First planned ultrasound, screening during pregnancy in the first trimester: when is it prescribed?
In medicine, screening refers to a set of different studies that are aimed at identifying a group at increased risk. Prenatal screening is a prenatal examination of a woman while she is expecting a child, designed to determine the factors of intrauterine development of the fetus, the likelihood of congenital defects of the fetus, as well as possible complications of pregnancy.
Given the high information content and safety of such procedures, they are prescribed every trimester, and in certain cases more often. Typically, the first screening is scheduled for a woman at 11-13 weeks. In addition, indicators obtained during the period 11-14 weeks can be considered reliable.
Nowadays, screening in the first trimester is recommended for all women. However, a number of factors make such an examination not just desirable, but mandatory:
- more than two miscarriages in the past
- During a previous pregnancy, fetal freezing occurred
- infection of the expectant mother with bacterial or viral infections
- the presence of genetic and chromosomal pathologies in family members
- taking medications that are prohibited while expecting a baby
- existence of a blood relationship between father and mother
- alcoholism and drug addiction in mother or father
- hazardous production conditions
- the woman giving birth is over 35 years old
- shortly before conception, the parents (or one of them) were exposed to radiation
Screening
Ultrasound is a study that allows you to assess the condition of the female uterus, as well as the embryo. The basis of this method is the principle of echolocation, in which ultrasound passes through tissue structures, is reflected, and then an image is displayed on the screen.
It should be noted that the first planned ultrasound is an extremely important stage in medical monitoring of pregnancy. After all, it is during this period that the laying of the organs of the future human being occurs, and the first examination may show severe disturbances in the development of the embryo. Therefore, the timing of the first ultrasound is strictly regulated in domestic medicine.
This informative diagnosis includes the following types of research:
- abdominal (the sensor is moved along the outside of the woman’s womb)
- transvaginal (a sensor is inserted into the vagina)
During the first ultrasound scan (usually at 12 weeks), the future baby is assessed for:
- presence of all limbs
- how the spine develops
- state of the brain (symmetry of the hemispheres, their structure)
- body length from coccyx to crown
- neck width
- head parameters
- vessels in the umbilical cord
- blood speed
Possible anomalies
It is important to note that identifying these risks does not necessarily mean that the baby has diseases, but is simply the basis for additional examinations and consultations. That is, the screening results do not indicate the disease, but the presence of typical markers. In order to refute or confirm the alleged diagnosis, a doctor may prescribe:
- consultation with a specialist – genetics
- prenatal non-invasive DNA test, which is today one of the modern diagnostic methods of very high accuracy and is based on molecular research
- invasive diagnostics (study of placental tissue and amniotic fluid). Such methods are prescribed when the risk of pathology is quite high (1:100), because they can cause a number of complications (infection of the embryo, miscarriage)
There are often cases when, despite a high level of screening risk, babies are born completely healthy. And some women believe that such examinations should not be carried out in the early stages in order to avoid stress due to the negative results obtained. After all, many families are ready to raise even an unhealthy child. However, it is still better to know in advance about possible problems and be prepared for them. But according to the law, the expectant mother has the right to refuse this examination.
In addition to the main parameters of embryo development, during the first ultrasound the following is determined:
- the number of embryos that are in the uterine cavity, as well as the condition of each of them
- the placental attachment site relative to the os of the uterus, which allows identifying the risks of premature birth
- indicators of the quality and quantity of amniotic fluid (normally their volume is approximately 50 ml, and they are updated daily)
- ovarian condition
- what tone is the uterus in?
- the presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency (loose closure of the cervix), which increases the risks
- premature birth
- placental abruption
- degree of placental aging
- the estimated date of onset of labor is calculated
- possible presence of tumors and cysts
Based on the screening results, the doctor decides on a more detailed examination of the expectant mother. Early diagnosis should not be abandoned, as it is very important for the following reasons:
- the most reliable information about the health of female organs and the embryo is determined at 12-13 weeks
- some indicators are informative only in early pregnancy (for example, measuring the thickness of the soft tissues of the cervical-collar region, which makes it possible to judge the presence of genetic abnormalities)
- if the forced need to terminate a pregnancy is confirmed, less significant damage is caused to the female body than at a later date
- it is possible to provide a woman with timely assistance and thereby avoid complications
First ultrasound scan during pregnancy
In some cases, the first ultrasound scan of the expectant mother is prescribed before the 12-week period for the following indications:
- uterine bleeding
- have had miscarriages or miscarriages in the past
- pain in the lower abdomen that is nagging in nature
- fertilization resulting from assisted reproductive technology (IVF)
- During previous pregnancies, various defects and anomalies were observed
- probability of multiple pregnancy
Biochemistry of venous blood during screening in the first trimester makes it possible to determine the following parameters:
- the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin, which directly confirms the fact of pregnancy (beta-hCG)
- the volume of plasma protein that ensures the condition and functioning of the placenta (PAPP-A)
Before IVF: qualitative examination
An additional examination is usually prescribed by a fertility specialist based on information about previous pregnancies, previous treatment methods, the woman’s bad habits, her age, diseases, and the health of her family and friends.
If a woman has previously had several ineffective IVF protocols, or they resulted in an undeveloped pregnancy, it is recommended:
- Study of autoimmune factors (antibodies to phospholipids in the blood, antibodies to hCG, lupus anticoagulant).
- Test for genetic predisposition to bleeding disorders or folic acid absorption disorders.
The presence of such problems without adequate treatment often leads to pregnancy loss in the early and late stages). In order to prevent the development of inflammatory complications of pregnancy (for example, intrauterine infection of the fetus or damage to it by a viral infection), it is important to undergo examination for toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes before the IVF program, so that, if necessary, all treatment is carried out before pregnancy.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis of embryos in an IVF program, which allows embryos with chromosomal abnormalities to be excluded from transfer, can help increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy outcome. Modern techniques make it possible to study embryos on all chromosomes, which, according to statistics, gives better IVF results and helps solve the problem of miscarriage.
First planned ultrasound, screening during pregnancy in the first trimester: how to prepare?
Typically, in the first trimester, prenatal screening consists of three stages:
Stage 1. General examination
A questionnaire is filled out for the woman, where her specific data is indicated:
- number of years
- presence of chronic diseases
- body weight
- possible bad habits (smoking)
- method of conception
- results of preliminary analyzes
The specified data is entered into a special computer program.
Stage 2 Ultrasound examination
If the examination will take place in a district clinic, prepare:
- a diaper that goes over the couch
- slippers or shoe covers
- a towel or napkin that will be needed to wipe the gel applied to the stomach from the stomach
- a condom that will be placed on the sensor for examining the vaginal
In private clinics, as a rule, all this is given to the woman by medical workers.
Preparing for an ultrasound
How to prepare for this procedure:
- In a couple of days, eliminate from your diet foods that contribute to the formation of intestinal gases, as they can distort diagnostic results
- an hour or two before the examination procedure, drink 0.7-1 liters of non-carbonated liquid. This is necessary in order to increase the volume of amniotic fluid, the amount of which is insignificant at this time. And it is possible to see the fetus well thanks to the liquid
- Before a vaginal examination, a woman must empty her bladder
There is no need to worry about the influence of ultrasonic waves on the health of the unborn baby or the condition of his mother. The doses and intensity of the procedure do not have any negative impact on the course of pregnancy.
Stage 3. Blood test
After the ultrasound (usually the next day), the woman donates venous blood for biochemical analysis. In order to obtain the most accurate and reliable results, you need to properly prepare:
- give up foods that can cause allergic reactions (chocolate, seafood, smoked meats) in a couple of days
- blood is taken on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be 5 hours before the collection procedure
- try to avoid excessive mental, emotional and physical stress on this day
Embryo implantation is a stage of pregnancy
The egg becomes an embryo at the moment when it manages to attach to the walls of the uterus and begins to grow. Implantation of the embryo after in vitro fertilization occurs on the 7th day after the procedure. The implanted fertilized oocytes must independently pass through the tubes and attach to the walls of the uterus. If this does not happen, then the female fertilized cell will be rejected as an unidentified object and pregnancy will not occur. The egg needs only 40 hours to attach and begin its development period. This period is called embryonic and lasts 8 weeks. In total, embryo implantation lasts up to the 20th week of pregnancy. During this time, the placenta is fully formed and then well protects the fetus from negative influences.
With in vitro fertilization, late implantation of the embryo may occur, which occurs on the 10th day. This is a pleasant event in the life of the attending physician and the woman, because the protocol becomes successful at the moment when disappointment has already appeared. When several fertilized eggs are implanted at once, a multiple pregnancy results. Twins after IVF are a common option for a successful protocol.
In order for the embryo to begin to develop after transfer, conditions must be created for pregnancy to occur. The hormonal system must prepare a layer of epidermis on the walls of the uterus with a certain thickness. Its size is very important for successful IVF. The content of necessary chemicals in the uterus must be sufficient for the further development of the embryo after IVF. Signs of pregnancy after IVF begin to develop after human chorionic gonadotropin enters the blood.
The appearance of the first signs of pregnancy after IVF
Signs of pregnancy are associated with implantation of the embryo and the appearance of a new hormone in the body, which provokes the development of nervousness, low mood and increased tearfulness.
Signs of pregnancy after IVF begin with toxicosis. This is the most pronounced sign of a developing embryo in the uterine cavity. Toxicosis during pregnancy after IVF is a consequence of stimulation of superovulation.
The second sign is an increase in basal temperature. In the first month of pregnancy it reaches 37.2ºC and indicates that the female body is being rebuilt and preparing to bear a fetus. Positive signs may include malaise, weakness, and deterioration in health. This is due to a general decrease in immunity, which suffered during the in vitro fertilization protocol. At this point, you need to eat foods that will naturally cleanse the body of toxins and saturate it with vital substances.
There may be hyperemia of the skin, hot flashes or chills. Such symptoms indicate the onset of hormonal changes during pregnancy. During this happy period for a woman, the mammary glands become more sensitive. They swell and the nipple halos begin to darken.
A woman's emotionally unstable state can also be a symptom of pregnancy. Women in the first trimester are very irritable, moody and often cry. But the most important sign that pregnancy has occurred after artificial insemination is a positive hCG test during IVF, the results of which indicate the successful completion of the protocol and the possible development of twins after embryo implantation has occurred.
First planned ultrasound, screening during pregnancy in the first trimester: what are the norms?
In order to decipher the results of the ultrasound scan, the doctor compares the identified parameters of the embryo with the normative ones for a specific period.
Averages
The coccyx-parietal size is the length of the embryo from the point of its crown to the coccyx; the dimensions of the legs are not taken into account. Too low CTE readings can usually indicate the following factors:
- the fetus is likely to have genetic abnormalities
- the embryo lags behind in its development due to illnesses of the woman herself or due to insufficient amounts of hormones
- an error was made when calculating the gestational age
The thickness of the collar space is the area in the cervical spine where fluid accumulates. And the greater the volume of the thickness of these tissues, the greater the likelihood of the presence of pathologies. In such cases, a repeat procedure is prescribed (at 14 weeks), and the woman is recommended to undergo genetic testing of the amniotic fluid.
It should be noted that before the 10th week, examination of this zone is uninformative, since the size of the embryo is too small during this period. And after 14 weeks, the lymphatic system is already formed and takes excess fluids from the cervical region. Therefore, the survey will also be unreliable.
The biparietal size of the embryo's head is an indicator that measures the space from one temple to the other. If its value is too large, it may be a sign of:
- large weight and size of the child
- hydrocephalus of the fetal head
- spasmodic growth pattern of the embryo
- tumors or hernias
Low rates are, as a rule, a consequence of abnormalities in the development of the head brain in the unborn baby.
Along with those listed during the first ultrasound examination, other indicators are also assessed, for example, whether the nasal bone is visible or not (the pathology of this area can be caused by chromosome mutations).
Standard indicators
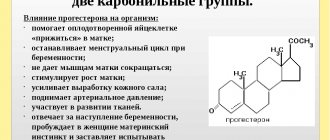
Beta-hCG is considered the main hormone of pregnancy.
The reasons for its increase are usually as follows:
- the timing of pregnancy is incorrectly determined
- chromosomal abnormalities (determined only taking into account other indicators)
- The expectant mother is diagnosed with diabetes
- tumor or hydatidiform mole in the embryo
- There are several embryos in the uterine cavity
- early toxicoses
Reasons for the decrease
PAPP-A protein is associated with pregnancy and increases weekly. Its indicators are assessed in comparison with the results of hCG and ultrasound.
It should be noted that the values in this analysis can fluctuate significantly, as they depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. Additional examinations are prescribed for severe deviations from the norm. In this case, certain pathologies can be diagnosed.
In cases of low PAPP-A, there is a high probability of:
- presence of chromosomal mutations in the embryo
- threats of miscarriage or dying
- monogenic syndrome
Exceeding the norm of this protein is less dangerous and may result from:
- incorrect pregnancy dates
- increasing uterine tone
- incorrect placental position (very low)
- too big fruit
Based on the obtained screening results, the MoM coefficient is determined, indicating the level of risk of deviation from the norm. It is calculated using certain formulas. The average norm in the trimester in question is considered to be 0.5-3 (and if the pregnancy is multiple, then the parameters increase to 3.5).
Ultrasound during pregnancy
It happens that the examination gives unreliable results. The reason for this may be the following factors:
- fertilization by IVF
- the presence of several embryos in the uterine cavity
- obesity or diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman
- psychological state of the subject
- amniocentesis
It is extremely important to do the planned first examination at the time prescribed by the doctor. The fact is that further indicators may change, and the picture of the child’s development may turn out to be very distorted, which will interfere with the correct and timely prediction of a possible deviation.
Please note: this article is for informational purposes only. Doctors strongly advise against deciphering the screening result yourself. This should only be done by a qualified specialist.
Childbirth
It is important to emotionally prepare the mother for childbirth. Based on how the baby and mother feel, the doctor chooses the method of childbirth. But as practice shows, caesarean section in this case is performed more often. But it is, of course, easier to recover after a normal birth. Even if this is not the first pregnancy.
During each pregnancy cycle, it is important to establish a relationship with your healthcare provider. Trusting relationships will help during childbirth, as well as in preparation before it.
Pregnancy is a wonderful stage in the life of parents. Thanks to IVF, all unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant will be put aside, and mom and dad will be able to see their long-awaited baby.
Features of ultrasound during pregnancy after IVF are significantly different from natural ones. During artificial insemination, ultrasound is often prescribed several times more often, and the first ultrasound is performed a little earlier than usual. It allows you to confirm the fact of successful embryo transfer and make sure that the pregnancy is proceeding successfully. When is the first ultrasound performed and what is looked at during the analysis?
First ultrasound after IVF, after embryo transfer: timing, norms
Unfortunately, some couples face problems conceiving a child. A unique technique can help in solving this problem - IVF (in vitro fertilization), the essence of which is that the egg is fertilized outside the female body.
IVF procedure
Proof that the long-awaited pregnancy has occurred is the result of an hCG test, which is carried out 10-14 days after the procedure. Typically, the level of hCG in the expectant mother in this case is higher than in naturally fertilized women.
The first ultrasound after IVF is scheduled earlier than during a normal pregnancy. As a rule, in case of a positive hCG result, an ultrasound examination is performed 21-28 days after embryo transfer.
The research procedure is usual:
- transvaginal – allowing a detailed examination of the uterine cavity and embryo in the early stages of pregnancy
- transabdominal – passing through the outer wall of the abdominal cavity
It should be noted that after IVF, the first ultrasound should be transvaginal, since it is performed 3-6 weeks after the transfer of embryos, which during this period are too small and difficult to examine with the help of an external examination.
The first ultrasound scan is an extremely important stage in monitoring a woman, as it allows:
- confirm pregnancy
- see the location of the fertilized egg
- determine the number of implanted embryos and their viability
- check the tone of the uterus
- detect developmental pathologies, as well as cases of frozen or ectopic pregnancy
- examine the condition of the ovaries in order to correctly adjust hormonal therapy
In the future, in cases of normal pregnancy, the woman is prescribed ultrasound according to the usual schedule:
- at 11-14 weeks
- at 18-21 weeks
- at 30-32 weeks
However, the treating doctor may prescribe an ultrasound examination more often - once every 2 weeks.
It is known that the IVF procedure gives positive results in 40-60% of cases. And if pregnancy does not occur as a result of artificial insemination, the woman is prescribed an ultrasound examination to determine the cause of the failure.
Cons of IVF
Of course, after pregnancy, the woman and the future father are in seventh heaven, however, as already mentioned, embryos do not survive in 50% of cases. It is worth noting that IVF is a very expensive procedure. Its cost amounts to tens of thousands of dollars, and this is not all that future parents will need to pay. Hormonal drugs are also expensive. To achieve pregnancy, sometimes it is necessary to carry out more than one in vitro fertilization procedure.
The second disadvantage is the extremely negative impact of the protocol on the woman’s body.
As a third condition, multiple pregnancies can be considered, but for some couples this is rather a big plus.
All of the listed disadvantages of IVF are nothing compared to the happiness and hope that it can give. Therefore, if it is possible and necessary to undergo the procedure, you should not be afraid of failure.
Can the first ultrasound not show twins?
Multiple pregnancies are not uncommon these days. Determining the number of embryos is possible already in the first trimester. In cases where a woman’s uterus is larger than it should be at a given period, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound.
During ultrasound scanning, the quantity is determined:
- heart rate
- amniotic sacs
- placenta
As a rule, such a procedure shows twins already in the early stages of pregnancy - at 5 - 7 weeks. The likelihood of identifying fraternal twins at the first ultrasound is especially high. And in cases of identical ones, multiple pregnancies are usually confirmed at 9-12 weeks.
However, it happens that the first ultrasound examination does not show that the expectant mother has two fetuses. Possible reasons are:
- an old device in which the beam length reaches only 18 cm. In such cases, the uterine cavity is partially visible during scanning, so the second fetus may not be detected
- inexperience of the medical worker conducting the study
In cases of suspected pregnancy, a woman with multiple births is recommended to undergo a 3D or 4D ultrasound. The resulting three-dimensional image will give a more accurate picture.
Multiple pregnancy
Often in the early stages, a doctor during an ultrasound examination discovers two embryos, one of which does not have an audible heartbeat. After some time, due to unclear circumstances, such an embryo dies. That is why we can speak with confidence about the presence of a multiple pregnancy only after 12 weeks.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that when confirming a multiple pregnancy, a woman will need to undergo more ultrasound scans (on average, monthly). This will allow timely detection of possible problems with the health of the mother and the development of the babies.
When ultrasound is contraindicated
There are no absolute contraindications for sonography. Ultrasound screening is not recommended under the following conditions:
- severe excessive and uncontrollable vomiting;
- an attack of eclampsia with fibrillary muscle twitching;
- increasing pain, which takes on the character of contractions, with bloody discharge;
- feverish increase in body temperature.
You can learn how a doctor should treat a pregnant woman after IVF from this video:
The first ultrasound examination after in vitro fertilization is considered one of the most important observations of the process of implantation of the fertilized egg. Its main task is to confirm the presence of pregnancy and the correct course of embryo development. It is absolutely safe for the expectant mother and her child.
Ultrasound on the first day of delay, in the first week after conception: what will it show?
On the first day of a missed period, an ultrasound scan will not be able to show the fetus. The embryo during this period is still too small in size and is only a cluster of dividing cells. 3 weeks after conception, the embryo reaches only 1 mm in length and is not a full-fledged embryo, but only a fertilized egg. Therefore, the ultrasonic equipment sensor simply will not detect it.
It becomes possible to see the embryo during scanning only 4-5 weeks after conception, usually at 7-10 days of delay. In this case, the study should be transvaginal, since it is more informative in this case. In very early stages of pregnancy, we can recommend a modern 3D ultrasound, which is more accurate and detailed.
On the monitor during the ultrasound you will be able to see:
- a small round or teardrop-shaped formation surrounded by a membrane and located in the upper region of the uterus (in conditions of normal intrauterine pregnancy)
- corpus luteum, which is considered indirect evidence of pregnancy, since with the onset of menstruation this gland usually regresses
However, it is impossible to speak with certainty about the occurrence of pregnancy at such an early stage, since there is a possibility of anembryony, a pathology in which there is no embryo inside the fertilized egg.
To avoid unnecessary worries, it is more advisable to perform the first ultrasound after 5 weeks from the moment of conception, when the embryo’s heart begins to contract, that is, from about the 10th day of a missed period. According to statistics, during this period the research results are reliable in almost 100 percent of cases.
Second trimester
Conducting a second ultrasound screening of pregnancy
Second trimester screening is an important part of pregnancy. Thanks to it, it is possible to identify all chromosomal abnormalities of the unborn child. Dangerous pathologies will also be identified. Before the ultrasound, it is recommended to eat something sweet, so the baby will be more active.
Ultrasound after IVF is performed a little more often. Each cycle of such a pregnancy has its own characteristics and deviations, which are important to identify at an early stage. When pregnancy occurs this way, women are more susceptible to complications. One of them is pathology of the placenta.
Because after IVF, miscarriages occur frequently. If you notice the slightest deviation in yourself, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Types of diagnostics
Currently, there are different types of examinations. The optimal type of procedure can only be determined with the assistance of an experienced specialist.
In most cases, a traditional ultrasound is performed after embryo transfer. In such a situation, no special preparation is required, since the procedure is easy to carry out. The sensor of the device is located on the front wall of the abdomen.
Recently, 3D ultrasound has become increasingly popular, which allows you to see the fertilized egg after IVF and correctly assess its condition. 3D involves a volumetric study of the embryo with the obligatory determination of the exact location. The expectant mother will see the monitor with the baby, and if desired, take the first photo of the unborn baby.
To fully monitor a woman’s condition, it is advisable to do an ultrasound of the mammary glands for IVF. This procedure also allows you to better understand the state of the hormonal system and determine the optimal actions not only for the onset of pregnancy, but also for maintaining it.
How is ultrasound performed?
During such a pregnancy, ultrasound scanning can also be performed in two main ways:
- transabdominal;
- transvaginal.
Both methods are allowed for IVF, since they do not pose any danger to the fetus and the expectant mother.
Transabdominal method
The study consists of installing a sensor that converts ultrasound waves on the skin of the abdomen in its lower parts. Therefore, the procedure is completely non-invasive and painless.
Preparation for the examination consists of following a certain diet to reduce gas formation in the intestines and filling the bladder for better visualization of the uterus. Approximately 2-3 days before the test, a woman should not eat foods that could potentially cause flatulence.
These include:
- all legumes;
- fresh vegetables;
- confectionery and bakery products;
- carbonated drinks and fast food products.
To fill the bladder cavity, you should drink about a liter of clean still water an hour and a half before the appointed time. As soon as the urge to go to the toilet appears, the procedure can begin.
The doctor does a study in several planes, after which all the results and his conclusions are recorded in the protocol.
Transvaginal method
In this case, the ultrasound sensor is directly inserted into the vaginal cavity, thereby achieving maximum proximity to the uterus and ovaries. This technique gives a more accurate and reliable picture compared to the previous method.
- In preparation, you only need to make sure that the intestines are not filled with gases, so for a couple of days it is recommended not to eat foods that contribute to flatulence.
- If a woman suffers from increased gas formation, then an hour before the examination it is necessary to drink several capsules of Espumisan or a bag of Smecta.
The ultrasound doctor puts a special disposable condom on the sensor and inserts it with gentle movements into the vaginal cavity about 5-6 cm. As a rule, the procedure is painless, and the woman may only feel some discomfort. Such proximity of the transducer to the organs being examined allows even a small embryo to be seen.
Therefore, the first ultrasound during IVF pregnancy should be performed transvaginally.
Explanation of results
Many pregnant women do not know when the first ultrasound is performed. The most accurate period for conducting the study is the period from 11 to 13 weeks, counting from the day of the last menstruation. It is especially important for women under the age of 18 and after 35 years of age if miscarriages, fetal death, abortions have already occurred, or hereditary diseases and genetic abnormalities have been observed in the family.
Ultrasound standards in the first trimester:
- measurement from the parietal point to the coccyx - CTE, at 11 weeks - 40-58 mm, 12 weeks - 47-73 mm;
- BPR - measurement of the distance between the protruding lobes of the crown - biparietal size, by the end of the 11th week 14-17 mm, 22 mm by 12, by the end of the 13th week - 25-26 mm;
- the length of the nasal bone, up to 11 weeks it can be determined, but it is difficult to estimate its size, at 13 weeks it corresponds to approximately 3 mm;
- Head circumference;
- the cranium should already be closed, the symmetry of the brain hemispheres is determined;
- TVP at 11 weeks is 1.4-2.3 mm, at 12 weeks – 1.7-2.4 mm, at 13 – 1.8-2.9 mm;
- the size of the heart muscle, the largest vessels, as well as the frequency of contractions are determined, normally at 11 weeks – 153-178, at 12 weeks – 150-172, at 13 weeks – 140-170 beats per minute;
- limb length;
- examination of the placenta;
- volume of amniotic fluid;
- umbilical cord and number of vessels;
- The condition of the uterus, tone, and cervix are assessed.
When performing a biochemical blood test, human chorionic gonadotropin indicators deserve special attention. If immediately after conception its quantity increases several times every day, then by the time of the first screening it has more stable indicators.
An increase is a signal of the development of genetic abnormalities, and can also be observed in diabetes mellitus and severe toxicosis. If the indicators are below normal, the cause may be fetal fading, the threat of miscarriage, the development of an ectopic pregnancy, or pathologies in the formation of the child.
Norm β-hCG in the first screening:
- from 10 to 11 weeks – 18-130 ng/ml;
- from 11 to 12 weeks – 13-126 ng/ml;
- at week 13 – 14 -115 ng/ml.
Each laboratory has its own hCG standards; the numbers may differ significantly; the consistency of the results depends on the established indicators in a given clinic. You cannot evaluate them yourself; only a doctor can do this.
The protein produced by the placenta, which determines its condition, is called protein-A (PAPP-A). If its indicators are significantly lower than normal, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage, genetic abnormalities - Edwards syndrome, Down syndrome. A slight increase is considered normal and does not have much significance for the diagnostic results.
What does the norm of protein-A (PAPP-A) show:
- from 10 to 11 weeks 0.8-4.7;
- from 11 to 12 weeks 1.2-3;
- at week 13 1.3-8.7.
Not only the amount of protein matters, but also the dynamics of growth. As pregnancy progresses, its amount should also increase.