The doctor scared me! He said that I would never be a grandmother if I did not immediately separate the adhesions on the glans penis of my child. But I can't make up my mind. After all, the child is not in pain. Help with advice. My son is 4 years old.
Calm down. Rest assured! Your future does not depend on whether the surgeon separates the adhesions or not. I advise you to check whether your son has redness of the foreskin. If “Yes,” then separation of the adhesions may be warranted.
But first you need to try to carry out hygiene procedures more carefully. Then, conduct an examination. In any case, there is no need to rush.
Phimosis - recognition
What is phimosis? And why is it dangerous? Phimosis is a narrowing of the opening of the skin of the foreskin, preventing the opening of the head. Phimosis does not go away without surgery. There are both congenital phimosis and acquired - after inflammation of the preputial sac, the medical name is balanoposthitis. The preputial sac is the space between the head of the penis and the skin of the foreskin. Phimosis is often accompanied by urination problems: the child urinates in a thin stream; during urination, the foreskin inflates with the flow of urine and increases in volume. Phimosis is a SURGICAL DISEASE that causes inflammation of the foreskin in more than half of the cases, which can lead to complications from the bladder and kidneys if not treated in a timely manner. Narrowing of the foreskin that does not allow exposure of the head of the penis in a 5-year-old child is a reason to consult a urologist. Physiological phimosis is a temporary condition in children when the glans penis does not open due to the presence of adhesions between the inner layer of the foreskin and the glans penis. In most cases it goes away on its own. I tried to open the head of my 3-year-old son’s penis, but I can’t even see it. When he pees, the skin around the head swells. Maybe we have phimosis? When should you see a urologist? How urgently does it need to be treated? If the head of the penis cannot be seen or when urinating the skin of the penis swells with urine, this means that there is a narrowing of the foreskin - phimosis. You should consult a specialist. An examination by a urologist-andrologist is also necessary if the opening of the foreskin in a child 6 years old is no more than 3 mm, or the head in a child 8-10 years old is not visible. In some cases, the head stops opening with age - this may be acquired cicatricial phimosis, which also requires treatment. There are also variants of phimosis, in which the head of the penis opens in a calm state and does not open during an erection. They are usually detected between the ages of 13-18 years. How can I determine if my child has phimosis? In children under 5 years of age, when the skin of the penis is moved towards its root, the head should appear. The diameter of the foreskin opening can be 3-6 mm. If, when the skin is moved, the head is not visible, then in most cases it is phimosis. The son spent the summer with his grandmother at the dacha, and when he returned, the head of his penis stopped opening. What to do?
This is a typical situation for the occurrence of acquired phimosis. It usually develops against the background of subacute inflammation of the foreskin. Externally, the penis is of a normal appearance. Gradually, the elasticity of the inner layer of the foreskin decreases and a rough whitish scar forms. Treatment is surgical. The type of operation is determined during examination.
Circumcision and other treatments for phimosis
My nephew is 8 months old. We want to circumcise him. Which method do you think is best for such a baby? I would not like to do a regular circumcision, as there is a lot of talk about complications. In our experience, the optimal method of circumcision for children in the first year of life is the American Hollister technology with rings. It allows you to relieve most children from anesthesia and get excellent cosmetic and functional results. What treatment options are there for phimosis? Is it possible to do without circumcision? Circumcision of the foreskin for phimosis is preferably performed before the age of 3 years, when the child is not aware of the loss of the foreskin, since sexual self-identification occurs at the age of 3 years. Moreover, up to the age of one year, you can use the wonderful American method of circumcision using a plastic ring, which allows you not to use suture material and at the same time avoid bleeding. At the age of 3 to 5 years, in some cases, cosmetic plastic surgery of the foreskin can be performed. Circumcision or plastic surgery is decided individually. Over 5 years of age, we prefer plastic surgery of the foreskin for primary phimosis and circumcision for acquired phimosis. I heard about foreskin plastic surgery for phimosis. What kind of operation is this? Can it be used on a 7 year old child? There are various options for plastic surgery of the foreskin, in particular the operation of Schloffer, Rosenberg and others. The foreskin is then cut longitudinally from the edge, with the intersection of the constricting ring. Stitches are then placed along the edges of the incision. Often, after classical operations, the head of the penis becomes visible, and below the head there is a “tongue” of the foreskin, which worsens the appearance of the penis. We have developed a cosmetic version of foreskin plastic surgery, without forming a “tongue”. This is an easier and less traumatic procedure for the child compared to other types of operations. At the same time, the aesthetic and functional results are much better. The appearance of the penis remains original, but the head opens freely.
We prefer to use foreskin grafting in children over 5 years of age.
Inflammatory diseases of the foreskin
Twice, with an interval of 4 months, my 3-year-old son experienced inflammation of the penis. O. balanoposthitis. What should I do? Repeated inflammation of the foreskin often occurs in children with phimosis, or decreased local resistance to infection. A diagnosis of chronic or recurrent balanoposthitis is often made. In these cases, the best treatment is circumcision of the foreskin. A 3-year-old child has periodic recurring inflammation of the tip of the penis. The skin turns red. There was discharge of pus twice. They were treated with baths and instillations. The doctor recommends circumcision. Is it possible to do without circumcision? It is possible, but it is fraught with serious problems. The first stage - in the cold period - outside of inflammation, the senechiae of the foreskin are separated. Then, daily hygiene procedures are carried out. a complete cure is unlikely. Typically, relapses of infection continue, often in a subacute form. Since antiseptics act superficially and do not enter the excretory ducts of the glands, relapse can occur in a short time after discontinuation of antiseptics. Infections of the preputial sac can cause ascending infection, urethritis, prostatitis, vesiculitis, cystitis and even pyelonephritis. Often there is a predisposition to infection of the foreskin associated with a decrease in local resistance, which lasts until adulthood. A man becomes a carrier of infections. Moreover, in an adult man the infection can be asymptomatic, and in women it can cause infertility and dangerous inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs. The risk of malignant neoplasms of the penis increases. After the separation of the “senechiae” on the head of the penis, the child has had itching, an unpleasant odor and red dots on the mucous membrane of the head for 2 months. The surgeon who separated the adhesions prescribed synthomycin emulsion, but it did not help. What to do? Your child probably has an infection of the foreskin that occurred after separation of adhesions and is not sensitive to treatment with synthomycin. It is necessary to find out the nature of the infection, after which treatment can be prescribed. Infections after separation of the senechiae of the foreskin occur in 15-25% of cases and require special treatment. If the adhesions of the foreskin are not separated, inflammation of the preputial sac is much less common. Therefore, we very carefully set indications for dividing the senechiae and do this only in children with a predisposition to inflammatory processes in the foreskin area.
Phimosis in a child 3 years old and younger
The vast majority of babies - over 95% - are born with congenital phimosis, which is considered a physiological norm. Only as you grow older and the size of the genital organs increases, the mobility of the preputial sac (foreskin) increases, and the head becomes exposed without auxiliary manipulations.
This opportunity does not appear before the age of two, but there is no need to sound the alarm even after reaching the age of six . Medical practice knows cases of natural elimination of phimosis at the age of 7–13 years, but after the start of puberty, the chances of spontaneous expansion of the foreskin ring are almost zero.
The occurrence of phimosis can also be initiated under the influence of other factors.:
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- mechanical damage to the penis;
- genetic features.
In the latter case, the boy may be diagnosed with a genetic anomaly associated with congenital insufficient tissue elasticity.
Among inflammatory diseases, the trigger for the appearance of phimosis can be balanoposthitis - inflammation of the foreskin.
The pathological condition leads to an increase in skin size, the appearance of purulent discharge and ulcers on the penis, which cause pain when urinating and walking.
For what reason does it occur, and is it necessary to treat phimosis in boys:
- up to 1 year;
- from 4 years to adolescence.
Circumcision of the foreskin in boys
If balanoposthitis becomes chronic and torments the child with frequent inflammation, an operation to circumcise the foreskin is prescribed. The indication for circumcision is pathological phimosis, in cases where drug treatment with glucocorticosteroids has not helped.
After the procedure, the problem causing the inflammatory process disappears. At what age is circumcision done? If surgery is not performed before age 3, it is recommended to postpone it until age 8. The surgical intervention itself takes place under general anesthesia and lasts several minutes. With proper care, the boy's wounds will heal in 3-5 weeks.
Types of disease
Children under two years old do not have problems with the foreskin: it is tightly closed and does not allow bacteria to penetrate inside. The exception is rough extraction of the head, associated with untimely opening of part of the penis.
Tears, microcracks, and bruises are the most common consequences of unprofessional intervention (stretching the flesh in infancy is contraindicated). Hence phimosis in children aged 2 years.
- Cicatricial phimosis . Due to inflammation of the foreskin, swelling and decomposition of urine occurs if it gets inside. Pathological changes necessarily include the appearance of adhesions - connective tissue between the head and the inner lobe of the foreskin. Attempts to expose the sensitive part of the penis end in severe pain, which is why the boy begins to cry or even scream. Cicatricial phimosis develops in a 2-year-old boy due to mechanical injuries.
- Hypertrophic phimosis . Unhealthy lengthening of the sac occurs mainly in obese children due to the formation of additional subcutaneous fat. Comparing this type with the scar form, urologists note the absence of gross changes.
- Atrophic phimosis . The child has critical compression of the ring of the preputial sac and there is pronounced atypical development of the tissue. The skin of the atrophic type is very thin and easily damaged. May have genetic causes.
Warning . A condition is considered dangerous to health when the head of the penis - even covered by the foreskin - is strongly compressed by the surrounding tissue. Phimosis in children 3 years of age requires diagnosis by a doctor.
Synechia of the foreskin in boys - normal or pathological?
The wisdom of nature is manifested in many things, especially with regard to defense mechanisms in newborns. The foreskin and natural secretions (smegma) protect the child’s genitourinary system from infections. Pathogenic microbes settle on sebaceous secretions and are then washed off with urine and water when washing the child.
The delicate skin of the penis and its head are fused together by adhesions. This phenomenon is called synechia. Fusion should not worry parents; this is a normal process. By the age of 6-8 years, the foreskin will open independently; in some children this happens earlier - at 3 years. In rare cases, it is delayed until adolescence, when surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Before the age of one year, the head opens in only 15% of boys; in most children it becomes mobile after 6 years. It is extremely dangerous to try to forcefully move away the fused parts; this will cause pain in the baby and lead to an inflammatory process.
Signs of a problem are:
- pain when urinating;
- swelling;
- swollen head of the penis;
- redness;
- itching in the foreskin;
- temperature rise to 38°;
- purulent discharge.
These are symptoms of balanoposthitis, in which the head of the prepuce becomes inflamed. In the acute stage, the disease is treated in 2-4 days, and in the chronic stage - over the course of months, and with varying success. If you find the listed signs of pathology in boys, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Surgical intervention
Assessing the degree of phimosis can be problematic, since stage 4 phimosis does not involve exposure of the head even in an erect state, and the appearance of potency in boys occurs only from 5–6 years of age.
Phimosis in a 2-year-old child requires surgical intervention only when there is a risk to the baby’s health . Phimosis in 1-year-old children may be normal, but this is also decided by the doctor.
The operation is possible on a voluntary basis for ritual reasons: circumcision of newborns and small children is carried out taking into account the ancient customs and beliefs of the Israelis.
Type of phimosis and feasibility of surgical correction:
- Physiological. Phimosis in a 1-year-old child disappears on its own and does not require surgical removal of the head from the foreskin ring. Observation by a pediatrician is sufficient.
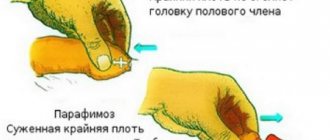
- Cicatricial phimosis in a 3-year-old boy. Surgery before the age of three is indicated only if paraphimosis (pinched head) occurs: long-term disruption of blood flow can lead to necrosis and even amputation of part of the penis. For the scar type, it is permissible to use both circumcision and intimate plastic surgery, which involves eliminating only cosmetic defects (scars).
- Hypertrophic . Phimosis in boys 3 years of age of this type may partially resolve after losing excess weight at an older age. Surgery is rarely indicated for a child, since this deficiency can be eliminated using conservative methods. With the development of an inflammatory process under the foreskin, phimosis can lead to acute intoxication of the body, chills and fever. Then the operation is mandatory.
- Atrophic . Surgical correction, which involves complete removal of the foreskin, is necessary in most cases
The indication for emergency surgery for phimosis in one-year-old children is a severe problem with urination - from partial closure to complete adhesive adhesion of the urethral opening (meatostenosis). This group also includes a complication such as meatitis - local inflammation of the urethral opening and adjacent dermis .
To prevent inflammatory processes during phimosis, after consultation with a urologist, antimicrobial ointments (Levomekol, Sentomycin emulsion, Dioxikol) are selected for local lubrication. Read about these and other ointments prescribed for phimosis in children in this article.
Doctors may also recommend using antiseptic liquids - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, sitz baths in a solution of chamomile, calendula, and string are also useful.
If phimosis is caused by a short frenulum of the penis, then circumcision - circumcision - is carried out simultaneously with plastic surgery of the frenulum, which cannot be corrected by conservative methods (stretching with fingers and using a Glanshy medical instrument).
Tissue dissection is usually carried out at an older age, but it must be taken into account that a short frenulum tightens the head and provokes its deformation changes during the child’s growth.
Important .
Blueness or redness of the head is an indication for urgent surgery.
Erection in children: when does it occur and how should parents react?
Erections in children can occur at absolutely any age. This is a normal condition. Most often, this phenomenon is uncontrollable; it is caused by hormonal changes in the body. In some cases, an erection can indicate various pathologies in the body, so it is very important for parents to notice everything in a timely manner.
Can a child have an erection?
Many people are interested in whether young children can have erections. The hormone testosterone is not at all necessary to start the process. It is able to enhance an erection, but it can easily exist without it, as confirmed by the results of numerous studies. The answer to this question is clear: a child can have an erection at absolutely any age. The mistake parents make is that they believe that this process occurs only due to sexual arousal. In children it is involuntary and has nothing to do with the sexual factor.
Infancy
An erection can occur even in a baby in infancy. The period of up to a year is considered calm; during this time, the reproductive system does not experience serious changes. For example, an erection in a baby can occur during sleep.
This does not occur due to sexual arousal, since the impulse transmission system is still completely absent. An erection can be caused by stimulation of external nerve impulses. Erection in infants can occur due to the following reasons:
- Bladder filling. Nerve endings are able to transmit a signal to the spinal cord, which sends an impulse to smooth muscle. As a result, a reflex erection occurs. It disappears immediately after emptying the bladder.
- When rubbing the groin area with panties or diapers. The child’s nervous system perceives tight clothing as an uncomfortable phenomenon, and the body necessarily reacts to this. If the child starts kicking his feet, this aggravates the situation. After the child is undressed, the erection will subside on its own.
Up to 7 years
At the age of 3-5 years, a boy begins to distinguish himself from the other sex. However, an erection cannot occur due to sexual arousal. During this period, the child begins to carefully study his body, parents should not scold him for this. It is this process that can be accompanied by an involuntary erection. Parents should explain that touching oneself is indecent. It is necessary to explain in a calm tone so as not to provoke psychological problems in the child.
Before the age of 5 years, an erection may appear due to a full bladder. Later, these 2 states will no longer be interconnected.
From 7 to 12 years
This period is accompanied by children becoming highly interested in their gender roles. Boys and girls stop playing together. During this period, interest in their body does not stop; boys can continue to explore themselves by touching the genitals.
At this age, the child has questions related to sex. It is very important at this time to answer all the questions yourself so that the children do not form the wrong picture.
An erection at this age may occur due to the development of the reproductive system. It may be involuntary. At this age, it appears quite often during sleep.
Adolescence
It is accompanied by puberty. It is at this age that teenagers have many questions related to sex. During this period, it is very important for parents to be able to give proper sexual education to their son.
Erections in teenagers occur for the following reasons:
- Complete formation of the genital organs. The sperm begin to accumulate and therefore come out.
- Psychological maturation. For the first time, teenagers begin to look at each other and show interest.
- Increase testosterone in the body. At this age, the hormone is produced in large quantities, so teenagers may experience sexual arousal.
- Socialization. Teenagers often come across sites with erotic content on the Internet, which arouses their strong interest. An erection can occur when remembering what you saw or your own fantasies.
Erection disorders in children
Erectile dysfunction in children is quite rare. A cause for concern is the situation when an erection is completely absent, since puberty is always accompanied by this very phenomenon.
Pain and discomfort during an erection are also a sign of concern. This may indicate third-party diseases in the body, as well as inflammatory or infectious processes. They may also be accompanied by itching, burning or redness. In some cases, this may indicate an allergic reaction, but most often it is a symptom of an infectious infection.
If an erection is accompanied by such manifestations, you should urgently contact a medical facility. Untimely measures can seriously aggravate this process and provoke the development of additional diseases.
What to do if your child has an erection?
If parents notice that their child has begun to have an erection, they should under no circumstances panic. This can frighten the child, which will subsequently provoke various psychological problems.
Parents should not make their son feel ashamed of this process. They must explain that this is an absolutely normal phenomenon that happens to all boys.
It is very important to provide your child with useful information about sex and the structure of the genital organs, otherwise he may receive distorted information from his peers. Then he will develop an incorrect worldview, which will hinder him in the future.
Parents of small children under 5 years of age need to take them to the toilet when they have an erection, since, most likely, this is what caused the erection of the genital organ. If this happened on the beach, then you can take the child to swim and distract him with some activities. For example, play games with him. At home, you can offer your child a cool bath.
Consequences for the child's health
With the natural opening of the head of the penis, the child does not have sexual and hygienic problems in the future - the preputial sac moves freely with both an erect and a quiet penis.
However, in some cases, boys experience relative phimosis, which forms a limited narrowing only during potency . Elimination of this feature is associated with personal motivation, the emergence of complications or sexual problems from the moment of sexual activity.
After surgery, the foreskin is permanently removed and the glans becomes permanently exposed. Immediately after the operation, the sensitive area becomes rough, associated with unpleasant sensations during tactile contact with clothing, objects, and even a stream of water.
After the skin adapts, all unpleasant conditions disappear, but the sensitivity of the head decreases. Many men regard this consequence as an advantage, since the duration of sexual contact increases.
The topic of circumcision in boys is also covered in our following articles:
- How is circumcision performed?
- recommended age for surgery;
- all about postoperative care;
- increased temperature after the procedure;
- Do boys need circumcision?
You can see what a child’s penis looks like “before” and “after” circumcision in this publication.
According to statistics, about 30% of boys under 10 years of age are circumcised for medical reasons .
Why is phimosis dangerous?
Phimosis can cause accumulation and stagnation of smegma (secret from the glands of the foreskin). Smegma deposits, if not properly hygienic, can promote the proliferation of various bacteria and lead to inflammation. With severe narrowing of the foreskin, urination becomes significantly more difficult (even to the point of acute urinary retention), and the risk of infections in the urethra increases. The narrowing of the foreskin is also fraught with paraphimosis, when the head of the penis, which is difficult to open, is severely pinched on all sides. This leads to swelling of the head, which makes it even more difficult to move it back. In such cases, immediate medical attention is necessary. Phimosis is also dangerous because the foreskin can adhere to the head of the penis: if the head is in close contact with the inner surface of the foreskin for a long time, their fusion can occur, and the longer this contact occurs, the greater the area and density of the fusion. In this case, surgical intervention is necessary.
Classification of childhood phimosis
There are such types of phimosis:
- Physiological phimosis. This is not a disease, but a temporary condition that is observed in newborn boys, children under one year old, and also in children under 5 years old. Moreover, it is not accompanied by any pathological symptoms: neither redness of the foreskin (preputium) or the head, nor pain in this area, nor difficulty urinating.
- The pathological type of phimosis is already a disease that requires treatment. Signs of this condition can be noted in childhood over 5 years of age, as well as in adolescence.
Symptoms, examination and diagnosis
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis. To do this, parents must show the boy to a specialist. The examination should be carried out by a urologist or surgeon. The main methods of therapy include medication, such as ointments and surgery.
Treatment of the problem in childhood, as well as in boys 13, 14, 15 years old, can be carried out using hormonal ointments. Steroids make the skin in this area more elastic and mobile. Such medications are used at home only as prescribed by a doctor. Drugs are often dispensed from pharmacies only by prescription.
Popular ointments for the treatment of phimosis in boys can be found in the table.
| Drug name | Action | Approximate price in rubles |
| Diprosalik | Helps soften and increase the elasticity of the foreskin | 600-700 |
| Cloveit | Contains clobetasol propionate, effectively eliminates forms of phimosis characterized by thickening of the prepuce | 250-300 |
| Elokom | Includes mometasone, used as a topical treatment or as an occlusive dressing | 300-450 |
| Beloderm | The cream effectively eliminates the inflammatory process | 200 |
| Hydrocortisone ointment | Has an anti-inflammatory effect, removes adhesions, and is often used for swelling and pain | 50-80 |
| Lokoid | Has a relatively small number of side effects and can be used up to three times a day | 300-350 |
| Triderm | Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects | 700-900 |
During the treatment of phimosis in a boy, ointments are applied exclusively to the foreskin area. Treatment of the genital organ should be carried out after performing hygiene procedures. During the procedure, the medicine should not get on the head, as there is a risk of developing some side effects.
The decision on whether or not to undergo surgery for phimosis is made solely by a specialist, based on visual examination data and tests obtained. The operation is performed in a hospital setting under local or general anesthesia.
Surgery is performed in several ways. Let's look at them:
- Classic or traditional. In this case, the surgeon makes axial incisions, thereby increasing the diameter of the foreskin opening.
- Circumcision. Here the surgeon completely removes the foreskin. Used in severe cases.
- Surgical intervention according to Shkloffer. It is carried out by zigzag dissection followed by suturing the edges of the wound. This type of treatment is performed under local anesthesia.
Minimally invasive techniques include laser treatment. In this case, a laser is used to remove the foreskin. The advantage of the technique is painlessness, a short rehabilitation period, and a small number of side effects. In addition, the laser is not dangerous to the child’s health and passes quite quickly. The disadvantage is the high cost and availability of the procedure. Not all patients can undergo such an operation.
How is this condition treated?
A baby usually does not require not only any treatment, but even compliance with any special hygiene rules. Over the age of one year, it is necessary to consult a doctor who decides whether surgery is necessary in this case, or whether conservative treatment can be used. His choice depends mainly on the severity of the disease:
- With 1 degree of narrowing in a child under 13 years of age, treatment is not carried out. No special diet requirements
- With grade 2, you can also do without surgery if you use the technique of gradually stretching the foreskin. Only a urologist shows the technique
- Grade 3 can be treated with conservative treatment along with dissection of the adhesions between the foreskin and the genital organ enveloping it
- for grade 4, only surgery will help.
Conservative therapy
For stage 3 phimosis, the doctor may prescribe treatment with drugs based on glucocorticoid hormones, applied topically in the form of ointments.
Thus, Prednitop, Pimafucort, and prednisolone ointment are used, the effect of which is to improve skin elasticity, eliminate inflammation, and accelerate healing. The use of these medications is combined with stretching of the preputial skin.
In case of complications - balanoposthitis, urethritis - systemic antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Surgical treatment
The operation is indicated for stage 4 narrowing of the hole. It is called circumcision or circumcision. The intervention consists of complete or partial excision of the prepuce under general anesthesia. The duration of the operation is about 20 minutes.
For hypospadias or epispadias, surgery is not performed, since the skin of the foreskin with this defect is used for plastic correction of the defect. Hydronephrosis is not a contraindication for circumcision.
Course of the postoperative period
After the operation, a sterile bandage is applied to the penis, which falls off on its own after 48 hours or is removed by doctors after this period of time. There is no need to remove it yourself, as it can cause bleeding from the postoperative wound.
In the first 2 days of the postoperative period, the child should not be bathed, only dried with a towel dipped in warm water. After 48 hours, the child can be bathed completely by calmly dipping the penis in warm water. The food does not differ from the child’s usual diet; the drinking regime should be a little larger.
For several days after the operation, the head of the genital organ will be red and swollen. Parents should pay special attention to the following signs:
- body temperature can rise only on the first day of the postoperative period, then it should be normal
- redness should not extend to the base of the penis or abdomen
- there should be no discharge from the urethra
- the amount of daily urine should not be less than usual
- the child should not refuse to eat or drink, be lethargic or sleepy.
In all these cases, what should parents do? Contact the operating surgeon to examine the child. This will help the urologist make the correct diagnosis and determine treatment tactics.