The third trimester of pregnancy is the final one in the development of the child, and every mother prepares for the birth of her baby.
Many women during this period listen to all their sensations. Often, at 38 weeks, the lower abdomen feels tight. The condition raises questions and fears for the expectant mother about the course of pregnancy.
The health and full development of a child depends on compliance with many factors.
You should pay maximum attention to your well-being and, if possible unusual symptoms appear, seek medical help as soon as possible.
38 weeks of pregnancy means that the baby will be born soon. In the last month of intrauterine development, a child very quickly gains the required body weight.
The belly increases even more, and the woman may feel unusual discomfort.
Do pulling sensations mean the onset of labor?
38 weeks of pregnancy is a serious period, which means that labor can begin at any time.
According to statistics, it is during this period that a large number of incomprehensible nagging pains in the lower abdomen occur.
This is because the uterus begins to prepare for childbirth and may contract from time to time. Most often, such symptoms do not mean anything terrible or dangerous for either the mother or the child.
As 38 weeks of pregnancy approaches, the fetus inside the uterus is positioned as it should be just before birth - upside down. The stomach drops noticeably.
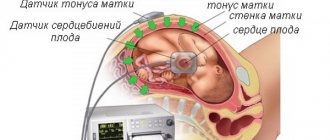
Training contractions are characterized by the fact that the lower abdomen begins to pull. The tone of the uterine muscles increases briefly, then stops.
This may happen once a day or several times in a row. You can determine the tone of the uterus by feeling the abdomen; if the surface is very hard, then there is reason to think about the imminent birth.
Contractions of a training nature can be assessed by the following criteria:
- The interval of contractions is initially too short (once every 3-7 minutes). When labor begins, contractions begin gradually (approximately 1-2 contractions every 2 hours).
- The discomfort was eliminated with an antispasmodic or a warm bath.
If after checking the type of contractions there is no relief, you should call an ambulance or go to the maternity hospital in your own transport. Most likely the birth process has begun.
Then the tension subsides and the uterus relaxes. If you put your hand on your stomach, you can feel its surface becoming soft and pliable again.
Typically, softness is restored gradually over several minutes.
Training contractions are very often present precisely from the 38th week of pregnancy. This means that the woman needs to check whether all things and documents have been collected for the maternity hospital.
Be ready at any moment to call an ambulance and go to the hospital. The nagging pain is similar to the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Every second woman is familiar with such sensations.
Contractions are usually not regular and usually last no more than 15-20 seconds. There are very long gaps between the appearance of uterine tone and its relaxation.
The reason to call an ambulance is to reduce the interval to 5 contractions in 60 minutes. Increased uterine tension means labor is approaching.
Not many pregnant women experience severe pain during training contractions. Severe pain may be associated with increased sensitivity or high activity of the uterus.
There is a small percentage of women who experience absolutely no unpleasant symptoms. In case of intolerable pain, it is recommended to take an antispasmodic.
The pregnancy period allows you to use the drug without harm to the baby. If the tone cannot be eliminated, then you need to call an ambulance.
During periods of training contractions, it is necessary to take a lying position, relax and avoid nervous and mental stress.
Sometimes a woman is advised to wear a prenatal bandage, which can reduce the likelihood of pain in the lower abdomen and reduce physical stress on the spine with a large fetus.
The load is especially high at 38 weeks of pregnancy, the stomach pulls down.
At what week of pregnancy can signs of labor appear?
The time at which signs of imminent labor appear, as well as the very fact of their appearance in general, is a purely individual matter: some notice the changes eloquently described on the Internet as early as the 36th–37th week, while others do not observe anything like that at all. Moreover, both extreme options are variants of the norm - after all, the issue here is in hereditary factors, and in the characteristics of a particular pregnancy, and in its order... In addition, the harbingers of childbirth are not at all described by medicine as obligatory, there are no official medical dates for their appearance. In other words, in a global sense, such signs do not indicate anything specific.
Each woman’s feelings 2-3 weeks before giving birth are also different. Some may experience pain, while others may not. So, you don’t need to listen too much. There are fetal movements - great. If regular contractions appear or your water starts to break, you go to the maternity hospital.
Obstetrician-gynecologist Elena Berezovskaya
https://klubkom.net/posts/42432
Nevertheless, it is the 38th week that is most typical for the appearance of tangible, bright signs, both in first-time mothers and in experienced mothers:
- in primiparous women, the date of the first appearance of precursors is, as a rule, significantly distant from the date of birth; at the same time, the date of birth for inexperienced expectant mothers often tends to be closer to 40 weeks;
- In multiparous women, signs of approaching labor appear closer to the date of delivery (an exception to the rule is prolapse of the abdomen), but the date of birth itself occurs earlier (often at the 38th week).
Multiparous women, whose first birth occurred by caesarean section, stand somewhat apart in the matter of the timing of manifestation of the precursors of labor. Due to the fact that the child did not pass through the birth canal, its elasticity is not reduced, and most of the signs follow the “scenario” of firstborns.
Signs of cervical dilatation
When the 38th week of pregnancy lasts, the lower abdomen pulls, this may be a consequence of the development of labor. The pain is similar in nature to menstrual bleeding.
If the pain does not cause serious discomfort, there is no need to worry about this condition. In this way, the body prepares for the upcoming birth.
Pain in the lower abdomen is sometimes a sign that the cervix is beginning to dilate. The process lasts from several minutes to several days.
Depending on the individual, at 38 weeks the cervix may take some time to dilate.
The intensity and severity of nagging symptoms come from the hormonal background of the mother and the diligence of the fetus.
If your lower abdomen feels tight at 38 weeks of pregnancy, you need to pay attention to possible discharge.
Dilatation of the cervix is accompanied by the following signs:
- The frequency of contractions increases. The periods of uterine relaxation become shorter. The more the neck is dilated, the more often and more intensely the pain is felt.
- A pulling sensation appears in the lower abdomen. As each contraction increases, the cervix opens wider, the pain syndrome becomes longer, and anesthesia may be required.
- As the cervix opens, the mucus plug comes away. Appears in the form of a thick white to yellow mucus. Sometimes there are spots of blood.
The cervix is an elongated organ of the female reproductive system. Consists of muscle tissue, similar to the structure of the uterus.
Before labor, the cervix is tightly compressed and protects the amniotic sac with the baby from harmful factors.
As the due date approaches, the cervix shortens and becomes much thicker. The initial opening occurs at 1-2 fingers (gynecological measurement).
As the contractions progress, it opens completely to allow the fetus to come out freely. Therefore, the 38th week of pregnancy is sometimes accompanied by the fact that the stomach is pulled down.
It is this process of temporary modification of the cervix that first causes nagging pain in the lower abdomen, and then a severe pain syndrome of a temporary nature.
The baby's movement is accompanied by a kind of tension of the cervical tissues over his head. The stomach feels tight at 38 weeks of pregnancy.
There are many ways that help alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of dilatation: a warm shower, light exercise on a large ball, massage of the sacral area.
At 38 weeks of pregnancy, the weight of the uterus and baby during a full pregnancy is approximately 12 kg. Therefore, manifestations of pain in the sides and lower back are possible.
The spine is not always able to cope with the growing load on it. The center of gravity changes, the stomach noticeably protrudes forward of the woman.
To distribute the center of gravity, a pregnant woman leans her body back a little, creating a serious load on the back muscles. The spine takes time to get used to.
A woman may complain that her lower abdomen is tight at 38 weeks of pregnancy. You may notice an increase in unpleasant symptoms with active, long walking or standing for a long time.
In order to reduce the spread of discomfort, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Use a specialized bandage for pregnant women. It will help to properly distribute the excess load. Eliminate the pathological effect of heavy weight on the spine.
- Perform simple exercises to unload your back. Swimming, fitball, warm baths (but not too hot) are recommended.
- Learn breathing exercises. Many breathing exercises, when performed correctly, help eliminate discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Modern expectant mothers use schools for pregnant women, which teach all the necessary techniques to ease contractions and directly the rules of behavior during labor.
Uterine tone
The end of pregnancy is accompanied by severe discomfort. In addition to pulling sensations in the lower abdomen at 38 weeks, pain of various types may occur caused by the weight of the uterus with the fetus.
Often the body does not have time to adapt to the stress that has arisen, so even a light walk or doing household chores can cause uterine tone.
The concept of uterine tone refers to prolonged tension in the muscular tissue of the organ, which threatens premature birth and fetal hypoxia.
The condition has the following symptoms:
- The stomach pulls down and hurts.
- When palpating the uterus, a pronounced hardness of the surface of the abdomen can be noted.
- In case of strong tone, a change in the shape of the abdomen may occur during tissue tension.
An antispasmodic (no-spa) and a warm bath will help relieve the tone of the uterus. In any case, consultation with a gynecologist is required.
You may need hospital treatment using droppers of the drug Genipral.
The pathology is dangerous due to rapid labor and the formation of fetal hypoxia. At 38 weeks, the uterine tone is usually removed and the baby is expected to be born soon.
At the same time, the lower abdomen pulls a little, but under the influence of the drug the symptom is eliminated.
Mom's well-being
Currently, the placenta weighs 1-2 kilograms and is 20 centimeters in diameter. The uterus moves 16-18 centimeters away from the navel, while it rises 36-38 centimeters above the pubic symphysis. At this time, the expectant mother begins to experience more discomfort: poor sleep, swelling, false contractions.
If at 38 weeks of pregnancy you begin to suffer from insomnia, then at night it is recommended to drink a glass of hot milk and lie down on your left side. To reduce swelling of the legs, you should not stand or sit for a long time, you should give up salty foods, and keep your legs elevated. When contractions appear, you can walk around the room to determine whether they are real or false. During movement, false contractions will disappear.
During this period, a woman feels heaviness in her chest, so it is advisable to wear clothes made from natural fabrics. At this time, a bra made of thick cotton fabric is suitable. The female body is preparing for childbirth, hormonal levels change, the pelvic bones move apart, ligaments and cartilage soften.
Placental abruption
Such a pathology as placental abruption is accompanied by a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen and copious purulent vaginal discharge with blood. Such discharge has a strong, unpleasant odor.
Such symptoms are very dangerous and indicate serious problems during pregnancy. Urgent medical attention is required.
When the disease occurs at 38 weeks, the stomach first feels tight, then more acute symptoms may appear.
Causes of placental abruption:
- Intoxication of the body.
- Nervous or mental experience.
- Endocrine and hormonal abnormalities.
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys.
- Severe aggravated toxicosis.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Past infectious disease.
- Cardiovascular system disorders.
- Malposition.
- Various pathologies of pregnancy.
Placental abruption is dangerous due to its negative impact on the fetus, oxygen starvation, and disruption of brain activity.
Risk factors include the following: smoking, alcohol consumption, unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy diet, abdominal injuries, family factors.
It is recommended to take into account all risk factors when planning pregnancy and try not to aggravate the pathological condition.
Exposure to infections
Intrauterine infection is also a common pathology during pregnancy. The disease is accompanied by vaginal discharge of a mucous, purulent or foamy nature.
Most often there is an unpleasant odor. Pulls in the stomach when exposed to infections during any week of pregnancy.
Fungal infection of the reproductive system provokes the appearance of white cheesy discharge with the smell of rotten fish.
Bacterial diseases cause yellow, green, or clear mucous discharge. Any infectious influence is extremely dangerous for the fetus and mother.
The most common types of infections:
- Ureaplasma.
- Mycoplasma.
- Thrush.
- Toxoplasmosis.
- Gardnerella.
There are a huge number of infectious diseases that are not necessarily sexually transmitted. Perhaps the development caused a decrease in immunity at 38 weeks.
In case of any deviations from the norm, it is necessary to determine the cause of the discharge and consult a doctor to receive adequate therapy.
A pregnant woman with infectious diseases must be hospitalized in a hospital, where she undergoes a full course of treatment that is safe for her and her unborn baby.
The penetration of pathogenic agents at 38 weeks of pregnancy can cause labor. But this is not the worst thing, because the fetus is already fully formed and physically ready to be born.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Despite the fact that a pregnant woman devotes herself entirely to the development of her unborn child, problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract cannot be ruled out.
Pregnancy at 38 weeks is accompanied by great pressure on the digestive organs. The intestines and stomach, under the influence of the ever-growing uterus, change their normal position.
This causes discomfort and sometimes a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen.
Among the most common problems with the gastrointestinal tract at 38 weeks of pregnancy, the following pathologies can be noted:
- Poisoning.
- Indigestion.
- Diarrhea (may be a precursor to labor).
- Low bowel activity.
- Disturbance of microflora (dysbacteriosis).
Following the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will help reduce the likelihood of developing diseases; in the absence of contraindications, moderate physical activity is necessary, which activates intestinal motility and prevents feces from accumulating.
What causes nagging, aching pain during pregnancy?
Pregnant women experience aching and aching in the lower abdomen, lower back, and limbs. This is explained by the changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother. The size of the uterus and body weight increase. The center of gravity shifts.
Muscles are constantly tense. There is a shift in the standard arrangement of internal organs.
According to localization, the pulling is located in the lower abdomen. The aching affects the elements of the musculoskeletal system.
To minimize discomfort, a set of measures is used that affects the range of fundamentals of life:
- A diet is assigned, acceptable and unacceptable foods are determined (spicy, fried, sweet, etc. may be prohibited).
- A recommended sleep and rest schedule is prescribed.
- Complete ban on tobacco, alcohol and drugs.
- Ban on certain types of exercise.
- Prescription of pharmacological supportive agents.
Changes to this preventive regimen are made directly by the attending physician.