense sports activities, heavy lifting;
- asthenic body type (lack of connective tissue);
- Constantly ignoring a full bladder/rectum;
- prolonged stress.
note
Early sitting of infant girls provokes the occurrence of a posterior bend of the uterus - a prejudice. The child begins to sit up independently only after sufficient muscle development, which is individual in each case and depends on associated factors (full term, illness, heredity).
Fixed retroflexion
Various diseases of the pelvic organs provoke the appearance of adhesions, as a result of which the uterus is firmly fixed in one position. This pathology can only be corrected through surgery.
There are other reasons for the appearance of a posterior bend of the uterus:
1 breastfeeding for a long period;
2 inflammatory diseases of the large intestine;
3 frequent constipation;
4 consequences of difficult childbirth.
Diagnostic measures. A gynecologist may suspect a posterior bend of the uterus even at the time of a bimanual examination. However, to confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is necessary.
Symptoms of a bent uterus
A woman may not be aware of excessive anterior bending of the uterus or retroflexion of the organ until the first gynecological examination. But in some cases, anomalies in the location of the fruit receptacle are accompanied by certain symptoms. Firstly, the patient may be bothered by pain during menstruation, the occurrence of which many associate with a previous inflammatory process of the appendages or uterus. The uterus, fixed by adhesions, is not able to contract freely and push out blood during menstrual bleeding. You may also experience pain in the lumbar, sacral regions and/or lower abdomen during sexual intercourse, after physical exertion, which contributes to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and lifting heavy objects. Such pain is also explained by the presence of adhesions in the pelvic cavity, their fixation of the fetal sac. Bend of the uterus anteriorly or its deviation posteriorly significantly changes the angle between the cervix and the organ, which is manifested by a disorder of menstrual function. The shedding of blood from the fetal sac occurs with difficulty, so menstruation becomes prolonged, scanty, and blood clots are present in the discharge.
Problems with urination and defecation cannot be excluded, especially in the presence of concomitant tumors of the uterus, appendages or intestines. A pronounced adhesive process in the pelvic cavity, which limits the mobility of the uterus and cervix, can cause miscarriage or absence of pregnancy.
How to get pregnant with a bent uterus
A number of women with hyperanteflexia or retroflexion of the uterus experience difficulty conceiving, which is not due to the position of the organ, but to the reason that determined its abnormal location. If the position of the fetal sac is incorrect, the location of the cervix also changes, which often rests against the vaginal wall, which makes it difficult for sperm to penetrate the cervical canal and the uterine cavity. Therefore, some positions for coitus that have become popular do not increase the likelihood of conception; the chances of successful fertilization will increase only if the underlying cause is eliminated and/or other factors of infertility are identified. With mobile (constitutional) retroflexion of the uterus, it is unprofessional to talk about difficulties with conception; in the absence of other reasons provoking infertility, pregnancy occurs on its own without any treatment or following recommendations.
Disorders of the ovaries
It happens that the ovary is located behind the uterus, located close to it and forming an inflection.
At the same time, patients often feel pain if any diseases develop in the reproductive organs. Doctors do not consider this disorder pathological. Usually the bend is observed during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that when the uterus increases, the distance between it and the appendages decreases. In this case, the left ovary is located closer to the uterine cavity, because it is located below the right organ from the very beginning.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing uterine retroflexion is not difficult. The abnormal position of the organ is detected during bimanual manual examination through the rectum or vagina.
The diagnosis is confirmed by examination in the speculum by anterior displacement of the cervix, its emphasis on the anterior vaginal wall. It is characteristic that when the uterus is not fixed, palpation can return the organ to its normal position. In the case of fixed retroflexion, attempts to return remain unsuccessful, the uterus is motionless, and its displacement provokes intense pain.
To clarify the diagnosis and identify the reasons for fixation of the fetal sac, instrumental methods are used: ultrasound with transvaginal and transabdominal sensors, MRI, hysterosalpingography. Additional examination allows us to identify adhesions, tumor-like formations of the reproductive system, endometriosis, and obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Treatment
Therapy for asymptomatic congenital uterine flexion is not indicated; the patient is only advised to limit heavy physical work and heavy lifting. Fixed retroflexion with a pronounced clinical picture and the presence of infertility requires treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of organ bending.
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the chances of returning the uterus to its normal position.
The patient is prescribed therapeutic exercises, according to indications - gynecological massage, wearing pessaries.
Gynecological massage is performed by a gynecologist who has undergone special training, after preliminary emptying of the rectum and urination. Sessions lasting 3 - 5 minutes in a course of up to 10 - 20. Gynecological massage helps to separate soft adhesions (long-existing, dense connective tissue cords are surgically dissected), normalize blood flow in the pelvic cavity and its organs, improve muscle tone of the uterus, eliminate pain and discomfort during coitus .
Contraindications for gynecological massage:
- inflammatory and infectious processes of the urinary and reproductive systems;
- temperature increase;
- menstruation;
- neoplasms in the pelvis;
- background processes of the cervix.
In case of acquired bending of the uterus, the cause of its occurrence is determined and appropriate treatment is prescribed: anti-inflammatory, fibrinolytic, vitamin preparations and physiotherapy: electrophoresis with enzymes, balneotherapy, paraffin therapy. A pronounced adhesive process in the pelvic cavity requires surgical dissection of the adhesions. If there are existing tumors that change the position of the uterus, they are removed surgically; if necessary, the organ is returned to its normal position using surgical correction.
Forecast, prevention
The prognosis for uterine retroflexion is favorable. Often, a pregnancy that ends in childbirth restores the normal position of the organ. Pregnant women with a bent/inverted uterus need preventive courses of conservation therapy.
Prevention measures include:
- limiting heavy physical activity and heavy lifting;
- moderate physical exercise (swimming, gymnastics, aerobics);
- timely emptying of the intestines and bladder;
- annual visit to the gynecologist;
- rational and balanced nutrition (prevention of genital infantilism);
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive sphere and endocrine disorders;
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- sleeping position: on the stomach;
- refusal of strength sports.
Sozinova Anna Vladimirovna, obstetrician-gynecologist
2, total, today
( 48 votes, average: 4.69 out of 5)
Vulvovaginal candidiasis: symptoms and treatment
Breast examination