Home / After childbirth / How long does it normally bleed after childbirth?
106140
0
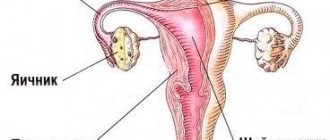
Postpartum bleeding is a normal process, which results in the natural cleansing of the uterine cavity from lochia and retained remnants of placental tissue. The severity of bleeding depends on its nature, total blood loss and duration. How long does blood bleed after childbirth is a question that concerns every young mother.
For many women, bleeding as a result of childbirth is not a cause for alarm and does not pose any threat. Abundant in the first days, it gradually decreases and disappears within a few weeks. Severe bleeding, which occurs with painful contractions and nagging pain, pronounced odor and putrefactive discharge, is not normal and requires urgent medical intervention.
Causes of bleeding after childbirth
Severe bleeding in the first hours after the birth of a newborn can be caused by:
- Poor indicators of blood clotting, individual for a woman in labor, as a result of which blood flows out of the genital tract in liquid streams without any symptoms of incipient thrombosis (thickened lumps, darkening of the color of the blood). It is not difficult to prevent such bleeding if, on the eve of giving birth, a woman undergoes an appropriate blood test for coagulation.
- Rapid labor, resulting in trauma to the birth canal.
- Incremental tissue of the placenta, as a result of which blood will bleed, since the uterus cannot fully contract.
- Unsatisfactory ability of the reproductive organ to contract due to overstretching of its tissues caused by a large fetus, multiple births and polyhydramnios.
- Gynecological problems associated with changes in the structure of the reproductive organ - uterine fibroids or fibroids.
Late bleeding may develop 2 hours after delivery and over the next 6 weeks.
Why does there bleed after childbirth in this case:
- particles of placental tissue are retained in the uterus;
- a bloody clot or several clots cannot leave the uterus as a result of its spasm in the cervical area;
- The recovery time of the uterus is delayed due to the inflammatory process in the pelvic area; this condition is characterized by an increase in general body temperature and prolonged bleeding.
Measures for the development of early postpartum hemorrhage
If bleeding increases in the first 2 hours after the end of labor (500 ml or more), doctors take the following measures:
- Emptying the bladder (if this has not been done before).
- Administration of uterotonics intravenously in increased dosage.
- Coldness in the lower abdomen.
- External massage of the uterine cavity
Place your hand on the fundus of the uterus and gently squeeze and unclench it until the uterus contracts completely. The procedure for a woman is not very pleasant, but quite tolerable.
- Manual massage of the uterus
It is carried out, as indicated above, under general anesthesia. A hand is inserted into the uterus and after examining its walls, the hand is clenched into a fist. The other hand massages the uterus from the outside.
- Tamponade of the posterior vaginal vault
A tampon soaked in ether is inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix, which causes a reflex contraction of the uterus.
If all of the above measures did not have a positive effect, and the bleeding intensified and reached 1 liter or more, the issue of surgical intervention is resolved. At the same time, intravenous administration of solutions, blood products and plasma is carried out to replenish blood loss. The operations used are:
- amputation or extirpation of the uterus (depending on the situation);
- ligation of the uterine arteries;
- ligation of ovarian arteries;
- ligation of the iliac artery.
How long does bleeding last after childbirth?
Every woman who cares about her health always asks her doctor about how and how many days the blood flows after childbirth. Normally, postpartum discharge lasts up to 6 weeks, but for many young mothers it ends a little earlier.
During this period of time, the mucous layer of the uterus is restored, and the organ takes on its prenatal form. After surgical delivery, bleeding continues longer because the muscles and walls of the uterus were injured during surgery, and it takes longer for it to return to its original state.
How much blood will flow after childbirth directly depends on the following factors:
- features of the course of pregnancy and labor;
- way of delivery - natural or surgical;
- natural contractile activity of the uterus;
- complications after childbirth, for example, inflammatory phenomena in the pelvic organs;
- features of a woman’s physiological status, health status;
- features of lactation - regular latching of the baby to the breast, breastfeeding on demand reduces the number of lochia and increases the contractile activity of the uterus, as a result of which the organ begins to cleanse itself more effectively.
To reduce the duration of postpartum bleeding and avoid possible complications, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- regularly empty the bladder and intestines so that overfilled organs do not create excess pressure on the uterus and do not interfere with its contractility;
- carefully observe hygiene rules to prevent infection of the birth canal;
- exclude physical activity and intimate relationships for 6 weeks after the birth of the child;
- sleep on your stomach, as in this position the uterus cleanses more intensively;
- establish breastfeeding as much as possible.
Despite the fact that bleeding after childbirth is a natural process, this condition requires attention from the woman and the doctor.
What can a woman do
To prevent bleeding in the late postpartum period, a young mother is recommended to follow simple instructions:
Watch your bladder
You should urinate regularly, avoiding overfilling of the bladder, especially in the first days after birth. While the woman is in the maternity hospital, visit the toilet every 3 hours, even if there is no desire. At home, also remember to empty your bladder in a timely manner.
Feeding your baby on demand
Frequently putting a baby to the breast not only establishes and strengthens physical and psychological contact between mother and baby. Irritation of the nipples causes the release of exogenous (intrinsic) oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions and also increases discharge (uterine emptying).
Lie on your stomach
In a horizontal position on the stomach, it not only enhances the contractility of the uterus, but also the outflow of secretions from it.
Normal bleeding
How long after childbirth bleeding normally occurs was stated above - about 6 weeks. Postpartum hemorrhage is divided into several stages, which differ from each other by specific features: coloring and intensity of discharge.
On the first day after birth, the amount of discharge will be greater than during normal menstruation. The blood will flow bright scarlet. On the first day, blood is removed from the vessels that attached the placental membranes to the wall of the uterus, so there will be a lot of it. Such bleeding is considered normal from the first to the fourth day after delivery.
Over the next 10-14 days, the amount of discharge decreases significantly. The scarlet tint of the discharge, which is accepted immediately after childbirth, at this time changes to faint pink, brownish or yellow. The uterus continues to contract, and after 2 weeks bleeding is minimized to a small amount of discharge per day.
Less commonly, bleeding continues longer, and until the 6th week of the postpartum period, a woman is bothered by uterine discharge with scarlet blood. If they are not abundant and inconsistent, there is nothing wrong with that. Most often, their appearance is preceded by physical exertion, nervous shock and other unfavorable factors.
Stopping late postpartum hemorrhage
Late postpartum bleeding, as already mentioned, occurs due to retention of parts of the placenta and membranes, less often blood clots in the uterine cavity. The assistance scheme is as follows:
- immediate hospitalization of the woman to the gynecology department;
- preparation for curettage of the uterine cavity (carrying out infusion therapy, introducing contractile agents);
- performing emptying (scraping) of the uterine cavity and removing remnants of the fertilized egg and clots (under anesthesia);
- an ice pack for 2 hours on the lower abdomen;
- further infusion therapy and, if necessary, transfusion of blood products;
- prescription of antibiotics;
- prescription of uterotonics, iron supplements and vitamins.
Pathological bleeding
We described above how long postpartum bleeding will last normally and what it depends on. But pathological conditions do occur.
The need for medical attention arises if postpartum discharge is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- they last more than 6 weeks;
- slight bloody discharge suddenly changes to bright scarlet blood;
- the woman’s well-being and general condition worsens;
- discharge is accompanied by significant pain in the lower abdomen;
- clinical manifestations of intoxication develop - body temperature rises, dizziness, general weakness, nausea, etc. appear;
- bloody discharge instead of physiological shades acquires yellow-green and dark brown colors, complemented by a repulsive odor.
Regardless of how much blood flows after childbirth, if the discharge becomes more intense and acquires a scarlet color and a liquid structure, you should urgently contact the ambulance service. Painful sensations, increased body temperature, changes in the nature and color of uterine discharge always become evidence of developed postpartum complications, for example, endometriosis, inflammatory process in the pelvis and other pathological conditions. In such cases, the correct course of action will be timely, thorough diagnosis and treatment.
How many days after delivery a young mother will have discharge is a controversial question. Postpartum bleeding normally lasts no more than 6 weeks, but this can be influenced by many factors, including the physiological characteristics of the woman.
During the postpartum period, the mother should monitor the nature of the bleeding, any changes and accompanying symptoms of this condition. If everything is normal, and the body recovers without complications after the birth of the child, then after 6 weeks any uterine discharge should stop.
Diagnostics
Collection of tests begins even before birth. Obstetric and gynecological statistics show that problems can be prevented if you conduct tests on hemoglobin levels, find out the number of red blood cells and platelets. In the third stage of labor, muscle flabbiness and weak contraction of the myometrium are detected.
The occurrence of bleeding leads to the need to determine its cause. When discharge continues for a long time in the postpartum period, diagnostic measures will help. For early bleeding after delivery, a hemostatic agent is used. They estimate how much blood the woman in labor has lost. This is an important aspect for choosing treatment measures.
Diagnostics is needed for a thorough examination of the integrity of the placenta and to identify birth injuries. If necessary, anesthesia is administered and the uterine cavity is manually examined to identify ruptures, clots, or tumors that interfere with the normal contraction of the organ. At a later stage, blood flows if there is a pathology, so the reason why it arose is first identified.
Methods for diagnosing the causes of bleeding:
- Ultrasound;
- Hysteroscopy;
- RDV;
- Coagulogram.
Using ultrasound, inflammation and placental polyp are detected, and the pelvic organs are studied. New pregnancy and first menstruation are excluded. Hysteroscopy is used to examine the uterine cavity.
If it is impossible to diagnose after natural childbirth using these methods, RDV is prescribed, then the blood is tested for coagulation, then sent for histological examination. Using mirrors, ruptures and inflammatory processes are detected. If the integrity of the placenta is violated, manual inspection and manual cleansing of the uterus are used.
Dangerous symptoms in the delivery room
After giving birth, the woman remains in the delivery room for 2 hours under the supervision of medical staff. During this period, hypotonic bleeding most often occurs. It is characterized by a sudden onset against the background of apparent well-being and a rapid course: in a short period of time, a postpartum woman can lose up to a liter of blood. Such a volume can be critical and lead to rapid decompensation, the development of hemorrhagic shock and death.
Therefore, in order to notice unfavorable signs in time, have time to respond to them and reduce the time for providing assistance, the patient does not shift from a chair to a couch or gurney: medical care will be provided in a gynecological chair if a critical situation develops.
How long does bleeding last after childbirth?
It all depends on individual characteristics. It continues directly in the delivery room, when transferred to the ward, and even during the first day it looks like liquid blood. By the second day, it is no longer blood, but lochia, thicker in consistency, containing a mucous component. Over the next four days, the discharge decreases, first becomes dark brown, and then gradually becomes lighter. Lochia continues to be released for another month.
Signs of bleeding in the early postpartum period are difficult to determine on your own. It is accompanied by weakness, which already worries a woman after childbirth. There may be a feeling of chills, but this is also a nonspecific symptom. After muscle tension during the period of pushing, a postpartum woman may experience a period of muscle tremors, which is difficult to distinguish from a state of severe blood loss.
While the patient lies motionless, blood can accumulate in the uterine cavity, gradually stretching it. When pressing on the uterus, a large amount of blood is released through the abdominal wall, sometimes with large clots. Gradually, normally this amount should decrease. But this does not happen with the development of pathology.
Blood pressure measurement is required. With a significant decrease in it, as well as an increase in signs of tachycardia, a conclusion is drawn about significant blood loss.
Why the bleeding doesn't stop
The causes of postpartum hemorrhage are a decrease in uterine contractility. This is influenced by several risk factors:
- large fruit;
- diseases of the blood coagulation system.
Frequent childbirth also increases the risk of excessive postpartum blood loss. If a woman has a gap between births of no more than two years, and more than four births, then hypotension must be prevented.
The immediate cause is most often the retention of parts of the placenta or fetal membranes in the uterine cavity. To prevent this condition, after the birth of the placenta, the midwife carefully lays it out on the diaper, blots away the blood, aligns and matches the edges. This allows you to assess whether all parts have separated from the walls of the uterus and come out.
The retention of any parts in the uterine cavity disrupts its contractility. The vessels to which the placenta was attached do not collapse and bleed. The release of active substances that prevent blood clotting from the placenta is also important.
Sometimes blood loss in the postpartum period is a consequence of tight attachment or. In the first case, the villi are woven into the tissue of the uterus and can be separated manually. But in the second case it is impossible to do this. The only way to save the woman is to perform a hysterectomy.
Emergency care for postpartum hemorrhage includes mandatory manual examination of the uterine cavity. The purpose of this manipulation is as follows:
- Determine the presence of placenta or membranes in the uterine cavity.
- Determine whether the organ has contractile potential.
- Determine if there are ruptures in the uterine wall.
- The ability to identify organic abnormalities that can cause bleeding, for example, a myomatous node.
The sequence of actions of a doctor during a manual examination includes the following steps:
- The volume of blood loss and the woman’s condition are assessed.
- The external genitalia are treated with antiseptics.
- Anesthesia and reducing drugs are given (or the administration of uterotonics is continued).
- The hand is inserted into the vagina and carefully into the uterine cavity.
- All clots and parts of pathological tissue are gradually removed.
- The tone of the uterus is determined. It should be tight.
- The arm is removed and the birth canal is assessed for damage that could also cause bleeding.
- The condition of the woman in labor is re-evaluated. Blood loss is compensated using solutions of crystalloids and colloids. If necessary, transfusion of blood plasma or formed elements is performed.
Additional steps to stop hypotonic bleeding after manual examination include the following:
- Introduction of additional cutting measures. Typically, a solution of methylergometrine is used for this purpose. It is administered while maintaining an oxytocin drip.
- Oxytocin can be injected into the cervix to improve its contractility.
- Tampons soaked in ether are inserted into the posterior vaginal fornix. The bleeding should stop reflexively.
- Blood loss is assessed and compensated.
The uterus does not always respond to ongoing activities and its contractility. This condition is called atonic bleeding.
If blood loss continues after manual examination, the following tactics are used:
- On the posterior lip of the cervix there are a lot of receptors that are responsible for contractility. Therefore, sutures with a thick catgut ligature are used in this area according to Lositskaya. The bleeding should stop reflexively.
- If ineffective, clamps are applied to the uterus, passing them through the vagina. This is due to the anatomical location of the uterine artery.
But if in this case the condition continues to deteriorate, the only way to help is surgery. During it, it is possible to save the organ if the intervention is carried out in a short time and special intraoperative methods are used.
Blood loss can be stopped reflexively by ligating blood vessels according to Tsitsishvili. To do this, the vessels that pass through the round ligament of the uterus and the ovarian ligaments are ligated. A more outdated method is electrical stimulation. The last resort is . It is resorted to when previous manipulations are ineffective, and if the loss is more than 1200-1500 ml.
Causes and characteristics of discharge
Postpartum discharge indicates the reverse development of the female reproductive organ. During the period of bearing a child, the uterus grew 500 times, the vessels of the placenta were firmly connected with its own blood vessels. This allowed the baby to receive the necessary nutrition and oxygen during intrauterine development.
During surgical intervention, a woman's uterus is more traumatized than during natural physiological childbirth. First of all, we are talking about an incision in the tissue of the uterus itself, through which the surgeon gains access to the baby. Placing sutures on the uterine incision is another factor for increasing discharge after cesarean section.
The doctor removes the placenta by hand after the baby is delivered. In this case, the vessels connecting the “baby place” with the uterus are injured, which causes subsequent bleeding.
The enlarged uterus, when there is no longer a need for such dimensions, begins to shrink, and in a relatively short time it will have to take on almost its previous size. This process also occurs with increased discharge, which doctors call lochia.
In the first three days, blood usually predominates in the lochia, which comes from damaged vessels of the placenta and the wound surface in the area of the incision. Laboratory testing reveals a large number of red blood cells in the discharge. Blood clots in the discharge during this period are also completely normal.
By the fifth day, the lochia begins to contain serous serum, ichor. If you examine it under a microscope, you will find that the discharge contains a huge number of leukocytes, and dead cells of the uterine epithelium can also be observed in them. By the end of the first week after natural childbirth, cervical mucus appears in the discharge. After a cesarean section, during the same period, particles of surgical threads may be found in the lochia, which are used to suture the incised wall of the uterus. These threads are self-absorbing, but their ends, which did not enter directly into the uterine tissue, are separated as the rest of the threads are absorbed and leave the uterine cavity in the traditional way - through the vagina.
Total blood loss depends on many factors - the presence or absence of complications, the woman’s weight and height.
After a natural birth, according to the BME (Great Medical Encyclopedia), a woman loses up to one and a half kilograms due to the discharge of lochia and contraction of the uterus. After a cesarean section, this number may be higher.
Does a woman lose a lot of blood?
In the first days after the birth of a child, a woman can lose up to half a liter of fluid, BUT this does not mean that she only loses blood. In addition to blood, the discharge contains:
- Mucus produced in large quantities by all glands located inside the uterus and vagina.
- Dead epithelial cells.
- Remnants of the placenta.
- Lymph.
Thus, blood accounts for half of the released volume. As the surgical suture heals, the blood vessels damaged as a result of the cesarean section will tighten, and the discharge will lighten.
Blood loss is compensated by self-production of blood. But still, you need to take into account that the volume of blood in the woman’s bloodstream is reduced, she may feel weak and lightly dizzy. During this period, it is useful for her to eat more apples and eat a little chocolate.
It is recommended to eat chocolate during blood loss
Why does bleeding continue for some time after gynecological cleansing?
The procedure for curettage of the uterine body consists of scraping its internal cavity, which removes the endometrial mucosa.
Cleaning is carried out for the diagnosis or treatment of a number of gynecological diseases, removal of tissue residues after childbirth, and for abortion.
The consequences of cleaning the uterine body depend on the method of operation. Traditional curettage is performed using a curette. A more gentle vacuum method involves removing the contents of the uterine cavity or collecting the test material through aspiration. Vacuum aspiration is carried out manually with a special syringe or using an electric aspirator.
Normally, after curettage of the uterine cavity, most women experience moderate bleeding for about 5-7 days, similar in nature to discharge during the menstrual cycle.
This is due to a violation of the integrity of the surface layer of the uterus, which is why it bleeds for some time after curettage. This helps remove formed blood clots, as well as renew and regenerate damaged endometrium.
Many women, neglecting the instructions of doctors, do not seek help if the discharge does not stop 10 days after the operation.
Although this often threatens with serious consequences. Therefore, after cleaning the uterus, it is important how much blood flows, as well as the amount, color, and smell of the secreted substance.