Even a minor operation can affect the nature of menstruation. This also applies to such relatively gentle surgical interventions as vacuum aspiration. Real menstruation after vacuum aspiration begins only on the 30-40th day. They are preceded by menstrual-like discharge, the arrival of which can be expected 4-5 days after the operation.
Alternative designs have also been explored. Overall, misoprostol 800 mcg provided the greatest clearance rate, with little additional benefit noted after the third dose. In women with 7 to 17 weeks' gestation, an 800 mcg vaginal misoprostol regimen resulted in an 80% success rate when measured by complete expulsion within 3 days of treatment. Efficacy is similar for all routes of administration, although gastrointestinal side effects are more common when misoprostol is administered orally or sublingually.
The next menstrual cycle begins on the day of surgery. Discharge preceding normal periods indicates that the damaged uterine lining is healing. If there are no pathologies, they are present for 5-10 days and have bloody inclusions. Sometimes during the first 2-3 days a mild pain syndrome is observed, but over time these sensations gradually disappear.
The optimal dosing schedule should be determined by route of administration. Vaginalized misoprostol has the longest half-life, with serum metabolites persisting for longer than 6 hours compared to approximately 2 hours after oral or sublingual delivery. Peak absorption of the serum is optimized by sublingual administration, which avoids first-pass hepatic metabolism that occurs after oral administration and variable absorption across the vaginal epithelium due to the presence of cervical mucus or blood in the genital tract.
Whether to make a vacuum or not should be decided by the woman herself, based on her moral beliefs and doctor’s recommendations. This is an approved method of getting rid of an unwanted pregnancy. Surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, and the duration of the operation varies from 2 to 10 minutes.
Normal discharge
The first menstruation after surgery is usually less intense. This condition is not considered pathological. It is explained by the incompletely restored functioning of the ovaries and insufficient thickening of the endometrium.
Ultimately, the optimal route of administration should be determined by patient preference, as the effectiveness of each approach is similar. When you consult with women about their needs using misoprostol, it is important to discuss common side effects. The bleeding pattern experienced as the tissue passes is usually described as heavier than the patient's normal menstrual flow and lasts approximately 3-4 days. This is followed by a transition to vaginal spotting, which may last a week or longer.
Hormonal levels after vacuum abortion
One common concern among providers considering treating outpatients with misoprostol is the potential for acute blood loss leading to hemodynamic instability and return to the emergency department. Although this is a legitimate concern that increases with gestational age, researchers reported a greater decrease in hemoglobin levels among patients treated with curettage compared with those treated with misoprostol.
For many young ladies, their periods come later after a vacuum. Some women can expect the arrival of “critical days” earlier than expected due to the stress on the body caused by the intervention.
The final return of the cycle to normal in women who have become mothers is observed within 3-4 months. For nulliparous young ladies, it is acceptable to be “late” for six months. After this, “critical days” again begin to come once a month regularly.
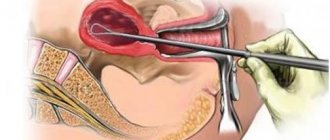
Surgical treatment of spontaneous pregnancy loss in the first trimester may involve forceful curettage, electric vacuum aspiration, manual vacuum aspiration, or a combination of vacuum aspiration and forceful curettage. It is performed in the operating room using an electric suction device and a rigid curette and usually involves general, intravenous or spinal anesthesia. Its effectiveness and complications have been widely studied.
Cervical ripening agents aid in patient comfort and reduce the complexity of uterine evacuation procedures. Available cervical ripening agents include misoprostol, mifepristone, and osmotic dilators. A recent meta-analysis compared the effectiveness of each approach and concluded that kelp, vaginal or sublingual mifepristone, and misoprostol are equally effective in reducing manual dilatation difficulty. When administered at least 2-3 hours before the procedure, misoprostol produced better results with fewer side effects when administered vaginally or sublingually rather than orally.
No allocations
Sometimes women complain that, despite discomfort in the lower abdomen, no. In this case, the following pathologies can be suspected:
- cervical stenosis;
- thrombosis;
- uterine bend.
In addition, it is logical to assume a new pregnancy or the presence of a hormonal disorder. The development of cervical stenosis is more typical for women who did not have time to become mothers. Vacuum aspiration involves enlargement of the cervical canal. Against this background, a decrease in the uterine cervix may be observed.
However, compared with mifepristone 200 mg 24 hours before the evacuation procedure, misoprostol by any route was less effective. Addition of agents such as ropivacaine and fentanyl to lidocaine has been used to enhance and prolong the analgesic effects. The use of minimal to moderate oral and intravenous sedation protocols for additional pain control was also supported. Anxiolytics such as lorazepam are often used in sedation protocols for in-office uterine evacuation, but they do not appear to significantly reduce pain in the hospital.
Pathology leads to the fact that the “necessary” layer of the endometrium is rejected, but the discharge has no opportunity to leave the uterine cavity. Over time, menstrual secretions accumulate and severe pain occurs. Against this background, the inflammatory process easily develops due to the proliferation of microorganisms in the secretions.
Comparison of surgical approaches
In fact, Allen and colleagues reported decreased patient satisfaction when lorazepam was added to sedation protocols.
A uterotonic agent may be administered postoperatively to reduce vaginal bleeding from both forms of surgical treatment. Typically, methylergonovine is used, but regimens vary between providers. A dose of 50 mcg is effective in the 12th week of pregnancy. These include cost savings, procedure time, procedural complications, and blood loss in the absence of harm in procedural completion rates. Due to the expansion of the veins located in the reproductive organs, thrombosis often develops. Appearing blood clots are an obstacle to the outflow of secretions. In this case, there is pain in the lower abdomen. If the disease is not treated, an inflammatory process develops in the uterine cavity, similar to that with cervical stenosis.
In the largest study to date, Goldberg and colleagues reported no significant difference in complication rates between the two approaches when performed at 10 weeks' gestation or earlier. The use of intraoperative ultrasound during evacuation procedures has been shown to reduce the formation of false passages in the endocervix during cervical dilatation, uterine perforation during probing or dilatation, and retention of postprocedural products of conception. Sharp curettage, often performed after vacuum aspiration to ensure complete evacuation, is associated with an increased risk of uterine perforation and Asherman's syndrome.
If the organ initially had an incorrect position, surgical intervention makes its deviation even stronger, which prevents the free flow of menstrual blood. Accumulated secretions in the uterine cavity cause inflammation and severe pain.
Due to refusal of hormonal contraceptives, a new pregnancy may occur. Theoretically, it can occur already in the first cycle after vacuum aspiration.
In a large Swedish observational study of 145 recognized perforations during first trimester uterine evacuation, 31% occurred during abrupt curettage. There are no data that have shown a reduction in retained products using sharp curettage. Ultrasonographic guidance during uterine evacuation in the first trimester of pregnancy is a safe and effective alternative to abrupt curettage in ensuring complete uterine evacuation.
In the United States, pelvic infections occur in 5% to 5% of patients after suction curettage, and the rate of infection is not related to the evacuation approach. Some receive risk insurance to reduce the overuse of antibiotic prophylaxis due to the low prevalence of postabortion infection.
Vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity: indications and contraindications for use
This procedure involves obtaining material contained in the uterine cavity using a special pump that creates negative pressure and soft tips. It comes in two types - electric and manual. In medicine, this method is called “vacuum excochleation”.
Such an intervention is considered a more gentle method than manual curettage, since the risk of trauma to the endometrium, myometrium and cervix is minimal.
Indications for the use of vacuum escochleation:
- abortion for up to 6 weeks in case of fetal pathologies and frozen pregnancy;
- remnants of parts of the fertilized egg after miscarriage, curettage or medical abortion;
- hydatidiform mole;
- biopsy of the contents of the uterus for diagnostic purposes;
- metrorrhagia;
- remnants of the placenta after childbirth;
- accumulation of blood or fluid in the uterus.
Contraindications:
- obstetric gestation period over 5-6 weeks;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- less than six months after the last abortion;
- infectious diseases;
- myoma;
- pathology of the uterus;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- chronic diseases incompatible with this procedure.
How is such an intervention prepared and carried out?
Preparation:
- Gynecological examination.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
- Consultation with a therapist.
- Clinical diagnostic studies: clinical blood and urine test, microflora smear, blood coagulation and biochemistry test, markers of hepatitis and viral infections, HIV, RW.
- Consultation with a psychologist (only necessary for termination of pregnancy without medical indications).
What does a mini-surgery look like?
- Vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity is carried out in an outpatient setting or in a small operating room if the woman underwent inpatient treatment.
- Before the procedure (30 minutes before), the patient takes medications designed to relax the cervix and alleviate pain (Atropine, Baralgin, Diphenhydramine, Drotaverine).
- The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The procedure itself lasts 5-10 minutes.
- After vacuum cleaning, the woman is advised to rest for several hours within the walls of a medical institution. During this time, the anesthesia will wear off, and the staff will assess the patient’s general condition. Normally, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, nausea, and sweating are possible.
- The doctor prescribes a course of drugs to prevent infection and painkillers, warns about possible symptoms, after which the woman is sent home.
Two weeks after the procedure, you need to do an ultrasound to make sure that the cleaning was successful, visit a gynecologist and get tested.
Advantages and disadvantages
Vacuum interruption has many advantages over other interruption methods. Firstly, during the intervention there is no need to expand the cervical canal, therefore there is practically no discomfort during such an abortion, and the development of cervical insufficiency as a complication is minimized.
When performing an abortion by suctioning the fetus, complications such as perforation of the uterine wall, which often occurs with traditional curettage, are excluded. A vacuum abortion takes about 10 minutes, after which the woman is left under medical supervision for another couple of hours. The procedure does not require general anesthesia and can be performed with local anesthesia.
But this abortive method also has some disadvantages. For example, it can only be carried out during a certain period. Incomplete suction of fetal tissue is also possible, in which case repeated aspiration or curettage is necessary.
Life after the procedure, risks and consequences
Reviews about vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity from real women on the Internet are contradictory. Some ladies who have undergone a mini-abortion write about complications after the procedure, such as:
- bleeding;
- inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages;
- damage to the uterine cavity and spasm of the cervical canal;
- hormonal disbalance.
You can also find reviews that aspiration of the fetal egg was not done completely, and therefore, on a repeat ultrasound, diagnosticians found remains of fetal tissue or accumulation of blood. As a result, repeated cleaning was prescribed. For some, after vacuum aspiration during a missed pregnancy, it was difficult to become pregnant again. There are many emotional responses associated with the moral aspect of the procedure.
Why doesn't menstruation start?
The absence of menstruation a month and a half after an abortion should cause concern. This could mean that:
- there was a malfunction in the body’s hormonal system, and there was no maturation of the follicle;
- if a woman has entered into an intimate relationship, the absence of menstruation may be a consequence of pregnancy;
Taking certain medications can cause a delay in menstruation
- the reason that there is no menstruation after a vacuum may be inflammatory processes in the uterus and closure of the cervical canal;
- Taking medications - anticoagulants, antispasmodics could also lead to the absence of menstruation.
Read more How long does a breast puncture take?
All these reasons require contacting a doctor in order to find out the true causes and eliminate them. Determining pregnancy using a test is likely to be inaccurate if there is a hormonal imbalance. The test can show the presence of pregnancy even if particles of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus.
When there is no menstruation for a long time after vacuum aspiration, this can cause dysfunction of the ovaries, which leads to the development of infertility, and can lead to premature menopause. Therefore, even in the absence of obvious signs of disorders in the uterus, it is necessary to take hormone tests and undergo an examination.
Who is contraindicated for vacuum abortion?
Like any procedure, the vacuum method of abortion has its own contraindications:
- The fertilized egg is outside the uterus (ectopic pregnancy). Abortion by vacuum in this case is simply impossible. After all, it is possible to cause incurable damage to the mother’s body.
- If a woman is sick (acute infectious diseases). There is a huge risk of infection in the uterine cavity.
- Physiological characteristics (poor blood clotting).
- If a woman gave birth less than a year and a half ago.
The process of performing a vacuum abortion (mini abortion)
Using an electric vacuum pump, negative pressure is created in the uterus. Under the influence of the apparatus, the fertilized egg is detached from the walls of the uterus and sucked into a prepared container. The process does not use metal dilators, thanks to which the cervix is not injured. The risk of infertility after a vacuum abortion is minimal.
Before starting the process of terminating a pregnancy, a woman undergoes a consultation with a gynecologist and undergoes the necessary tests. Standard blood and urine tests, blood clotting tests, ultrasound, hepatitis and HIV tests are standard.
After a thorough check of the tests, the patient is allowed to have a vacuum abortion. The entire process is carried out by a qualified doctor in a specialized institution (hospital).
The vagina and cervix are treated with an antiseptic, and anesthesia is injected into the cervix. If necessary, in cases where the woman has not given birth before, the cervix is dilated for further insertion of a rigid tube. The fertilized egg is sucked out using a tube.
During the procedure, the woman may feel cramps, which stop immediately when the tube is removed. During the removal of uterine tissue (abortion), symptoms of nausea, weakness and excessive sweating are possible.
The duration of the procedure is 5–10 minutes, after which the patient rests in the ward where her condition is observed.
Upon discharge, antibiotic treatment is prescribed to prevent inflammation, as well as painkillers if the pain is too intense.
Features of post-abortion discharge
In the first days after vacuum aspiration, the patient experiences bloody discharge that has nothing to do with menstruation, although it is very similar to it in structure and consistency. The duration of such discharge is about 1-1.5 weeks. To alleviate the condition, experts recommend that patients during this period:
- Direct all efforts to restore the body, and, therefore, get more rest;
- Avoid coffee and dark chocolate and follow a healthy diet;
- Eliminate unhealthy habits;
- Take temperature measurements before bed and in the morning.
Consequences of a vacuum mini abortion
Any abortion, even a mini abortion (vacuum) is an invasion of the natural process of the body. Any invasion, especially surgically, has its consequences. This is stress throughout the body, which is clearly expressed by tangible symptoms.
Discharge after vacuum abortion
Bleeding begins immediately after aspiration. This is a natural reaction of the body to such interference. Many women think that these are ordinary periods, but this is not the case.
The duration of bleeding should not exceed 10-14 days. Abundance should decrease with increasing time after abortion.
Bleeding is not normal if:
- accompanied by unbearable pain;
- the abundance of discharge does not decrease;
- blood clots are present.
If you have such indicators, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Pain after vacuum abortion
Pain in the lower abdomen is expected after a mini-abortion. Associated with uterine contractions. Lasts about 3-5 days. They are not subject to treatment.
Pain and swelling in the vagina are also normal and disappear after a few days.
Chest pain usually does not bother patients, due to the fact that a mini-abortion is performed for a short period of time. But they can rarely be present; it depends more on the woman’s physiology.
How to cope with pain?
Before treating pain after an abortion, you need to know exactly its cause.
The first thing you should think about if your back hurts after an abortion is the regimen. You can't lift weights for a month. If pain has already appeared, rest will help. This pain is easier to prevent, since after an abortion, gymnastics and massage are prohibited.
Mild (or moderate) back and lower back pain associated with the natural process of uterine contraction does not require special treatment. You need to wait 2-3 days, the pain will disappear.
Increasing pain in the lower back, high temperature are symptoms that indicate that tissues of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus. Self-medication is unacceptable. You need to urgently contact a specialist who will conduct an examination. Most often, an ultrasound is prescribed and, when the diagnosis is confirmed, repeated curettage. The pain stops after 1-2 days.
Back pain caused by endometritis disappears within 2-3 days from the start of treatment, which should be carried out by a doctor (the full course of treatment is 7-10 days).
Does your lower back hurt after an abortion? This may be a normal symptom associated with the physiological characteristics of the body, but when, against the background of increasing pain, the temperature rises and heavy bleeding appears, urgent consultation with a specialist is needed.
A mini-abortion is a vacuum aspiration (suction) of the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity in the early stages of pregnancy.
Termination of pregnancy using vacuum suction has greatly reduced and weakened the harmful effects on the reproductive system of women. Modern gynecology no longer uses metal dilators, which injure the cervix. In addition, a mini-abortion does not require general anesthesia, which is so dangerous for the human body, but is performed under local anesthesia.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and takes a few minutes. After the operation, the woman is advised to lie down for a while and after two hours she is allowed to go home.
From the first day after artificial termination of pregnancy, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics and hormonal contraceptives to prevent infection and restore the woman’s menstrual cycle.
Menstruation after vacuum abortion
It is impossible to say exactly when your period will begin, because this process is individual. From the day of the mini-abortion, about 40 days pass before the start of menstruation.
Full restoration of the menstrual cycle depends on whether the woman has given birth previously or not. For those who have given birth, this period is shorter (about 3 months). For others, this process can take a long time (up to 6 months).
During the first menstruation, discharge may be scanty. If the menstrual cycle has not returned within a couple of months, you need to consult a gynecologist.
If you don't have your period for a long time after an abortion, take a pregnancy test. The result is positive - the vacuum abortion was not successful or you have an ectopic pregnancy. If the result is negative, you should wait a little longer.
How to understand that complications have arisen
It also happens that menstruation began around the due date, however, the appearance of it frightens the patient, because the discharge has an abnormal consistency, color, smell or structure. Abnormal discharge usually indicates the development of serious complications of abortion and can manifest itself in various forms. Any gynecological intervention, be it vacuum abortive aspiration or traditional curettage, cannot pass without a trace for a woman and will immediately affect the condition of the body. Therefore, patients are especially advised to monitor not only the nature of the discharge immediately after an abortion, but also the structure of the first menstrual bleeding.
- If the first menstruation after an abortion has an intense red or bright scarlet hue, then this sign may indicate intrauterine bleeding. If a sanitary pad is not enough even for an hour, and the bleeding itself continues with similar intensity for quite a long time, then you need to urgently contact a gynecologist.
- If the menstrual discharge has acquired a yellowish-white tint and an unpleasant, fetid odor, then such vivid symptoms indicate developed inflammation, which is often accompanied by hyperthermic symptoms.
- If menstruation is too painful and scanty, and then stops, appearing again a day or two later in an equally scanty amount, then this may indicate thrombus formation in the cervical lumen. A similar complication can also manifest itself as a complete absence of menstruation against the background of severe pain in the abdomen. The clot prevents the bloody masses from coming out, which leads to the development of deadly intrauterine inflammation.
- No less dangerous are menstruation, which is accompanied by copious discharge of mucous accumulations or clots. They may indicate the incompleteness of the vacuum mini-abortion, which requires repeated suction of the fertilized egg or cleaning of the uterus using the traditional curettage method.
Any abortion, whether performed using pills, vacuum aspiration or curettage, poses a certain threat to the female body. Therefore, patients who decide to take such a desperate step need to be extremely attentive to the signals that the body gives after an abortion procedure in order to avoid serious complications and irreversible consequences. One of these signals is a delay in menstruation, indicating infection or inflammation, severe hormonal imbalance and other deviations from the norm that require qualified medical intervention.
Complications after vacuum abortion
Complications after a vacuum mini-abortion are quite rare, but this possibility cannot be completely ruled out.
Perforation of the uterus
. With a vacuum abortion, it can only occur due to mechanical expansion of the cervix with a special instrument.
Incomplete removal of the fertilized egg.
It manifests itself in heavy bleeding and incessant pain in the lower abdomen. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
Cervical spasm.
The cervix closes quickly and blood remains in the uterine cavity. This causes constant pain and fever. Urgent hospitalization is required.
Ectopic pregnancy.
If during the vacuum procedure the pregnancy was in the tubes, then it remains. Symptoms include abdominal pain and pain during intercourse. Surgery required.
A woman after a mini-vacuum abortion should visit special support groups or consult a psychologist. After all, abortion not only causes physical harm, but also emotional harm. It is necessary in any way to prevent the occurrence of depression, which will only slow down the process of recovery of the body.
The video will tell you in more detail about the consequences of abortion.
For most women, the words “vacuum aspiration” evoke associations with unwanted pregnancy. Indeed, this technique is often used to perform an abortion. But there are other reasons for doing it.
Causes of pain
The most “harmless” reason why lower back pain may appear after an abortion is a violation of the regime. Unpleasant sensations can occur due to playing sports or lifting weights.
Mild nagging pain in the back after an abortion is considered normal
. This is explained by contraction of the uterus after termination of pregnancy.
Pain in the back and lower back can be explained not only by physiological reasons. There are cases when parts of the fertilized egg remain in the uterus. These residues become the cause of infection in the body. They prevent the uterus from contracting, so a woman may be tormented by severe growing pain in the abdomen, radiating to the lower back and sacrum, and copious (sometimes heterogeneous) discharge. This situation can arise both during a surgical abortion, when the doctor blindly scrapes out the wall of the uterus, and during a medical abortion (in the case of an incorrectly selected dose of the drug).
The uterine cavity after an abortion is a large wound, which is favorable for the proliferation of microbes (blood is a nutrient medium). Against this background, inflammation may occur - endometritis. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by lower back pain and irregular menstruation.
How to do vacuum aspiration
Vacuum aspiration is considered to be an essentially small operation, during which the contents of the internal part are removed using suction. In this case, the organ is minimally injured. Only the endometrium of the uterus is removed, and the walls of the organ and its cervix remain undamaged.
Before vacuum aspiration is performed, the woman must undergo tests, the purpose of which is to determine the gestational age during abortion and the presence of inflammatory processes. The procedure itself is performed on an outpatient basis and takes only 10 minutes.
First, the external genital organs are treated with an antiseptic, then anesthesia is given. The procedure is performed either under general anesthesia or using local anesthesia. In the latter case, the woman feels tolerable pain in the lower abdomen.
The tip of the pump is inserted into the uterus. In this case, for nulliparous women, the cervix is first dilated with a special instrument. Using a pump, the contents of the uterus are exfoliated and brought out. Then active contraction of the uterus begins, stopping after the tip is withdrawn.
Vacuum aspiration - indications
This procedure is used quite often to terminate a pregnancy. But at the same time, the pregnancy period should be short - less than 5 weeks, or rather up to 21 days without the next menstruation. In addition to abortion, there are other indications for vacuum aspiration:
- Termination in case of pathologies of pregnancy development.
- To improve uterine contraction in the postpartum period. Vacuum aspiration removes the remains of the placenta and blood clots, which prevent the organ from fully contracting.
- In case of spontaneous miscarriage to remove the remains or in case of missed abortion.
- During inflammatory processes in the organ cavity.
- To obtain samples of endometrial pathologies for subsequent histological examination.
- When there is uterine bleeding or accumulation of blood or other fluid in the uterus.
There are a number of contraindications to vacuum aspiration. These include:
- The pregnancy is too advanced.
- Exacerbation of chronic inflammation or acute inflammation.
- Infectious process.
- Improper development of the uterus.
- Neoplasms in the uterus that deform it. For example, if there is .
- Other serious illnesses of women.
- Less than six months have passed since the previous termination of pregnancy.
Signs of pathology
We told you how many days after an abortion menstruation usually occurs if the patient is in good health. But this operation does not always end successfully. If your period begins a little earlier or your period does not come after an abortion, it is better to go to the clinic.
So, you should be wary of critical days, which may begin earlier. But don't confuse them with bleeding, which everyone has. A woman’s period a week after an abortion, which began immediately after the operation, is the consequences of this procedure; in fact, these are not critical days. When removing the fetus, the doctor injures the vessels, so blood will flow from them until they are completely healed.
Much depends on exactly what kind of menstruation after an abortion. If the following symptoms appear, you should immediately go to the clinic:
- The discharge has an unpleasant odor or has an unusual consistency: it is too liquid or clots have appeared in it.
- Clots in menstruation are yellow and contain bloody impurities.
- Menstruation is accompanied by unpleasant sensations that were not there before.
All these are signs of infection. If they make themselves felt, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment, otherwise chronic diseases and then infertility may appear.
Recovery after vacuum aspiration
Since the operation lasts only a few minutes and does not cause much harm to the organ, the woman can go home 1 hour after it is performed. For about two weeks after vacuum suction, a woman may experience slight bleeding similar to menstruation. During this time, you must use sanitary pads. Do not use sanitary tampons for this purpose during the first month after surgery.
Often after surgery, a woman feels tired and may feel dizzy. This is a normal reaction of the body. It is best to stay at home and rest for the first 24 hours after surgery. If there is a feeling of discomfort or pain, you can take a painkiller.
In the following days, you must continue taking painkillers. If the operation was performed under general anesthesia, then avoid any activities that require high concentration for another 38 hours.
2 weeks after vacuum aspiration, the woman must return to the antenatal clinic and undergo a control ultrasound. If the results show that the uterus is not completely cleaned, then the procedure is repeated or the organ cavity is cleaned by manual curettage.
Sexual activity is prohibited until the discharge has completely stopped, and then it is necessary to protect yourself with contraceptives. This is necessary to prevent a new pregnancy and to reduce the risk of disease. If there are signs of infection, such as nausea, a strong odor from the discharge, unbearable pain in the lower abdomen, bloating, intense bleeding with the presence of clots, consult a doctor immediately.
How soon should your period start?
The beginning of the cycle is the day on which the operation is performed. The first menstruation after an abortion comes 35-45 days after the operation. Over time, over the course of 3-4 months, the cycle will gradually decrease until it returns to its usual schedule (24-30 days). The duration of the first menstruation after an abortion may not take the usual 3-7 days, but much longer - up to 10 days. If bleeding persists for a longer period or heavy periods are observed after an abortion, you should consult a doctor.
Menstruation should not be confused with uterine bleeding, which occurs due to poor cleansing and leaving fetal particles in the uterus. Uterine bleeding can occur at any time. Bleeding can also occur due to physical exertion or early intimate relationships.
Pregnancy after abortion
Most women mistakenly believe that after an abortion they will not become pregnant until at least their first menstruation. It's not like that at all. With a successful uncomplicated abortion, a woman is capable of pregnancy within 2 or 3 weeks. Therefore, if you do not burden yourself, then you may not wait for menstruation.
The female body perceives termination of pregnancy as the beginning of the next cycle. In this regard, a new egg immediately begins to mature. This means that a couple of weeks after the abortion, ovulation will occur and around the same time a new pregnancy may occur. But since the endometrium does not have time to fully recover in such a short period of time, the development of pregnancy in this case is impossible and a miscarriage occurs.
You should not plan a pregnancy for at least six months. During this time, it is necessary to do everything possible to restore health, use contraception during sex. In some cases, the recovery period can last for a year.
Abortion by vacuum aspiration and its consequences
There are two methods of vacuum aspiration (also called suction aspiration).
- Manual vacuum aspiration. This procedure can be used approximately 5 to 12 weeks after your last menstrual period (early first trimester of pregnancy). It involves using a specially designed syringe to perform suction. This method is not available everywhere, but may be more affordable than machine suction in some geographic areas.
- Machine vacuum aspiration. This procedure is a common method used in the first 5 to 12 weeks (first trimester) of pregnancy. Machine vacuum aspiration involves the use of a hollow tube (cannula) that is attached to a bottle and a pump that provides a gentle vacuum action. The cannula is inserted into the uterus, the pump is turned on, and the tissue is gently removed from the uterus.
What are the reasons for the absence of menstruation?
There are often cases when, after an abortion, especially a medicinal one, menstruation does not come for a long time. This may mean that fetal rejection did not take place, and that the discharge that the woman saw resulted from endometrial rejection. However, such a fetus can no longer be preserved, since it is damaged and, most likely, will develop pathologies. You can find out whether the entire fetus has come out or not using an ultrasound.
After an abortion, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound
Lack of menstruation after an abortion may be due to:
- new conception;
- changes in hormonal levels resulting from termination of pregnancy;
- inflammation;
- endometrial hyperplasia;
- fibromyosis or uterine cystosis;
- endometriosis;
Therefore, in case of delay, it is necessary to undergo an examination to find out the reasons.
Manual vacuum aspiration procedure
Manual vacuum aspiration usually takes 5 to 15 minutes. It can be performed safely in a clinic or doctor's office using a local anesthetic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen. The procedure includes:
There may be some bleeding for a couple of weeks after vacuum aspiration. It may feel similar to menstrual bleeding. this time until it stops. This type of surgical abortion is performed on women. between 7 and 15 weeks of pregnancy.
- A numbing medicine (local anesthetic) is injected into the cervix.
- If necessary, a small instrument is inserted into the cervix to slightly dilate it. However, in most cases the extension is not necessary.
- A thin tube is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. A hand-held syringe is used to suction tissue from the uterus. As the tissue is removed, the uterus will contract. Most women experience cramps during the procedure. The cramps go away after the tube is removed. Some women also experience nausea. sweating and feeling weak. But usually the symptoms are less severe than with machine vacuum aspiration.
Machine vacuum aspiration procedure
A few hours or a day before the machine vacuum aspiration procedure, an osmotic cervical dilator may be placed in the cervix to slightly open (dilate) it. Immediately before the procedure, antibiotics are given to prevent infection. They may also be given a medicine called misoprostol to soften the cervix before the procedure.
Machine vacuum aspiration usually takes 10 to 15 minutes. It can be performed safely in a clinic or doctor's office under local anesthesia. The procedure includes:
- You are placed on the examination table in the same position as for a pelvic examination, with your feet on the gynecological equipment and lying on your back.
- A speculum is placed in the vagina.
- The vagina and cervix are cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- A numbing medicine (local anesthetic) is injected into the cervix. Medicine for pain or sedation, in addition to local anesthesia, can be taken orally or through a vein. Vasopressin, or a similar drug. slowing down uterine bleeding. may be mixed with local anesthetic to reduce blood loss.
- The cervix is grasped using a device that holds it in place.
- The cervical canal is opened (expanded) with a small device. Dilatation reduces the risk of any cervical injury during the procedure.
- A thin, hollow tube (cannula) is inserted through the cervical canal and a gentle vacuum is applied to remove tissue from the uterus. As the tissue is removed, the uterus will contract. Most women experience cramps during the procedure. The cramps go away after the tube is removed. Some women also experience nausea, sweating and a feeling of weakness.
Tissue removed from the uterus during a vacuum aspiration procedure is examined to ensure that the tissue is completely removed and the abortion is complete.
Sometimes a dilatation and curettage procedure is necessary after vacuum aspiration if not all tissue has been removed. A dilatation and curettage procedure uses a sharp surgical instrument to remove tissue from the uterine cavity.
What to expect after surgery
Vacuum aspiration is a minor operation. Normal recovery includes:
- Irregular bleeding or spotting during the first two weeks. During the first week, avoid tampons and use only pads.
- Cramps, similar to menstrual pain, that may be present for several hours, and possibly several days, as the uterus shrinks back to its pre-pregnancy size.
- Emotional reactions lasting 2 to 3 weeks.
- Take the full course of prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Rest easy during the first day. You can carry out your normal activities the next day, depending on how you feel.
- Acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) or ibuprofen (such as Advil) may help relieve the pain of cramps.
- Do not have sexual relations. at least one week. Use birth control methods after an abortion. Also use condoms. to prevent infection. You may start using certain contraceptives immediately after the vacuum aspiration procedure.
Signs of complications after vacuum aspiration
Call your doctor immediately. if you have any of these symptoms after an abortion:
- Heavy bleeding. Both medical and surgical abortions usually cause bleeding that differs from the normal menstrual cycle. Heavy bleeding may mean: Clots larger than a golf ball appear for 2 hours or more.
- Using more than two large pads per hour for two hours straight.
- Heavy bleeding lasting 12 hours.
Make an appointment with your doctor. if you have any of the following symptoms after a recent abortion:
- Bleeding (not spotting) for more than two weeks.
- New, unexplained symptoms that may have been caused by medications taken during treatment.
- No menstruation for 6 weeks after the procedure.
- Signs and symptoms of depression. Hormonal changes after pregnancy can lead to depression, which requires treatment.
Why is vacuum aspiration performed?
Vacuum aspiration is done in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Vacuum aspiration can be done as:
- Induced therapeutic abortion
- After an unsuccessful medical abortion
- Upon fetal death (missed spontaneous abortion)
- In case of incomplete miscarriage (incomplete spontaneous abortion)
How successful is the procedure?
In the first trimester, surgical abortions are safe and effective and have few complications.
In rare cases, the aspiration procedure does not successfully terminate the pregnancy. This is more likely to happen during the first weeks of pregnancy. Among manual aspirations performed before 6 weeks, about 3 in 100 are unsuccessful and a repeat procedure is necessary.
Risks of Vacuum Aspiration
Surgical abortions in the first trimester are considered the safest surgical procedures. The risk of complications is low. Some minor complications include:
- Damage to the lining of the uterus or cervix.
- Infection. Bacteria can enter the uterus during the procedure and cause an infection. This is more likely if you have an untreated condition. for example, a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that existed before the procedure. Symptoms of fever, pain and weakness in the abdominal area usually begin 2 to 3 days after the procedure. Taking antibiotics during or after the procedure reduces the risk of infection.
Rare complications are possible:
- A hole in the wall of the uterus (uterine perforation, rare), which most often occurs when the cervix dilates. Bleeding is usually minimal and there is no need for recovery. If bleeding is a concern, laparoscopy (a procedure that uses a lighted viewing tool) can be used to see if the bleeding has stopped.
- Tissue remaining in the uterus (undistributed products of conception) usually causes recurring cramping abdominal pain and bleeding for a week after the procedure. Sometimes prolonged bleeding does not develop until several weeks later.
- Blood clots. If the uterus does not contract to expel all the tissue, the cervix may become blocked and begin to prevent blood from leaving the uterus. The uterus becomes enlarged and painful, often causing abdominal pain, cramping and nausea.
Repeated vacuum aspiration and medications to control bleeding are used to remove retained products of conception or blood clots.
Undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy after manual or machine vacuum aspiration
There may be an undiagnosed ectopic (tubal) pregnancy that was not detected before the abortion procedure. Although a pregnancy test. passed before the procedure, positive, the pregnancy itself is not in the uterus. Thus, this method of abortion does not terminate the pregnancy. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occurring after an abortion procedure may include:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain that gets worse
- Pain during intercourse
- Vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness or fainting. caused by blood loss
An ectopic pregnancy requires urgent medical attention. Call your doctor immediately if you have symptoms of a possible ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms of complications
The main sign of complications after surgery is the fact that the girl does not have menstruation. Often this condition is accompanied by pain localized in the groin area of the abdomen. Main reasons:
- Possible hormonal imbalance. Even such a gentle operation as vacuum aspiration is a serious shock to the reproductive system of the female body.
- Cervical stenosis. To carry out manipulation in nulliparous women, it is necessary to artificially dilate the cervical canal. If it is damaged during surgery, the opposite may occur - narrowing. As a result, it happens that the rejected functional layer of the endometrium remains in the organ cavity, and this threatens its inflammation.
- Deep vein thrombosis of the pelvic organs. As a result of the operation, thrombi may form - blood clots that impede blood circulation in the organs. The larger the caliber of the vessel, the more dangerous the consequences. In the best case, endometritis, accompanied by acute pain in the projections of the organs.
- Bend of the uterus. In case of the initial pathological position of the organ, the operation can worsen the tilt, as a result of which the contents of the uterus cannot be evacuated into the external environment.
- New pregnancy. If you refuse to take hormonal and traditional contraceptives, pregnancy may occur in rare cases.
Read more What causes uterine endometriosis
Other important symptoms of complications in the female reproductive system:
- Menstruation is intermittent and accompanied by pain. This is often a sign of an inflammatory process in the endometrium. Discomfort may also be due to the fact that during the operation the uterus shrank as a result of spasm. In this case, antispasmodics will help relieve this condition.
- The discharge is very abundant. This manifestation may be due to hormonal imbalance or be a symptom of open uterine bleeding. Other reasons are ovarian pathology and endometritis. If the amount of bleeding is such that hygiene products require replacement every 2-3 hours, you should seek emergency care.
- Menstrual blood has an unpleasant odor and an unusual color. Typically, this is a symptom of inflammation and infection. Unhealed foci of damage to the integrity of the uterine mucosa are subject to inflammation, as a result of which fluid - exudate - comes out of them. Otherwise it is called ichor. It has a yellowish tint, contains a large amount of proteins, as well as blood cells, most of which are leukocytes, indicating the acute nature of the pathology, and is a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms, which give the discharge a specific odor.
- Symptoms of general intoxication appeared: low-grade fever, chills, weakness, headaches. This means that an infection has entered the body through the damaged mucous membrane.
- Menstrual blood contains clots and tissue fragments. Normal secretions contain only small pieces of endometrium, as well as large amounts of enzymes. The presence of large clots and tissue remains in the discharge indicates a poorly performed or unsuccessful operation. In such cases, ultrasound examination and monitoring of the patient's condition are required.
If you notice one of these symptoms, you need to see a doctor. After all, any complication after vacuum aspiration leads to acute disease of the female genital organs, and the consequences are very dire: chronic pain and infertility.
Vacuum aspiration, performed for the purpose of termination of pregnancy, for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, is a serious intervention in the vital functions of the reproductive system of the body. Vacuum aspiration affects the functioning of the body’s endocrine system, makes changes to the structure of the uterus, and therefore, to a greater or lesser extent, is a traumatic procedure. Menstruation changes after vacuum aspiration. Their stability and the nature of bleeding are disrupted. For some women, it takes up to six months to restore the reproductive function of the body.
Vacuum aspiration – has a strong impact on women’s health