Conditions in which the legs swell during pregnancy may be normal or indicate serious health problems. In any case, it is worth contacting your personal gynecologist to determine the cause of excess fluid accumulation. If the edematous syndrome is caused by gestosis, then the expectant mother must be hospitalized and receive quality treatment. Otherwise, the risk of bleeding, premature placental abruption, and fetal death increases.
Physiological edema is harmless and can be easily eliminated. If the accumulation of fluid is caused by various pathologies, then inpatient treatment is carried out. Treatment consists of changing lifestyle, taking vitamins and medications, and performing special procedures. Early prevention will help minimize complications, alleviate the condition of the expectant mother and give birth to a healthy baby.
Physiological edema
During pregnancy, hormonal levels change several times, which affect the functioning of all systems and organs. The changes are aimed at creating the “mother-placenta-fetus” system. It is needed to ensure that the mother’s body functions adequately and provides the fetus with everything necessary for normal development. Often the normal course of pregnancy is complicated by edema.
Pregnant women are interested in why their legs swell during pregnancy.
The causes of physiological edema are:
- An increase in the concentration of progesterone (pregnancy hormone produced by the ovaries). Due to hormonal changes, salt and fluids are retained in the blood, and intestinal motility decreases.
- Growth of the uterus. The height and weight of the fetus increases, so the uterus also grows. In the second half of the 2nd trimester, the uterus compresses the organs in the pelvis, and also, when lying on the back, compresses the inferior vena cava, disrupting the flow of blood through the femoral veins.
- Passive lifestyle or excessive physical activity. In such cases, “gravitational” edema may occur - hydrostatic pressure in the vessels of the legs increases, which leads to an increase in filtration force. Then water from the capillaries escapes into the surrounding tissues.
- Eating excessive amounts of salt or spicy foods. Hormonal changes may cause you to crave salty foods. Even with a one-time violation of the diet, the risk of tissue pastiness (unexpressed swelling of the skin, pallor, decrease in its elasticity) in pregnant women increases. This painful condition eventually progresses to swelling. When the provoking factors (salty/spicy foods) are eliminated, the edema syndrome quickly disappears.
- Hot weather and the resulting excessive fluid intake is another common reason why legs swell during pregnancy. The most vulnerable places are the legs and feet. During the heat, the pores in the walls of blood vessels expand, through which fluid seeps into the surrounding tissues. As the provoking factors disappear, the swelling disappears.
Reference. The likelihood of edema syndrome increases in women of the hypersthenic type. They can be identified by well-developed muscles, short stature, rounded shapes, plumpness, and short limbs.
Physiological edema in a pregnant woman is considered normal, it does not threaten health, and is easy to eliminate.
Causes
Provoking factors:
- imbalance of hormones and changes in the hormonal levels of a pregnant woman;
- bearing several fruits at the same time;
- constantly growing uterus;
- consumption of alcohol, nicotine;
- excess weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- abuse of salty foods;
- poor nutrition;
- prolonged standing or sitting.
Often edema during pregnancy occurs in the later stages, the reasons lie in the gained kilograms, increased stress on the body and nutrition.
During gestation, a woman usually gains 10-12 kg and half of this is water. And at the same time the amount of sodium in the tissues increases, it is this that prevents fluid from leaving.
Then, as the uterus enlarges, pressure occurs on the small vena cava. This also has a negative effect on the body.
A slight swelling of the legs and feet is considered normal. It appears more often in the afternoon. Usually returns to normal after sleep or prolonged rest. By 36-38 weeks, the labia may also temporarily swell, this is also allowed.
Pathological picture.
- If the face, hands and wrists are noticeably swollen, and protein is found in the urine during tests, this may indicate problems with the kidneys.
- Stress on the heart and bloodstream can also cause water retention. Characteristic signs are that when a woman in labor stands, her legs suffer. If in a lying position - back and stomach. Additionally, severe shortness of breath, increased heart rate and fatigue appear.
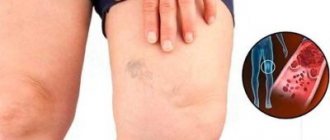
- Impaired fluid drainage is a sign of developing venous disease. A woman experiences pain in her legs, discomfort, numbness, the vessels become swollen and possibly even deformed.
- Allergies - develop quite often and can provoke Quincke's edema.
Pathological edema
If symptoms of edematous syndrome appear, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist to exclude its pathological origin. This condition may be associated with pregnancy or be triggered by other factors.
Causes of pathological edema:
- Impaired metabolism of calcium, vitamin C, P, and group B elements. This condition leads to an increase in the permeability of blood vessels through which water enters the tissue.
- Hypertension is a common cause of swelling of the lower extremities.
- Diseases of the kidneys and other organs of the genitourinary system also provoke edema syndrome.
Attention! Pregnant women should undergo urine tests at intervals of 2 weeks in order to promptly identify and treat kidney diseases. Diagnostic signs of pathology are an increase in the concentration of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and the appearance of protein in urine. Timely therapy will help avoid complications during childbirth or the birth of a low-weight baby.
- Increased blood viscosity.
- Anemia.
- Varicose veins This pathology occurs when there is a violation of blood circulation or lymph drainage in the vessels of the lower extremities. A one-sided lesion is often observed, for example, the left leg swells during pregnancy.
- Violation of the water-salt balance due to the accumulation of sodium (salt) in the blood.
- Endocrine pathologies. In the early stages, swelling is caused by hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones). The problem is also common among patients with diabetes or obesity.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Important! One of the most dangerous causes of leg swelling in later stages is gestosis (late toxicosis). This is a serious condition that is manifested by edema, a persistent increase in blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine. It can cause death of the mother and/or fetus.
Reasons for development
Hidden edema is a consequence of disorders of the cardiovascular and urinary systems, water and electrolyte imbalance. Swelling often occurs in pregnant women.
Failure of metabolic processes
Electrolyte imbalance provokes fluid retention in the body. This condition occurs when the levels of sodium, potassium, magnesium or calcium deviate from the norm. The accumulation of sodium, which retains water, and the lack of potassium, which removes it, predisposes to the development of edema.
People who consume large amounts of salt are most susceptible to excess sodium in the body. This is fraught with the development of swelling, hypertension, and kidney disease. Another likely cause of electrolyte imbalance is increased insulin levels. The latter promotes the accumulation of sodium in tissues, which leads to its excess.
Products containing large amounts of sodium - milk, meat, eggs, cereals, legumes, seafood. If the level of this mineral is elevated, they should be excluded from the diet.
External factors
Changing diet and stress negatively affect the body. The latter is also susceptible to environmental influences. External factors provoking hidden edema:
- hot weather - with profuse sweating, more free fluid accumulates, the blood becomes thicker;
- cold season - at low temperatures, vasospasm occurs, which provokes the accumulation of fluid and the cessation of its secretion;
- deviation of humidity indicators from the norm - disrupts the process of sweating;
- strong wind - its effect is similar to low temperatures, leading to loss of heat in the body.
To prevent the development of hidden edema, it is necessary to dress appropriately for the weather and maintain a drinking regime. Too low and high temperatures should be avoided to prevent malfunction of the blood vessels and excretory system.
Pregnancy
During gestation, the load on a woman’s cardiovascular system increases. The number of arterial vessels necessary to nourish tissues and organs is often less than the number of venous vessels that direct blood flow to the heart. Instability of blood circulation leads to hidden swelling.
This pathology is more difficult to identify in pregnant women due to constant weight gain. To identify it, diagnostics is necessary. Swelling can be suspected by a large volume of the abdomen, inappropriate gestational age, or by a smaller volume of urine excreted while still drinking plenty of fluids.
Pregnant women with excessive weight gain are advised to periodically test for hidden edema and monitor for signs of its manifestation.
Swelling can disrupt the development of the fetus and reduce the amount of oxygen it needs, supplied with the mother’s blood. Therefore, women expecting a child need to reduce the amount of salt in their diet. If you are prone to hidden edema, it is not recommended to drink more than 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
Instability of cardiac activity, changes in blood pressure and decreased permeability of vascular walls lead to circulatory disorders. As a result, metabolic processes fail, which causes the accumulation of free fluid in the body.
In these pathologies, in addition to testing, diagnostics of the functionality of cardiac activity is used to identify hidden edema.
Edema due to chronic heart pathologies is constant. With temporary disturbances in cardiac activity, they are short-lived and disappear without medical intervention. Their treatment is necessary in any case - it relieves the burden on the vascular system and improves the patient’s well-being.
Pathologies of the excretory organs
One of the most common reasons for the development of hidden edema is renal failure. With low functionality of these organs, fluid is not completely eliminated. Swelling may also occur in diseases of the bladder and urethra. Often the cause of diseases of the excretory organs is an infectious lesion, as a result of which the outflow of fluid is disrupted.
Development mechanisms
As mentioned, swelling of the legs is caused by excess fluid. The body of a healthy person consists of 75–90% liquid. In pregnant women, its amount increases to 6 - 8 liters: approximately 4 - 6 liters of water are placed outside the tissues, and 2 - 3 liters - inside the cells. Closer to the 3rd trimester, up to 3 liters of water accumulates in the fetal tissues, placenta and amniotic fluid. Approximately 3 liters are spent on increasing the volume of circulating blood, as well as enlarging the uterus and growing glandular breast tissue. As can be seen from these calculations, the water load increases, which often leads to edema syndrome.
The second important factor in the appearance of edema is protein concentration. This indicator depends on the amount of protein food consumed and its transformation into albumin (the main blood protein that the pregnant liver synthesizes from amino acids).
The third most important factor in the development of leg swelling is the level of sodium chloride or salt, which enters the blood mainly from food. Sodium metabolism is influenced by hormonal levels and the degree of permeability of capillary walls.
The lower extremities swell when the hydrostatic pressure of the blood in the capillaries increases, the pressure in the interstitial space (fat tissue, muscles) decreases, as well as the osmotic pressure of the plasma. Due to a decrease in pressure in neighboring tissues and an increase in the permeability of capillary walls, water seeps into the tissues, accumulates there, and then edema occurs.
Pregnant women experience swelling when the volume of interstitial (inside the tissues) fluid increases by 15–20%. For example, when 2 to 3 liters of water accumulate in the tissue spaces of a woman weighing 70 kg, pronounced edema appears. If its amount is below 2 liters, then the pathology has a hidden course.
Most often, swelling is localized in the calves, ankle, and feet. Fluid accumulates in areas where fatty tissue is present, venous pressure is increased, and tissue pressure is decreased.
Reference. Depending on the size of the area, the following types of edema are distinguished: hidden (there are no visible signs of fluid retention), local (on the feet or ankles), widespread (ankles, calves, feet swell), anasarca (fluid accumulation over most of the body).
Edema can be inherited
The risk group for the development of edema includes:
- expectant mothers who previously suffered from gestosis;
- women who have been diagnosed with multiple pregnancies;
- genetic tendency to edema;
- poor living conditions for a pregnant woman or work in hazardous work;
- overweight expectant mothers;
- patients who were previously diagnosed with diseases of the endocrine glands, heart, kidneys, and liver.
There is also an increased risk of fluid retention in women who become pregnant for the first time before the age of 18 or after 30 years.
Swelling during pregnancy
Swelling, large or small, of the hands, feet, and swelling of other localizations in one way or another accompany most pregnancies. It is a rare woman who has carried and given birth to a child and does not face this problem. Edema is a pathological accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space of tissues and organs. This manifests itself as swelling in one place or another of the body. The swelling itself may either not manifest itself at all or only cause discomfort. However, this may be a sign of another formidable pathology. Edema syndrome accompanies many diseases of different organs and systems of the body: inflammatory, cardiovascular, renal, endocrine.
During pregnancy, edema is associated with increased permeability of capillaries - the smallest vessels, which leads to the leakage of fluid from the bloodstream into the tissue.
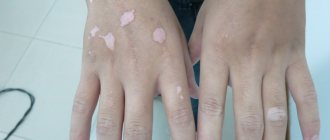
The most common areas to swell are the fingers and toes, as well as the ankles. The condition is aggravated by hot weather. It is easiest to notice swelling in places where rings are worn on the fingers, where, after removing them, circular grooves remain that persist for some time. Swelling on the ankles and shins is easy to check yourself. Using your thumb or index finger, press on the skin in the area of the front surface of the leg or ankle, pressing it against the bony protrusion. If there is swelling, after the finger is removed, a depression visible to the eye remains. If the hole is not clearly visible, but a slight impression is still felt when holding a finger, this is the mildest degree of edematous syndrome, often called “pasty.”
It is necessary to distinguish between physiological and pathological edema during pregnancy. There are no clear criteria for separating these two concepts; the boundary is very fluid, and diagnosing a particular woman is difficult even for highly qualified specialists. However: physiological edema , as a rule, is not pronounced, has a pasty character and is often localized in the area of the hands and feet. They, unlike pathological ones, do not lead to the development of complications and either go away on their own or accompany the entire pregnancy, without causing much trouble to the woman, except for worry about the impeccability of her appearance.
Pathological edema is part or a symptom of a broader concept - gestosis. At the same time, the classic triad of symptoms for this disease is the development of edema, proteinuria (excretion of protein in the urine, which is absent normally), arterial hypertension (increased blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg). The name comes from the Latin word - pregnancy, and reflects the essence of the disease. That is, this pathological condition is caused by pregnancy itself and does not occur outside of it. The reasons for the development of gestosis, despite the close attention of scientists and doctors for many decades, are not fully understood and depend on many factors. Many studies have been conducted on this topic, but there is still no consensus on the true reasons for its occurrence. The only certainty is that the disease is directly related to pregnancy. This condition never occurs outside of pregnancy and when it ends, most often a successful recovery occurs.
Degrees of edema
Clinically, pathological edema in pregnant women is classified according to degrees, or stages, which are also included in the diagnosis.
Hidden edema is manifested by increased weight gain, nocturia (frequent night urination), decreased diuresis (the amount of urine excreted, normally not less than 30-40 ml per hour, depending on the amount of fluid consumed).
1st degree - legs and hands swell;
2nd degree - swelling moves to the abdomen;
3rd degree - swelling spreads to the face;
Grade 4 - anasarca (generalized edema).
Swelling usually begins in the feet, often in the ankles. As the disease progresses, swelling spreads from bottom to top. However, sometimes the hands swell first, only then the feet, less often the swelling is localized on the face and hands. When the face swells, its features become coarser, and swelling on the eyelids is especially noticeable. The labia often swell. In the morning, swelling is less noticeable. More precisely, we don’t see them, the liquid doesn’t disappear anywhere, it’s just distributed more evenly throughout the body during the night when we sleep. After all, we usually do this in a lying position. During the day, due to the fact that we are more in an upright position, swelling, according to the laws of physics, “flows” down and is localized on the lower extremities, reminding us of pain and fatigue in the legs, marks from shoes and socks. There may be accumulation of fluid in the cavities inside the body (hidden edema).
The severity of edema syndrome often does not correspond to the severity of the disease. Even with severe edema, a pregnant woman may not have any complaints, and her general condition remains satisfactory. However, in more than 90% of cases, the disease progresses to the next stage, and symptoms of hypertension and proteinuria appear.
The risk group for the development of gestosis includes:
•women whose previous pregnancy was complicated by the development of gestosis;
•pregnant women with concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system (hypertension), diseases of the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism disorders (obesity);
•young (under 18 years old) pregnant women, primigravidas after 30 years of age;
• those who suffered from toxicosis in the first half of pregnancy (vomiting of pregnant women, drooling, etc.);
•pregnant women with detected hidden edema;
•pregnant women with occupational hazards;
•pregnant women with unfavorable social and living conditions.
Complications of edema during pregnancy
Swelling itself, as mentioned above, can only cause cosmetic concerns, in contrast to the edema that accompanies gestosis. The most dangerous complications of gestosis are preeclampsia and eclampsia - a generalized convulsive seizure that can result in respiratory arrest, cardiac arrest and death.
Preeclampsia, that is, the condition preceding the onset of eclampsia, is characterized by the following symptoms:
Preeclampsia and its dangers
Late toxicosis develops after 18–20 weeks of pregnancy, its symptoms appear from 26–28 weeks. According to statistics, this complication is diagnosed in 25–30% of expectant mothers. The pathology is accompanied by hidden or obvious swelling, increased blood pressure, and protein in the urine. The main triad of symptoms is supplemented by nausea, vomiting, headaches, muscle spasms, fever, drowsiness or excessive agitation.
Doctors distinguish between the following degrees of gestosis:
Treatment of swelling of the legs below the knees
- 1st degree – the lower extremities swell due to a decrease in the daily volume of urine and fluid retention inside tissue cells.
- Grade 2 – fluid accumulates in the tissues of the lower extremities and the anterior abdominal wall. Blood pressure also increases and protein appears in the urine.
- Stage 3 – preeclampsia. At this stage, the legs, arms, stomach and even the face swell greatly. Cerebral circulation is impaired.
- 4th degree – eclampsia. General swelling appears and spreads to most of the body. This stage has the most severe course, accompanied by a critical increase in blood pressure and convulsions.
Reference. Generalized edema occurs in diseases of the kidneys and heart. In the first case, the fluid is retained mainly in loose tissue (for example, eyelids), and in the second, swelling is formed under the influence of gravity (on the legs).
First the ankles swell, then the pathology is understood above. In the morning, swelling is less noticeable, since excess fluid is evenly distributed throughout the body, and in the evening it settles on the stomach and legs.
The fact that gestosis is developing can be understood by the fact that the pregnant woman quickly gains weight, and the amount of fluid drunk exceeds that excreted.
Late toxicosis is complicated by nephropathy, which causes bilateral kidney damage. This condition is accompanied by edema, hypertension (up to 135/85) and proteinuria (protein in the urine). Due to pressure fluctuations, the risk of bleeding, placental abruption, and fetal death increases. The daily volume of urine excreted is reduced to 500–600 ml or less. The prognosis worsens if nephropathy is provoked by arterial hypertension, kidney inflammation, heart defects and other pathologies.
If left untreated, preeclampsia develops. This stage of gestosis threatens kidney dysfunction, hemorrhages, premature birth, oxygen starvation, slow growth of the fetus, and its death during intrauterine development or after childbirth. Preeclampsia is manifested by an increase in blood pressure to 160/110 or more, the presence of 5 g of protein in the urine per day, a decrease in urine output to 400 ml, a decrease in platelet levels and impaired liver function.
Eclampsia is characterized by convulsive seizures, hemorrhagic stroke (intracerebral hematoma, subarachnoid bleeding), cerebral and pulmonary edema, retinal detachment, hemorrhage in the liver, kidneys, and coma.
To avoid dangerous conditions, the expectant mother should contact a gynecologist at the first signs of leg swelling in order to undergo an examination and find out the cause of its occurrence.
Edema: symptoms, causes and treatment
- Main causes of edema
- Consequences of edema
- Fighting swelling
Swelling can be hidden or obvious. Obvious swelling is easy to recognize immediately - a limb or area of the body increases in size, and stiffness in movement appears. Hidden edema may be indicated by a sharp increase in body weight or a decrease in the frequency of urination.
The most common type of edema is peripheral edema, which occurs when the ankles, feet, legs, or area around the eyes become swollen. But sometimes, in severe conditions, swelling of the entire body develops. This type of swelling is called anasarca.
Main causes of edema
Sometimes swelling occurs if a person is forced to remain in one position for a long time . For example, you may notice swelling in your legs after a long airplane flight.
In women, edema can develop during menstruation due to changed hormonal levels. Pregnancy is also a condition that promotes the development of edema. In this case, the volume of circulating blood increases and, under the influence of the growing uterus, pressure on the internal organs and tissues increases.
Taking certain medications (medicines to control blood pressure, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, oral contraceptives, some medications for the treatment of diabetes) also provokes the development of edema .
However, in some cases, edema occurs as a result of serious illnesses that require immediate consultation with a doctor.
Chronic heart failure
The heart plays the role of a pump in our body, thanks to which blood circulates from the lungs to the organs and tissues, saturating them with oxygen. If the work of the heart is disrupted, blood is retained in the periphery, and the person develops swelling of the legs, ankles, and lower back.
Usually the legs swell in the late afternoon. When you press on the area of edema, a dimple is left that slowly disappears. As the disease progresses, the flow of blood from the lungs is impaired. Then a cough and moist wheezing appear.
In severe cases, the outflow of blood from internal organs is disrupted. Fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, and the stomach increases in size. This condition is called ascites.
Kidney diseases
With kidney disease, conditions are created for sodium and fluid retention in the body. Unlike cardiac edema, renal edema increases in the morning. Swelling of the face and area around the eyes is common. The arms and legs swell, especially the ankles and shins.
When kidney function is impaired, the so-called nephrotic syndrome develops. In this case, protein is lost in the urine, the protein content in the blood decreases, and conditions are created for the accumulation of fluid in the tissues. You may notice that your urine becomes foamy, your appetite decreases, and weight gain occurs due to fluid retention in the body.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Some hereditary diseases, hepatitis B or C, alcohol abuse, and endocrine disorders can lead to liver cirrhosis. If the liver malfunctions, the outflow of blood from the internal organs is disrupted, protein production in the body decreases, swelling of the legs develops, and fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
Early symptoms of liver cirrhosis may include nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness, and increased fatigue.
Impaired blood flow
If an obstruction occurs in the path of blood outflow, edema develops. This can happen, for example, if the deep veins of the legs are blocked by blood clots. If you have deep vein thrombosis, you may feel pain in your leg or notice redness.
In addition, a growing tumor can interfere with the flow of blood through the lymphatic or blood vessels. These conditions are life-threatening and require urgent medical attention.
Allergic reaction
Allergic edema can be caused by foods, medications, flowers, animals, or insect bites, to which a person has developed hypersensitivity. The difference between allergic edema is that it develops suddenly, literally in a few minutes. The person does not experience pain, but allergic edema is one of the most life-threatening. Swelling of the larynx and tongue can cause suffocation and death.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious complication of pregnancy. Edema in preeclampsia is accompanied by increased blood pressure and impaired renal function. This is a very dangerous condition that threatens the life of both the mother and the unborn child. Therefore, you should visit your doctor regularly during pregnancy. Only he will be able to distinguish minor swelling during pregnancy from a critical condition.
Consequences of edema
It is important to recognize edema that poses a threat to human life. First of all, this is allergic swelling. If it develops, the person must be helped immediately, otherwise death due to suffocation is possible. It is extremely dangerous if the swelling has developed due to a blood clot. The clot or part of it can move further along the blood vessels. Then there is a risk of developing a heart attack, stroke and other life-threatening conditions.
If edema is one of the symptoms of preeclampsia, it can threaten placental abruption, fetal death, retinal detachment, stroke, and eclampsia (convulsions that can be fatal).
With constant and progressive swelling of the legs, stiffness in movements increases, difficulties arise when walking; skin stretches; the elasticity of arteries, veins and joints decreases; the blood supply is disrupted and the risk of infection of the area of edema and the development of ulcers on the skin increases.
Fighting swelling
Minor swelling may go away without the help of a doctor. If swelling persists for a long time or develops suddenly, this is an alarming symptom. You need to see a doctor urgently.
In case of allergic edema, it is necessary to immediately stop the patient’s contact with the allergen that caused the edema and take antihistamines. If you have allergies in your home, consult your doctor about what medications should be in your home medicine cabinet.
If swelling is associated with dysfunction of the heart, kidneys, liver, or vein thrombosis, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment for the underlying disease.
In addition, special diuretics are prescribed that remove excess fluid from the body. After prescribing appropriate treatment, it is important to follow the doctor's recommendations. You may need to change your eating habits and lifestyle.
The following measures will help reduce the severity of edema and prevent its recurrence.
Moderate physical activity
Even if you are unable to engage in active sports due to illness, your doctor will advise you on possible physical exercises. When muscles contract in the area of edema, conditions are created to remove excess fluid.
Massage
Stroking the swollen area in the direction of the heart will help remove excess fluid from the swollen area.
Diet
Excess salt in the diet contributes to fluid retention in the body. Depending on the severity of the disease, your doctor will advise how much you need to limit your salt intake. Sometimes it is enough to add a little less salt to your food.
For more severe illnesses, you will have to avoid salt altogether. In this case, the diet should be balanced, containing a sufficient amount of protein, vitamins and microelements. Published by econet.ru.
Author Irina Kologrivova
PS And remember, just by changing your consciousness, we are changing the world together! © econet
Did you like the article? Write your opinion in the comments. Subscribe to our FB:
Signs of edema syndrome
Inexperienced expectant mothers may not notice the symptoms of leg swelling if they have not previously encountered such a problem and are pregnant for the first time. Physiological fluid retention occurs after approximately 30 weeks, and pathological - after 20 weeks.
Signs of swelling of the lower extremities during pregnancy:
- On the lower part of the legs there are traces from socks, tights, and shoes.
- Swelling of the ankles and legs is noticeable even in the morning.
- The pathological process spreads to the feet, lower abdomen, face (eyelids, cheeks, nose), and later to most of the body.
You can identify hidden swelling of the legs yourself:
- Habitual shoes become narrow, so it’s difficult to squeeze your feet into them, and you can’t fasten the zipper on your boots. This symptom becomes more pronounced after a long walk. Often pregnant women complain that they feel heavy and their legs hurt.
- A dent remains on the skin after pressing with a finger. If you press on the suspected area of fluid retention and then release it, a dent will remain on it for some time. For comparison, normally there is no depression.
- Increase in body weight. With regular weighing, weight increases by 300 g or more in 7 days.
- The ankle circumference has increased by more than 1 cm. Measurements should be taken once a week.
A dent in the skin that slowly disappears indicates tissue swelling
You also need to monitor your daily diuresis. The doctor will advise you on how to correctly calculate the volume of fluid consumed and urine excreted. If the difference is more than 25%, then this indicates the development of hidden edema.
With severe swelling, the pregnant woman gets tired faster, feels heaviness in her legs, and feels thirsty. Nephropathy is manifested by edema, increased blood pressure, and the appearance of protein in the urine. Preeclampsia is accompanied by headaches, heaviness in the occipital region, pain in the liver, epigastrium (epigastric region), nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Memory weakens, drowsiness, insomnia, mood swings, and visual disturbances occur. These symptoms indicate a cerebrovascular accident.
Symptoms of eclampsia:
- increased blood pressure;
- decrease in the volume of urine excreted – 400 ml per 24 hours;
- impairments of vision, hearing, coordination, attention;
- nausea, vomiting.
The most dangerous manifestation of eclampsia is convulsive seizures, which are provoked by irritating factors (pain, loud sound, bright light, severe stress). Such an attack can result in loss of consciousness, cessation of breathing, and sometimes - intracerebral hemorrhage and death. But in most cases, consciousness returns, and the woman feels general weakness and pain in the head.
Treatment methods
Treatment is determined by the cause of hidden edema. In the presence of primary pathologies, the underlying disease is initially eliminated. In this case, the swelling disappears on its own. To speed up its elimination or get rid of it in the absence of visible reasons, you must do the following:
- exclusion of salt, fatty, sweet and smoked foods from the diet;
- regular moderate physical activity;
- eating large amounts of vegetables and fruits;
- compliance with the drinking regime - about 1.5-2 liters per day;
- wearing compression stockings;
- taking rosehip decoction or cranberry juice to get rid of excess fluid.
If the volume of free fluid is small, compliance with these rules is often sufficient for recovery. In more severe cases, the intervention protocol for hidden and obvious edema is determined by the doctor.
Diagnostic measures
To identify the cause of leg swelling, you need to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis:
- History taking, visual examination. The doctor asks the expectant mother about the symptoms that bother her, their age, duration, and development. He examines the patient and palpates areas of fluid retention.
- A general and biochemical urine test is performed to determine the amount of protein.
- Coagulological studies make it possible to assess the state of the blood coagulation system and identify thrombosis.
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests.
- Blood pressure measurement.
- Control of daily diuresis.
- Monitoring the dynamics of weight changes.
- Calf circumference measurement.
- Calculation of the body mass index of a pregnant woman. To do this, the weight of the body is divided by its length.
- Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the fundus using an ophthalmoscope.
To assess the condition of the fetus and uteroplacental blood flow, ultrasound and Doppler examination are prescribed. If gestosis is suspected, consultation with an ophthalmologist, therapist, neurologist, nephrologist and other specialists is necessary.
Attention! You should immediately consult a doctor if swelling in a pregnant woman’s legs increases rapidly, rising from the ankles to the lower leg, lower abdomen. If this symptom is accompanied by increased blood pressure, then preeclampsia is most likely developing. Although this condition sometimes occurs without significant swelling.
Diseases of the urinary system
They can become a pressing problem for a person of any age. They often develop several weeks after an acute infectious process. It is the hidden swelling that transforms into visible swelling that is the initial symptom of renal failure.
Independent attempts to eliminate them can only worsen the situation. Consultation with a specialist is required, often a water load test and other studies. Subsequent treatment tactics are also determined by the doctor.
It is necessary to understand that tissue swelling that is not visible to the eye requires observation and a subsequent visit to the doctor, regardless of the person’s gender and age. A simple test can help you avoid serious health problems.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HpQjZ2YqFBI&t=44s
Methods to combat swelling
The doctor will tell the expectant mother what to do if her legs swell. If physiological edema was detected after diagnosis, then use the following methods:
- Eliminate salt from your diet, which retains excess water in the tissues. Discard the spice or greatly reduce its daily dose. The ban includes pickles, sausages, canned goods, sauerkraut, snacks (chips, crackers), etc. The above products not only contain a lot of salt, but are also rich in chemical additives that disrupt fetal development, cause food poisoning and allergies.
- Enrich your menu with dietary meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, veal), vegetables, fruits, whole grains (porridge, bread), herbs, and dairy products. Boil, steam, bake (without oil), stew. Avoid frying, which produces carcinogens. Do not overuse coffee, tea (up to 2 cups per day), drink still mineral water, compotes, juice from fresh fruits, vegetables, berries, diluted in half with water. The expectant mother should consume no more than 2800 - 3500 kcal per day. After all, one of the reasons for leg swelling is excess weight. To control it, you need to count calories.
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day in small portions, but often. The daily fluid volume can reach 3 liters (including liquid food and other drinks other than water). If it is limited, the condition of the walls of the venous vessels will worsen, the blood volume will decrease, and the risk of blood clots will increase. In case of gestosis, it is better to replace water, which washes out beneficial substances from the body, with weak tea with milk and juices. These drinks remove excess fluid from the tissues, then swelling decreases.
- Take diuretics only for medical reasons, as they wash away beneficial substances (potassium, calcium, magnesium, etc.). As a rule, pregnant women take homeopathic medicines or herbal infusions with a weak diuretic effect (bearberry, lingonberry leaves, parsley decoction).
- Give your legs a rest, keep them at a slight (up to 30 cm) elevation to restore blood circulation.
- Lie down to rest on your left side. In this position, the kidneys work better, are less stressed, and remove excess fluid from the body faster.
- Do light exercises, walk more often (2 - 3 hours per day), swim, and do yoga. Avoid excessive physical activity. If you work sedentarily, get up every hour to do exercises.
- Wear a bandage, compression tights or stockings. These devices will help relieve stress from your back, legs, and support your stomach. The doctor will tell you how to choose a bandage or tights, taking into account the size, degree of compression, and how to wear them correctly.
- According to the gynecologist's indications, attend sessions of balneotherapy or water immersion compression. These physiotherapeutic procedures increase blood volume due to the external pressure of edematous tissues, accelerate blood flow in the pelvis and abdominal space, increase the daily volume of urine, then the edema subsides.
Attention! In 40% of women, the lower limbs swell, discomfort and heaviness appear at the initial stage of varicose veins. If such symptoms recur, be sure to visit a doctor, because at an early stage the pathology is easier to cure. Creams with extracts of horse chestnut, hazel, etc. will help alleviate the condition.
It is also recommended that expectant mothers sleep at least 8 hours a day, wear comfortable, not tight clothes, take vitamin and mineral complexes with B elements, vitamin C, P, iron, calcium, potassium, etc.
As you can see, physiological swelling of the legs does not require special treatment. It is enough to slightly adjust your lifestyle and follow the recommendations of the gynecologist in order to alleviate the condition and prevent complications.
Legs should be allowed to rest on an elevated surface after physical activity.
Determining the presence of edema
Edema is the accumulation of fluid in cavities and tissues due to an imbalance of water balance.
Edema appears in acute inflammatory diseases of the kidney parenchyma, affecting the glomerular and tubular apparatus of the nephron. Renal edema begins in the face, grows quickly and disappears quickly (the skin is pale, warm and motionless).
Swelling that appears due to diseases of the cardiovascular system and in pregnant women increases in the evening on the lower extremities (cold, mobile, bluish to the touch, disappears after pressure.)
Pastiness—minor swelling is not visually detectable; when pressed, there is no noticeable dimple, but when held with a finger, it is detected.
In the development of edema, the main role is played by increased diffusion of fluid from blood vessels into the tissue and fluid retention by the tissue.
Edema fluid usually accumulates in the lowest parts of the body.
When the body is in an upright position, swelling appears on the legs and increases in the evening.
In lying down patients, the pain first appears in the lumbar region. Renal edema appears on the face under the eyes due to looseness of the subcutaneous tissue.
Edema can be obvious or hidden.
The appearance of obvious edema is preceded by a hidden period of fluid retention, which is manifested by a decrease in the amount of fluid secreted and an increase in body weight (determined by daily weighing).
In severe cases, massive swelling of the legs and torso occurs. When you press on the skin in places where swelling occurs, a hole that does not disappear for a long time remains, and folds of linen are imprinted on the skin.
- weigh on an empty stomach at the same time, in the same clothes;
— measure daily water balance, i.e. the ratio between the liquid consumed per day and the amount of urine excreted;
Daily recording of these data allows us to judge the dynamics of edema - its decrease or increase.
All patients with edema should be under the supervision of a doctor who prescribes a diet with limited salt and liquid.
studopedia.org - Studopedia.Org - 2014-2019. Studiopedia is not the author of the materials posted. But it provides the opportunity for free use (0.001 s).
source
When examining the skin, the nurse pays attention to the presence of edema.
Edema is the accumulation of fluid in tissues. Characteristic of chronic heart and kidney diseases.
If the patient has edema, it is necessary to pay attention to its location, consistency, and severity. In case of severe swelling, the contours of the limbs and joints are smoothed, the skin is tense, transparent, sometimes bursts and liquid seeps through the cracks. Long-term swelling causes trophic disorders of the skin: it thickens, becomes rough, and becomes inelastic.
Swelling can be local or general.
Local edema is caused by local processes (compression of veins, impaired lymph outflow). Sometimes local swelling occurs as a result of an allergic reaction of the body, most often to drugs, food, or insect bites. Swelling of inflammatory origin is also possible, the main symptoms of which are skin hyperemia, pain, and fever.
General edema may appear in patients with heart disease, kidney disease, or malnutrition (cachexia).
· by pressing a finger on the skin: if there are any, a hole remains at the place of pressure, which does not disappear for a long time;
· calculating the water balance (the fluid consumed and the amount of urine excreted are recorded) The daily water balance is the ratio between the amount of fluid excreted from the body and the amount of fluid injected during the day. The fluid contained in fruits is taken into account (conventionally, fruits and vegetables are considered 100% products consisting of water, etc.
the amount of liquid received with them is determined by their weight), first courses (one plate of soup - 400-450 ml, of which ½ liquid part, ½ thick part), third courses - 100% liquid and parenterally administered solutions are considered. To account for the water the patient drinks in the morning, he is given a carafe of water, from which only he drinks water.
· when weighing the patient (in case of accumulation of fluid in the body, body weight increases sharply);
hydrothorax (fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity);
hydropericardium (fluid accumulation in the pericardial cavity);
ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity);
anasarca (general swelling of the trunk).
In chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, swelling usually appears towards the end of the day. If the patient walks (vertical position of the torso), swelling is localized in the lower extremities, while in bed - in the lumbar region.
Daily diuresis is the amount of urine excreted by the patient during the day. Daily diuresis in adults ranges from 800 ml to 2000 ml and depends on age, temperature and humidity of the environment, nutritional conditions, physical activity and other factors and should be 75-80% of the amount of fluid administered, 20-25% of the fluid is excreted through sweat and breathing and a chair.
On average, the daily diuresis of a healthy person is approximately 1500 ml; daytime diuresis is approximately 2 times greater than nighttime. Daily urine is collected in a separate container. The amount of urine is measured after each urination during the day. Diuresis is measured as follows: after emptying the bladder from 6 a.m. during the day, the patient collects urine into a graduated vessel.
Edema is detected visually, by palpation, by measuring the volume of the limbs, their fragments and by weighing the body. The presence of edema is indicated by puffiness of the face, swelling of the eyelids, swollen eyes, an increase in the volume of the entire body or its individual parts. Edema is especially often localized in the lower extremities.
Swelling of symmetrical areas and parts of the body indicates generalized edema (cardiac, renal, hypoproteinemic, etc.). Asymmetrical edema is characteristic of local processes - disruption of local blood and lymph circulation, trophism, as well as inflammation and injury. When examining the body, you need to pay attention to the imprints on the skin from the folds of clothes, shoes, belts, buttons, elastic bands of socks, bed.
Edema is manifested by swelling, pallor, cyanosis or redness of the skin. With significant swelling, the skin stretches greatly, becomes pale, shiny, cracks appear through which a cloudy, pale edematous fluid oozes. Significant swelling smooths out natural pits and depressions, bony protrusions (for example, ankles) “sink” into the soft tissues, and stretch scars may appear on the legs and abdomen. With massive edema, the abdomen enlarges due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites).
Inflammatory edema is often asymmetrical, more limited, and is accompanied by redness of the skin, pain, and increased local temperature. Any swelling is easier and more significant where there is loose tissue: eyelids, face, genitals, and lower limbs.
By palpation, swelling is detected or confirmed by compression with the index or thumb in places where there is a dense surface under the skin and subcutaneous tissue: the back of the foot and hand, ankles, tibia, sacrum. This manipulation can also be performed in any place where tissue swelling is visible or suspected.
During compression, the finger is carefully plunged into the tissue until it feels like it is touching a hard surface. After removing the finger, if there is no swelling, the tissues immediately straighten out; if there is swelling, then a hole remains for 1-2 minutes, then it disappears. With long-standing edema, the skin and subcutaneous tissue thicken and there may be no pit.
Taking your finger away from the skin, you need to make a sliding movement with 1-2 fingers over the area of compression. This technique confirms the presence of a hole and even slight indentation and unevenness, which occurs with minor swelling. If, during compression, the finger feels doughy, but the hole is not visible or a barely noticeable trace of pressure remains, then this is called pastiness, which indicates a slight swelling of the tissues.
In places where there is no hard base under the skin and soft tissues, swelling can be detected by grabbing a fold of skin and fat and squeezing it between the fingers. Long-lasting dents indicate tissue swelling.
Palpation of the skin in the presence of edema is cold and painless. Only with inflammatory edema is it hot to the touch. If edema is visually suspected, but finger compression does not form a hole, then the following are assumed: • old edema, • false edema.
False edema occurs with myxedema and scleroderma. Edema can be detected by measuring the circumference of the limbs in symmetrical areas, measuring the circumference of the abdomen and chest. This is especially important during dynamic monitoring. Edema is detected by systematically weighing a person.
source
Treatment of severe conditions
In case of gestosis and the complications it causes, it is necessary to hospitalize the pregnant woman. Near the ward there should be an intensive care unit and a department for premature babies. In the most severe cases, doctors decide to terminate the pregnancy early.
When treating gestosis, doctors pursue the following goals:
- normalization of central nervous system functionality;
- restoration of blood circulation, activity of the blood coagulation system;
- resumption of metabolic processes;
- strengthening the vascular wall;
- normalization of blood pressure;
- restoration of water-salt balance.
Therapeutic measures can prevent and eliminate complications of pregnancy and intrauterine development.
The duration of treatment for mild nephropathy is from 2 to 4 weeks. In severe forms of the pathology, which are accompanied by general edema, the expectant mother is in the hospital until delivery.
If the pregnant woman’s condition is satisfactory and there are no fetal abnormalities, then the woman can give birth naturally. If blood pressure increases, cerebrovascular accident, or intrauterine hypoxia occurs, surgical delivery is performed.
Diagnosis of internal edema
Doctors call them pasty. In such cases, systematic monitoring of a woman’s weight helps, because pathology reveals itself as uneven, sharp changes in weight.
It is much easier for doctors to diagnose pastous edema. Diuresis helps them with this. Swelling is always associated with fluid retention in the body. This is what is monitored by diuresis, a daily measurement of fluid intake and output. Normally, a woman excretes up to 75% of all liquid she drinks through urine. The remaining 25% is excreted through sweat and breathing. If the results of diuresis show obvious deviations from the norm, then the woman probably has hidden edema. This diagnostic study is carried out over three days.
The most important
Swelling of the legs during pregnancy may be normal or indicate severe pathologies. If you notice that your usual shoes have become too small, marks from socks and tights remain on your ankles, and the daily volume of urine has decreased with an increase in the amount of fluid you drink, then rush to the gynecologist. The doctor will conduct a urine test, blood test, and prescribe other tests to determine the exact cause of the disorder. The presence of swelling in the legs and other parts of the body, the presence of protein in urine, and a persistent increase in blood pressure indicate gestosis. In this case, the expectant mother needs to be hospitalized to undergo treatment and monitor the condition of the fetus. In severe cases, the pregnancy will have to be terminated early. To prevent gestosis or get rid of physiological edema, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, control body weight, blood pressure, and regularly visit a gynecologist in order to notice problems in time and carry out treatment.
How to get rid of hidden internal edema during pregnancy
It is necessary to combat this pathology with the help of nutritional adjustments and special exercises so that water does not linger in the tissues. If a woman is resting, then it is better to place a bolster or pillow under her feet to improve blood circulation in tired legs. You cannot sit or stand for a long time, as this leads to stagnation of fluid in the body. A knee-elbow position is recommended several times a day to increase blood flow.
To get rid of internal edema during pregnancy, you need to adhere to a strict diet:
- Completely eliminate salt from the diet;
- Do not reduce the amount of water consumed;
- Eliminate flour and sweet foods;
- Limit the consumption of salty, smoked and fried foods;
- The diet should consist of many fruits and vegetables.
Once a week or two you should use a fasting day based on apples, cottage cheese, kefir, and vegetables. Only one product is consumed throughout the day, which helps reduce the occurrence of edema reactions. You can arrange such days only after consulting a doctor.
Among the folk methods, the benefits of consuming cranberry and lingonberry juice are highlighted; infusions of birch buds, parsley or strawberries will help remove internal swelling during pregnancy.
Treatment with medications is used when there are no results after a diet or if the potential risk of complications is too high.
Based on materials from empiremam.com