Some women are interested in the question: can ovulation occur while taking birth control pills? The answer may be ambiguous. The effect of these drugs is to, figuratively speaking, “put to sleep” the ovaries and prevent the egg from breaking out.
As a result, the likelihood of fertilization is reduced to a minimum. However, there are cases when, regardless of taking contraceptives, pregnancy still occurs. Why does this happen, how do contraceptives work, and what happens if you stop taking the pills?
Operating principle OK
If we talk about whether another ovulation occurs when taking tablet contraceptives, then the activation of this process cannot be ruled out. The mechanism of action of hormonal contraceptives on the female body directly depends on the type of tablet contraceptives. These drugs are conventionally divided into combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and progestin drugs that do not contain estrogens.
Combined contraceptives
Combination medications such as Yarina, Janine, Klayra and Jess contain estrogen elements of natural or synthetic origin. The main function of estrogens is to maintain the menstrual cycle, as well as prevent intermenstrual bleeding. The mechanism of action of combined oral contraceptives is based on suppressing the growth of follicles and inhibiting the process of maturation and release of the egg into the abdominal cavity.
Progestin drugs
Progestin drugs do not have an estrogen component, and their effect on the female body is multidirectional. First of all, this group of contraceptives changes the degree of viscosity of cervical mucus, making it thicker, thereby making it difficult for sperm to enter the cervical canal.
In addition, progestin contraceptives act on the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity, preventing implantation of a fertilized egg. As a rule, the active ingredient of drugs from the group of gestagens is desogestrel. This powerful substance of hormonal nature, with minimal dosage, has a pronounced contraceptive effect.
What are oral contraceptives and how do they affect the female body?
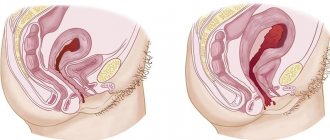
Oral contraceptive is the safest and most reliable way to protect against unwanted pregnancy, which is based on the inhibition of the secretion of gonadotropic hormones (FSH, LH and hCG) by the pituitary gland. It is follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) that determines the development of the dominant follicle, its rupture under the influence of luteinizing hormone (LH) and the subsequent release of the egg from it for fertilization. There are no hormones FSH and LH - no follicle and egg, which means no ovulation. Under the influence of OK, a woman’s reproductive system becomes incapacitated; it seems to turn off the switch of the main function - childbearing.
In addition to the most common effect - suppression of ovulation, OCs can have a number of other effects on a woman’s body:
- decreased activity of movement of the villous epithelium of the fallopian tubes;
- thickening of cervical mucus and, as a result, difficulty in moving sperm into the uterine cavity;
- a change in the endometrial layer, leading to difficulties in implanting an egg into it.
It is worth noting that taking oral contraceptives is not always associated with preventing pregnancy. Many women take OCs to treat certain diseases associated with gynecology, dermatology, hematology and oncology.
As a medicine, OK are taken:
- for acute manifestations of PMS;
- with hormonal infertility;
- with prolonged, heavy and/or painful monthly bleeding;
- with uterine bleeding, etc.
You should never engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, and especially when the problems relate to hormones. Therefore, the right to choose contraceptives should belong to a specialist who will prescribe OCs after examination and tests.
When prescribing birth control pills, the doctor must take into account the individual characteristics of the body, the general health condition and the woman’s phenotype.
Reasons for ovulation
There are several main reasons under the influence of which ovulation can occur with hormonal contraceptives. Among these reasons are:
- Failure to comply with the individually prescribed regimen for using a hormonal drug. Very often, women, due to lack of experience, do not adhere to the medical regimen for taking a hormonal drug, which was drawn up by the attending gynecologist. Against the background of changes in the balance of sex hormones, a woman may ovulate.
- Structural and functional pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. If a woman has certain diseases of the digestive tract, then the process of absorption of the components of the product may be disrupted.
- Combined use of hormonal drugs with other groups of medications, resulting in a decrease in the effectiveness of birth control pills.
- Individual immunity to the prescribed drug. In some patients, ovulation occurs after discontinuation of OCs and while taking them if a particular drug is not suitable for the female body.
In addition, the contraceptive effect of hormonal tablet contraceptives can be reduced or eliminated when the tablets are used in combination with alcohol.
Important! If a woman has just started using a hormonal drug, then during the first ovarian-menstrual cycle, her body is not under reliable protection from the onset of an unplanned pregnancy. The reason for this is the insufficient accumulation of the active substance of the drug in the body, as well as the lack of necessary hormonal changes.
Reasons for missed periods after discontinuation of OC
Answering the same question frequently asked on the Internet, “after Yarina, Ovidon, etc. no periods,” several reasons can be given.
Any of the listed reasons must be confirmed by tests and examination in a specialist’s office. Only he can prescribe the correct treatment in case of illness and advise about pregnancy. In any case, the question is “why is there no menstruation after Yarina?” has the answer, and you can only determine which one is right for your individual case by consulting with your doctor.
To sum up everything written above, we can say that the body has many reasons to delay the arrival of menstruation, but your health is one. Therefore, take care of it and always maintain it in good condition.
Effect on ovulation
Combined oral contraceptives have a significant impact on the process of maturation and release of the egg. Unlike COCs, progestin contraceptives (mini-pills) do not affect the ovulation process in the female body, since their main effect is a change in the viscosity of cervical mucus. During the entire period of taking combined oral contraceptives, the female body receives hormone replacement therapy, as a result of which the natural hormone-producing function of the ovaries is inhibited.
After discontinuation of COC use, the ovaries begin to produce hormones in significant quantities, which leads to the development of the so-called rebound effect . The essence of the rebound effect is a significant increase in female fertility and an increase in the likelihood of pregnancy during unprotected intercourse to the maximum.
The approximate time of ovulation after stopping birth control pills is individual for each woman. Some patients completely restore fertility within 3 months from the moment the drug is discontinued. Not every woman can boast of a quick restoration of ovulation after taking birth control pills. At least 60% of women of reproductive age can count on complete restoration of reproductive function within 6-12 months from the date of discontinuation of the contraceptive.
Possibility of ovulation and conception while taking OK
At least 2% of women taking hormonal contraceptive tablets experienced an unplanned pregnancy. Despite the high effectiveness of tablet contraceptives, there is a minimal percentage of the likelihood of ovulation occurring. Women are at greatest risk during the first month of taking OCs. That is why, during the first cycle from the moment of starting hormonal contraception, a woman is recommended to protect herself during ovulation, since the risk of an unplanned pregnancy is at least 50%.
What to do if there is no ovulation after taking OK?
The total duration of the stage of restoration of female fertility directly depends on the duration of taking oral contraceptives. It takes us an average of 3 to 12 months to fully restore the hormone-producing function of the ovaries. There is a separate theory according to which for every year of continuous use of contraceptive tablets, there are at least 3 months of rehabilitation.
The rate of restoration of fertility is influenced by factors such as the woman’s age, previous infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, the presence of chronic diseases of organs and systems, as well as the state of the immune system. Often, women notice that after stopping the OC there is no ovulation.
If a woman does not become pregnant within 1 year after stopping the pill contraceptive, subject to regular attempts, then we are talking about probable infertility caused by ovarian hypofunction. This condition occurs in rare cases when a woman has been taking hormonal pills continuously for a long period of time. If there are no signs of ovulation within 12 months from the date of discontinuation of the drug, the woman will need additional therapy aimed at stimulating the hormone-producing function of the ovaries. You can recognize the restoration of fertility after taking OCs by the following characteristic symptoms:
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen on the right or left.
- Increase in basal temperature.
- Increased sexual desire.
- The appearance of characteristic viscous transparent discharge from the genital tract.
The onset of ovulation can be recognized using ultrasound technology.
During the diagnostic process, the growth of the dominant follicle will be determined. In addition, during a general gynecological examination, a characteristic expansion of the lumen of the cervix will be visualized. There are also separate rapid tests that can detect egg maturation. You can do some of these tests yourself at home. A few days before ovulation, the concentration of chlorides in the salivary fluid increases, which is due to the influence of estrogens. Tests such as Your Cycle, EVA-TEST D, Maybe-MOM and OVU-test help determine this parameter.
How does stopping OC affect the body?
Very often on the Internet you can come across the question: “After Yarina there is no period.” And this is not groundless. The abolition of oral contraceptives does not pass without a trace for any woman, be it Yarina, Ovidon or Regulon. One of the manifestations of the effects of OC withdrawal is a delay in menstruation. But don't panic and ring all the bells. Menstruation directly depends on the hormonal balance in the body. If for a long period this balance was disturbed and artificially maintained in a completely different “key,” then it will take some time for it to completely restore its previous natural indicators. Absence of menstruation for up to six months is normal. If the delay lasts longer, then this is a definite reason to visit a gynecologist.
In addition, there are often cases when the abolition of OCs leads to chaos in other “departments” of the female body:
- hair becomes brittle and dry;
- the skin may become less smooth, rashes or pigmentation may appear on it;
- the menstrual cycle has changed radically (become shorter or longer) compared to what it was before taking OK.
In this way, the body becomes “outraged” and expresses dissatisfaction with the change in hormonal regime. He is already accustomed to the fact that half the work of producing hormones is done for him by drugs. And after their abolition, he is forced to “work” himself.