The human body is inhabited by many tiny “tenants”. Taken together, this is a whole system with its own irreplaceable functions. It weighs about 2 kg. It consists of 10 14 cells, which is tens of times the number of structural elements of the host itself.
The favorite habitat of microorganisms is the intestines. Useful species help in the breakdown and absorption of food, in maintaining biochemical balance. Pathogenic bacteria do not interfere with them, but only for the time being. Various factors can disturb this “idyll”. Read on to find out how to restore it.
Normal intestinal microflora: lactobacilli + bifidobacteria
Beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract produce a number of enzymes to break down nutrients. The absorption of vitamins A, E and D, the production of B vitamins, biotin, ascorbic, nicotinic, and folic acids are also provided by representatives of normal intestinal microflora. They are involved in the formation of immunity and the fight against pathogenic microbes.
Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria normally make up 90% of the intestinal microflora. The content of these same microbes in the digestive canal of an adult should be at least 80%. The imbalance of intestinal microflora is called “dysbacteriosis”.
The ratio between beneficial and harmful microbes is disrupted after taking antibiotics, with food poisoning and helminthic diseases. The risk group includes children and the elderly, as well as people who often experience stress and are malnourished. Rotavirus infection also has an adverse effect on the intestinal microflora. Read more about the drugs used for treatment here.
Diet for pregnant and lactating women with microflora disorders
For intestinal dysbiosis in pregnant and lactating women, diet is the safest treatment measure. To normalize metabolic processes and the functioning of the digestive tract, it is recommended to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
The diet is based on porridge, lean meat and fish, which are steamed, stewed or boiled. Vegetables, fruits and herbs are also useful. They can be consumed fresh or cooked - this should be decided by the doctor. Fruits are acceptable in the form of fruit drinks, compotes, and purees.
Dysbacteriosis and its manifestations
An imbalance of beneficial microflora in the intestines is called dysbiosis. It manifests itself as follows, depending on the severity of the problem:
- Regular bloating, discomfort and rumbling in the stomach in the morning and after meals. If these symptoms are not caused by a one-time intake of mixed or low-quality food, then it is worth reviewing the diet, adding more vegetables and fruits to the diet, and not mixing foods that have different digestion times.
- Decreased appetite, alternating constipation and diarrhea, nausea, unpleasant taste in the mouth, bad breath, bloating accompanied by pain in the intestines.
- The intestines become inflamed, it stops working fully, feces lose their homogeneous shape, and food comes out undigested. In addition to problems with the digestive tract, a person suffers from chronic fatigue, as he develops anemia.
Consequences of intestinal microflora imbalance:
- disorders of all types of metabolism in the body;
- drop in enzymatic activity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- weakened immunity;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- deterioration in the appearance and properties of the skin;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disorders of the respiratory system, heart, blood vessels.
Important! Folk and home remedies are most effective when used only in the early stages of dysbacteriosis. In more serious cases, you should definitely consult a doctor.
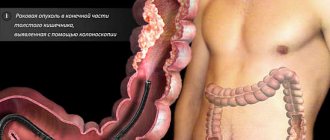
Doctors receive information about the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic intestinal microflora from a coprogram and bacteriological examination of stool. Only after studying the test results is the patient prescribed treatment. For dysbacteriosis in older people, colonoscopy is often used - the introduction of an endoscope to examine the surface of the colon from the inside and identify polyps.
Diagnostic methods
Only a doctor can diagnose dysbiosis. Therefore, you should not thoughtlessly start taking products to restore microflora. The doctor will collect information about the symptoms, their duration, and degree of manifestation. He will perform palpation in order to initially exclude concomitant diseases, after which he will prescribe a series of tests. Be sure to carry out blood tests for general, biochemical analysis, and feces in order to determine the possible cause and extent of the disease. If necessary, an endoscopy is performed, in which a smear is taken from the intestinal walls to determine the bacteria. Colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, fluoroscopy, irrigoscopy or gastroscopy procedures are less commonly prescribed as informative ways to assess the condition of the intestine.
These measures are necessary, because without knowing what bacterium has infected the intestines, it will not be possible to find an effective treatment. It is important to remember that any negative manifestation of the disease must be suppressed before serious complications arise, such as intoxication of the body.
Reasons for the development of dysbiosis
A person, and therefore his body, is constantly influenced by many factors. Some contribute to imbalance and disorder in the functioning of its internal systems. The intestinal microflora is no exception.
Dysbacteriosis can lead to:
- taking medications - antibiotics, hormonal and others;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- infectious intestinal diseases;
- endocrine diseases;
- helminthic infestation;
- poor nutrition;
- change in climate and water due to relocation, travel;
- stress and unhealthy lifestyle.
Not all problems are caused by the person himself - sometimes circumstances lead to the fact that the digestive system cannot function normally. However, both voluntary and involuntary unfavorable factors can be minimized without taking the problem to the extreme.
Restoring the balance between “good” and “bad” bacteria
In infectious diseases and prolonged diarrhea, pathogenic microbes in the intestines are activated. At the same time, beneficial species are suppressed and their numbers are reduced.
What to take to restore intestinal microflora:
- Prebiotics that create conditions for the growth of beneficial microflora.
- Enterosorbents for binding and removing harmful metabolic products.
- Probiotics with cultures of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and E. coli.
- Enzymes to facilitate the work of the digestive glands and stomach, small intestine.
- Vitamins to improve metabolism and restore intestinal function.
- Folk remedies for diarrhea or constipation.
Complex therapy includes treatment of the primary disease, so doctors prescribe antibiotics and intestinal antiseptics. The doctor must choose the drugs taking into account the causative agent of the disease. The doctor also prescribes medications for helminthic and parasitic diseases.
Drug therapy
Various medications are used to normalize the intestines. They can be divided into several groups:
- Probiotics. They are also called toothiotics. Such products are natural, as they are based on bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. There are two types of dentists:
- single-component – represented by Lactobacterin, Baktisubtil, Normoflorin-L (B), Bifidumbacterin;
- multicomponent - represented by Linex, Acylact, Normorphlorin-D, Acipol, Narine.
- Prebiotics. They include a nutrient medium - it is necessary for the proliferation of the necessary microorganisms. Among such drugs are Hilak-forte, Duphalac.
- Synbiotics. This group is a complex of previous drugs. It includes Bifidobak, Laminolact, Bifidumbacterin-multi.
- Antibacterial agents. They suppress the proliferation of pathogenic environments. They often resort to Tetracycline, Metronidazole, Penicillin.
The course of treatment depends on the factors that caused dysbiosis. For example, to recover from antibiotics, antibacterial agents are first used, and then medications from probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics are used.
Solutions, tablets or capsules with probiotics are taken for at least two weeks to prevent imbalance of intestinal microflora during antibiotic treatment. Therapy for dysbacteriosis against the background of helminthic infestation and chronic diseases of the digestive system takes longer - from 4 to 6 weeks.
Treatment after poisoning is different. In this case, restoration of not only the intestines, but also the stomach is required. In addition to probiotics and prebiotics, you will need digestive enzymes. Usually these are Creon or Panzinorm tablets.
And here you can learn about the most effective drugs for the treatment of dysbiosis.
Enterosorbents - “sponges” for toxins
Sorbents reduce the growth of pathogenic microflora and promote the removal of toxic substances from the intestines. They take drugs from this group after poisoning, for infectious and allergic diseases. A side effect of enterosorbents is constipation. Therefore, during treatment, increase water consumption.
Modern enterosorbents:
- Lactofiltrum.
- Enterosgel.
- White coal.
- Smecta.
Entrosorbents are not absorbed by the intestinal walls; they only bind toxins released during the digestion of food and the activity of harmful microbes. They are then excreted with metabolic products. Sorbents usually do not absorb large molecules of nutrients and vitamins, but with long-term use they reduce their amount.
Important! If during treatment you still experience frequent constipation, the body’s protective functions decrease, weakness and apathy appear, you need to visit a therapist - perhaps the reason is not dysbiosis at all, but another disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
Probiotics
It is easier to restore the microflora by introducing “good” microorganisms into the stomach by taking live cultures in the form of probiotics. There are several groups:
- Single-component ones - “Bifidumbacterin”, “Acipol”, “Lactobacterin”, “Profifor”.
- Multi-component - “Linex”, “Bifiform”.
- Compositions with a competitive effect - "Baktisubtil", "Enterol", "Baktisporil" - spores for displacing pathogenic microflora without colonization.
Lactobacilli
The active formula contains live lactobacilli, endowed with immunomodulatory properties. Bacteria are able to form a protective layer and suppress “bad” microflora. The drugs are mono- and multi-component, which are available in the form of tablets, powders, and suppositories. The peculiarity of the treatment is compatibility with antibiotics, no age restrictions.
Bifidobacteria
The gastric flora contains these microorganisms in the overwhelming majority. Bacteriacins have an antimicrobial effect, therefore preventing the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. If they are lacking, conditions are created for the development of staphylococci and Candida fungi. The drugs of choice are Biovestin, Probiform, Bifinorm. Available in the form of tablets, suspension, powder, suppositories.
Collections of bacteria
The drug has no age restrictions and excellent compatibility with antibiotics.
The basis of the active formula is eubiotics. The representative of the group is “Linex gastro”, containing lactobacillus, a bifidobacterium of animal origin. This composition accelerates the regeneration of flora. Features: no age restrictions, excellent compatibility with antibiotics. But if you are prone to allergies, you should take the drug with caution and only as prescribed by a doctor.
Other drugs
Popular alternatives to the above drugs are:
- Bifikol powder based on Escherichia coli;
- protective capsule "Bifiform" with enterococci faecium (feature - dissolution of the shell at the right time in the required area of the gastrointestinal tract);
- Duphalac and Romphalac are prebiotics with lactulose, which additionally restore blood pressure.
- "Hilak Forte" with a prebiotic formula (a special feature is the possibility of use for prevention).
Folk remedies
In normalizing microflora, you should not neglect folk remedies. They can cope well with minor problems or complement drug treatment. Traditional medicine usually means inexpensive but effective remedies. The active components of medicinal plants protect the intestinal mucosa from damage and irritation by pathogenic microbes. Aqueous infusions of herbs weaken acute inflammatory reactions and reduce pain. Drinks made from leaves, flowers and fruits are drunk in small sips between meals.
Herbal remedies that help restore intestinal microflora:
- Calendula, St. John's wort, ginger, thyme suppress the proliferation of harmful microbes.
- Chamomile, yarrow, and sage have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- The fruits of fennel, anise, and dill reduce gas formation and cramps.
- Elecampane, flax seeds, marshmallow have an enveloping effect.
- Oak bark and bird cherry fruits help with diarrhea.
To restore intestinal microflora, you can choose one of the following recipes:
- Infusion of dill seeds. You need to pour 4 tsp. mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Take the infusion once every 2 hours.
- Cabbage brine. Half a glass before each meal is enough. Brine activates the growth of beneficial bacteria.
- Herb tea. You can choose any base with an antiseptic effect - plantain, chamomile, St. John's wort, black currant.
- Infusion of elecampane. You need to fill a tea boat of crushed roots with a glass of cold water overnight. In the morning, strain the mixture and drink 50 ml before each meal.
- Delicious treatment. You need to chop dried apricots and prunes, add honey - all ingredients in equal volumes. Take a tablespoon in the morning on an empty stomach. This recipe is great for kids.
Important! Despite the popular belief that herbs only bring benefits, you should consult your doctor before using them.
How to restore the balance of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract?
There is no single protocol for the treatment of such a condition as dysbiosis.
There is no such independent disease. This is just a condition that reflects varying degrees of disruption of processes in the gastrointestinal tract, provoked by a change in the balance of the intestinal microflora. Therapeutic therapy is determined depending on the reasons that caused the pathological process and may be different in each specific case. The therapy is complex, including: antibiotic therapy, treatment with special drugs - prebiotics and probiotics, to restore intestinal microflora and complex drugs (symbiotics), a properly selected diet and correction of concomitant disorders with enzymes, vitamins and sorbents.
Oddly enough, therapy begins with the use of antibiotics, intestinal antiseptics and bacteriophages, which, unfortunately, destroy not only harmful, but also beneficial flora.
Separately, it should be noted the effectiveness of probiotics, which include microorganisms that are not the natural flora of the digestive tract. Living in the lower gastrointestinal tract, for a month they have a depressing effect on the pathogenic flora, gradually displacing it, and are subsequently replaced by obligate microorganisms.
In parallel, teas and infusions from herbal infusions can be prescribed, which have the suppressive property of potogenic microflora - combined infusions consisting of three components:
- 1st - from St. John's wort, lingonberry and calendula.
- 2nd - including yarrow and cinquefoil grass, eucalyptus leaves.
- 3rd – a combination of sage, oregano and plantain.
The last stage of treatment includes the prescription of immunomodulatory agents that help improve immune functions and a more intensive restoration process of microflora in the intestines - preparations based on echinacea and propolis, herbal preparations that stimulate immune functions.