In vitro fertilization has become so firmly established in medical practice that even people far from medicine know about the existence of this method. However, despite this, few of the expectant mothers and fathers preparing to become eco-parents for the first time can explain exactly how the IVF procedure occurs.
So what exactly is the process of creating a test tube baby?
- Additional procedures
How can you give birth if you are infertile?
Previously, the diagnosis of infertility was like a death sentence. Infertile couples had no treatment options for this disease. The marriage was falling apart. Some did not lose heart and took children up for adoption. Others simply lived alone.
In the 20th century, IVF appeared in medicine and gynecology in particular. Those married couples who have been unable to get pregnant for more than a year know exactly what this is (it is after a year of unsuccessful attempts to conceive that infertility is diagnosed). Others who have just wondered what this procedure is should begin to understand this issue.
Types of protocols
The stages of IVF and their duration depend on the type of protocol. During the consultation, the gynecologist describes in detail the artificial insemination scheme for patients. Depending on the health status of the partners, the type of protocol is selected:
- in a natural cycle;
- super short;
- short;
- long;
- using cryopreserved cells (cryoprotocol).
Regardless of the type of protocol, an IVF cycle consists of several steps. Only the duration of the stages and the scheme of implementation differ.
What is IVF?
This abbreviation stands for in vitro fertilization. The phrase means that fertilization will take place outside the mother's body. I would like this method to be trouble-free and allow all women to give birth to children, but this, unfortunately, is not the case. The technology is successful only half the time.
Moreover, the effectiveness may be even lower than 50%. The result largely depends on the health of the future parents (physical and emotional state). Therefore, it is so important to go to a clinic with experienced doctors and modern equipment. After all, in order to increase the chances of a positive result from this expensive procedure, your health needs to be brought back to normal, and without a competent specialist it will be very difficult to cope with this alone. Let's take a closer look at how IVF occurs and what it is.
ISD
In the event that it is discovered that the spouse’s sperm is of poor quality or the barrier of incompatibility is insurmountable, the couple, on the basis of joint consent, is offered artificial insemination with donor sperm. This fertilization is abbreviated as ISD. The process of introducing sperm from a donor is not much different from introducing sperm from a husband. ISD and ISM occur under the same conditions. How many times can ISD be performed? Exactly as much as ISM - from 2 to 4 times per menstrual cycle. Artificial insemination is performed by first preparing the woman’s body. On the day of favorable conception, prepared donor sperm is injected into the uterine cavity. One ISM procedure is equivalent to complete sexual intercourse. According to statistics, the effectiveness of ISM is on average 40%, and ISD in 70% of cases.
How is in vitro fertilization done?
It all starts with an examination of both men and women; they must pass many tests. This is done in order to detect diseases that may have a negative impact on the ability to conceive. If they are found, the doctor will treat them. It is very important to approach the procedure as healthy as possible. This will increase the chances of a successful IVF pregnancy.
First stage
At the first stage, general preparation of the body is carried out. After all, IVF is not a simple procedure, it involves taking many hormonal drugs and the body must be ready for this “shake-up”. The preparatory stage begins with passing all the necessary tests and examinations. It is best for a married couple to go through them at the same time.
List of examinations before IVF.
During hormone therapy, a woman should especially closely monitor the functioning of her body and immediately inform her doctor if something goes wrong. Sometimes, it will be better for a woman to stay in a clinic under the supervision of doctors for the entire IVF period. This measure is used quite rarely; usually the woman injects herself with drugs and undergoes training on an outpatient basis.
Based on the test results, an individual training course will be prescribed. From this moment on, the woman will be under close medical supervision. He must monitor the process of taking hormonal medications and do blood tests regularly. This will provide a general picture of the body’s reaction and preparation.
During this time, the man should undergo his own treatment, if necessary. Very often, men who seek help from a reproductive center have problems with the genitourinary system. In this case, he will undergo the treatment prescribed to him, which may include medications and various procedures.
Second phase
In the second stage of IVF, you need to obtain eggs. At the first stage, with the help of hormonal drugs, eggs of the required size and quality were “ripened” in the female body. Good eggs are fertilized well. At the second stage, drugs are prescribed to stimulate superovulation. At the right time, the required number of eggs for IVF will be removed from the follicles. Let's take a closer look at how this happens?
Using ultrasound, doctors observe how the follicles grow. At the right moment, when they reach the optimal size, the eggs will be extracted using puncture. The puncture is made with a special long needle. Naturally the question arises, does it hurt? This is written about in great detail and shown in the video here.
Follicle puncture during IVF.
The operation is performed in a gynecological chair in a lying position. The puncture is performed under intravenous anesthesia. The woman won't feel anything. The needle is monitored using ultrasound; accuracy in this matter is extremely important. The specialist must have the necessary experience so as not to damage the fallopian tubes or ovaries.
The operation itself lasts about 10 minutes. After this, the woman comes out of anesthesia and remains in a supine position for about 20 minutes. And after a couple of hours she can go home. All collected genetic material of a woman is sent for storage. The eggs will be kept in a favorable environment until the next stage.
Third stage
In order for the long-awaited pregnancy to occur, something else is needed. It's the man's turn to contribute to the common cause. He must donate sperm. This is usually done independently in a special room at the clinic. Once the man's genetic material has been obtained, fertilization can begin.
This method of fertilization is used in standard IVF.
Typically, fertilization occurs in test tubes or in special containers. They combine male and female cells without outside help. Fertilization occurs. Sometimes additional fertilization methods may be needed, such as ICSI, PIXI or IMSI. These technologies are usually used for the second IVF, when the first failed. They are described and shown in more detail here.
This is how egg fertilization is done using ICSI.
After this, the process of growing embryos begins. They will be in special conditions for several days. Usually, when the embryo reaches the age of 5 days, it is implanted into the expectant mother. Five-day embryos (blastocysts) take root better than others (read more about this here).
Final stage
After the embryos are grown to the desired state, they will need to be transferred into the uterine cavity. This stage is called transfer (another name for replanting). It is not as scary as a puncture; it is done without anesthesia. If the patient is still in pain, she can be given local anesthesia. Next, using a special catheter, the embryos will be transferred to the uterus.
Transfer of embryos to the uterus is done without anesthesia and occurs in 10-15 minutes.
You can transfer no more than 3 embryos. Now they are trying to transfer one embryo to exclude multiple pregnancies, which are very dangerous for the mother. The procedure lasts about 10 minutes. After the transfer, the woman remains in a lying position for about an hour. After rest she can go home.
From this moment on, the woman begins taking hormonal maintenance medications prescribed by her doctor. This course is prescribed to prepare the endometrium of the uterus for successful embryo implantation.
In addition, a woman should take drugs to increase uterine tone and sedatives. Stress at this time can be detrimental to the unborn child; implantation may not occur. Therefore, it is very important not to work at this moment, but to be at home in a comfortable environment. The slightest physical activity should be completely excluded (even house cleaning). It is best to go on a two-week sick leave, which can be prescribed by a clinic doctor.
Japanese way
The essence of the technique is to use several oocytes in patients with weak follicles. The biomaterial used must produce high quality embryos. If the ovaries are severely depleted, there is no point in stimulating the maturation of follicles.
When choosing the Japanese method, IVF is carried out over several menstrual cycles in a row.
A mandatory stage of the procedure is cryopreservation of embryos. This manipulation is considered necessary due to the use of a device that slows down the growth of the endometrium. The likelihood of the embryo's viability is unlikely. In the subsequent menstrual cycle, the effect of hormones ceases, and the conditions for the development of the embryo become as favorable as possible.
The Japanese type of IVF allows you to avoid complications due to its gentle nature.
When can pregnancy be confirmed?
After 14 days, pregnancy can be shown by a regular pregnancy test. However, it is best to do an hCG test. This test shows the onset of pregnancy more accurately. In addition to this analysis, an ultrasound examination will be performed 3 weeks after the replantation. Only after an ultrasound can the doctor say with confidence whether pregnancy has occurred or not and whether everything is okay with the fertilized egg (it may be empty).
If pregnancy has begun, it must be continued and supported with medications prescribed by the doctor. If the embryo does not implant and pregnancy does not occur, the uterus will clear itself during menstruation. In this case, you need to try to gather your strength, recover and do a second IVF. According to statistics, it is the second artificial insemination that is more effective than the first.
Peculiarities
IVF is a procedure in which an egg is collected from a woman using a puncture method, then it is fertilized under special conditions, and the grown embryo is implanted into the uterus. The IVF protocol involves hormonal preparation before puncture, as well as hormonal support for pregnancy after embryo transfer.
The indication for artificial insemination is female and male infertility. It is diagnosed if conception has not occurred within a year of constant unprotected sexual life.
The procedure is not performed if the parents have a history of serious genetic pathologies that are likely to be passed on to the child, if the woman is mentally ill. Also, the procedure is contraindicated in case of pathologies in a woman, when it is not possible to bear a child.
The final stage of the procedure
How IVF is done is described in detail in this article. If the procedure is completed positively, then the woman is asked to register at her place of residence. In some cases, the clinic takes responsibility for managing pregnancy until a certain period. This is usually required for multiple pregnancies.
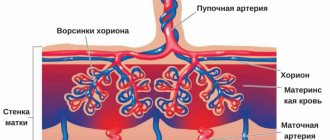
Hormonal support is provided for up to 15-20 weeks. After this, all drugs are gradually discontinued. At this time, the placenta, which supplies the fetus with everything it needs, is already formed and working at full capacity.
Basic methods
The in vitro fertilization procedure can be divided into groups and subgroups. Among the set of methods, two forms of manipulation stand out:
- IVF in a natural cycle (EC) - involves manipulation without the use of stimulating drugs, when female gametes mature under the influence of their own hormonal levels;
- IVF in a stimulated cycle - the procedure is carried out using modern medications that cause superovulation in a woman.
Preparation for IVF and the artificial insemination procedure itself is called a protocol. The protocols in IVF are as follows:
- super-long (2-6 months) - before receiving eggs, a woman takes hormones that force the body to plunge into an artificial menopause;
- long protocol (6-8 weeks) – begins from the 20th to 25th day of the menstrual cycle and involves the use of hormones that make the ovaries completely under the control of specialists;
- short protocol (one cycle) – starts from 3-5 DC and involves the use of stimulant drugs without prescribing gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists.
- super short or Japanese - prescribed to women with disabilities and involves the use of minimal doses of stimulants.
Assisted reproductive technologies allow you to use additional capabilities:
- cryoprotocol – previously frozen embryos are transferred without superovulation stimulation (eggs can also be frozen);
- ICSI – necessary when the quality of sperm decreases; it involves the intracytoplasmic introduction of a male cell into a female one;
- protocol with donor material – involves the use of a donor egg or sperm;
- GIFT – embryo transfer is carried out not into the uterus, but into the cavity of the fallopian tube, which creates the maximum naturalness of the process.
A woman cannot decide for herself how the process itself will go. The duration and type of protocol, along with additional methods, are selected in accordance with the performance of the reproductive organs.
Contraindications you need to know about
Before IVF is done, the woman must be thoroughly examined. If any contraindications to manipulation are identified, then you should avoid it. These include the following situations:
- therapeutic and psychological pathologies incompatible with pregnancy;
- deformation of the uterine cavity, in which the attachment of embryos is unlikely;
- tumors of the uterus and ovaries, which can grow with hormonal preparation;
- malignant diseases even in the stage of regression;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs of a woman or man.
In each situation, the couple is considered individually. If contraindications are identified, the specialist will definitely inform you about this.