Diplegia - what is it?
Cerebral palsy is one of the most common pathologies of the nervous system in children.
The spastic form of cerebral palsy occurs due to damage to the precentral gyrus of the brain, which provides motor function.
Because of this, the functioning of the nervous system, muscles, joints, brain and other organs and systems is disrupted.
The conduction of nerve impulses to the limbs is also disrupted, which leads to movement disorders.
Damage to the nervous system can be a consequence of birth trauma, or occur in utero during pregnancy.
Often, the diagnosis is made within the first 6 months of the baby's life. There is a delay in physical development: children cannot hold their heads up for a long time, sit up, and cannot crawl. Due to impaired innervation of the lower extremities, many children do not walk until they are 3-4 years old, after which normal walking is almost impossible. This is associated with asymmetrical muscle damage and tetraparesis.
The most common is spastic diplegia of the lower extremities - the arms suffer less severely with this pathology. In this case, increased tone of the foot flexor and hip abductor muscles with fully or partially preserved tendon reflexes is revealed.
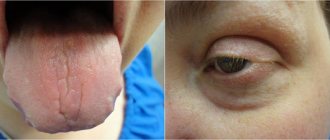
Speech development is often impaired. In some cases, hearing deteriorates. Damage to the optic nerve leads to blurred vision, strabismus, and blindness.
Diplegia was first studied by the English obstetrician Little. He was the first to describe what it is and what are the main reasons for its occurrence. Therefore, diplegia is often called Little's disease or Little's syndrome.
This type of cerebral palsy is the most common and accounts for more than 75% of the total number of patients. Children need constant care and medical supervision. Because of this, diplegia is not only a medical problem, but also a social one.
What causes lead to cerebral palsy
- Genetic factor (at the time of birth the brain is underdeveloped, defective)
- Ischemia (impaired blood supply) or hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the brain, usually during pregnancy or childbirth
- Infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy (rubella, etc.)
- Infectious diseases of the child (meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, arachnoiditis)
- Pathology of pregnancy
- Mechanical factor (trauma during or before or shortly after childbirth)
- Hemolytic disease of newborns (incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus).
Dangerous symptoms that suggest cerebral palsy in children in the first months of life:
- The baby gets tired quickly during feeding
- Lack of movements or, on the contrary, unnecessary movements
- Does not master motor skills according to age (can’t hold his head up, doesn’t roll over, doesn’t sit up, etc.)
- Convulsions
- Doesn't make any sounds
- The limbs are very tense or, conversely, flaccid.
- Moves limbs on one side only (for example, only the right arm)
Primary signs of cerebral palsy:
- Impaired muscle tone (spasticity, rigidity, hypotonia, dystonia)
- Restriction or impossibility of voluntary movements (paresis, paralysis)
- Balance imbalance
- Speech disorders
- Coordination problems (falls for no reason, nods head, makes uncontrolled movements of arms or legs)
The main problems experienced by children with cerebral palsy:
- Violation of postural control - the inability to control one’s own posture. This includes: the ability to maintain body symmetry,
- the ability to transfer body weight in all directions and return to the starting position,
- the ability to maintain a straight posture relative to gravity, the ability to move without excessive effort
- in some cases - spasticity (involuntary painful muscle contraction), uncontrolled movements of the arms or legs
Causes
The precentral gyrus gives rise to the pyramidal tracts, which are responsible for the motor function of the nervous system. For normal operation of the structure, a sufficient amount of oxygen is necessary. This is only possible if there is good blood circulation and the required amount of oxygen is supplied. When the gyrus is damaged, the transmission of impulses from the motor nuclei to the limbs is disrupted. In 40%, the pathological process is accompanied by damage to the cranial nerves.
The main causes of diplegia are:
- Prematurity – premature birth most often leads to diplegia. This is due to the underdevelopment of the nervous system;
- Intrauterine hypoxia : smoking during pregnancy, working in hazardous industries, maternal anemia and others increase the risk of giving birth to a sick baby;
- Asphyxia of the newborn - after birth there is no spontaneous breathing. This occurs when there has been an intrauterine infection, amniotic fluid enters the respiratory tract, or fetal pathology;
- Birth trauma - can occur due to complicated childbirth, a narrow pelvis in the mother, weak labor, or during the birth of a large fetus. The use of auxiliary instruments may result in birth injury to the newborn.
Important! Pregnant women with pathologies and bad habits have an increased risk of having a baby with cerebral palsy. They need constant medical supervision to reduce their risk.
Classification
Depending on the damage and clinical picture, diplegia is classified according to severity. There are three degrees of Little's disease:
- Mild – a child up to 6 months grows and develops normally. Afterwards, spastic paresis of the legs is discovered. In the future, the child can walk independently without the use of aids;
- Average – often accompanied by moderate mental damage. The child moves only with crutches due to spasticity. Normal adaptation in society is possible;
- Severe – detected in the first days of life. The lower extremities, where severe tetraparesis is noted, are more severely affected. In most cases, it is not possible to adapt a child to society.
Symptoms
Due to the physiological characteristics of young children, symptoms of spastic diplegia are often detected no earlier than 6 months after birth. This is due to the fact that normally, children under 4 months can maintain muscle hypertonicity, which is necessary for the normal condition of the fetus in the womb. This will not detect spastic cerebral palsy, since their manifestations are the same.
The main symptom of diplegia is the persistence of muscle hypertonicity in children older than six months. This may indicate a diplegic form of cerebral palsy, manifested by spastic tetraparesis and flaccid paralysis.
People with diplegia have a typical gait: their knees rub against each other, their legs are abducted and extended, they walk on their toes. The hands are practically not affected and function normally.
Depending on the degree of damage, children experience the following symptoms and manifestations:
- Easy stage – up to 6 months the child grows and develops normally. Continued increased tone of the legs and arms is the main complaint with which parents consult a doctor. The baby does not control his movements, his arms and legs are slightly bent, and it is difficult to straighten them due to their tone. The child sits up late and crawls. Begins to walk by the age of 3-4 years. Despite the difficulties in walking, it is possible to walk independently without special equipment;
- Medium – diplegia is more pronounced, which allows it to be detected earlier. The newborn does not gain weight well, lags behind in physical development, eats poorly and sleeps restlessly;
- Severe – the baby’s legs and arms are strongly compressed and cannot be straightened during passive extension. ZRR is often detected. Many are diagnosed with intellectual impairments.
In adults, the main symptoms of spastic cerebral palsy are hypertonicity and tetraparesis. Many of them can only walk with crutches or a cane. They rarely use a wheelchair.
Postures for spastic diplegia
Muscle dysfunction can be complicated by contractures and problems with the joints and spine. The patient is unable to fully straighten the joints, especially the lower extremities: ankles, knees, and less commonly the hips.
If the cranial nerves are damaged, there may be problems with other organs and systems. So, if the optic nerve is damaged from an early age, vision begins to deteriorate and strabismus occurs. Parents note that the child cannot recognize objects for a long time and does not remember the people around him for a long time. This indicates poor vision. It is also possible that the auditory nerve may be damaged, causing hearing loss. Facial paresis occurs when the facial or trigeminal nerve is damaged. In this case, facial expressions are disrupted: amymia, hypomimia, facial asymmetry, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out, the tongue deviates to the side.
In 25% of patients, mental development is impaired, leading to mental retardation. This is manifested by a violation of the mental state. They have difficulty learning and remembering new information, and it is difficult for them to play group games that require following rules. The majority are diagnosed with RRR and ZPR.
How does cerebral palsy manifest in children at 6 months?
If the child was born premature or had low body weight, if pregnancy or childbirth had any complications, parents should be extremely attentive to the baby’s condition so as not to miss the alarming signs of developing paralysis.
True, the symptoms of cerebral palsy before one year are little noticeable, they become expressive only at an older age, but still some of them should alert parents:
- the newborn has noticeable difficulties with sucking and swallowing food;
- at one month of age he does not blink in response to a loud sound;
- at 4 months does not turn his head in the direction of the sound, does not reach for the toy;
- if the baby freezes in any position or exhibits repetitive movements (for example, nodding his head), this may be a sign of cerebral palsy in newborns;
- symptoms of the pathology are also expressed in the fact that the mother can hardly spread the newborn’s legs or turn his head in the other direction;
- the child lies in clearly uncomfortable positions;
- The baby doesn't like being turned over on his tummy.
True, parents need to remember that the severity of symptoms will greatly depend on how deeply the baby’s brain is affected. And in the future they can manifest themselves as slight clumsiness when walking, or severe paresis and mental retardation.
With cerebral palsy, symptoms at 6 months are more pronounced than in the infant period.
So, if the baby has not lost the unconditioned reflexes characteristic of newborns before the age of six months - palmar-oral (when pressing on the palm, the baby opens his mouth and tilts his head), automatic walking (raised by the armpits, the baby puts his bent legs on a full foot, imitating walking) - this is an alarming sign. But parents should pay attention to the following deviations:
- periodically the baby experiences convulsions, which can be disguised as pathological voluntary movements (so-called hyperkinesis);
- the child begins to crawl and walk later than his peers;
- symptoms of cerebral palsy also manifest themselves in the fact that the baby more often uses one side of the body (pronounced right-handedness or left-handedness may indicate muscle weakness or increased tone on the opposite side), and his movements look awkward (uncoordinated, jerky);
- the baby has strabismus, as well as hypertonicity or lack of tone in the muscles;
- a baby at 7 months is not able to sit independently;
- trying to bring something to his mouth, he turns his head away;
- at the age of one, the child does not speak, walks with difficulty, relying on his fingers, or does not walk at all.
Diagnostics
A pediatric neurologist is involved in diagnosing spastic diplegia . It takes into account the results of laboratory and instrumental studies, conclusions of specialists, anamnesis of pregnancy and childbirth, and the clinical picture.
Diagnostic measures:
- Neurological examination - a specialist checks tendon reflexes to confirm hypertonicity. Particular attention is paid to the knee and Achilles reflex. Using special equipment, detects disorders of skin sensitivity;
- Electroencephalogram - carried out to study the bioelectrical activity of the brain. Necessary for differentiating spastic diplenia from epilepsy;
- Electroneuromyography – allows you to identify or refute other neuromuscular diseases;
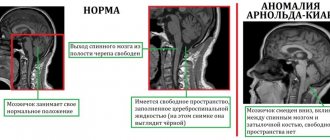
- MRI is the most accurate method for diagnosing the brain, allowing you to identify any abnormalities in its structure with an accurate determination of localization.
Reference. Before the fontanelle closes, an accessible and informative way to examine the brain is neurosonography. An absolutely safe method, which is carried out within a few minutes, allows you to identify structural changes, neoplasms and other diseases of the central nervous system.
Additionally, consultation with an ophthalmologist is required, who determines the decrease in visual acuity and examines the fundus using ophthalmoscopy.
An ENT performs audiometry to detect hearing loss.
A mental examination is carried out by a neurologist at an early age, and a psychologist in children of preschool and school age. Their task is to identify mental retardation and mental retardation and determine the degree of mental retardation.
Many symptoms of Little's disease, including spastic paraparesis, can often be detected in other types of cerebral palsy, genetic mutations, hereditary and degenerative conditions of the nervous system, and dysmetabolic disorders. Since the treatment of these conditions differs significantly, it is important to accurately determine the diagnosis.
Effective diagnostic techniques
It is important to identify cerebral palsy in newborns in the maternity hospital in order to begin treatment as early as possible. Then it will be as effective as possible. A thorough examination by a qualified pediatrician will identify warning signs.
If alarming symptoms are detected, hardware diagnostics are prescribed - ultrasound of the brain, electroneurography, electromyography, electroencephalography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
Monitoring the baby becomes the responsibility of a neurologist. Additionally, consultation with an otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist, or epileptologist may be required.
It is important to differentiate pathology from the individual characteristics of the baby. Some babies up to six months experience slight trembling of the chin and hands, and high tone of the limbs. Normally, such excitability disappears without a trace when the baby begins to crawl and stand on its feet.
Treatment
Little's disease, like other forms of cerebral palsy, is an incurable disease. There is no etiological therapy that would completely eliminate the defect. The main task of doctors and parents is to improve the general condition of the child, prevent complications and adapt him to society. For this purpose, various methods are used: conservative therapy, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises. The most effective way is to combine different methods.
Conservative therapy
Medicines improve the trophism of nervous tissue, ensure sufficient blood circulation, and relax spasmodic muscles. The following drugs are used for this:
- Neurometabolites – nourish the brain with useful components, saturate it with oxygen, improving its performance;
- Muscle relaxants – relieve muscle spasms;
- Vascular medications - dilate blood vessels, improving blood circulation and tissue trophism;
- Nootropics – indicated for improving cognitive abilities. Improves brain performance;
- Botulinum toxin is necessary for the prevention of contractures.
Important! Only a doctor after a thorough examination can prescribe medication. Using medications without a doctor's prescription can lead to deterioration in health.
Physiotherapy
The use of physiotherapeutic procedures significantly reduces the manifestations of diplegia. To achieve maximum results, it is recommended to undergo regular treatment in specialized institutions. The following procedures are often prescribed:
- Massage – helps to relax and strengthen muscles, improves blood circulation, prevents contractures. It also has a beneficial effect on the psyche;
- Electrotherapy is especially indicated when the patient is 1-2 years old. Reduces the passage of pathological impulses from the brain to the muscle. Relaxes muscle spasm;
- Mud therapy – prevents contractures, reduces arthralgia and joint complications, reduces muscle spasms;
- Ultrasound therapy – eliminates contractures;
- Magnetic therapy – relaxes and soothes the muscles.
It is permissible to undergo two physical procedures per day.
Physiotherapy
It is recommended to start exercise therapy classes as early as possible. Special exercises help prevent the development of contractures, strengthen muscles, and help maintain joint mobility. A well-chosen set of exercises will keep your child active and help him learn to walk independently earlier. With a milder course of diplegia, physical education allows you to adapt to society and become more independent.
Swimming has the best effect on the body. Exercises in water do not load the joints, have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, activating the central nervous system, while having a calming effect on the psyche.
If speech development is delayed, sessions with a speech therapist are indicated. Mental disorders are corrected with a psychologist or psychiatrist.
It is important to provide the patient with the necessary equipment for free and safe movement. For this purpose, various walking devices are used: crutches, canes, walkers. In severe cases, a person can only move in a wheelchair.
Depending on the patient's condition, the patient should be provided with comfort and safety at home. Due to muscle spasticity in this form of cerebral palsy, there is an increased risk of falls and injuries. To exclude this, relatives should provide the living space with auxiliary devices: railings, handles in the bathroom, silicone anti-slip mats, etc.
With mental retardation, patients need constant monitoring and care. It is important that all dangerous objects are out of their reach.
In some cases, relatives cannot provide full care for the child. Then it is possible to undergo treatment in specialized institutions: boarding schools, sanatoriums.
How is cerebral palsy treated?
Treatment of cerebral palsy is complex and should begin from the first weeks of life. In an infant, the brain has a great ability to recover, which helps in achieving much more significant results than at an older age.
When treating cerebral palsy, symptoms in infants are of primary importance, since therapy is strictly individual, long-term and complex. Its basic principles boil down to preventing the development of pathology in the future, as well as the occurrence of irreversible residual processes.
In the first months of life, in the treatment of cerebral palsy, medications are used to reduce intracranial pressure (dehydration using a mixture with citral or diacarb, and magnesium is administered intramuscularly). At the same time, drugs are used that increase metabolic processes in the child’s brain (B vitamins).
Great importance is also given to the use of drugs that stimulate the development of the nervous system (glutamic acid, Aminalon, vitamin B6, Nootropil, etc.).
If the symptoms of cerebral palsy manifest themselves in increased excitability of the baby, then sedatives are indicated for him, and convulsive syndrome is treated with such drugs as Luminal, Benzonal, Chlorocon, etc.
Particular importance is attached to physical therapy, special massage, as well as stimulation of mental development through speech therapy and pedagogical classes.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery is not favorable. Little's disease is an incurable diagnosis for which no treatment has yet been developed. Provided that all doctor's recommendations are followed, patients can live to old age. Due to persistent defects, they cannot lead a full life and need help and care. When choosing a profession, health characteristics are also taken into account. In severe cases, the person is unable to work and needs 24-hour care. With a mild course and normal mental state, it is possible to lead a full lifestyle, subject to regular preventive treatment.
What do you need to remember?
- Spastic diplegia is the most common type of cerebral palsy;
- The main causes of diplegia are birth injuries, fetal hypoxia, and pregnancy pathologies;
- Diplegia is classified into mild, moderate and severe stages of severity;
- Diplegia is characterized by muscle hypertonicity, most pronounced in the lower extremities;
- The diagnosis is established on the basis of neurological examination and examination of the brain;
- Therapy is aimed at preventing the progression of disorders;
- The prognosis for recovery is not favorable;
- The pathology is complicated by contractures, joint pathologies, and muscle atrophy.
Literature
- Badalyan L.0., Zhurba L.T. Cerebral palsy. - Kyiv: 1988. - 245 p.
- Semenova K.A. Questions of the pathogenesis of cerebral palsy. //Journal neuropathol. and a psychiatrist. - 1980. - No. 10. -P.1445- 1450.
- Badalyan L.O., Zhurba L.T., Timonina O.V. Questions of classification of cerebral palsy // Journal of Neuropathology and Psychiatry. - 1987.- No. 10. - P. 1445-1448.
- Hagberg V., Hagberg G., Olow 1. //Acta.Paediatr. - 1993. - Vol.82. — P. 387-393. (thirty)
Drug treatment and surgical assistance
For this disease, the doctor calculates the therapeutic course individually. Usually nootropic pharmaceuticals are recommended to improve cerebral blood supply, muscle relaxants, antidepressants, antipsychotics, antispasmodics.
Surgical treatment is used in cases where conservative methods are powerless. This may involve brain surgery to correct neurological defects. Spinal rhizotomy helps relieve muscle hypertonicity, which leads to severe pain. To stabilize the skeletal structure, tendon or bone transplantation is possible, most often on curved limbs.
Cerebral palsy is a chronic disease, but not progressive. With the right therapy, noticeable improvements in the child’s motor abilities are possible. But due to the immobility of muscles and joints, the disease can lead to pathological consequences: hemorrhages, problems with eating, and somatic diseases.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor. Be healthy!
Treatment of cerebral palsy always occurs comprehensively and continuously. The earlier it was started, the better results can be achieved. It is believed that the most visible results can only be achieved by treating a disease that was identified in the first months of life, which is very difficult to do with cerebral palsy. The brain has the ability to recover only in infancy, and this diagnosis, as a rule, is made to the child later. This explains the difficulty of timely diagnosis and the duration of treatment for cerebral palsy.
With cerebral palsy in newborns, symptoms can vary. Therefore, the treatment of infants is strictly individual and depends on the type of symptoms. First of all, it is aimed at preventing further development of the disorder. Infants are prescribed medications that can reduce intracranial pressure.
Great attention is paid to stimulating the development of the nervous system. For this purpose, medications such as Aminalon, Nootropil, glutamic acid, etc. are prescribed. Convulsive symptoms are relieved with the help of Luminal, Chlorocon and Benzonal, and in case of increased excitability, sedatives are prescribed.
However, for cerebral palsy, treatment with medications alone is not enough. Special massage and physical therapy play an equally important role here. Only constant and long-term lessons will help the child learn new movements and learn to do something without outside help. Success largely depends on the perseverance of the parents, since massage and exercises must be repeated every day.
Physiotherapeutic methods are also used in treatment, such as heat and mud baths, balneotherapy, ozokerite, acupuncture, shiatsu, electrophoresis, etc.
The use of a “spiral” suit leads to good results. By stimulating the body's various capabilities, it can reduce muscle spasticity and help the child acquire new motor skills. This costume is not the only one of its kind. Orthopedic pneumatic overalls and an Adele suit can also work wonders. After using them, many disabled children took their first steps.
The mental state of the mother also plays an important role in the upbringing and treatment of a sick baby. A disabled child is often capricious and does not do exercises, does not allow massage, etc. Here you need to turn on your imagination and introduce game moments into the physical education process. For example, a child will gladly try to pick up candy from the floor than anything else, and try to help his mother in some way if she praises him for any achievements.
It is important that cerebral palsy is not a disease that tends to progress. Therefore, do not lose hope and give up! The future of a child with cerebral palsy depends entirely on the parents, on their patience, strength and desire to help their child.