03.22.2018 Category: Diseases and complicationsAuthor: Anna Trofimova
OGA is a term that accompanies pregnancy management with any deviation from the norm. According to statistics, in Russia about 80% of women have OGA, and their number does not decrease from year to year. When compiling an anamnesis, all previous pregnancies are taken into account, regardless of their outcome, as well as gynecological diseases and operations.
- What can a woman do
Fight infections!
- Hormonal swing
Table of thyroid hormone norms
- By gender
- Video about hormone tests before a planned pregnancy
- At-risk groups
Components of the OAS
A pregnant woman may have a burdened obstetric-gynecological history if the following factors have been present in the past:
- Abortion. Artificial termination of pregnancy negatively affects women's health - a hormonal imbalance occurs, leading the body to stress, and the risks of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the reproductive system increase.
- Miscarriage. This includes miscarriages (before 28 weeks of gestation) and preterm birth (28 to 37 weeks). If spontaneous abortion occurs 2 or more times in a row, then the woman is diagnosed with recurrent miscarriage, in which each subsequent pregnancy is in danger of being terminated.
- Early placental abruption. Premature placental abruption can occur at any stage of pregnancy and can be partial or complete. In any case, this is a serious pathology that requires treatment and careful monitoring of the pregnancy.
- Complications during childbirth. Trauma to the birth canal, ruptures, abnormal labor, large blood loss - all this and much more can lead to problems in subsequent births.
- Pathologies in previously born children. In this case, doctors carefully monitor the pregnant woman and find out the causes of the pathologies of the previously born child in order to exclude the same problem.
Thus, OAGA accompanies pregnancy when one or more points are identified. In this case, indications for establishing a complicated medical history can also be the stillbirth of a baby or his death in the first 4 weeks, Rh conflict of parents, pathologies of the woman’s genital organs, hormonal imbalance and menstrual irregularities, etc.
Placental abruption is one of the reasons for the diagnosis of OGA in the future
Like most pregnant women, my medical record for pregnancy management included the inscription “OAGA”. The diagnosis was made due to previous two failed pregnancies - spontaneous miscarriages in the early stages. In this regard, from the 4th week of gestation, the doctor prescribed Duphaston as a maintenance hormonal drug and additional ultrasound examinations in the first and second trimesters.
Varicose veins
– affects mainly the lower extremities and the external genital area. Most often, varicose veins are first identified during pregnancy. The essence of the disease consists of changes in the wall and valve apparatus of the peripheral veins.
Uncomplicated varicose veins are manifested by dilated veins (which is perceived by pregnant women as a cosmetic defect) and pain in the lower extremities. Complicated varicose veins suggest the presence of other diseases, the cause of which is a violation of the venous outflow from the lower extremities. These are thrombophlebitis, acute thrombosis, eczema, erysipelas. Fortunately, complicated varicose veins are rare in young women.
For varicose veins, pregnant women are recommended to bandage the lower extremities with elastic bandages or stockings, and periodically elevate the extremities to improve venous outflow from them. Hemorrhoids , which often occur during pregnancy, are also based on venous thrombosis, therefore, a diet aimed at preventing constipation is necessary. In case of severe varicose veins with insufficiency of the venous valves, surgical treatment is sometimes performed even during pregnancy.
Childbirth in patients with varicose veins is often complicated by premature placental abruption and postpartum hemorrhage. Childbirth is carried out through the natural birth canal, if pronounced varicose veins of the external genitalia do not prevent this. In the postpartum period, physical therapy and elastic compression of the lower extremities are necessary.
What to do if a pregnant woman is bitten by a wasp: first aid and approved medications
Insect bites are very painful for many people.
The larger the insect, the more frightening it is to the potential victim, and pregnant women feel especially vulnerable in this regard. This is understandable: the expectant mother is responsible for the baby growing inside her.
Wasp on the hive
Seeing a wasp, for sure, every pregnant woman will certainly be worried: will she bite? What if trouble did happen? How dangerous is a wasp sting for pregnant women, and what kind of emergency care do victims need?
Wasps are a fairly large family of insects, numbering several hundred species, among which the most common are social and floral ones. Externally, representatives of different families are similar.
They differ from bees in their more elegant body structure, which is not so abundantly covered with hairs.
Comparison of the body structure of a wasp and a bee
Black and yellow striped or spotted color is the typical color of these insects. On average, wasps reach 2.5 cm in length, but there are also larger representatives of the family - hornets.
wasp sting
At the same time, during an attack, the striped predator uses not only its sting, but also its jaws. The wasp's venom enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
You can read our article on a similar topic: A child was bitten by a wasp: first aid
However, its concentration is so insignificant that, apart from a local reaction, often nothing bothers even a pregnant woman.
How dangerous is a wasp sting for pregnant women? If an insect stings, the poison will undoubtedly penetrate the mother’s body, and although the blood flow between the woman and the fetus is common, the baby is not in serious danger. The bitten liver is a reliable protector against poisons and toxins; it will cleanse the blood before it penetrates the placenta.
However, the poison also contains a protein, to which those predisposed to allergies may have a reaction.
In addition to swelling and swelling at the site of the bite, quite dangerous other symptoms may occur:
- swelling of the larynx, suffocation;
- increased blood pressure;
- vomiting, nausea;
- malfunction of the central nervous system, etc.
If such symptoms occur, you should seek medical help as soon as possible: in this case, the lives of both mother and child are at risk!
Hornets, which look much larger than regular wasps, are also capable of attacking.
Hornet sitting on a finger
However, the fear of them is greatly exaggerated: the poison of both wasps and hornets is less toxic compared to that of bees. And on the scale of pain, the bite of the latter ranks after the wasp and bee!
You may also be interested in our article: First aid for a hornet bite, what to do immediately
Breast-feeding
Therefore, there is no need to stop breastfeeding.
However, precautions should be taken if:
- the mother’s body is susceptible to wasp venom and responds with an allergy to it;
- the mother had to take medications to eliminate the symptoms of an allergic reaction;
- After the bite, the woman feels unwell, her blood pressure has increased or her temperature has risen.
In this case, you should consult your pediatrician or an experienced lactation consultant.
First aid for a wasp sting during pregnancy is as follows:
- if the sting still remains, it is important to remove it using sterile tweezers;
- the bite site should be treated with a disinfectant: chlorhexidine, peroxide or alcohol-containing liquid; soap and water will also do;
- To relieve swelling, you can use cold - ice or traditional methods: applying a cabbage leaf, half a tomato or potato;
- If allergies occur, take an antihistamine approved during pregnancy.
If a wasp sting has serious consequences, it is better not to hesitate and consult a doctor.
What drugs can be used without worrying about the condition of the fetus?
No-Shpa
No-spa has been known on the pharmacological market for quite a long time and is a safe drug that relieves spasms.
Tablets "No-shpa"
The active ingredient drotaverine does not affect the autonomic nervous system.
Drotaverine (an analogue of No-shpa) in ampoules for intravenous injection is quite safe to use topically, applying a compress to the bitten area - this will numb the pain and will not have any effect on the blood flow.
Menovazin
For topical use, you can use the drug Menovazin, which is safe for wasp bites during pregnancy. It contains menthol, novocaine, alcohol and benzocaine.
The drug "Menovazin"
Thanks to the active components, Menovazin relieves itching, swelling and pain.
The drug can be used by applying to the skin 2-3 times a day. However, if there are local allergic reactions with hypersensitivity to the components, the use of Menovazin should be abandoned.
Paracetamol
For a pronounced effect of pain relief and reduction in temperature (if it rises), as well as if a fever occurs from a wasp sting, Paracetamol can be used during pregnancy.
Packaging of the medicine "Paracetamol"
This drug is one of the safest for expectant mothers, and even with an overdose, its consequences are rarely critical.
If taken in a reasonable dosage, medications containing ibuprofen will not cause harm. They act similarly to paracetamol.
Other
A local analgesic effect for a wasp sting during pregnancy can be achieved using:
- the good old “Star”;
- tea tree oil;
- Fenistil gel;
- calendula ointment.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of flies from your apartment
Greatly exaggerating the danger of a wasp sting, many pregnant women, in a panic, begin to indiscriminately use all available drugs - from painkillers to antibiotics, thereby causing much more harm to the baby than the insect.
Therefore, the main rule here is: do not panic, do not take anything from the first aid kit unless necessary.
Panicking is not conducive to good decision making.
If negative consequences appear, seek help from a doctor.
Conclusion
Summer, holidays in the country or being in nature are often overshadowed by insects, and stinging ones are especially dangerous among them.
Therefore, it is important for pregnant women to follow all safety measures to protect themselves from attacks by dipterans.
When you see a striped insect, you should not make sudden movements. A wasp sting poses a danger for a pregnant woman only if she has an allergic predisposition, but is it worth the risk when not only the health of the expectant mother herself, but also her baby is at stake?
Pyelonephritis
Quite widespread among women of childbearing age. This is an inflammatory disease of a microbial nature that affects the tissue of the kidney and the walls of the collecting apparatus. During pregnancy, pyelonephritis is often detected for the first time, and long-term chronic pyelonephritis often worsens due to the fact that pregnancy places an increased functional load on the kidneys. In addition, the physiological bends of the ureters are aggravated, which creates favorable conditions for pathogens to live in them. The right kidney is affected somewhat more often than the left or both.
A contraindication to pregnancy is a combination of pyelonephritis with hypertension, renal failure, as well as pyelonephritis of a single kidney.
Pyelonephritis is manifested by lower back pain, increased body temperature, and detection of bacteria and leukocytes in the urine. The concept of “ asymptomatic bacteruria ” is distinguished - a condition in which there are no signs of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, but pathogenic bacteria are detected in the urine, which indicates that they inhabit the renal pelvis and urinary tract in abundance. Like any inflammatory process, pyelonephritis is a factor in intrauterine infection of the fetus and other elements of the fetal egg (chorioamnionitis, placentitis). In addition, pregnancy in patients with pyelonephritis is much more often complicated by gestosis with all the troubles that accompany gestosis.
Pyelonephritis and asymptomatic bacteruria are subject to mandatory treatment with antibiotics and agents that improve urine passage. Delivery is carried out in the conditions of the II obstetric department. Childbirth proceeds without any special features. Children born to mothers with pyelonephritis are much more likely to be susceptible to purulent-septic diseases.
Statistics for Russia
According to statistics in Russia, the number of pregnant women diagnosed with OHA is increasing every year. Currently, a complicated medical history accompanies about 80% of pregnancies, i.e. 8 out of 10 expectant mothers have certain risk factors during the period of bearing a child.
In 50% of pregnancies with a complicated obstetric-gynecological history, patients require inpatient hospitalization, where close monitoring and timely treatment are provided.
Heart defects
– can be congenital or acquired (rheumatic). Heart defects are diverse, so the course of pregnancy in patients with defects and its prognosis are very individual. A number of severe defects are an absolute contraindication to pregnancy - these are decompensated defects with severe circulatory failure, atrial fibrillation, the presence of rheumatism in the active phase, cyanosis (congenital defects of the “blue type”).
The remaining pregnant women with defects are observed by the gynecologist in close contact with the therapist. Even if a pregnant woman feels good, she is sent for planned hospitalization at least three times during pregnancy: at 8-12, 28-32 and 2-3 weeks before birth. In the absence of heart failure, delivery is carried out through the vaginal birth canal. To stop pushing, obstetric forceps are sometimes used; delivery is possible under hyperbaric oxygenation conditions. Particular attention is paid to adequate pain relief in order to prevent an increase in the load on the heart under stress. Caesarean section has no advantages in women with heart defects, since the operation itself is no less a burden on the cardiovascular system than natural childbirth.
What to do if you are bitten by a wasp during pregnancy
Wasp on the hive
In most cases, a wasp sting during pregnancy or lactation is no more dangerous than during any other period of a woman’s life. The mother herself will, of course, suffer to one degree or another from pain, swelling and itching, but the bite will most likely have absolutely no effect on the health of the fetus or an already born child (through milk).
The only thing you should prepare for if a pregnant or nursing mother is bitten by a wasp is that you will have to endure pain and itching for some time, because it is not recommended to use special medications at this time - they can cause some harm to the baby.
However, there are still cases where a stinging insect attack on a pregnant woman can be truly dangerous. So, for example, if a wasp sting caused an overly pronounced allergic reaction, then such an immune response from the mother’s body is quite capable of having a negative impact on the condition of the fetus.
However, expectant mothers who are highly sensitive to insect bites are usually well aware of this feature of their body, so they are usually ready to take the necessary measures in advance.
“For example, I was also bitten by a wasp when I was pregnant. Nothing bad happened. There was no severe swelling or allergies. My arm hurt, as usual, it was swollen a little below the elbow, and that’s all. And my gynecologist told me that there was nothing wrong with it. So stop panicking and go for a walk.”
Svetlana, Kirov
As medical practice shows, during pregnancy, a wasp sting can be dangerous, including due to incorrect actions on the part of the expectant mother.
Most of the remedies used to relieve swelling, itching and pain in “normal” life are not recommended for use during pregnancy.
However, in fact, a considerable percentage of women, trying to protect their baby, strive at all costs to treat the bite with at least something.
It is a simple misunderstanding of the potential dangers of medications that often leads to the fact that such “treatment” creates a rather serious threat for the expectant mother to the development of the child - especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, when all the organs of the fetus are formed.
Therefore, remember: if you are suddenly bitten by a wasp during pregnancy, it is prohibited to use any medications without consulting a doctor. This is exactly the case when it is better to do nothing than to mess things up yourself.
A child carried by a healthy pregnant woman is 100% protected from wasp venom. From a physiological point of view, it is not so difficult to explain: during a bite, the toxin enters the mother’s blood, and along with it necessarily passes through the liver, where it undergoes a kind of biological “utilization.”
Wasp venom is also unable to penetrate the placenta, so its direct contact with the fetus of a pregnant woman is excluded. Even if the wasp sting fell on the stomach, resulting in a noticeable lump, there is no need to worry.
The poison is even less likely to penetrate breast milk. To do this, it also needs to pass through the liver of a nursing mother, and then somehow be able to get directly into the mammary glands. In a normal situation, this is excluded, therefore, as during pregnancy, a wasp sting during breastfeeding does not pose any danger to the child.
“We were very lucky with our pediatrician. Such a balanced, generally impenetrable woman. She has enough experience for others to last five lifetimes. When I was once bitten by a wasp while breastfeeding, I was so worried, I was afraid that I would have to interrupt breastfeeding, and this was in the third month. I called her, barely able to speak from fright.
Oksana, Moscow
As mentioned above, the vast majority of medications are prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding, including those that are usually used to eliminate the symptoms that appear after a wasp sting. This is one of the important problems that worries pregnant and lactating women.
So, if you were bitten by a wasp during pregnancy, you should not use, for example, the following drugs:
- Aspirin, which is usually used to relieve pain after a bite and relieve fever if it suddenly rises;
- Diphenhydramine, which prevents the spread of edema;
- Advantan is an ointment intended to limit swelling and relieve itching.
“We once had a situation where a nursing mother was bitten by a wasp in the wild. As luck would have it, it happened in the heat of the day, but there wasn’t a single car in the village—everything was in the field. The girl was blown to pieces, her legs were swollen, and there was also a small child, not even six months old. I was still little then, I lived in a neighboring house, I was scared.
But good, then the ambulance arrived from the regional center in half an hour, probably. The doctor looked at it and said that there was no need to do anything, because medications could cause even more trouble. And indeed, the very next day everything returned to normal for mom. The bite itself was very large, but the swelling subsided and the milk did not disappear.”
Tatiana, Art. Kamenskaya
When breastfeeding, the independent use of any antihistamines is prohibited, including the most “favorite” ones in such cases: Suprastin, Loratadine and Diphenhydramine.
If these drugs are used in the first trimester of pregnancy, they can have a mutagenic effect on the developing fetus, and in the later stages can lead to premature birth. This means that if a pregnant woman shows even the slightest signs of an allergy to a wasp sting, she should go to the hospital as soon as possible.
On a note
During pregnancy, under the strict supervision of a doctor, it is allowed to use Suprastin, Fenistil and Zyrtec. However, they are used only in special cases when these drugs are vital for the mother’s body.
If a pregnant woman is bitten by a wasp, in order not to harm the baby, it is best for her not to use medications at all. This rule is also relevant for breastfeeding women.
However, there are still medications approved for use in expectant or current mothers:
- Menovazin is an inexpensive and effective ointment for eliminating pain and itching at the site of an insect bite;
- Paracetamol, recognized by WHO experts as the most harmless pain reliever and anti-inflammatory drug for pregnant women;
- No-Shpa is also a very well-known drug for relieving pain syndromes.
Important!
Before using the drug No-Shpa, you should definitely consult a doctor, since in some cases this drug can cause premature dilatation of the cervix and, as a result, premature birth.
The above medications can only be used to eliminate local symptoms. If a wasp bites a pregnant or lactating woman, resulting in a generalized allergic reaction, the victim should immediately consult a doctor.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Treating walls against dampness
“Don’t worry so much about this bite. It's a big problem, there's a lump on your hand. My father is a beekeeper, while I was living in their village in the fifth month, I was bitten ten times by both bees and wasps. And nothing.
It hurt and went away. I drank Paracetamol and completely forgot about these problems. If you were able to turn on the computer after the bite and even started a discussion here, then nothing bad will happen to you.
Relax."
Inna, Kyiv
A wasp sting becomes truly dangerous during pregnancy when it provokes a general allergic reaction. This sting result can pose a serious threat to both the fetus and the mother.
Let's identify the main symptoms of a wasp sting allergy, which should be taken as an alarm:
- very extensive swelling, both local (over the entire arm or leg) and general, spreading to the entire body;
- hives all over the body;
- shortness of breath, headaches, dizziness;
- increased heart rate;
- nausea, vomiting;
- chest pain.
If any of these symptoms appear, the pregnant woman should be immediately taken to the hospital, or an ambulance should be called for her, making sure to explain to the doctors that the victim of a wasp sting is expecting a child.
In case of an acute allergic reaction, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock and even death are possible.
To summarize, we can say that a wasp sting during pregnancy or during breastfeeding for the most part does not pose a serious danger to the mother and baby. However, these happy periods in a woman’s life require due attention and “supervision” from loved ones and doctors, so that in case of a possible threat, they have time to react in time.
Bronchial asthma
- a disease of an allergic nature. Pregnancy sometimes eases the course of asthma, sometimes it significantly worsens it.
Bronchial asthma during pregnancy requires the usual treatment for this disease with bronchodilators, used mainly in the form of inhalations. Asthma attacks are not as dangerous for the fetus as is commonly believed, since the fetus is much more resistant to hypoxia (oxygen starvation) than the maternal body. Management of childbirth against the background of bronchial asthma does not require any significant adjustments.
Factors leading to aggravated medical history during pregnancy
Among the reasons why a woman may be diagnosed with OHA are:
- Socio-biological disadvantage. The absence or insufficient amount of funds to purchase the necessary medicines, vitamins, quality food, clothing and much more often leads the expectant mother to stress, which negatively affects the pregnancy. This group includes women without education and without work (or with low-paid work), leading an immoral lifestyle, as well as pregnant women who are forced to earn money through hard physical labor. In this case, pregnancy most often occurs with pathologies, which poses a threat to the health and life of the unborn child.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. The environmental conditions in which the expectant mother lives also make a certain contribution to the well-being of pregnancy. The release of harmful substances into the atmosphere from factories and industrial facilities, increased air pollution from vehicles, and poorly purified water negatively affect the quality of life of a pregnant woman, which accordingly leads to a deterioration in the health of the woman and her fetus.
- Diseases in future parents. Genetic diseases, alcohol abuse and smoking, as well as drug addiction of one of the parents can lead to serious problems with the baby’s health. Mother's diseases (asthma, diabetes, heart disease, vascular disease, kidney disease) can cause pathologies in the child.
- Age of the woman in labor. Complications that arise during pregnancy and childbirth are often caused by the too young (under 16 years old) or mature (over 35 years old) age of the first-time mother. This is explained by the physiological characteristics of the female body, which best copes with bearing and giving birth to children between the ages of 18 and 30.
- Complications of the current pregnancy. These include pelvic or transverse presentation of the fetus, infection of the fetus or internal genital organs of the mother, severe toxicosis, gestosis, premature placental abruption.
Most of the factors leading to OGA are controllable. Therefore, future parents are obliged to adequately analyze the situation and plan the pregnancy responsibly.
Late pregnancy is one of the factors leading to OGA
Some advice for pregnant women
Do you have OAA during pregnancy? What it is, you now know. Now there is no need to panic, it is better to listen to some advice. For the correct and full development of pregnancy, it is necessary to attend consultations with specialists, follow all recommendations and prescriptions prescribed by them, and lead a correct lifestyle. It is important not to miss appointments with the doctor, and also to tell him truthfully all the necessary information so that the unborn baby is born healthy.
A lot depends on the mother herself, so every effort must be made to ensure that the pregnancy proceeds easily and the upcoming birth is successful.
Sources:
https://studopedia.ru/11_224515_anamnez.html https://vashnevrolog.ru/metody-diagnostiki/chto-oznachaet-akusherskij-anamnez-i-dlya-chego-on-provoditsya.html https://autogear.ru/ article/256/790/oaa-pri-beremennosti-chto-eto-takoe-kak-rasshifrovat/
Preparing for a new pregnancy and preventing complications
A woman who has had failed or complicated pregnancies and childbirths, gynecological operations or diseases, and other negative episodes in the past should not despair. In this case, you need to carefully prepare for a new pregnancy and take measures to prevent possible complications.
So, at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, the expectant mother should:
- seek advice from a gynecologist and at the same time describe to him as accurately as possible all previous situations related to “women’s” health - this will allow the doctor to draw up a complete medical history of the patient;
- take a test for TORCH infections (rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, STDs);
- take hormone tests and, if necessary, adjust hormonal levels;
- do an ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs;
- visit a geneticist, psychologist (on the recommendation of the attending physician).
These measures when planning pregnancy are minimal. In each individual case, the doctor may prescribe additional examination necessary for a particular patient.
With the onset of pregnancy with a concomitant diagnosis of a complicated obstetric and gynecological history, a pregnant woman is obliged to adhere to preventive measures to prevent the development of complications. These include:
- regular scheduled visits to your doctor;
- examination by specialized specialists, to whom the gynecologist refers according to an individual pregnancy management plan;
- diagnosis and treatment of identified abnormalities and diseases.
At the same time, future parents should not forget about the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle both throughout pregnancy and at the planning stage. A pregnant woman, including those with OHA, is strongly recommended to eat a nutritious and varied diet, breathe fresh air, and maintain a regime of wakefulness and rest. And also one of the key components of a successful pregnancy is a positive attitude and psychological balance.
Every woman expecting a baby is required to visit the attending physician according to the pregnancy management plan
Arterial hypotension (hypotension)
– quite common in young women and is manifested by a persistent decrease in blood pressure to 100/60 mmHg and below. It is not difficult to guess that problems with hypotension begin in the first trimester, when blood pressure already tends to decrease.
Complications of arterial hypotension are the same as with hypertension. In addition, during pregnancy there is often a tendency towards post-term pregnancy, and childbirth is almost always complicated by weak labor forces.
Treatment of hypotension during pregnancy consists of normalizing the work and rest regime, taking general tonic drugs and vitamins, and hyperbaric oxygenation is also used. Delivery is carried out through the natural birth canal. Sometimes prenatal hospitalization is required before giving birth in order to prepare the cervix for childbirth and prevent post-term pregnancy.
Wasp stings during pregnancy - protection
When a wasp stings, the main component of the poison, histamine, acts. And the body’s reaction will always resemble an allergy. Security and protection measures are reviewed.
An allergic reaction to a wasp sting will most often be false. At the same time, bees and wasps sting equally painfully.
In a small number of cases, that is, in a small number of people, wasp venom actually causes an allergy. Bee venom is a more serious allergen. And if we talk about pregnancy, you will notice that the poison secreted by insects is not able to penetrate the placenta.
The problem lies in the use of drugs that eliminate itching, pain or swelling: almost all of them are contraindicated during pregnancy.
A bee's sting almost always, that is, in 99% of cases, remains on the skin. And a wasp sting cannot remain on the skin in principle. And guided by this rule, you can find out who exactly stung - a bee or a wasp.
They say that the wasp can sting again. In reality, she will have to accumulate poison, which will take not a single hour. The stinger is torn off from the bee's body, and therefore it dies. The wasp's sting is designed differently.
If we talk about poisons, they contain different components. The main allergen will be a special protein.
Aralia nectar100 grams
| Vodka or alcohol | 150 ml |
| Aloe juice | 50 ml |
The so-called mast cells are susceptible to the action of the protein. They produce histamine. Actually, any allergic reaction is the production of histamine in mast cells, and nothing more.
Let's say histamine enters the blood from the sting, or more precisely, from the sac of poison. Then the symptoms will resemble a real allergic reaction:
- Redness will appear;
- The vessels will dilate;
- Pain and itching are also mandatory symptoms.
If the histamine was not produced from histidine stored in mast cells, then the allergy is false. And this means that in this case you can’t expect Quincke’s edema. Namely, it poses a danger to life.
From all that has been said, we can draw an optimistic conclusion: if there is no sting, the consequences will be limited to local swelling. Which will go away on its own over time. But there is no need to rush to conclusions:
- The sting may simply get lost;
- In 1% of cases it remains with the bee;
- Hornet venom contains acetylcholine. It slows down the heartbeat, enhances the functioning of the glands and at the same time causes bronchospasm.
We can optimistically say that an allergy to bee venom is not typical for all people, but only for 5% of the population. But pregnant women are at risk, and nothing can be done about it...
Beekeepers themselves are also at risk: every fifth of them suffers from an allergy to bee venom.
We suggest you read: What to do if a fly flies into your ear
In any case, regardless of the composition of the poison, a large amount of fluid will help rid the body of toxins. And it is advisable not to make sudden movements after a bite - this way the swelling goes away faster.
And since a wasp sting during pregnancy is dangerous for the mother, but not for the fetus, protective measures can be limited to two: take a horizontal position, drink more liquid.
But then you need to be sure that it was the wasp that bit or stung.
With a wasp sting
All advice refers to one case - only a wasp bit. So, there is no sting in the wound, but you need to carry out treatment:
- The wound is cleaned with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide or ammonia;
- Lemon juice is applied to the wound site;
- You can apply a slice of lemon or a cloth soaked in juice to the bite site. Or apply ice - it prevents the spread of the poison.
As for “standard” medicine, it has developed many drugs for such cases: fenistil-gel, psilo-balm, etc. But you need to take into account contraindications.
All balms and gels are used with caution in the last two trimesters: they cannot treat too large areas of the skin with them!
If a bee stings
First of all, the sting should be removed. Remove it with tweezers or hands soaked in alcohol. The most important thing in this operation is not to touch the bag. There is always a large amount of poison left in it...
When the sting is removed, the bite site is treated with alcohol, ammonia, etc. And then wash with boiled water and soap!
Soap has an alkaline pH and is listed here for a reason.
In the second step you can use:
- Fenistil-gel or psilo-balm, but only in the first trimester or on a very small area of skin;
- Ice is used to localize swelling.
Lemon will not help here, but just the opposite. Further, to improve the general condition, it is recommended to take a diphenhydramine tablet. But it is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Fighting allergies
Contraindications are always indicated in the instructions for medications. And one feeling arises: not a single anti-allergy drug is compatible with pregnancy. This statement turned out to be correct:
- Diazolin is not contraindicated only in the third trimester, and it is better if the drug is prescribed by a doctor. Daily dosage – 300 mg (150 mg with a break), onset of action – after 2 hours.
- Loratadine, Cetrin - it is very undesirable to take them at any stage of pregnancy, although the effect begins an hour after administration;
- Suprastin is contraindicated.
In general, the drugs work like this: take a pill, then the effect will appear, but perhaps the treatment will last another 12-20 hours.
The very first action will be to call an ambulance.
And the doctor, having arrived at the scene, can give two injections:
- Adrenaline with a concentration of 0.1%;
- Prednisolone (intramuscular).
After an injection of prednisolone, the allergy subsides immediately. Only this drug is very rarely used during pregnancy. The most risky periods will be the first and last two months - then prednisolone is contraindicated!
Allergies during pregnancy are dangerous: treatment rarely goes without consequences. Previously they used Chlor-Trimeton, also known as Chlorpheniramine, and now Diphenhydramine or Actifed. These drugs, available in tablet form, have a pronounced sedative effect. And a strong effect on the central nervous system affects the development of the fetus.
Both bees and wasps are equally annoying:
- Black, dark blue and dark red shades, as well as all rich colors and clothes with large patterns;
- Velvet;
- All pungent odors have a negative effect on wasps and bees equally.
The bee protects her hive, but the wasp simply stings. To protect yourself, you should not run or wave your arms, but in the case of bees, you should not run towards the hive.
If there is sugar syrup in an open container, it will immediately attract insects. Both wasps and bees love sugar, syrup and honey. And they are afraid of gasoline vapors. A wasp will die if gasoline gets on it, but this experiment was not carried out on bees...
Scheme of histamine action at the level of tissues and cells using the example of an allergic reaction
Wasp venom and bee venom contain histamine. And the insect simply cannot sting without causing allergies. Another question is whether this allergy will be false.
Case from practice:
- They didn’t know what to do if a pregnant woman was bitten by a wasp - she was simply offered plenty of drink.
- After a couple of hours the symptoms went away on their own.
With bees, the question is not so simple: it will not be clear whether the effect of histamine is manifested or whether a real, “true” allergy is developing. In defense of bees, one thing can be said: they have a sac of poison - smaller than that of wasps and hornets. And the venom of the Brazilian wasp is a cure for oncology.
Common mistakes
Let the bite site be below the elbow. Then you need to immediately remove all jewelry - rings, bracelets, watches. Regardless of whether the sting is from a bee or a wasp, the swelling will always be severe. But you cannot squeeze out the sting by squeezing the skin with your fingers - you need to try to pull it out.
It may be difficult to determine the type of insect. Then the wound is disinfected, and then ice and possibly gel or balm are used. At the same time, we must not forget about contraindications. To protect yourself from allergies, take:
- Diazolin (2 x 150 mg with a break) - only if it is the third trimester, and most likely with consequences for the fetus;
- Loratadine (10 mg), Cetrin (2 5 mg each with a break) - almost always with consequences for the fetus;
- Actifed (60 mg), Diphenylhydramine (30 mg) - these drugs affect the central nervous system, which cannot but cause consequences.
The break should be several hours.
Bee venom can cause allergies. But it does not cause it in everyone. However, the risk of getting an allergic reaction during pregnancy is increased by 4-5 times!
Apitherapy – no allergies
Even if the allergy did not manifest itself before, this does not mean that it will not manifest itself at the moment. You should not make typical mistakes, and of course, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Repeated exposure to the allergen usually causes a stronger reaction!
More information
Every wasp's venom is alkaline, while bees' venom is acidic. In the first case, acids help, in the second - soap or a paste of soda and water. Bees can leave the sac without having time to squeeze out the poison. And if you get rid of the pouch, there will be no allergies.
Histamine causes a predictable reaction - redness of the skin, etc. What remains of one bee's bite can be seen in the photo.
The poison would have been carried by the lymph if ice had not been used. But everything was limited to a false allergy in one small area.
The worst thing is if the wasp stings in the area of the face, as well as the collarbones or neck. Then the swelling can compress the carotid artery.
Running is useless
You can't run away from a bee, but you can run away from a wasp. In the first case, the speed should exceed 22 km/h, in the second - 9-10. But a bee without nectar and pollen flies even faster. But with pollen, that is, pollen, it is not capable of stinging.
Usually the beekeeper places the hives closer to the honey plant. In the worst case, the distance is 2-3 km. But bees can fly for nectar up to 7 km from the hive.
In open areas, the “dangerous distance” increases to 14 km.
There is a queen bee in the hive. And it only stings insects. Wasps have a sting designed to attack everyone, so they don't die. And the bee will not die if it attacks other insects or the bee.
How to protect yourself from bee and wasp stings
It's obvious that it's best for a pregnant woman to avoid bees and wasps to avoid being stung, but these creatures can easily fly through open windows into your home or car. Here's what you can do to reduce your risk of being stung:
- stay away from beehives, trash cans and fruit trees;
- keep food covered during a picnic;
- Avoid wearing bright colors and floral patterns that attract insects;
- Avoid wearing scented lotions, colognes, perfumes, hairsprays and deodorants;
- avoid wearing sandals and walking barefoot on the grass;
- use window screens;
- use insect repellent.
When encountering a bee or wasp, you should not run, wave away , or try to swat the insect - sudden movements can make it feel threatened and provoke an attack. You just need to slowly move away, then the insect will lose interest and fly away.
If an insect still manages to bite a pregnant woman, the main thing is not to panic . You can’t just give up on the bite and do nothing.
It should be remembered: it is especially important for pregnant women to protect themselves from insect venom, and the sooner a woman begins to act to protect herself and her child from the consequences of a bite, the less likely there are unpleasant consequences.
What would that mean? A dictionary of terms that reveals the secrets of medical records
Quite often, when reading the notes in the exchange card and the referral for tests, the attention of expectant mothers is attracted by incomprehensible medical terms.
Anamnesis (from the Greek anamnesis - memory) is the features of the patient’s medical biography, which she sets out on the basis of active questioning from the doctor, since it is important to record certain facts that are important for a given clinical situation in order to predict and carry out appropriate prevention of pregnancy complications.
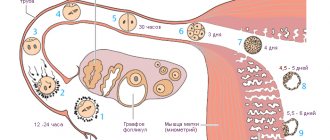
OAA - burdened obstetric history - is the presence in the past of various complications associated with pregnancy and childbirth, such as spontaneous miscarriages, abortions, premature births, bleeding during childbirth, the birth of a child with malformations, surgical delivery. For example, a history of premature birth will serve as a basis for more careful monitoring of the condition of the cervix and uterine tone in a pregnant woman, since the risk of miscarriage in this case is increased. If there are serious complications that are highly likely to play a significant role in the management of this pregnancy (for example, stillbirth), the doctor can write a diagnosis of COAA (that is, an extremely burdened obstetric history), thereby emphasizing the importance of the closest attention to the patient.
OGA - burdened gynecological anamnesis - indicates the presence of gynecological diseases in the past (inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages, disorders
Source
Menu
Navigation
Login
Tag Cloud
online now
News Sochi.MD
Diseases and pregnancy
Over the past decades, life has made significant changes in the relationship between doctor and patient. Currently, a phrase like “The doctor forbade me from giving birth!” make you smile and seem borrowed from a women's magazine from the middle of the last century. Now doctors don’t “prohibit” anything, and even if they decided to prohibit it, patients, it seems, would not be in a hurry to follow such directives. A woman has the right to independently decide the issue of motherhood; both current legislation and common sense speak about this.
Meanwhile, it should be noted that over these decades, the health indicators of the female population of Russia have not improved significantly. In addition, the proportion of older women giving birth is increasing year by year - a modern woman often strives to first strengthen her position in society and only then have children. It is no secret that over the years we do not get any younger and accumulate a number of chronic diseases that can affect the course of pregnancy and childbirth. The presence of chronic extragenital diseases in a pregnant woman is also called a burdened somatic history (OSA) .
Modern science knows several thousand diseases. Here we will talk about diseases that are most typical for women of childbearing age and their impact on the gestational process.
Hypertonic disease
is one of the most common chronic diseases among young women. It manifests itself as vascular spasm and a persistent increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. In the first trimester of pregnancy, blood pressure usually decreases somewhat, which creates the appearance of relative well-being. In the second half of pregnancy, blood pressure increases significantly, we take
Source
The importance of obstetric history is very great for the current pregnancy. And although this concept has not received official recognition in medical reference books, where there are concepts of hereditary history, professional, social and epidemiological, not a single obstetrician will deny the importance of OAA.
What is considered a burdened obstetric history? If a woman has had an induced birth in the past, single or multiple abortions, miscarriages, anomalies of the placenta and its premature detachment, the birth canal has been injured, there are adhesions on the fallopian tubes, scars on the uterus, there was a threat of uterine rupture, a naturally anatomically narrow pelvis, there was fetal asphyxia (when the umbilical cord was wrapped around the neck) or the birth ended in stillbirth - this affects subsequent pregnancies and their outcome. Also, the obstetric history is influenced by the perinatal mortality of children born to a woman, the condition of previous children after birth, birth injuries of children and the presence of congenital defects and pathologies.
All these features must be taken into account in order to minimize the development of pathologies in the next fetus. If a caesarean section is being considered, the doctor’s arguments should be supported, for example, by fetal X-rays.
Timely identification of the causes of stillbirth and infant mortality in the perinatal period has a positive impact on the management of other pregnancies and childbirths. Often, stillbirth and congenital defects have several causes: for example, intracranial injury during the birth of a large fetus in a woman with an anatomically narrow pelvis, incompatibility of mother and child according to the Rh factor, childbirth in adulthood in the presence of hemolytic disease of the newborn (incompatibility of the blood of mother and child by antibodies).
The number of women in Russia diagnosed with OAA is about 80%, and this number does not decrease from year to year and
Source