News on the topic of caesarean section at 38 weeks
Read more
Inducing labor increases the risk of needing a caesarean section
In the most complex physiological process that is childbirth, there seems to be no place for outsider intervention, but doctors have learned to induce labor artificially, which is a blessing when there are indications for this: protracted labor, danger to the health and life of the mother and child, and the like. However, there is also a growing trend in the world to induce labor “by order” of a woman in labor, who thus wants to “fit” the birth of a child into the world with her vacation, so as not to lose a prestigious and highly paid job. A new study by American doctors suggests that labor induction significantly increases the risk of complications, leading doctors to ultimately perform a caesarean section.
Read more
Caesarean section is easier for the mother, but unsafe for the baby
American experts found that, compared with births occurring at 39 weeks or later, repeat cesarean sections performed before 39 weeks of pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of severe complications in newborns. The latter may subsequently experience respiratory distress syndrome, requiring artificial ventilation in intensive care units.
Read more
Caesarean section risks childhood obesity
In Western countries, primarily the United States, the number of cesarean sections is steadily increasing, which are often not performed for medical reasons. Scientists warn that in many cases this leads to early obesity in children.
Read more
Caesarean section “optional” will be canceled
From September 1, clinics in several US states will introduce a strict rule according to which cesarean sections will be performed strictly for medical reasons. Thus, the local Ministry of Health wants to stop the “fashion” for such operations.
Read more
The number of Caesarean sections in the United States reaches a record high
American obstetricians sounded the alarm: in 2007, 32% of newborns were born by cesarean section. Medical statistics show that the number of such operations increased by 53% between 1996 and 2007. Meanwhile, WHO considers the optimal figure to be 15% of children born through such an operation, out of the total number of newborns.
Read more
Gynecologist of the French Minister of Justice broke the Hippocratic Oath
French gynecologist Claude Debache, who delivered the baby of Rachida Dati, the country's justice minister, so that she could resume her duties within five days, risks being struck off the medical register for he revealed confidential information about the operation to the press. The woman underwent a caesarean section using a special method, which is practiced at Dr. Debache's clinic.
Read more
Mothers who gave birth naturally are more responsive to their baby's cries
Researchers' finding sheds light on the causes of postpartum depression in women who have had a caesarean section.
Read more
Children born prematurely are more at risk of developing various complications than others.
The birth rate of premature babies has increased significantly in the United States in recent years. According to the latest data, in most cases such births were carried out by caesarean section
Vaginal birth and the risk of cerebral hemorrhage in newborns
Approximately a quarter of clinically healthy infants born per vias naturalis have small intracranial hemorrhages, which is not observed in newborns born by cesarean section
Why is the baby so big?
Risk factors for having large children are: heredity, diabetes, some other endocrine diseases, increasing the duration of pregnancy, etc.
Increasing the duration of pregnancy can lead to the birth of large babies. In this case, both prolongation of physiological pregnancy and true post-maturity are possible.
Prolonged pregnancy is considered to be one that lasts longer than the physiological one by 10-14 days and ends with the birth of a functionally mature child without signs of post-maturity and “aging” of the placenta.
True post-maturity is characterized by the birth of a child with signs of post-maturity and pronounced changes in the placenta.
In this case, signs of overmaturity are the absence of vernix lubrication, dryness, and maceration (wrinkling) of the skin. The fetus's need for oxygen increases during postmaturity, and the placenta can no longer provide the fetus with the required amount of oxygen and other substances important for life. The amount of amniotic fluid also decreases. With significant overuse, an admixture of meconium (original feces) appears in the waters and their color becomes greenish or grayish.
Pregnant women with diabetes must be hospitalized in the department of pathology of pregnant women in the maternity hospital in the second half of pregnancy (no later than the 32nd week). There they are examined in detail, and doctors decide on the timing of their delivery. Artificial premature birth (not earlier than the 36th week of pregnancy) is carried out in cases where a woman carrying a large fetus exhibits progressive late gestosis, significant polyhydramnios, and decreased blood sugar, since this poses a risk of intrauterine fetal death and birth trauma . During childbirth, insulin administration is necessary. Insulin treatment continues in the postpartum period, taking into account the level of sugar in the urine and blood.
The cause of the large size of the fetus can be an edematous form of hemolytic disease - a serious condition associated with incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus according to the Rh factor. This disease occurs when a pregnant woman with Rh-negative blood carries a fetus whose red blood cells contain the Rh-positive factor inherited from the father. As a result, the fetus develops anemia (the hemoglobin content in the blood decreases), which is often accompanied by jaundice. In the most severe forms of hemolytic disease, anemia and jaundice are accompanied by general swelling, accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the fetus, and enlargement of the liver and spleen. It should be noted that in a mother with Rh-negative blood and an Rh-positive fetus, pregnancy does not always proceed in this way. The situation is less favorable if the pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus is repeated, a previous transfusion of Rh-positive blood was performed (even long before pregnancy), and also if the pregnant woman suffered from influenza or other infectious diseases.
In order to prevent hemolytic disease in subsequent pregnancies, women with Rh-negative blood are administered anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin immediately after birth.
And yet, most often the reason for the large size of the baby is heredity . So, if the child’s parents had a large birth weight, it is likely that the baby will also be large.
The formation of a large fetus can also be caused by improper nutrition of the pregnant woman. Thus, an excess of carbohydrates (pasta, bakery, confectionery) in the diet contributes to fluid retention in the body, maternal obesity and the formation of an overly large fetus. In this regard, most experts recommend limiting the consumption of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates, especially in the second half of pregnancy, to 300-400 g per day.
There is also a tendency for a larger fetus to form during the second and subsequent pregnancies . According to statistics, the second child is 20-30% larger than the first. It can be assumed that this is determined by several factors. One of them is psychological, that is, when carrying a second baby, the expectant mother is calmer, since she is no longer familiar with pregnancy and childbirth. Another reason may be that during the second pregnancy, the mother’s body is already trained to bear a baby; blood circulation in the uteroplacental and fetal placental vessels provides a greater supply of nutrients to the fetus than during the first pregnancy.
It is worth noting that with a genetically determined birth of a large fetus, the baby’s body length is also quite large, so the size of the fetus is proportional. In this case, the size of the baby's head, which plays the main role during childbirth, is also quite large. If the reason for the high weight is some pathology (for example, hemolytic disease of the fetus), then the size of the fetus can be increased due to swelling of the soft tissues. During post-term pregnancy, the bones of the fetus are less mobile and adapt less well to the mother’s birth canal, which creates additional difficulties and predisposes the mother and fetus to injury during childbirth.
C-section.
The 37th week of pregnancy is critical, since it is now that complications can develop, such as fetal hypoxia, various infections, oligohydramnios, and others. Caesarean section at 37 weeks is also not uncommon. This is an emergency operation, which is carried out solely according to indications, if there is a possible threat to the life of the child and mother. Caesarean section at 37 weeks of pregnancy is performed on approximately every twentieth woman. And this is not without reason. After all, the risk is justified. Indications for caesarean section are very diverse. The most common is a discrepancy between the size of the fetal head and the mother's pelvis. In such a situation, childbirth is either completely impossible, or there is a great risk of injury to both the child and the woman. Sometimes the size of the small pelvis is normal, but the fetus is large or even gigantic, which is not uncommon. A fetus is considered large if it weighs more than 4 kilograms at the time of birth. Giant, if more than 5. In this case, they resort to emergency surgery. The second reason may be various complications from the fetus, for example, acute hypoxia. At the same time, the baby suffers from a lack of oxygen, which can lead to his death. Umbilical cord entanglement. Often, a fetus that moves very actively can become entangled in the umbilical cord, which will lead to asphyxia and malnutrition. Then a caesarean section at 37 weeks is done on an emergency basis.
Another indication for cesarean section is pathology of the placenta or threat of miscarriage. Placental abruption is a serious complication that requires urgent measures.
The absolute indication is intrauterine fetal death, uterine rupture in combination with severe bleeding. The relative indication for surgery is oligohydramnios. This pathology can occur due to pathology of the fetal bladder due to injuries, as well as insufficient formation. The reason for this may be kidney diseases of the fetus and mother, infections and others. Many expectant mothers will be interested in how a caesarean section is performed. This operation is quite simple. A large incision is made first in the skin, subcutaneous tissue of the abdomen, then in the uterus and amniotic sac, and the baby is removed. This procedure is performed under anesthesia. Children are usually healthy. Another important question will be when can a caesarean section be performed, and at what period. It depends on the maturity of the fetus. Currently, even children weighing 500–600 grams are being nursed. But the mortality rate is very high. If the period is long - more than 30 weeks, then the probability of a favorable outcome is more than 90%.
An interesting fact is that an incorrectly positioned fetus is another indication. The most physiological is the cephalic presentation, but if it is pelvic or transverse, especially in combination with a narrow pelvis, then there is a threat to the life of the mother.
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that the 37th week of pregnancy may, in some cases, be the last week before childbirth. This phenomenon is not uncommon. In addition, if there are severe complications of pregnancy, there is no need to be afraid of a cesarean section, since this operation can save the life of the child and his mother.
Breech presentation: what is dangerous and what to do
Breech presentation occurs in 3-5% of pregnancies. Natural childbirth in this case is considered pathological due to the large number of possible consequences and complications. In this case, a caesarean section is performed, especially if the fetus is male. If a similar effect is observed, special gymnastics can and should be done; a method for breech presentation as an external obstetric rotation can also be used.
The effectiveness of these actions is unpredictable. The baby can turn over into the correct cephalic presentation and vice versa into the pelvic presentation even after obstetric rotation. But this procedure is done only at 34–38 weeks. Please note that in multiple pregnancies, usually one child has a breech position and the other a cephalic position. If you are pregnant with twins or triplets, only your doctor can give advice.
The doctor can give all the necessary recommendations only after 32 weeks in order to eliminate the consequences as much as possible. At 30 weeks you don't have to worry about this. Its movements in the uterus are normal and imply normal development.
Woman's behavior at home after PCS
When switching to a more familiar diet, you still need to monitor your diet. In this regard, you should consult not only your doctor, but also your pediatrician.
After a planned caesarean section, you can shower after 1-2 weeks. But a bath (not a hot one!) - only after 1.5 months.
It is necessary to explain to the husband that, for at least 2 months, the woman is contraindicated in heavy physical activity and sexual intercourse. Last but not least, you need to think about contraception. The next pregnancy can be planned no earlier than in 2 years.
Especially for beremennost.net Olga Rizak
Type of Caesarean
Carrying out a cesarean section at 38 weeks
During pregnancy, the gynecologist assesses how risky natural labor may be. If problems or prerequisites arise, the doctor has the right to prescribe a cesarean section.
However, the need for a cesarean section is not always easy to determine. There are cases when the course of pregnancy changes significantly and the doctor must urgently decide which option will lead to the least damage to the mother and child.
Based on the indicators, there are several types of cesarean:
- Planned – it is carried out starting from the 38th week. The prerequisites for the operation are the onset of labor;
- Planned - carried out in the case when labor has begun, but it is accompanied by a number of circumstances that aggravate the situation. Based on these circumstances, the doctor has the right to perform an operation;
- Emergency – carried out if it is necessary to immediately complete the birth. It is carried out when unexpected complications arise that may pose a threat to the life of the mother or baby.
Depending on the characteristic features, the doctor is obliged to focus on one of the types and, if possible, warn the woman in labor.
News on the topic of caesarean section at 38 weeks of pregnancy
Read more
Inducing labor increases the risk of needing a caesarean section
In the most complex physiological process that is childbirth, there seems to be no place for outsider intervention, but doctors have learned to induce labor artificially, which is a blessing when there are indications for this: protracted labor, danger to the health and life of the mother and child, and the like. However, there is also a growing trend in the world to induce labor “by order” of a woman in labor, who thus wants to “fit” the birth of a child into the world with her vacation, so as not to lose a prestigious and highly paid job. A new study by American doctors suggests that labor induction significantly increases the risk of complications, leading doctors to ultimately perform a caesarean section.
Read more
Caesarean section is easier for the mother, but unsafe for the baby
American experts found that, compared with births occurring at 39 weeks or later, repeat cesarean sections performed before 39 weeks of pregnancy are associated with a higher risk of severe complications in newborns. The latter may subsequently experience respiratory distress syndrome, requiring artificial ventilation in intensive care units.
Read more
Caesarean section “optional” will be canceled
From September 1, clinics in several US states will introduce a strict rule according to which cesarean sections will be performed strictly for medical reasons. Thus, the local Ministry of Health wants to stop the “fashion” for such operations.
Read more
A pregnant Spanish woman who suffered brain death was taken off life support
Last weekend, doctors at a clinic in the capital of Ireland, Dublin, disconnected a young woman who was 18 weeks pregnant from the ventilator system. This decision was made by the court, coming to the conclusion that the fetus is doomed anyway...
Read more
Caesarean in Brazilian, or in search of pregnancy
A rare case for modern medicine occurred in the Brazilian city of Cabo Frio. Doctors at one of the local clinics performed an emergency caesarean section on a 37-year-old woman - but did not find a fetus in the uterus. The pregnancy turned out to be false.
Read more
A woman who beat breast cancer gave birth to a child contrary to predictions
An English woman who fought breast cancer twice was assured by doctors that she would never be able to have children. Imagine their surprise when they found out that she was five weeks pregnant. Doctors had no doubt that 36-year-old Michelle Raftery had less than a 5% chance of becoming a mother even with the help of artificial insemination, because during treatment for cancer she had to take many drugs. Contrary to all forecasts, on March 27, the baby Michelle gave birth to last year turned one year old.
Read more
Children born prematurely are more at risk of developing various complications than others.
The birth rate of premature babies has increased significantly in the United States in recent years. According to the latest data, in most cases such births were carried out by caesarean section
Read more
The longer the child spends in the womb, the better he will learn
Normal gestation periods are considered to be from 37 to 40 weeks. Babies born before this period are considered premature and therefore more prone to health problems. However, it turns out that not everything is so simple with those who were born on time.
Read more
Miraculously surviving quadruplets celebrate their first birthday
Multiple pregnancy is always a very difficult test for the mother and for the babies who live in her womb for 9 months. The risk of various pregnancy complications increases noticeably when there are two twins, the risk is even higher when triplets are due, and pregnancy with four twins at once is a very difficult test of the strength of all five “main characters” - mother and children (we’re not even talking about doctors goes). The other day, four toddlers, who were born under dramatic circumstances, turned one year old - suffice it to say that the “largest” of the babies weighed only 965 grams at birth.
Large child. Possible complications of pregnancy and childbirth
“The hero is born!” - hears a young mother whose newborn weighs more than 4 kilograms. Many parents are convinced that a large child is good: if he weighs a lot, it means he is strong and healthy. Unfortunately, this widespread opinion is not always justified - the birth of a child with a large weight is sometimes associated with some problems.
First, let's define the terms. If the baby's weight at birth is 4000-5000 g, the fetus is considered large. With a weight of 5000 g and above, the fruit is called giant. In this case, the child’s height is not taken into account, although, as a rule, the body length of such a “hero” also exceeds the statistical average. So, if the fetal “height” of 48-54 cm is considered normal, then in large children this figure can be 54-56 cm. It should be noted that in recent years there has been an increase in the average weight, height and physical development of newborns. This is probably due to improved working, living and nutritional conditions for pregnant women. According to research, the number of newborns with a birth weight of 4000 g and above is 5-10%. The birth of giant children is much less common.
Baby development at 38 weeks
Now the child’s weight can reach 3 kg, and his height is 45-46 cm. He still “eats” through the placenta. His body loses lanugo (original fluff), and the original lubricant becomes noticeably less. Now he is becoming more pretty, the baby has accumulated fat reserves, and his face and body are acquiring “angelic” features.
Boys' testicles are already descending into the scrotum this week. The child is already fully formed: the lungs are open and ready for the first breath, the “power” of the heart muscle is enough to provide the body with blood, and the kidneys and intestines regularly remove all harmful substances, the brain is also ready for the baby to exist outside the womb.
The child has grown and is cramped in the uterus, so he still moves less often. However, all movements became more coordinated. The normal heart rate is within 160 beats/min. The baby is ready to be born.
Reasons why a large baby is born
There is a popular opinion that a baby with a large weight is born to people who themselves are quite large in size. Allegedly, heredity is to blame. In practice, the type of figure and differences in the skeleton, laid down genetically, begin to appear much later.
There are fixed reasons why a large fetus appears. Therefore, you can immediately know about them in order to avoid falling into a risk group. Popular factors are:
- Unbalanced maternal nutrition. Eating large amounts of carbohydrates, being overweight or obese.
- Having children. According to statistics, each subsequent child born to a mother is larger in size. The second birth, as well as all subsequent ones, can become a risk factor in favor of having a big baby.
- Lifestyle. If a woman leads a sedentary life, then this is also an impetus for the formation of a large baby.
- Interruptions in metabolism. Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism - all this leads to large amounts of glucose entering the baby’s blood. As a result, his body weight grows at a rapid pace. The presence of polyhydramnios and a large fetus is the first reason to send the mother for blood sugar tests.
- Long-term use of medications. This hypothesis has not yet been strictly confirmed by research, but it is also used by different doctors. The list of drugs that are at risk can be obtained from obstetricians.
- Thick placenta. It produces increased nutrition for the fetus, and therefore the child grows in size.
- Attachment of the placenta to the posterior wall of the uterus. This point relates to the past. In this case of fastening, there is an increased supply of nutrients.
- The gestation period is too long. This can be diagnosed as early as 40 weeks. For example, the fetus will be large if the child’s fontanelles are already closing, there is dry skin, long nails, hair, etc.
- Multivitamin complexes. This theory also has no scientific evidence. It is believed that if a woman has used such drugs, she may be diagnosed with a large fetus.
Doctors, when they suspect the presence of a child with a large body weight, seek to understand why this happened. In some cases, this helps to identify diabetes mellitus, eating disorders, etc. in the mother. Very often, a pregnant woman has enough time to ease the course of labor and bring the weight of the fetus to normal. However, the main question is how to determine that the fruit will be large?
future child
Height - 48 cm, weight - 2800 g.
If you are carrying twins, birth usually occurs at 37-38 weeks. There is some chance of giving birth early if this is not your first child. However, there is no clear relationship; many gave birth to their first child earlier, and their second later.
In any case, remember that you can give birth at any time! The baby sinks more and more into the lower pelvic region, every day closer and closer to the exit. Because of this, pain in the perineum, spine, and legs becomes almost habitual.
He is almost completely wrinkle-free - his skin is smooth and pink. The child continues to gain weight by 14 g per day. Myelin, which conducts nerve impulses, is formed in the brain at tremendous speed. By the way, for some parts of the brain this process will continue after birth.
Signs that there will be a large fruit
Doctors usually do not make mistakes with this diagnosis. There are clear signs that a pregnant woman will have a large fetus.
A large baby is a fetus whose birth is difficult due to its weight or size. When a woman in labor has a narrow pelvis, it will be difficult for her to give birth to even a baby weighing 3.5 kg.
Dimensions are set at the ultrasound stage. As a result, doctors make a conclusion whether the fetus will be large or not. If the pregnancy is full-term, then the standards for the fetus are as follows (for 40 weeks):
- BPR: 93.7-93.9 mm.
- LTR: 119.8-120 mm.
- DB: 75.7-75.9 mm.
- SDGK: 99.7-99.9 mm.
- SJ: 108-108.2 mm.
If the fetal indicators exceed these standards, then the expectant mother is at risk.
There are also indicators that apply to the woman in labor herself:
- Weight gain per week (without swelling and gestosis): 500 g.
- Coolant: 100 cm.
- VDM: 40 cm.
To estimate the approximate weight of the baby, you can multiply the coolant indicator by the GMR. However, this estimate is very, very approximate.
Indications for caesarean section
A caesarean section has to be resorted to when the pregnancy is complicated and natural childbirth becomes dangerous. It’s good if obstacles are discovered long before birth, then the doctor can plan the operation in advance and prepare the woman in labor. In this case, a caesarean section is called planned.
These are any complications during childbirth that disrupt their normal course and threaten the life and health of mother and baby.
Weakness of labor, not amenable to therapy; Discrepancy between the sizes of the mother's pelvis and the child's head (clinically narrow pelvis);
Premature placental abruption with severe bleeding; Placenta previa with severe bleeding; Threat of uterine rupture; Oxygen starvation of the fetus that cannot be treated
Woman's health status:
- diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, asthma;
- serious vision problems;
- recent traumatic brain injury;
- oncology;
- pathological disorders of the cardiovascular or central nervous systems;
- very narrow, deformed pelvis;
- age after 30 years.
Seam features:
- longitudinal suture placed during the first cesarean section;
- the condition of the seam is questionable if there is a threat of its divergence;
- the presence of connective tissue in the scar area;
- abortions after the first caesarean section.
Pregnancy pathologies:
- incorrect presentation or large size of the fetus;
- multiple births;
- After the first operation, too little time has passed: up to 2 years;
- weak labor activity;
- post-maturity.
Pathological conditions
The pathological condition of the fetus is the most unpleasant thing that an expectant mother can expect and brings her unnecessary suffering. Also, pregnant women with health difficulties may experience problems with their illness. The variety of symptoms is so wide that all pathologies fall under the jurisdiction of doctors; only they can make decisions and think about how to treat a pregnant woman.
The tone of the uterus may suggest discharge, including minor bleeding. The intensity is purely individual. As a rule, this condition requires the woman to be placed in a hospital for observation. But exactly the 30th week of pregnancy is not critical and does not require urgent hospitalization, except in cases where the pregnancy was previously assumed to be pathological.
General recommendations include the following. A pregnant woman should be regularly observed by a doctor, attend ultrasound scans on a schedule, take tests and keep up to date with her health status, especially with expected pathologies. Otherwise, she should not worry about medical issues - this is the prerogative of doctors. If your doctor says everything is fine with you, look forward to your baby!
Signs of imminent labor in multiparous women
What are the warning signs of labor for multiparous women at 36, 37, 38, 39 and 40 weeks, what can and should the expectant mother pay attention to? What features of the course of pregnancy at this stage are of interest to obstetricians-gynecologists?
Many women know that even with a full-term pregnancy, labor can begin a little earlier. Even 3 weeks before the expected due date based on obstetric gestational age.
And when the 35th or 36th week of pregnancy, the harbingers of labor may already appear in multiparous women. Although, there are women who do not notice them at all. So what are these signs?
1. The level of the fundus of the uterus becomes lower. More typical for the first pregnancy, such signs of labor may be absent in multiparous women. That is, their stomach may drop several hours before giving birth. And sometimes even during childbirth.
During this period, the uterus, which was located in the abdominal cavity during pregnancy, descends into the pelvic area. It becomes easier to breathe and eat, heartburn does not hurt so much, the uterus stops squeezing the lungs and stomach. Less pleasant companions to a lowering abdomen are frequent urination, which has nothing to do with diseases of the urinary system; daily stool can become liquid, which often leads to exacerbation of hemorrhoids, and before childbirth this is especially unpleasant in all respects. This happens because the prolapsed uterus now begins to put pressure on the lower bowel and bladder.
2. Another characteristic symptom of approaching labor is the release of the mucus plug. Normally, the 38th week of pregnancy gives such characteristic harbingers of labor in multiparous women. The cervix is ripening. The body begins to prepare for childbirth by changing its hormonal levels: the hormone progesterone, which maintains pregnancy, is replaced by the hormone estrogen, which softens the cervix and prepares it for the normal course of labor. The cervix, reliably protected by a “plug” of mucus during pregnancy, begins to open slightly, and a small lump of mucus comes out of the vagina. This process is called “removal of the mucus plug.”
Normally, this is a clear, thick mucous discharge, approximately equal in volume to one tablespoon. It may be pinkish or have small streaks of blood. Also, a mucus plug may appear from the vagina in parts over several days.
It is important not to confuse the passage of a mucus plug with bleeding associated with placental abruption. In this case, bright scarlet blood is released, not just streaks in the mucus
3. Harbingers of the onset of labor in multiparous women at 40 weeks are training contractions. They are also called false. But doctors prefer the name - preparatory.
An intelligent organism knows what is coming to it soon and wants to “practice” a little. False contractions may appear during the last week before birth. Training contractions are usually irregular: your stomach may “rock”, as with uterine tone, or contract several times a day for a couple of hours. Don't worry, it's not birth yet.
Labor contractions usually occur 20-25 minutes apart at the very beginning. Moreover, their intensity is constantly increasing. And if you take a couple of antispasmodic tablets, a warm bath, or try to sleep, the spasms will not disappear.
Medical consultation is necessary only in the case of painful and prolonged training contractions that prevent a woman from sleeping and cause severe discomfort. If you just endure them, you can literally run out of steam before giving birth, and then a complication such as weakness of labor is likely to occur - this is an indication for drug stimulation, which is quite painful, and in case of protracted labor and the serious condition of the fetus - an emergency caesarean section.
Inexperienced future parents usually look forward to meeting their baby, and consider that when the 39th week of pregnancy or even the 40th week of pregnancy has already begun, the harbingers of labor are a reason to immediately get ready and go to the maternity hospital. However, normally, such phenomena as the passage of a mucus plug or training contractions are only a sign that everything is in order with the body, the necessary processes of preparation for childbirth are proceeding according to the plan created by nature. Childbirth is already close, but this “close” can take a period of time from several days to a couple of weeks. The main thing in these last weeks is less worry and worry, more pleasant thoughts about a close meeting with the dearest person in your life.
Other possible harbingers of early labor in multiparous women at 37 weeks and later:
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- weight loss;
- pain in the pelvis due to its expansion;
- the desire to wash the dishes, tidy up, do repairs, buy more for the baby.
Fetal movements
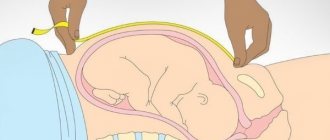
Photo of the belly at 30 weeks of pregnancy
At the 30th week of pregnancy, the baby’s activity is determined to understand whether there may be any difficulties (for example, the fetus will take a head-up position with a breech presentation). To do this, you need to measure the number of shocks in the uterus. There should be at least 6 movements per hour while awake. Within 10 hours - at least 10 movements, within 12 hours - at least 24 movements. The stomach may move at some points; this is relatively normal for active children after childbirth.
Planned caesarean at 38 weeks
In the morning they took me for an enema, after which I washed myself and shaved, gave me a local nightie and took me to the operating room. Honestly, my knees were shaking.
They laid me on the operating table, connected some sensors (to measure pulse, pressure, heartbeat), an anesthesiologist came, gave me an injection in the back and off I went (I had spinal anesthesia, so I saw and heard everything). After the injection in the back, I felt warmth in my legs, but after 5 minutes I couldn’t feel my legs at all. And after another 5 minutes they took my beloved son out of me. The fear immediately subsided and I almost burst into tears. While they were stitching me up (about 40 minutes), I watched as the nurses took care of my baby. They weighed him (3130g), measured his height (51 cm), head and chest volume (35.33), dressed him and placed him on my chest, and then took him away. They stitched me up and took me to the recovery room, where I lay for a day.
2 hours after the operation, the anesthesia began to wear off, I began to slowly feel my legs, and then such pain began! I thought I was going to die! By the way, my son was with me all the time, nurses often came and helped care for the baby. A day later they transferred me to a regular ward and made me walk. Walking is a big word, it's more like crawling along the wall. And you also need to take care of the baby. Well, my son slept most of the time, as if he felt that his mother needed strength.
We were discharged on the fourth day.
Now 1.5 months have passed, nothing hurts, the seam is neat (smile). My son is growing by leaps and bounds.
Features of the rehabilitation period
The postoperative period is very important for a woman in labor. After a cesarean section, it is important to remember the following rules:
- In order to remove anesthetics from the woman’s body as quickly as possible, it is recommended to drink as much fluid as possible.
- For faster healing of the suture and to minimize the likelihood of damage to it, you should not neglect a special postpartum bandage.
- In order for a woman to quickly recover and return to a full life, it is important to maintain bed rest and move as little as possible at first.
- Do not neglect prescribed painkillers. If the mother's condition worsens, the doctor has the right to prescribe an additional series of medications.
You should not be afraid of surgery; cesarean sections are often performed. Often, fear of a cesarean section among women in labor arises as a result of a lack of knowledge about the procedures that await them, which is completely in vain.
If a woman is well acquainted with the operating process, and the therapy is carried out by an experienced specialist, the likelihood of a smooth pregnancy and a favorable outcome is quite high.
Caesarean section 38 weeks pregnant. Preparing for a planned cesarean section
If you know that you are having a planned caesarean section, then you should think in advance not only about choosing a maternity hospital, since each maternity hospital has its own characteristics of the operation itself, pain management, and postoperative management, but also talk with your doctor.
Depending on your condition and indications for a planned cesarean section, you will be hospitalized at the maternity hospital at approximately 38-39 weeks, i.e. 1-2 weeks before the expected birth. When preparing a pregnant woman for a planned cesarean section, a detailed examination is carried out, including blood and urine tests, determination of blood type and Rh factor, and determination of the degree of vaginal cleanliness; A comprehensive assessment of the fetal condition is carried out - ultrasound examination and cardiotocography. If necessary, drug correction of identified deviations in health status is carried out. If you have decided on a clinic and have completed all the examinations and consultations in advance, then if there are no complications and the fetus is in good condition, you can go to the hospital one or two days before the operation.
On the eve of the operation
The doctor determines the date of the operation after receiving the examination results - the baby is full-term and ready to be born. As a rule, elective surgery is scheduled for the morning. On the eve of the operation, your attending physician and anesthesiologist will talk with you, who will tell you what kind of anesthesia you will be given and the events before, during and after the operation, find out whether you have had anesthesia before, your reaction to them, whether you suffer from allergies to medications . You will certainly be asked to sign a consent to the operation and the proposed method of pain relief. When prescribing the drug, the anesthesiologist must check your body weight and, if necessary, weigh you.
Eating the day before surgery should be light. At 18:00 you are allowed to drink a glass of kefir or tea. And then the usual “nothing by mouth” rule applies - no liquids or food should be consumed
, otherwise, while under anesthesia, the contents of the stomach may enter the respiratory tract.
Before the operation, a set of hygienic measures is carried out: hair on the pubic area and lower abdomen is shaved, the pregnant woman must take a hygienic shower the day before. At night you will be offered a light sedative.
Day of surgery
Early in the morning (or 2 hours before surgery), the woman is given a cleansing enema - this is a standard procedure before any abdominal surgery.
Since during any operation on the abdominal organs, blood stagnation may occur in the veins of the legs and pelvis, measures must be taken to prevent the formation of blood clots (deep vein thrombosis). To do this, a pregnant woman’s legs are wrapped in elastic bandages up to the upper third of the thigh, which is why many maternity hospitals require you to bring 2 elastic bandages of at least 2.5 m each before the operation. Bandages can be replaced with anti-varicose compression stockings.
After this, the woman changes into a clean shirt, shoe covers are put on her feet, and a special cap is put on her head. Then the woman in labor is placed on a gurney, covered with a sheet and taken to the operating room.
As a rule, you are allowed to take only flip flops, a robe, a bottle of still mineral water, a mobile phone and a charger. All other items are packed in plastic bags, signed and handed over to the storage unit. After you are transferred from the recovery room to the postpartum ward, the midwife will bring all your belongings.
Before surgery
Immediately before the operation, a catheter is inserted into the bladder on the operating table, which will be removed a few hours after the operation. These measures will help you avoid kidney problems in the future. After anesthesia, the woman is placed on the operating table, the nurse treats the lower abdomen with an antiseptic solution; A screen (screen) is installed at chest level so that the woman in labor does not see the surgical field.
At the time of the cesarean section, the woman in labor lies on her back, perhaps with a pillow under her hips or on a surgical table tilted to the left at an angle of 15-20°, this is necessary in order to divert the uterus from large blood vessels and reduce the likelihood of a drop in blood pressure, which can lead to a lack of oxygen and an attack of dizziness.
In some maternity hospitals, one of the mother's relatives is allowed to be in the operating room; this could be a husband, mother, sister, or friend.
Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist
At the 39th week, it is possible to schedule a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist. On the eve of the meeting, it is necessary to undergo tests, directions for which were issued at the last meeting:
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis.
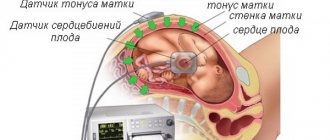
It is necessary to do a fetal cardiotocography (CTG), the results of which are transferred to the doctor.
At the appointment, the gynecologist will perform the usual actions:
- interview the woman about changes in well-being, the presence of precursors of labor and unpleasant sensations;
- will measure general health indicators: body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate;
- will assess the size of the uterus according to the timing: measure the circumference of the abdomen, the height of the uterine fundus;
- palpates the abdomen to determine the position of the baby’s body;
- listen to the fetal heartbeat using a stethoscope;
- will weigh the pregnant woman and calculate the body weight gained since registration.
This week it is possible to conduct an examination in a gynecological chair. Usually gynecologists warn about this at the previous meeting. The examination allows you to assess the condition of the cervix and understand the need to issue a referral for hospitalization.
At the end of the appointment, the gynecologist can set a date for the next appointment, which will occur in a week, or issue a referral for hospitalization. If the doctor decides to postpone hospitalization, the pregnant woman is given directions for urine and blood tests.
Ultrasound
At the 39th week of pregnancy, routine ultrasound is not performed. It is possible to conduct an ultrasound examination for medical reasons. Most often it is used to exclude possible pathologies of the fetus or to study the characteristics of its location in the uterus.
If desired, a woman can have an ultrasound done for a fee to confirm the successful course of the pregnancy.
Uterus and belly
At the 39th week of pregnancy, the uterus increases slightly, reaching a height of 38-40 cm. Its fundus is located at a height of 15-17 cm above the navel.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the woman, the stomach may be in a different position this week: high (supporting the lungs and diaphragm) or low (increased pressure on the pelvic organs). Abdominal prolapse may occur gradually, or may not occur at all. Both of these abdominal positions are normal.
Discharge, bleeding, menstruation
The volume of discharge at the 39th week remains virtually unchanged compared to the previous 2 weeks, but significantly exceeds the amount of discharge during the previous pregnancy.
Normally, the color of the discharge should be light or milky; a slight inclusion of light mucus with blood streaks is acceptable. This is the release of the mucus plug that kept the uterus sealed. Once a woman has noticed the beginning of her separation process, taking a bath or swimming is not recommended.
The separation of the mucus plug is a harbinger of labor, which appears at different times in each specific case. In some women it occurs 1-2 weeks before giving birth, in others - at the beginning of the birth process. If a pregnant woman notices the appearance of mucus in the discharge, it is necessary to strengthen control over her well-being; it is possible that labor will begin in the near future.
The smell of the discharge is normally almost imperceptible and has a slight sour tint. If there is a sudden change in odor, you should immediately consult a gynecologist for advice.
At week 39, unwanted discharge may appear. You should consult a doctor if the discharge becomes green, yellow or gray, with an unpleasant odor.
If the discharge is pink, red or brown, you should contact the emergency department of the maternity hospital for advice. Normally, there should be no spotting or bleeding; an examination by a specialist is necessary.
Nutrition for a pregnant woman at 39 weeks