Is it possible to get pregnant with a follicular cyst? Most women wait for conception with special trepidation and are proud of their pregnancy. Thus, they realize their destiny and feminine nature. Giving life to another person is a great responsibility, and by accepting it, you will have to give up a carefree existence and concentrate entirely on your main task.
It would seem that a follicular ovarian cyst and pregnancy are completely incompatible things. In most cases, the development of any tumor formations (even benign ones) prevents the birth of a new life. However, in practice it often turns out that pregnancy occurs during illness or when the woman does not yet know about it. What are the dangers of a follicular cyst during pregnancy? Can it prevent you from bearing a healthy child?
First of all, it is worth remembering that it is possible to get pregnant with a follicular cyst. Sometimes a pregnancy test shows a positive result just at the moment when a woman, for health reasons, is in no way ready for it.
But, I would like to assure those who are scared and doubt whether they can give life to a tiny creature. Having children is the greatest happiness, a blessing given from above. If you unexpectedly discover a positive test, just be happy. It is quite possible that in relation to the pregnancy itself, the disease will not turn out to be a significant obstacle.
Is it possible to get pregnant if you have an ovarian cyst?
It all depends on the location of the growth, whether one organ is affected or both. There are these types of cysts:
- corpus luteum;
- endometriotic;
- paraovaryl;
- follicular;
- dermoid;
- polycystic disease;
- malignant formations.
Such types of cysts as endometriotic and follicular can create great obstacles to conception. Pregnancy with paraovarian, dermoid cysts is permitted only if it does not tend to increase, and its size does not exceed 3 cm. And only the corpus luteum cyst is considered absolutely safe for the fetus, even moreover, it contributes to the formation of the embryo and its attachment to the wall of the uterus.
With a cyst of the right ovary
If only the right ovary is affected, the chances of successful conception are reduced by 50%. A follicular cyst, in the presence of which the egg cannot leave the follicle, does not contribute to conception. If it was formed only on the right female organ, then the egg during ovulation will come out of the left one after one cycle.
The endometrial type of formation creates unfavorable conditions for the origin of life. Even if it has formed on only one ovary, the formation can cause adhesions in the uterus and block the path of the fertilized egg to the uterus.
With a cyst of the left ovary
If there is one healthy female organ, conception is possible, since one of the two organs will be in working condition.
In addition, types of diseases such as paraovary and dermoid cysts do not prevent the release of the egg from the follicle, which means they do not interfere with conception. At the stage of planning a child, you must definitely come for a consultation with a doctor.
It happens that a woman has health problems and does not even know it. If a cystic bladder was detected during an examination of the female genital organs, it is worth undergoing treatment before conception.
If the cyst is on both ovaries
The ability to get pregnant largely depends on the type of cystic suture. A follicular cyst or polycystic disease on both ovaries makes a woman completely infertile. With medicinal, surgical treatment, and rehabilitation, conception is excluded. If there are malignant tumors on both the right and left sides, urgent surgery will be required. In particularly advanced cases, removal of the ovaries is not excluded.
As for safer formations when planning pregnancy: if the growth does not exceed 3 cm in size and does not increase, then with constant monitoring by a doctor, conception and gestation are not prohibited.
What to do with a cyst
Unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant are a reason for a thorough examination. If the diagnostic results confirm the presence of a follicular cyst, it is necessary to urgently begin its treatment. Doctors say that depression and emotional stress have a negative impact on the treatment process.
There are two main methods of treating cysts: conservative and surgical. A conservative treatment method involves taking hormonal medications, vitamin complexes and homeopathic remedies, which eliminate the risk of relapse. The use of natural decoctions and infusions for medicinal purposes is permitted after consultation with your doctor.
If the follicular tumor twists, ruptures, bleeds, or if drug therapy is ineffective, the patient is advised to undergo surgery - laparoscopy.
Removing a benign tumor during pregnancy is prohibited, since surgical intervention can worsen the well-being of the expectant mother and affect the development of the fetus.
Is it possible to get pregnant and give birth with an ovarian cyst?
From what is known about this disease, we can conclude that with certain types of it, the possibility of becoming pregnant is not excluded.
Does it interfere with getting pregnant?
Diseases such as polycystic disease, follicular and endometriotic formations make conception almost impossible, and if both organs are affected, the woman is considered infertile.
Does it affect conception?
In the presence of such types of blisters as paraovary and dermoid, nothing prevents the release of the egg from the follicle, as well as its passage into the uterus. Therefore, such formations do not affect conception in any way.
But if the presence of a formation on the female genital organs changes the hormonal levels, it becomes difficult to correctly determine the time of onset of ovulation. With hormonal imbalance, the days of menstruation may shift, accompanied by an abundance of blood and severe pain.
You need to be very careful if you have an endometriotic cyst. This disease causes processes in the uterus in which the embryo cannot reach it and attach to its walls. If you do get pregnant, it will be ectopic. It is worth getting rid of such a disease surgically at the stage of planning a child.
How does it affect an existing pregnancy?
A functional cyst and pregnancy are completely compatible concepts.
During the prenatal period, hormonal levels change, during which formation decreases. Until 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, the disease completely disappears.
Surgical treatment is required if we are talking about polycystic disease. Its proximity to pregnancy can lead to consequences such as miscarriage, fetal death and premature birth. If this syndrome is present, regular ultrasound monitoring is necessary. During fetal enlargement, the uterus puts pressure on the formation, which can have the following consequences:
- the vascular pedicle of the cyst is twisted;
- rupture of formation, hemorrhage.
The occurrence of abdominal pain, increased heart rate, nausea, fever, bleeding from the vagina - all this is an indication for immediate consultation with a doctor.
Impact on childbirth
If the formation increases by more than 5 cm during the prenatal period, the doctor will advise the woman to undergo surgery no earlier than 15-20 weeks of pregnancy. If this is not done, and the formation continues to increase, this will be an indication for a cesarean section.
Pregnancy and childbirth due to ovarian cysts: risks and prognosis
Ovarian neoplasms can lead to the development of the following complications:
- Impaired implantation and death of the embryo before delayed menstruation. Hormonally active ovarian formation leads to an increase in estradiol. Hormone imbalance prevents endometrial proliferation. The embryo cannot penetrate the wall of the uterus and dies within 2 weeks;
- Spontaneous miscarriage in the first and second trimester of pregnancy. A growing cyst changes hormonal levels and also puts mechanical pressure on the uterus. The development of the embryo is disrupted and it dies in the early stages;
- Premature birth (after 22 weeks). A large formation interferes with the full growth of the uterus and the development of the fetus and can lead to premature termination of pregnancy. A premature baby needs intensive care and long-term rehabilitation.
On a note
The connection between hormonally active ovarian formation and regressive pregnancy is being studied, but so far this hypothesis has not been confirmed.
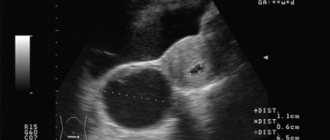
Follicular cyst and pregnancy can be diagnosed simultaneously during the first ultrasound examination.
Sometimes, on an ultrasound, specialists can detect a follicular cyst along with the fetus.
Further tactics will depend on the course of the pathology:
- Small tumors (up to 3 cm) do not interfere with fetal development. Monitoring the growth of the lesion throughout pregnancy is indicated;
- Large formations (from 3-4 cm) more often lead to termination of pregnancy and the development of complications.
During pregnancy, the ovarian cyst is gradually pushed aside by the growing uterus. Compression of the formation can lead to the development of complications:
- Cyst rupture. Accompanied by sharp pain in the lower abdomen and bleeding from the genital tract;
- Torsion of the tumor stalk. Partial torsion leads to a gradual increase in pain and tension in the abdominal muscles. With complete torsion, the pain will be sharp, severe, unbearable.
Rupture and torsion are complications that are life-threatening for the woman and the fetus. Emergency hospitalization to an obstetric hospital and surgical treatment are indicated.
In addition to the development of complications, the following conditions may be the reason for surgery:
- Compression of closely located pelvic organs - bladder and intestines;
- Rapid growth of the tumor;
- Suspicion of malignant degeneration.
It is important to know
A follicular cyst is not capable of degenerating into cancer, but another malignant tumor may be hiding under the guise of a harmless formation.
As planned, surgery is performed in the middle of the second trimester - at 16-20 weeks. At this time, the risk to the fetus is minimal, and there is every chance of maintaining the pregnancy. If life-threatening complications develop, cyst removal is possible at any time.
In the first half of pregnancy, the operation is performed laparoscopically.
The laparoscopic method of removing an ovarian cyst is a modern, gentle way to get rid of the pathology without causing harm to the fetus.
Small incisions are made through which the cyst is removed using an atraumatic instrument. If indicated, the ovary may be removed. After the operation, medications are prescribed that reduce the tone of the uterus and help maintain pregnancy.
In the second half of gestation, the issue of performing a cesarean section with extraction of the fetus and subsequent removal of the cyst is decided. If possible, doctors try to extend pregnancy to 37 weeks.
During pregnancy, the neoplasm can behave differently. In most cases, spontaneous regression of the lesion is observed before 20 weeks. Much less often, the formation persists in the second half of gestation. Uncontrolled growth of the cavity with the development of complications is possible.
An ovarian cyst is not an indication for induced abortion. But if a woman decides to terminate her pregnancy, she can plan to conceive a child again no earlier than 3 months after the medical abortion. After a surgical abortion (curettage of the uterine cavity or vacuum aspiration of the fertilized egg), it is recommended to wait 6 months.
Prevention of possible complications
It is worth getting rid of education before conception. With some types of disease, pregnancy cannot occur. In others it can, but during pregnancy it continues to grow, creating risks for the health of the baby and the expectant mother. There is a situation in which the bubble disappears as the fetus grows.
In any case, the doctor should monitor the condition and changes in the formation during pregnancy, and if the condition worsens, prescribe appropriate treatment or offer to remove the cyst surgically.
When planning a child with an ovarian cyst, constant medical supervision is required. Only he will be able to determine its type and predict how the formation will affect conception and gestation.
Useful video
The patient’s inability to become pregnant is one of the main reasons for an examination by a gynecologist, as a result of which the presence of cystic formations is diagnosed. The cyst itself on the ovary is considered a benign formation and often resolves on its own, but at the same time it is dangerous due to its increase in size and possible degeneration into a malignant formation that produces cancer cells.
Whether it is possible to become pregnant with an ovarian cyst and how appropriate this is in each specific case without further treatment, only the attending physician can tell you after conducting a series of studies and tests. Even with a positive answer from a specialist, constant monitoring of the body’s condition and strict adherence to all prescribed recommendations are required.
Right or left - what's the difference?
Clarifications are often added to questions about whether it is possible to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst. For example, is it possible to get pregnant with a right ovarian cyst? The ovaries are paired formations that function identically. Therefore, a cyst appears on one due to the same disturbances in the functioning of the body as on the second. But the clinical picture is sometimes slightly different.
The blood flow in the right ovary is more active, since the right part of the paired organ is part of the abdominal aorta. Due to greater blood pressure, some cysts progress faster. It is the right ovarian cyst that causes the most complications. Whether you can get pregnant depends on the type of cyst. Due to increased blood flow, hemorrhagic cysts grow rapidly. This neoplasm manifests itself as a result of complications.
Since the cyst shell is stretched, the vessels in it may burst. Blood enters the cavity, replacing the serous fluid. The more blood the cyst collects, the faster it grows. A hemorrhagic cyst on the right ovary is more likely to rupture. The disease is accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms:
- sharp pain that does not go away after menstruation;
- a drop in blood pressure, which indicates bleeding;
- abdominal enlargement and asymmetry.
The left ovary is connected by blood flow to the renal artery. The blood pressure in it is lower, so hemorrhagic cysts develop less frequently. Is it possible to get pregnant with a left ovarian cyst? The examination will tell you, since the possibility of conception depends on the type of cyst. Pathology of the left ovary is dangerous due to the absence of pronounced symptoms. Often only an examination reveals the presence of pathology when it has already grown to a large size. Large dermoid or paraovarian cysts put pressure on the ovary and other internal organs. Because of this, the following symptoms develop:
- feeling of heaviness or fullness in the abdomen;
- intestinal problems, frequent constipation;
- constant urge to go to the toilet “in a small way;
- pain during movement and physical activity if the leg of the cyst itself is pinched.
How does a cyst affect the possibility of conception?
Patients with an ovarian cyst always have a chance to get pregnant again, since small tumors do not affect the functioning of the entire reproductive system of the female body.
Often, it is the onset of pregnancy and a sharp change in hormonal levels that lead to the fact that a hollow tumor with internal fluid resolves on its own.
But this is only possible with minor benign formations, and also if the detected ovarian cyst does not increase in size, for example, a follicular hollow tumor of the right ovary. With any other option, conservative or surgical treatment is first prescribed, and then the patient’s real chance of becoming pregnant after surgery is determined (subject to the full restoration of the entire system).
A cyst has a negative effect on conception if it grows rapidly. The tumor begins to put pressure on neighboring organs, and also interferes with the functioning of the ovary itself and the fallopian tubes. Due to the presence of formation, the follicles cannot ensure their normal development, which means that disturbances appear in the maturation and release of the egg, ovulation is either delayed or does not occur at all.
If everything happened normally at the stage of release of the egg, then its further fertilization is at risk, since it cannot normally enter the uterine cavity. The main danger of this situation is that fertilization can take place in the fallopian tubes, causing an ectopic pregnancy. In such cases, timely hospitalization and a series of surgical interventions are necessary. That is why, if there is a cyst, it is first recommended to cure the pathology, and only then pursue the desired pregnancy.
There is no difference in the location of the cyst, for example, in the area of the left ovary. It is important to conduct a thorough examination and take a balanced approach to the issue of the risk of pregnancy in the presence of the pathology itself. The presence of a cyst can be suspected by the presence of the following symptoms:
- a feeling of soreness in the lower abdomen, which increases at the beginning of menstruation;
- increased urge to urinate, as well as constipation, pathological retention of feces in the intestines due to pressure exerted by the cyst;
- failure of an already established menstrual cycle (especially if the tumor itself is capable of producing hormones);
- a noticeable increase in the size of the abdomen due to the rapid growth of the tumor.
Lack of timely and correct treatment of an ovarian cyst can lead to rupture of the formation, which, according to symptoms, can be classified as peritonitis.
Signs of education
Without undergoing a special examination, it is almost impossible to detect the presence of a cyst. The fact is that its lifespan is often short. Since it does not have time to reach a significant size, it cannot be felt during a gynecological examination.
It does not cause any pain as long as its size remains within 5 cm. Large cysts can cause discomfort in the form of the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent and painful urination;
- specific vaginal discharge;
- disruptions of the menstrual cycle;
- development of severe hormonal imbalance.
Important! When a cyst ruptures, a woman experiences severe pain and internal bleeding develops.
Pain symptoms appear only with large tumors or the development of complications
It also happens when a follicular cyst is confused with pregnancy. The symptoms of ectopic fertilization of the egg are very similar to a progressive pathology of this kind.
The influence of various formations on pregnancy
A hollow tumor with internal fluid may differ in its location and structure, which in turn determines the degree of its influence on the patient’s ability to become pregnant.
Corpus luteum cyst
The corpus luteum is the reproductive gland, which is formed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. A cyst in such cases may appear due to an increase in the amount of adenohypophysis hormone. The process of ovulation (the release of a mature egg) does not depend in any way on the development of the tumor, so this type of hollow tumor does not affect the ability to get pregnant. On the other hand, after conception itself, the patient must be under the close supervision of a doctor in order to promptly prevent a possible threat to the full development of the fetus.
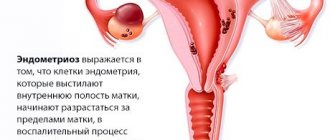
Endometrioid cyst
The neoplasm in such cases is localized in the ovarian region due to pathological growth of the endometrium in it (damage to the uterus by endometriosis).
The possibility of becoming pregnant in such cases is extremely low and requires removal of the tumor followed by hormonal treatment even before conception.
If a cyst is discovered after pregnancy, it must be monitored. As a rule, an endometrioid type tumor does not affect the growth and development of the fetus.
Paraovarian
This type of hollow tumors forms in the area of the fallopian tube and appendages. The pathology is usually asymptomatic, so patients often find out about the presence of a paraovarian cyst when they are already pregnant. The chances of getting pregnant are quite high, but during the development of the fetus it is extremely important to monitor the behavior of the cyst, since it is considered safe only if its size does not exceed 2.5 - 3 cm in diameter.
Follicular
A follicular cyst is one of the types of hollow formations that sharply reduce the chances of achieving the desired pregnancy, since it has a direct effect on the process of ovulation (the release of a mature egg from the follicles). We are talking about disturbances in the process of maturation of the follicle, which does not rupture in time and does not release the finished egg. In addition, such tumors interfere with the formation of new functional follicles with the subsequent onset of ovulation.
There is a chance of pregnancy in such cases if the cystic lesion is distributed only on the left or right ovary. The presence of bilateral cystic formations excludes the patient’s ability to become pregnant completely.
Dermoid
In such cases, the tumor forms on a stalk, usually due to disturbances in the process of tissue cell division (differentiation). A hollow tumor does not in any way affect the process of maturation and release of the egg, and therefore does not interfere with pregnancy and the bearing of a healthy fetus. New growths that rapidly increase in size can pose a danger. Moreover, this concerns not only the chances of getting pregnant, but also the danger of pathologies in the development of an existing fetus.
Pregnancy after cyst treatment
A significant increase in the chances of getting pregnant and fully bearing a healthy child is the main argument for timely treatment of the pathology even before the desired fertilization occurs. The choice of treatment method for the disease (conservative or surgical) is made exclusively by the attending physician, taking into account not only the stage of development of the disease, but also the age of the patient and her general state of health.
To conceive a child after treatment for endometrioid type cysts, the doctor first determines the cause of their appearance and carries out appropriate treatment of the formation, as a rule, it is complex (including surgery, medications and physical therapy sessions). After tumor removal, special hormonal therapy may be recommended.
In cases of diagnosis of a dermoid type tumor with mandatory surgical removal of the pathology, it may take several months to restore the functionality of the reproductive system. In such cases, the doctor recommends postponing pregnancy for 3 to 6 months after surgery.
If a hollow tumor degenerates into a malignant formation, the doctor prescribes its removal followed by oncological treatment. The possibility of planning pregnancy after recovery is determined individually in each individual case. This also applies to other types of cystic formations.
To increase the chances of pregnancy, the attending gynecologist, in addition to the treatment itself, may recommend:
- follow the principles of proper nutrition with the complete exclusion of fatty, smoked and fried foods from the menu (it is better to steam recipes);
- completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages;
- establish daily consumption of fermented milk products, freshly squeezed juices and cereals, which in turn allows you to quickly restore the microflora;
- supplement the diet with complex vitamins;
- avoid serious stress, overwork and heavy physical activity;
- try to stay in bed longer after surgery.
The duration of the treatment course and the dosage of prescribed drugs is determined exclusively by the attending physician and is strictly observed by the patients.
Ruptured ovarian follicular cyst
- heavy physical activity;
- inflammatory process in the pelvis;
- intense sexual intercourse;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the digestive organs.
As a result of the rupture of the cyst, acute pain appears in the lower abdomen. It may be accompanied by loss of consciousness or a sharp rise in blood pressure. In some cases, nausea and vomiting occur. The opening of internal bleeding is indicated by pallor of the skin and a weakened state. If the tumor ruptures, immediate hospitalization is necessary.
Laparoscopy is a modern method of surgical intervention and diagnosis of growths and neoplasms in the abdominal cavity and pelvic area. The apparatus for performing the operation is equipped with cold light and a video camera, which allow you to examine the object in detail. After surgery on the ovaries, gynecologists advise abstaining from sexual intercourse for 2 months of observation.
Menstruation is not disrupted, but attempts at fertilization are recommended to begin 6 months after the operation with a mandatory visit to the doctor for examination. If an ovarian cyst ruptures, it is possible to become pregnant already in the first month after the operation, but it is better not to rush. The probability of conception is 85%.
Artificial insemination
In medical practice, IVF (in vitro fertilization) in the presence of an ovarian cyst is considered possible if its location does not in any way affect not only the onset of pregnancy, but also the process of fetal development. In this case, the patient undergoes mandatory examinations and tests, the results of which determine the possibility of successful artificial insemination without prior treatment of the cyst itself.
In addition to the chances of a successful pregnancy, the chances of full gestation and development of the fetus itself with the subsequent onset of labor must be assessed.
It is possible to get pregnant with an ovarian cyst, but not in all cases. Due to the cyst, complications may develop during pregnancy. That’s why it’s so important to plan a pregnancy and prepare for it. Preliminary diagnosis of partners when planning pregnancy allows you to avoid many possible problems after conceiving a child. Modern gynecologists always recommend examination. Sometimes a woman has a tumor of the gonads at this stage. Whether the presence of a problem will affect conception can only be said after finding out the cause of its occurrence. Sometimes, an ovarian cyst can lead to infertility.
This is what a left ovarian cyst looks like.
Is it possible to get pregnant?
An ovarian cyst does not independently affect the meeting of an egg with a sperm. When the female gamete leaves the follicle and sexual intercourse takes place at the same time, conception is possible. An ovarian tumor, as the only disease of the female body, does not prevent the formation of an embryo - this is a physiological process that is difficult to influence.
It’s another matter if, in addition to an ovarian cyst, a woman is diagnosed with infertility. A formed tumor on the gonad interferes with its function of growing a follicle, in which, in turn, an egg is formed. Not all neoplasms have this effect on the ovary, only some types. Experts suggest that the size of the cyst affects the likelihood of conception, because... a large tumor fills almost the entire ovary.
But don’t worry, not every tumor interferes with the process of egg maturation. Functional cysts, as a rule, have no effect on ovulation, and if they have any negative effect on menstruation, it is insignificant. But other types of tumors, even small ones, can cause disturbances in the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Without an examination, no doctor can say whether a cyst has become an obstacle to pregnancy. To answer, you need a lot of data: the origin of the tumor, its type and size, location. All these questions can be answered only after an ultrasound examination.
How to increase your chances?
A cyst is usually a pathology with a good prognosis. If you have an ovarian cyst, you can become pregnant by regularly visiting your doctor and following the following prevention recommendations:
- Annual ultrasound diagnostics will help to detect pathology in a timely manner.
- Avoid casual sex - inflammatory processes during TORCH infections can trigger the development of a cyst.
- Control your weight. Obesity often provokes endocrine system problems.
- Move more.
- Don't let a cold run its course. Complications from an illness suffered “on the legs” can also cause pathology.
- Doctors recommend sticking to proper nutrition. Your body needs strict adherence to your diet.
Corpus luteum cyst
Such a phenomenon as a neoplasm on the corpus luteum during pregnancy is often diagnosed by doctors. It is formed after the dominant is broken. The corpus luteum is so named because of the lutein it contains, which gives the gland its red-orange color. The formation appears after ovulation and is responsible for supplying the body with progesterone, a hormone that maintains the normal course of pregnancy.
A corpus luteum cyst is a neoplasm containing lutein.
The corpus luteum cyst, like the corpus luteum itself, also supplies an important hormone - progesterone, but in larger quantities. The cyst helps prevent premature detachment of the endometrium even before the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus, and reduces the contractile activity of the uterus.
If the attachment of the embryo is successful, the neoplasm will remain functional until the formation of the placenta. This means that the presence of a corpus luteum tumor formed on the ovary is extremely important for successful conception. The cyst does not interfere with, but promotes pregnancy. In women expecting pregnancy, a neoplasm of the corpus luteum can be detected at the first ultrasound.
Endometrioid cyst
If a woman is diagnosed with this type of tumor, her chances of successfully conceiving are significantly reduced. A cyst is formed due to the spread of the functional layer of the uterus beyond its boundaries. Factors influencing the appearance of endometrioid cysts have not been fully identified. Experts suggest that the problem occurs due to hormonal imbalance.
Diagnosed genital endometriosis indicates that the pathological process is advanced. The ovaries begin to work incorrectly, and an adhesive process occurs in the pelvis. It is extremely difficult to get pregnant with this disease. But ectopic pregnancy is a common occurrence with genital endometriosis. The adhesions will prevent the embryo from entering the uterus, and it will have to remain either in the fallopian tube or on the ovary, which has a mucous layer similar to the lining of the uterus.
The photo shows an endometrioid cyst.
Often, an unhealthy growth of the endometrium of the uterus (adenomyosis) is also diagnosed with an endometrioid cyst. If the reproductive system is in this condition, then the chances of conception and implantation of the embryo into the uterus are low. It all depends on what stage the disease is at and what actions the woman takes to eliminate the problem. Most likely, pregnancy with an endometrioid cyst will not happen, but there is always a small chance.
Paraovarian cyst
Pregnancy with such a neoplasm is quite possible. The tumor differs from others in shape and location - it forms on the appendage, and not on the ovary itself.
The cause may be:
- hormone imbalances;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- problems of the endocrine system.
The tumor is small in size and does not cause inconvenience and does not interfere with the normal functioning of the reproductive system. Cysts 5 cm or more are pedunculated. They also do not affect the conception and bearing of a child, but complications may arise and surgery to remove the tumor may be required. Therefore, if a paraovarian cyst was diagnosed when planning a pregnancy, then it is advisable to get rid of the problem even before conception.
Sometimes it is not the tumor itself that affects the conception and bearing of a child, but the reasons for its occurrence.
If an infection is to blame for the appearance of a cyst, perhaps its pathogens will disrupt the growth of the endometrium and the production of cervical mucus, and these processes are very important for successful conception.
The influence of neoplasm on conceiving a child
Pregnancy in women with a detected follicular cyst is extremely rare. The pathology negatively affects conception and can cause infertility. Many women manage to become pregnant only after surgical removal of the lesion in the ovaries.
To conceive a child, complete ovulation is necessary. The egg needs to mature and be released from the ovary. In the presence of a follicular cyst, this is impossible. The formation can no longer release the egg and at the same time it interferes with the maturation of new oocytes. While the lesion exists in the ovary, follicles do not develop and ovulation does not occur.
As a rule, pregnancy does not occur in the presence of a follicular cyst.
Getting pregnant with a follicular cyst is possible only in exceptional cases. To do this, it is necessary for another follicle to mature in the ovary - the same or collateral one. In a different situation, this would lead to the conception of twins. Hormonal imbalance leads to the fact that one follicle becomes a cyst, and the other safely leaves the ovary and ruptures. The egg meets the sperm and fertilization occurs. The second follicle continues to grow and reaches a size of 10-12 cm.
Follicular cyst and pregnancy
This type of tumor of the left ovary can affect conception. It is formed due to a hormonal imbalance. However, most often a follicular cyst of the right ovary is observed, since the mechanisms of blood supply in both sex glands differ.
Due to an imbalance of hormones in a certain cycle, the dominant follicle does not rupture and does not release an egg, but continues to grow. If the follicle reaches 2.5 cm, it will no longer be able to perform its function. Education remains until the start of the next cycle. Accordingly, the meeting of the female gamete with the sperm will not happen, pregnancy will not occur.
However, there is still a chance of conception. The tumor may decrease in size within 1-3 months. If ovulation occurs in a healthy ovary in the next cycle, then pregnancy is possible. The main thing is that the tumor-free sex gland works correctly.
If an ovarian cyst is discovered after pregnancy
There are cases when an ovarian cyst is discovered in a pregnant girl, and the patient asks: “If you have an ovarian cyst, can you get pregnant?” becomes completely irrelevant.
If the cyst is small in size and does not bother the woman, then the patient is simply observed.
At the same time, there are often cases when a cyst involutions during pregnancy - that is, a reverse reaction develops (the cyst decreases in size until it disappears completely).
This happens because the hormonal balance (due to disturbances in which the tumor develops) is leveled out, since the female body devotes all its strength to maintaining the process of continuing life. The placenta surrounding the fetus produces huge amounts of progesterone (its deficiency also affects the formation of cysts). And the body of the expectant mother begins to produce hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which stimulates the thyroid gland and its production of hormones.
Pregnancy can proceed normally with an ovarian cyst if the following factors coincide:
- The cyst is no more than 8 cm in size (6 cm if we are talking about endometrioma)
- The cyst stops growing
- The level of tumor markers is within normal limits
If at least one factor is violated, surgery to remove the cyst is recommended.
The situation is more complicated with patients diagnosed with an endometrioid ovarian cyst, since such a tumor can cause miscarriage or termination of pregnancy.
Medical practice records conflicting facts regarding the behavior of endometrioma during pregnancy. There are cases when, under the influence of hormonal changes in the body, the tumor stopped growing. But it happens that a hormonal surge, on the contrary, provokes rapid growth and subsequent rupture of the cyst, leading to termination of pregnancy. In addition, there is a high risk of tumor transformation into a malignant form.
Is it possible to get pregnant with a dermoid cyst?
Dermoid cyst is a congenital neoplasm. It cannot appear suddenly. It is usually diagnosed during the first ultrasound examination, which is prescribed to a girl for the first time. The cause of the tumor is the incorrect distribution of germ cells at the moment when the girl’s organs are formed in the womb.
The neoplasm has several layers:
Initially, the cyst is small in size, but under the influence of hormones during puberty it grows. Therefore, it is possible to detect the problem either during puberty or in the time period immediately after it.
A small dermoid cyst does not affect the process of conception, does not make adjustments to the functioning of the ovaries and does not create a situation with a lack of hormones. After its detection, doctors decide whether surgery to remove the tumor is necessary or not. If a small cyst does not grow over time, then it is simply monitored. But it is usually recommended to remove a large tumor, and only then plan a pregnancy, since changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy can negatively affect the tumor, and it will increase in size.
Pregnancy after cyst removal
Removing the cyst significantly increases the chances of conception. However, it is important to know what kind of neoplasm took place and the reasons for its occurrence. It is also necessary to assess the girl’s overall health.
After successful removal of an ovarian cyst, it will be easier to get pregnant and carry a healthy child.
If an endometrioid cyst has been diagnosed, then pregnancy is likely after finding out the causes of the problem and its elimination. The doctor usually prescribes hormone therapy. Late stages of the disease are curable if you approach the problem comprehensively (use several methods to combat it). The result will be given by: surgery, medication treatment and physiotherapy.
Conception is also possible after getting rid of a dermoid cyst, but only after 3-6 months. Doctors recommend waiting just this period to increase the chance of successful conception. A dermoid cyst is usually operated on in cases where it grows or is large in size.
But removal of malignant tumors does not provide a 100% guarantee of pregnancy, since part of the gonad is removed along with the tumor. If the operation was performed at an early stage of the disease, and at least some part of the ovary was preserved, then successful conception is possible. However, it is impossible to predict how the body will react to pregnancy, during which hormonal changes occur. Therefore, the tumor may reappear. Many doctors suggest removing the gonad completely to prevent this from happening.
Surgery for torsion of the cyst pedicle
Timely surgical intervention for torsion of the cyst leg or apoplexy significantly increases a woman’s chances of successful conception in the future. Most patients manage to save part of the ovary. Therefore, the likelihood of pregnancy after surgery to remove a tumor is high if the woman has no other health problems.
How to remove an ovarian cyst
Laparoscopy and laparotomy are the main methods used by surgeons to remove ovarian cysts. If a low-traumatic technique is used, then a woman has a much greater chance of becoming pregnant. After the operation, the patient needs to wait a certain period (from 1 to 6 months), and only then plan a pregnancy. During this period, the woman must use protection, since the gonads are not ready to function as usual. They need time to recover. As well as the required level of hormones. The surgeon and gynecologist will tell you in detail about the period of recovery of the body after the operation and give recommendations regarding rehabilitation.
Write in the comments if you had a cyst in the ovary, and were you able to get pregnant after its removal? How did you discover it? What medications did the doctor prescribe? Share your experience and advice with other readers, it will help them a lot. Ask questions, our specialists are always ready to help. Don't forget to rate the article below with stars. Thanks for visiting. Be always healthy!
Types of cystic neoplasms
Characteristic signs of neoplasms will be:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- irregular nature of menstruation, disrupted cycle (acceptable delay is 2-3 days);
- dizziness, attacks of nausea after sexual intercourse and physical fatigue;
- increased frequency of urination;
- heat;
- swollen belly;
- hypotension, hypertension;
- sudden weight loss.
Cyst types:
- Follicular. When the follicle does not burst and the egg does not release into the abdominal cavity, a follicular cyst forms. Reason: hormonal imbalance. The cyst disappears either on its own or as a result of taking medications. If it grows more than eight centimeters, it is removed.
- Paraovarian. When secretions accumulate in the epididymis, a paraovarian cyst grows. It may go unnoticed until examined by a doctor. There are complications when the menstrual cycle goes wrong. Suppuration of the formation is not excluded. The cyst is removed using the enucleation method.
- Endometrioid. There is such a disease - endometriosis, when endometrial tissue extends beyond its boundaries. Thus, an endometrioid cyst grows in the ovary. It is often asymptomatic and can lead to menstrual irregularities and cause infertility. Such a formation is treated either with medications, or by doing laparoscopy and removing the cyst (or the entire ovary).
If you find yourself with any of the above symptoms, then you need to go and get examined without wasting time. The doctor will prescribe:
- blood test for hormones;
- Ultrasound;
- computed tomography;
- laparoscopy.
When examined, an ectopic pregnancy is very similar to the symptoms of a cyst. The doctor will recommend a pregnancy test or an ultrasound to rule out a dangerous condition.