Reasons for appearance
What is sciatica? In 95% of cases it develops due to osteochondrosis and only in 5% - as a result of injuries, wear of discs and vertebrae. Osteochondrosis, in turn, develops with physical inactivity and increased weight. The causes of radiculitis may be:
- spondylosis;
- intervertebral hernia;
- tumors;
- arthritis;
- anomalies in the development of the spinal column (sacralization, accessory ribs, vertebral aplasia).
Provocateurs include hypothermia, infections (LUES, TBC, meningitis, influenza, tick-borne encephalitis), and back injuries.
Often sciatica occurs due to the inability to distribute the load on the spine and correctly lift weights and objects from the floor. High heels for women increase the load on the lower back and knees. This gradually leads to the appearance of muscle tension. Improper lifting of weights and sudden bending lead to stretching or rupture of the fibrous disc ring, as a result of which the gelatinous substance of the disc protrudes outward and an intervertebral hernia occurs.
Compression of the root in these cases causes severe pain. Radiculitis often occurs during pregnancy, when there is intense weight gain, hormonal changes, and the spine and muscles are not ready for this.
Radiculitis is often caused by psychosomatics, especially in women. Their back muscles are often the result of unresolved negative emotions. Such clamps are easier to treat than organic lesions of the spine. Psychosomatics explains the appearance of muscle tension by saying that stress causes constant tension in the body, negative emotions accumulate. Outwardly, this manifests itself as prolonged muscle spasms as a response. Moreover, all muscles that can contract are spasmed.
Radiculitis and its symptoms: causes in men
Radiculitis is a pathological condition that affects the nerve fibers of the spinal cord. The disease is accompanied by pain in different parts of the back and impaired motor abilities.
The type of radiculitis is determined by the location of the affected tissue. The most common is lumbosacral radiculitis.
The acute form of lumbar radiculitis is characterized by short-term manifestations, so patients rarely consult a doctor during this period. The lack of adequate treatment leads to the formation of a chronic form of pathology, in which attacks of pain become more frequent and more intense.
Radiculitis is not considered an independent disease, but is regarded as a sign of the development of back diseases. The main cause of radiculitis is spinal osteochondrosis and its complications - intervertebral hernia, protrusion.
To understand how to cure radiculitis, you should also know its causes. Since sacral radiculitis is a set of symptoms, therefore, there are many reasons for its appearance:
- Vertebral injuries;
- Disease, for example, arthritis;
- Osteochondrosis. In 95 cases out of 100, the causes of the disease are its manifestations;
- Osteophytes are bony protrusions resulting from pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Heavy load in the lumbar region, as well as hypothermia;
- Physical inactivity as a result of a sedentary lifestyle;
- Pregnancy - significant manifestations can occur in the third trimester, when the center of gravity shifts due to sudden weight gain;
- Sciatica;
- Stress, poor diet, colds.
Constant attacks of radiculitis are most often caused by:
- Chills;
- Excessive physical training;
- Hypothermia;
- The sharpness of movements of the lumbar vertebra.
The disease can develop against the background of various problems in the body, which include:
- narrowed vertebral canals;
- spinal injuries;
- destructuring of intervertebral discs;
- hernia;
- tumor.
All these factors can affect the dysfunction of the medullary root and provoke the appearance of radiculitis in both women and men.
The most common causes of the development of such a painful symptom as radiculitis are the following diseases:
- intervertebral hernia;
- osteochondrosis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- dystrophy.
Another name for lumbar radiculitis is “lumbago,” which means the location of the problem is the lower back (“lumbus”). The lumbosacral type of radiculitis is more common than other types.
This form of the disease manifests itself as a result of mechanical destruction of joints, intervertebral discs, ligaments, muscles, and fibers in the back area. Such dystrophic changes are called discogenic lumbosacral radiculitis and sciatica.
In the first case, the roots of the spinal cord are affected, and in the second, the sciatic roots. Symptoms of lumbosacral radiculitis are similar sensations of pain inherent in other types of this disease.
Often, people confuse radiculitis with other diseases with similar symptoms. For example, with varicose veins or damage to internal organs. The main signs of radiculitis are as follows:
- The pain is sudden in nature, it tends to disappear and then reappear in a more intense manifestation;
- In a lying position with the leg raised up, the pain becomes much stronger;
- If a person suffering from radiculitis tries to get up from a lying position, he will unconsciously bend his leg;
- When coughing or sneezing, the pain becomes much stronger;
- When the head or body is tilted (depending on the location of the disease), the pain syndrome increases;
- A person feels much better being in a stationary position;
- The exacerbation of symptoms occurs mainly at night;
- Sweating increases and complexion changes.
Symptoms of radiculitis in women may be similar to signs of a disease of the reproductive system. This is how urological, gynecological and even sexually transmitted diseases can manifest themselves.
Signs of radiculitis in men resemble in their manifestation symptoms of diseases of the kidneys, pancreas or gall bladder. But, it should be remembered that in both cases there may be exceptions.
Treatment can be medicinal and non-traditional. Doctors prescribe non-steroidal drugs with an analgesic effect. In addition, local products can be used - ointments, gels, rubs. Radiculitis is also treated with hirudotherapy, acupuncture, visiting a Russian bath, massages, manual therapy, and surgery.
Medicines used for treatment include non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics, glucocorticoids, vascular drugs and antihypoxants, antibiotics, chondroprotectors, neuroprotectors, blockades.
When a lumbago occurs, you should take Ibuprofen or Ortafen, Diclofenac tablets. If the indicated drugs are not at hand, if the pain intensity is low, you can take analgesics: Paracetamol, Metamizole, Pyraminal, Butadione and Indomethacin.
After this, the patient should take a comfortable position and lie down in a warm bed. Glucocorticoid drugs are prescribed when the long-awaited effect is not obtained.
They are able to relieve inflammation and perform decompression. These are Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone, Lemod, Medrol, which will need to be taken as prescribed.
If damage and regeneration of the roots are detected, biological stimulants are prescribed - Plazmol, aloe extract and FiBS. Rubbing is also used in the sore area:
- Camphor alcohol;
- Formic alcohol;
- Chloroethyl;
- ointments based on snake or bee venom;
- Novocaine.
A patch (pepper or Nanoplast) can also be used.
The main thing when detecting signs of the disease is to immobilize the patient, providing him with rest and bed rest. If possible, the affected area should be secured with a special corset. It is very important that the surface on which the patient will be located is hard and straight.
After drug treatment, through which normalization of general well-being is achieved, restorative procedures are prescribed. Most often, massage, physiotherapy and acupuncture are practiced.
There are several ways to treat radiculitis with folk remedies:
- It is necessary to apply fir oil to the area affected by the disease using massaging movements. The greatest effectiveness can be achieved if the procedures are carried out after taking a bath;
- For radiculitis in the lumbar region, a mixture of grated potatoes and gasoline helps a lot. Both components must be in equal proportions;
- Pork fat and finely chopped garlic must be mixed in a 2:1 ratio. Apply the resulting ointment with rubbing movements onto the affected area;
- Warm compresses from grated radish can significantly eliminate painful signs of the disease. To do this, you need to wrap the vegetable pulp in some kind of fabric, wrap it with parchment on top, and then insulate it again by wrapping it all with another layer of fabric;
- Burdock soaked in cold water must be applied to the sore spot and secured with a bandage. After some time, the pain will subside;
Symptoms
Radiculitis often occurs against the background of lumbar osteochondrosis ; the disease can occur in acute or chronic forms. The first sign of the disease is lumbago, accompanied by sharp pain.
can occur in a latent form for a long time until it transforms into an acute form. The symptoms of the disease are very different; most often the patient feels wandering pain in the lumbar region, neck, and legs.
Such manifestations are often accompanied by a burning sensation in the extremities, sensory disturbances, tingling, and numbness. The disappearance of sensitivity is associated with compression, which makes the normal transmission of impulses between neurons difficult.
A significant increase in pain during coughing and sneezing indicates a chronic form of radiculitis.
Classification of the disease
Radiculitis is divided according to the location of the lesion in 4 main sections of the spine: cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral. The course can be acute or chronic. Radiculitis is primary and secondary:
- Primary include any acquired pathology that causes radiculitis.
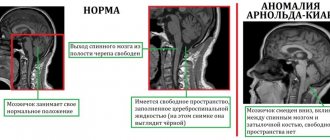
- Secondary - radiculitis with congenital anomalies of the spinal cord and spine.
Most often, lumbosacral radiculitis occurs due to the increased load on this part of the back.
How to treat sciatica
To restore the range of motion of the spine, the human body needs moderate physical activity. This method not only stops the process of vertebral degeneration, but also improves muscle elasticity. Patients often feel relief as a result of gymnastic exercises. If gymnastics does not help, then it is recommended to treat lumbosacral radiculitis by choosing a different approach. Is it possible to treat lumbar radiculitis in several ways?
Doctors do not prohibit combining therapy methods if they benefit the patient. No matter how many methods exist, they all answer the question of how to quickly cure sciatica.
There is a multivariate therapy to relieve pain from this disease, which helps to forget forever about the question of what to do with radiculitis. For example, if you have acute radiculitis, then in its initial phase it is recommended to use a warm heating pad or ice packs. They need to be applied to the sore spot for about 20 minutes.
Diagnosis of lumbar radiculitis
It is very important to correctly diagnose the disease and consult a specialist in time. The effectiveness of treatment will largely depend on this. In this case, the diagnosis must be detailed and comprehensive.
First of all, it is necessary to find out which specific spinal roots and vertebrae are under attack due to radiculitis. A comprehensive study is required:
- To begin with, specialists collect a complete medical history of the patient.
- The next step is to determine exactly how long the disease has been progressing. Typically, lumbar radiculitis begins quite acutely, with obvious symptoms already at an early stage of the disease.
- A thorough external examination of the back is required. Palpation is carried out. This is how the doctor can accurately determine the source of pain. A spinal root or a nerve that is inflamed is detected.
- A general urine test is performed. It is necessary to exclude renal failure. This is very important, since it is kidney failure that has a number of symptoms that are very similar to the signs of lumbar radiculitis. It is necessary to make sure that the doctor is dealing with radiculitis in order to prescribe the correct treatment and correctly administer drug therapy.
- A general blood test is also required. It helps determine whether there is an inflammatory process in the patient's body. Inflammation is usually indicated by an increase in the level of white blood cells and lymphocytes in the blood. ESR analysis is also carried out.
- Now there is a good modern method for diagnosing the disease - computed tomography. With its help, the doctor will be able to find out whether there are infringements of the spinal roots. Foci of inflammation are also visible on computed tomography.
- X-ray of the spine also does not lose its relevance. The study gives good results: it is possible to determine the specific places where the spinal roots are pinched.
- It is important to diagnose the condition of the spinal nerves. To do this, electromyography is performed.
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which is a more in-depth study, is of great importance. It also determines the exact localization of infringements and inflammations. In this case, such a study reveals the specific force with which the spine compressed the spinal root. Unfortunately, functional innovative equipment for MRI is not yet available in all medical institutions.
Symptomatic manifestations
The first signs of radiculitis are pain and loss of sensitivity. The main symptom is pain. At first it is diffuse, similar to myositis or lumbago. When a radicular syndrome is formed, it is localized.
Cervical radiculitis is localized in the neck, its pain intensifies with any movement of the head, so the patient keeps his head in one inclined position (increased lordosis). The pain is one-sided, the tone of the neck muscles is increased. Due to the onset of pain, dizziness may occur and gait may become uneven. This is the result of impaired blood circulation in the brain.
Thoracic radiculitis - with radiculitis of this part of the spine, severe girdle pain is felt throughout the chest, radiating to the arms. The extension of the fingers and hand is impaired, swelling and coldness of the skin of the hand appears. Cardialgia and compression behind the sternum - spondylocoronary syndrome - may appear. Nitroglycerin is not effective.
Lumbosacral radiculitis - pain occurs with any movement or bending. It spreads to the buttocks, thighs, and feet. When suffering from lumbar radiculitis, the pain dulls at times, but with any movement it returns and intensifies. At the onset of the disease, lumbar radiculitis occurs as lumbago, lumbodynia and lumboischialgia.
With lumbago in the lower back, a sharp, sudden sharp pain appears in the lumbar region (lumbago), which occurs more often when muscles are overstrained: lifting weights, hypothermia, or sharp bending. Movements in the lower back are sharply limited, muscle tone is increased, and they are painful on palpation. Lumbar lordosis disappears. It is impossible to stand or walk.
Lumbodynia is a dull, low-intensity but constant pain. It is impossible to walk or sit. Symptoms of tension become weakly positive:
- Lasega - lying on his back, the patient raises his leg, and pain appears from the lower back to the buttocks and foot;
- Wasserman (Matskevich) - when lying on your stomach, trying to raise your leg gives pain in the thigh, lower leg and groin.
With lumboischialgia, pain in the lower back can be acute and subacute and radiates to the leg. Then the patient is forced to look for a protective forced position: when lying on his stomach, put a pillow on him, sit with his leg bent under him, resting his hands on the bed. When walking, the support is on the healthy leg.
The second most common symptom is complete or partial loss of sensitivity in the area of innervation of the affected root. And this applies to all its types. Severe radiculitis can lead to leg paresis, muscle weakness and atrophy, and the appearance of paresthesia and burning sensation in soft tissues. Defecation and urination may be impaired. Symptoms include:
- sluggish reflexes;
- vegetative symptoms in the form of increased sweating;
- paleness of the face;
- worsening at night.
All these signs distinguish radiculitis from other pathologies of the back and legs.
If we are talking about primary radiculitis, it is supplemented by symptoms of the underlying disease. For example, with ARVI it can be fever, rhinitis, chills, etc.
When it comes to radiculitis in women, the question always arises whether their lower abdomen can hurt as a manifestation of clinical symptoms, since this is a woman’s sacral zone. The answer is that women do not experience abdominal pain with radiculitis. Women also take a forced pose - on their sides, backs, all fours. The nature of the pain in the lower back is pulling and aching along the entire surface of the leg to the foot.
Characteristic for women are paresthesias of the legs and impaired movement in them. Frequent, painful urination is also typical for women.
Signs of radiculitis in women generally do not differ from those in men. The symptoms are the same, but the frequency of pathology is less common. The only peculiarity of radiculitis in men is the addition of manifestations of impotence and erectile dysfunction.
Surgical treatment
If the patient’s health does not improve within 3-4 months, the attending physician will suggest treating radiculitis with surgery. The operation is performed if:
- Manifested neurological signs;
- Degenerative changes in the discs;
- Obvious disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
There are several types of surgical intervention. In a minor open surgery, one intervertebral disc pressing on the sciatic nerve is removed. If spinal canal stenosis is detected, and the patient finds it difficult to tolerate the most simplified physical activities, then a laminectomy is prescribed. This surgery removes the bone where the nerve is pinched.
Therapeutic diet
To reduce the load on the spine, the patient should get rid of excess pounds, if any, and carefully monitor proper nutrition. To do this you need:
- Limit the amount of salt you consume;
- Add fortified foods (fruits, vegetables, freshly squeezed juices) to your healthy diet;
- Eat a lot of dairy products (add kefir to your diet in the evenings);
- Avoid sauces and canned foods; exclude smoked, fried, spicy, fatty foods from consumption;
- Add lean types of meat to your diet and eat fresh fish;
- The consumption of alcohol, coffee, and strong tea is strictly prohibited.
It is useful for this disease to use:
- Dried fruit compotes. If you add honey to it instead of sugar, it will bring doubly benefits. Let this drink brew in the evening. And in the morning during breakfast, you will enjoy this drink;
- Nectar from apples and celery. Done in equal proportions, it is recommended to drink twice a day;
- Lemon juice. Dilute with water and season with honey. To prepare the tincture, you will need 11 lemons, which are ground through a meat grinder, and 1 liter of honey. After preparation is completed, the mixture is placed in the refrigerator and eaten before meals three times a day, one tablespoon.
Specialists: therapist, neurologist will tell you more information about the consequences of radiculitis, symptoms and treatment.
Prevention
Preventive measures include eliminating the causes that provoke radiculitis:
- maintain correct posture;- — sleep should be on a flat surface, the ideal solution is an orthopedic mattress;
- - swimming is the best remedy against spinal diseases;
- - exclude salt from the diet if possible;
- - exclude fatty, fried, smoked foods, coffee;
- - control your weight;
- - provide the body with necessary vitamins and minerals;
- - Avoid lifting heavy objects.
Preventive actions
In addition to collecting anamnesis and examination, an X-ray of the spine, CT and MRI are required. Diagnosis of radiculitis is determined by checking the symptoms of tension:
- Bekhterev;
- Neri;
- Bonnie;
- Dezherina.
X-rays provide reliable information about the damage and its location in the spine. Osteochondrosis is usually detected. If necessary, a lumbar puncture may be performed to clarify the diagnosis; this will result in increased protein in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Prevention of radiculitis involves regularly performing therapeutic exercises, regardless of exacerbations; it will strengthen the natural muscle corset. It is necessary to exclude hypothermia and sudden movements. It is necessary to harden and normalize weight.
If you have a hard mattress, it is advisable to place a pillow under your neck and lower back. It is better to use a semi-rigid mattress. When picking something up from the floor, you only need to bend your legs, not your back. While sitting, do not drop your head forward or lower it, do not hunch.
Types of radiculitis of the lumbosacral area
Depending on how the disease manifests itself, there are three types of radiculitis: lumbodynia, sciatica and lumboischialgia.
Lumbago
Translated from Latin as “loin.” The term characterizes a sharp shooting pain in this area. Attacks of lumbago often last from several minutes to several hours, and when shooting pains are observed for many months, it is customary to talk about lumbodynia.
The mechanism for the appearance of lumbago: first, a displacement or change in the structure of the lumbar vertebrae occurs, which then causes pinching of the nerve endings.
This process leads to severe pain in the lower back, muscle hypertonicity and impaired motor activity. The muscles spasm, the patient freezes, leaning forward, and can no longer move; any action aimed at changing the position causes an attack of severe pain.
The patient cannot straighten up either independently or with outside help.
Lumbago is provoked by:
- significant physical activity;
- excessive muscle tension, for example when lifting weights (pain manifests itself at the time of exertion and continues after it);
- a sudden change in temperature, for example, when doused with ice water after a steam room.
It is expressed by the presence of shooting pain in the area of the sciatic nerve. The patient feels a burning and tingling sensation in the area of the buttocks, thighs and lower legs for quite a long time, the pain does not go away even in sleep.