1st trimester screening is a diagnostic test that is carried out for pregnant women at risk from 10 to 14 weeks. It, being the first of two screening observations, allows you to determine with great accuracy how high the risk of giving birth to a sick fetus is. This examination consists of two parts - donating blood from a vein and ultrasound. Based on them, taking into account many of your individual factors, the geneticist makes his verdict.
Screening (from the English “screening”) is a concept that includes a number of activities to identify and prevent diseases. For example, screening during pregnancy provides the doctor with complete information about the various risks of pathologies and complications in the development of the child. This makes it possible to take full measures in advance to prevent diseases, including the most severe ones.
What is pregnancy screening
The examination includes two procedures: ultrasound and biochemical screening, during which markers specific to the “interesting” position are detected in the blood. These research methods can tell the doctor a lot: whether the baby’s growth rate corresponds to the gestational age and whether there are any pathologies in its development. The test results are interpreted taking into account the age and body weight of the expectant mother, as well as the presence of chronic diseases and bad habits.
Of primary importance is a comprehensive examination for pregnant women in the following high-risk groups:
- the expectant mother celebrated her 35th birthday;
- in the patient’s family there were cases of the birth of children with Down syndrome and other anomalies due to genetics;
- women who had a spontaneous abortion or gave birth to sick (genetic abnormalities) children;
- victims of infectious diseases that overtook women some time after conception.
When deciphering the data obtained as a result of the examination, the specialist pays attention not only to absolute indicators, but also to deviations corresponding to the timing of screening during pregnancy. All doctors agree that the results of a clinical blood test cannot be taken as the ultimate truth and a final diagnosis cannot be made on this basis. Whatever the results of the study, there is always the opportunity to undergo additional examination.
Cost of ultrasound diagnostics
An ultrasound at 10-11 weeks is a routine screening and can be done free of charge in many antenatal clinics.
If you want to undergo examination in another clinic, on average you will have to pay 700-800 rubles for the procedure. For ultrasound, you can purchase a photo of the fetus for 100-300 rubles.
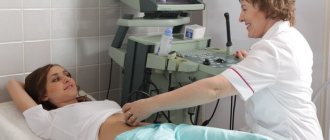
Ultrasound diagnostics at 10-11 weeks of pregnancy informs about the presence of gross malformations of intrauterine development and pathologies of the reproductive organs. If the results are in doubt, it is vital to undergo a comprehensive examination. Based on its results, it is necessary to make a rational decision - to try to eliminate factors that have a detrimental effect on the fetus and maintain the pregnancy, or to resort to drug termination in case of irreversible pathological processes.
When is the first screening done?
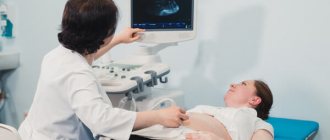
At the initial stage of gestation, an ultrasound machine is used to determine the main parameters of the growing baby. The laboratory assistant examines the child’s internal organs, paying attention to the location of his arms and legs. In addition, the procedure makes it possible to see the position of the placenta and evaluate its structure.
By the characteristics of the baby’s physique during this period of pregnancy, they can judge whether the fetus is forming correctly.
If a deviation in the child’s development from generally accepted norms is detected in time, the doctor will have time to conduct an additional examination, think about and develop tactics for further management of the pregnancy.
During the procedure, the specialist examines the following specific features of the developing child:
- Coccygeal-parietal distance (CPD)
11 weeks - from 34 to 50 mm;
12 weeks - from 42 to 59 mm;
13 weeks - from 51 to 75 mm.
- Condition of the nasal bone
At 11 weeks of pregnancy it should be clearly visible, but its size is still difficult to determine. Screening at 12 weeks of pregnancy shows that the nasal bone has grown - its size now ranges from 2 to 2.5 mm or more. At 10-12 weeks of gestation, the bone is clearly visible in 98% of healthy babies.
- Neck thickness (TCT)
In other words, these are folds in the neck area.
11 weeks – from 0.8 to 2.2 mm;
12 - 13 weeks - from 0.8-2.7 mm.
- Heart rate (HR)
11 weeks – from 155 to 178 beats per minute;
12 weeks – from 150 to 174 beats per minute;
13 weeks – from 147 to 171 beats per minute.
- Biparietal size
This is the distance between the outer and inner edges of both parietal bones.
11 weeks – from 13 to 21 mm;
12 weeks – from 18 to 24 mm;
13 weeks – from 20 to 28 mm.
A poorly defined maxillary bone between 11 and 13 weeks may indicate a high risk of developing Down syndrome in the baby.
Determination of embryo viability
A fetal ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy shows the baby's heartbeat. It begins at week 5 and only at the first screening can you make sure that there is no possibility of freezing.
The full viability of the embryo is determined by the heart rate. Normally they should be from 90 to 110 beats/min. These are important indicators that include the size of the fetus, ultrasound at 11 weeks. Modern equipment allows you to view all the baby’s organs and exclude the presence of pathologies or congenital defects. For example, Down syndrome or Edwards syndrome. Therefore, women are sent for a full and in-depth diagnostic study.
What does it show
What do they look at at the first screening? The length of the embryo is assessed (this is called the coccygeal-parietal size - CTR), the size of the head (its circumference, biparietal diameter, distance from the forehead to the back of the head).
The first screening shows the symmetry of the cerebral hemispheres and the presence of some of its structures that are required during this period. Also look at the 1st screening:
- long tubular bones, the length of the humerus, femur, forearm and tibia bones is measured
- Are the stomach and heart located in designated places?
- the size of the heart and the vessels emanating from them
- belly size.
Symptoms of 11 weeks of pregnancy
Symptoms at 11 weeks of pregnancy are very individual. Let's talk about the most common ones.
Toxicosis, constipation, heartburn
Want something interesting? Sometimes toxicosis causes severe discomfort and disrupts normal lifestyle. It is better to inform your doctor about it and undergo the necessary therapy to alleviate your condition. But in most cases, toxicosis subsides at this time. However, if you still feel slight nausea in the morning, it will soon go away completely or the manifestations of toxicosis will become much easier. Nausea may be replaced by other “joys” of pregnancy – heartburn and constipation, which are also signs of hormonal changes.
Don't ignore problems like this!
Constipation is not just a discomfort, it is a reason to consult a doctor, because it can lead to complications (for example, hemorrhoids). The accumulation of fecal matter in the body poisons it.
But we hasten to reassure you, not all women complain about having this kind of problem, so you shouldn’t worry or get ready for it in advance!
Breast swelling and pain
Some mothers notice changes in their breasts. Hormones begin to prepare you for breastfeeding. You may notice breast swelling, darkening of the nipples, and pain may also occur. Some feel these manifestations more strongly, some less, and some do not have them at all. Everything is very individual.
How noticeable are fetal movements?
Not all mothers feel fetal movements at this stage. Women with a slender figure, as well as those who are carrying a second or third child, are able to feel the movements a little earlier than others, but still not at the 11th week. It is simply quite difficult to distinguish the baby’s gentle and barely noticeable movements from processes in the intestines. Be patient and you will probably feel them very soon!
How to prepare for your first screening
Preparation for the procedure begins within the walls of the antenatal clinic, where the expectant mother can ask the gynecologist any questions that interest her. The specialist will tell the woman about the importance of the first screening and explain how to prepare for it.
The laboratory usually performs ultrasound and biochemical blood tests on the same day. The examination is completely painless; the most unpleasant moment can only be considered the blood sampling procedure.
Screening is carried out early in the morning, before breakfast. 1 - 2 days before the procedure, the expectant mother should pull herself together and give up her favorite foods, including chocolate, seafood, meat and all fatty foods. A forced diet is considered the key to accurate screening results.
The doctor will most likely advise the woman to abstain from sexual intercourse, otherwise the overall picture of the tests may be distorted.
Before going to the laboratory, a pregnant woman should weigh herself. The laboratory technician will enter data on the patient’s body weight into a special form immediately before the ultrasound procedure and blood sampling for analysis.
Before screening, it is better not to drink water, but if the desire is irresistible, then no more than 100 ml.
First trimester screening is carried out in two stages:
- First, an ultrasound screening is done. If this is done transvaginally, then no preparation is required. If it is done abdominally, then it is necessary that the bladder is full. To do this, you need to drink half a liter of water half an hour before the test. By the way, the second screening during pregnancy is carried out transabdominally, but does not require preparation.
- Biochemical screening. This word refers to taking blood from a vein.
Considering the two-stage nature of the study, preparation for the first study includes:
- bladder filling – before 1 ultrasound screening
- fasting at least 4 hours before taking blood from a vein.
In addition, you need a diet before diagnosing the 1st trimester in order for the blood test to give an accurate result. It consists of eliminating chocolate, seafood, meat and fatty foods the day before you plan to attend a screening ultrasound during pregnancy.
If you plan (and this is the best option for perinatal diagnostics in the 1st trimester) to undergo both ultrasound diagnostics and donate blood from a vein on the same day, you need:
- throughout the previous day, deny yourself allergenic foods: citrus fruits, chocolate, seafood
- exclude completely fatty and fried foods (1-3 days before the test)
- before the test (usually blood is donated for 12-week screening before 11:00) go to the toilet in the morning, then either do not urinate for 2-3 hours, or drink half a liter of still water an hour before the procedure. This is necessary if the examination will be performed through the abdomen
- If ultrasound diagnostics are done with a vaginal probe, then preparation for 1st trimester screening will not include filling the bladder.
Indications for use
An ultrasound of the fetus in the first trimester provides for a thorough examination and diagnosis by a doctor who monitors the development of the child and the young mother. Before this period, the woman must register. Many people undergo ultrasound examinations, but pregnant women are in the vulnerable category. Doctors strongly advise screening in the 1st trimester to eliminate dangers to the life of the unborn baby. Main indications:
- the mother has given birth to children or a child with developmental disabilities;
- have a child with genetic diseases;
- age – 35-40 years;
- suffered from infectious diseases during gestation;
- have previously taken large amounts of alcohol or drugs;
- there were cases of frozen pregnancies;
- potential father is a close relative;
- took medications prohibited during pregnancy;
- there are hereditary diseases in close and distant relatives;
- spontaneous miscarriages.
Results and standards of the study
As a result of a biochemical blood test, the values of free beta-hCG and protein-A (PAPP-A) are of greatest value to the doctor.
In a pregnant woman, the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is increased. The concentration of a specific substance increases rapidly in the first weeks after fertilization of the egg. It is by this sign that one can judge whether pregnancy has taken place or not within 6 to 7 days after intercourse.
Starting from the 12th week of gestation, hCG levels in the body begin to gradually decrease, and throughout the second trimester its level remains practically unchanged.
The norms of free hCG during pregnancy are:
- from 17.4 to 130.4 ng/ml at 11 weeks of gestation;
- from 13.4 to 128.5 ng/ml at 12 weeks of gestation;
- from 14.2 to 114.7 ng/ml at 13 weeks of gestation.
A free hCG level that is higher than normal may indicate the following conditions:
- multiple pregnancy;
- Down syndrome;
- severe toxicosis.
Significantly underestimated indicators of this substance indicate the following probable pathologies:
- non-developing pregnancy;
- delayed fetal development;
- the likelihood of spontaneous miscarriage;
- Edwards syndrome.
The standards for the substance PAPP-A are:
- from 0.46 to 3.73 mU/ml at 11 weeks;
- from 0.79 to 4.76 mU/ml at 12 weeks;
- from 1.03 to 6.01 mU/ml at 13 weeks.
A high content of PAPP-A in the blood is not of particular diagnostic significance for a doctor, but a low level of this substance makes one wary, since it may be a consequence of the following disorders:
- pathology of the development of the fetal neural tube;
- frozen pregnancy;
- the likelihood of spontaneous abortion;
- risk of premature birth;
- Rh conflict between mother and child;
- Edwards syndrome;
- Down syndrome;
- Smith-Opitz syndrome;
- Cornelia de Lange syndrome.
Biochemical analysis of the first screening during pregnancy makes it possible to detect fetal pathologies in the form of Down, Patau and Edwards syndromes in 68% of cases.
Taking into account ultrasound data, the reliability of blood test results is confirmed in 90% of cases. However, experts always remember that for some reasons the data obtained may be distorted.
For example, the results of a biochemical blood test depend on many factors, among which the greatest influence on the composition of the blood is:
- multiple pregnancy;
- pregnancy obtained through the IVF procedure;
- the patient’s large body weight (the larger it is, the higher the levels of specific substances in the blood);
- a course of treatment with drugs whose active substance is progesterone;
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman;
- high risk of spontaneous abortion;
- incorrectly determined gestational age;
- depressed state of the expectant mother due to psychological trauma.
If the data obtained as a result of the first screening during pregnancy does not differ too much from the norm, doctors will try to allay their concerns at the second screening. This is a mandatory procedure for the second trimester of pregnancy.
What happens to mom at 11 weeks
You are already accustomed to your condition. Outwardly, it is still difficult to guess that you are carrying a new little life under your heart, internally your body has been completely rebuilt and is ready for global changes. However, the feelings of anxiety, emotional instability and worry that are characteristic of the first weeks of pregnancy may not have completely receded.
How to overcome mood swings
If an unstable mood (emotional swings, irritability, anxiety, inexplicable anxiety and tearfulness) persists, it is advisable to seek help from a professional psychologist. People close to you can also help. On their part it is enough:
- empathy (sympathy and acceptance);
- patience;
- caring attitude towards you and your condition.
You shouldn’t use your condition to manipulate your loved ones; it can undermine relationships and cause irritation.
Abdominal growth rate and weight gain
In the eleventh week, calories are burned much faster than before pregnancy, since the metabolic process is 25% faster. The volume of circulating blood also increased. You may feel internally hot, sweat profusely, and feel very thirsty.
Weight may just begin to increase, and women suffering from toxicosis may even lose several kilograms. Both of them say nothing about the course of pregnancy. Weight gain is recorded and noted only in the second and third trimesters.
You may notice a small belly . The uterus is located directly above the pubis, and if you have a very slender figure, then regular jeans may no longer fasten, and low-rise clothes may cause discomfort. This is a great reason to treat yourself to shopping in search of new, comfortable and beautiful clothes for pregnant women. Mothers who were actively involved in sports before pregnancy can still safely wear regular jeans and trousers at the 11th week. Strong lower abdominal muscles prevent the stomach from relaxing, so it looks smaller and neater.
Nature of discharge and deviations
Vaginal discharge may appear. If they are light and the smell is almost imperceptible, then this is normal. Any deviation is a reason to consult a doctor.
The most common disease during pregnancy is thrush or candidiasis. It is caused by fungi of the candida species, which live in the body, but do not manifest themselves and do not cause concern in the absence of favorable conditions. During pregnancy, when the body's forces are aimed at developing the fetus, the immune system may be weakened, and these fungi begin to actively multiply, displacing the normal flora of the vagina.
Itchy, white, cottage cheese-like discharge indicates the onset of thrush. To solve this problem, you can try traditional methods or use topical medications prescribed by your doctor. However, consultation with a gynecologist is mandatory.
Thrush is not just a discomfort, but also a serious danger to the development of the fetus . The fungus can be transmitted to the fetus not only during childbirth, but also during intrauterine development, affecting the normal course of pregnancy.
Also, remember that foul-smelling discharge can be a symptom of various diseases. They cannot be ignored! You must immediately undergo an examination, find out the cause and start taking medications prescribed by your doctor.
Any inflammatory diseases or infections must be treated before birth to avoid infection of the baby.
Possible deviations
Normally, the diagnostic results of the 1st trimester end with a risk assessment, which is expressed as a fraction (for example, 1:360 for Down syndrome) for each syndrome. This fraction reads like this: in 360 pregnancies with the same screening results, only 1 baby is born with Down pathology.
Decoding the 1st trimester screening standards. If the child is healthy, the risk should be low and the screening test result should be described as “negative.” All numbers after the fraction must be large (greater than 1:380).
A poor first screening is characterized by a “high risk” entry in the report, a level of 1:250-1:380, and hormone results of less than 0.5 or more than 2.5 median values.
If the 1st trimester screening is bad, you are asked to visit a geneticist who will decide what to do:
- schedule you for a repeat study in the second, then screening in the 3rd trimester
- propose (or even insist) on invasive diagnostics (chorionic villus biopsy, cordocentesis, amniocentesis), on the basis of which the question of whether this pregnancy is worth prolonging will be decided.
What influences the results
As with any study, there are false positive results from the first perinatal study. So, with:
- IVF: hCG results will be higher, PAPP will be lower by 10-15%, the indicators of the first screening ultrasound will increase the LZR
- obesity of the expectant mother: in this case, the levels of all hormones increase, while with low body weight, on the contrary, they decrease
- 1st trimester screening for twins: the normal results for such a pregnancy are not yet known. Risk assessment is therefore difficult; Only ultrasound diagnostics is possible
- diabetes mellitus: the 1st screening will show a decrease in hormone levels, which is not reliable for interpreting the result. In this case, pregnancy screening may be canceled
- amniocentesis: the rate of perinatal diagnosis is not known if the manipulation was carried out within the next week before blood donation. It is necessary to wait longer after amniocentesis before undergoing the first perinatal screening of pregnant women.
- psychological state of the pregnant woman. Many people write: “I’m afraid of the first screening.” This can also affect the outcome in unpredictable ways.
What are obstetric weeks
Gestational age can be determined in embryonic weeks and obstetric weeks. Embryonic development begins at the moment of conception and lasts 38 calendar weeks. Obstetric period is calculated by the date of the last menstruation. It is two weeks longer than the embryonic one. In weeks, the obstetric period is 40 weeks or 280 days.
One obstetric week, like a calendar week, is equal to 7 days. Obstetric weeks begin to count from the first day of the last menstruation. It turns out that 9 calendar months + 1 week are added to this date.
The best time for the first screening is 11,12, 13 obstetric weeks. Examination is acceptable for another 6 days after the 13th week.