Abdominal obesity is the most common, but at the same time the most dangerous type of excess weight. It is worth noting that the disease most often affects males, and develops relatively rarely in women. Both an incorrect lifestyle and reasons that have a pathological basis can serve as a source of the disease. In addition, the influence of genetic predisposition cannot be excluded.
Online consultation on the disease “Abdominal obesity”. Ask a question to the specialists for free: Endocrinologist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention and prognosis
In addition to the gradual increase in abdominal volume, the clinical picture consists of the following signs: fatigue, decreased performance, shortness of breath, decreased sexual desire and infertility.
Only a clinician can make a correct diagnosis and find out why a person develops abdominal obesity, based on information obtained during a physical examination, laboratory tests and instrumental procedures.
You can get rid of the accumulation of fatty tissue in the abdominal area using conservative methods, for example, by taking medications and performing gymnastic exercises aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles. However, in particularly severe cases, the only treatment option is surgery.
Etiology
Abdominal obesity is most often a consequence of an unhealthy lifestyle, namely poor nutrition. However, overeating is not the only predisposing factor leading to the development of such a pathology.
The disease can be caused by:
- disruption of the functioning of the hypothalamus, in which the food center that regulates satiety is located. Such a deviation leads to the fact that no matter how much a person eats, he constantly feels hungry. In such situations, it is not enough just to follow a gentle diet and exercise - the basis of therapy is the work of the psychotherapist with the patient;
- a lack of serotonin, which is a hormone responsible for mental stability and positive emotions, which is why it is also called the hormone of joy. A deficiency of such a substance leads to the development of a depressive state, which some people prefer to combat by consuming large amounts of junk food;
- sedentary lifestyle - sedentary working conditions and complete refusal of sports significantly increases the likelihood of accumulation of excess body weight;
- long-term addiction to bad habits, namely drinking alcoholic beverages, which, in turn, increases appetite;
- hormonal imbalance;
- irrational use of medications, namely hormonal and psychotropic substances.
Do not forget that the cause of abdominal obesity is genetic predisposition. Knowing this, a person can independently prevent the accumulation of large amounts of adipose tissue in the peritoneal area - to do this, it is enough to lead an active lifestyle and eat right.
In female representatives, such a disorder is often a consequence of pregnancy and labor.
Causes of abdominal obesity
As mentioned above, abdominal obesity occurs due to poor nutrition, but the reason may lie in another:
- SEROTONIN DEFICIENCY – this hormone is the core of psychological stability, it is also called the hormone of joy. A deficiency in the body causes depression, which leads to increased calorie consumption;
- LACK OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY – refusal of sports exercises and inactivity, deposits fat reserves in the body;
- BAD HABITS - which last for more than one year and over time, millimeter by millimeter, increase the size of the waist to terrifying sizes;
- HORMONAL DISRUPTION - few people realize, but increased or decreased concentrations of certain hormones do terrible things to weight and the amount of accumulated fatty tissue;
- INCREASED MEDICINE TAKING – this applies to both hormonal and psychotropic medications.
In addition, it is worth remembering that genetics also affects abdominal obesity. To avoid this, it is necessary to adhere to a nutritious diet from an early age. In girls, this is especially evident in the postpartum period.
Classification
Abdominal obesity in women and men has several course options:
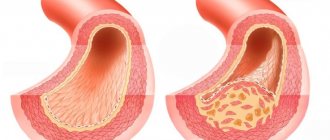
- accumulation of fat cells directly under the skin is the most favorable type of disease, since it responds well to conservative therapy, consisting of therapeutic exercises and diet. Complications in such cases develop extremely rarely;
- the formation of adipose tissue around vital organs - while getting rid of extra pounds is much more difficult. In addition, there is a high probability of life-threatening consequences. Therapy often includes medical intervention.
Pathology has three degrees of severity:
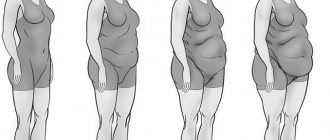
- Stage 1 - waist circumference in men does not exceed 94 centimeters, and in women 80 centimeters;
- Stage 2 - indicators for males vary from 94.2 to 101.3 centimeters, for females - from 81.2 to 88.6 cm;
- Stage 3 - in such cases, the waist circumference in men is 102.6 cm or more, and in women - 88.9 centimeters or more.
Stages of abdominal obesity
Symptoms
With abdominal obesity, the clinical picture will include a combination of the following signs:
- increase in the volume of the abdominal cavity;
- cell resistance to insulin, which almost always leads to type 2 diabetes;
- increased blood tone;
- dyslipidemia;
- changes in blood composition;
- decreased sexual activity;
- shortness of breath that appears even with minimal physical activity;
- male and female infertility;
- menstrual irregularities in females;
- rapid fatigue and decreased performance;
- development of a depressive state;
- heartburn that occurs due to the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus;
- Varicose veins;
- development of sleep apnea syndrome;
- frequent exposure to colds;
- disruption of the functioning of the digestive system.
It must be taken into account that the accumulation of adipose tissue around internal organs can lead to the appearance of symptoms indicating their dysfunction. The most common targets are:
- heart and liver;
- kidneys and pancreas;
- vessels and omentum;
- large and small intestines;
- lungs.
It is noteworthy that similar clinical signs of obesity are observed in women and men.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist or endocrinologist can find out the reasons for the accumulation of excess body weight in the abdominal area and prescribe adequate treatment. In addition, consultation with a nutritionist is necessary.
The process of diagnosing abdominal obesity in men and women includes several stages, the first of which is aimed at:
- studying the medical history - this will allow us to establish a pathological predisposing factor;
- collection and analysis of life history - this should include information regarding nutrition, physical activity, mental health and addiction to bad habits;
- a thorough physical examination - including palpation and percussion of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity, measurement of abdominal circumference and determination of body mass index individually for each patient;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to compile a complete symptomatic picture, determine the severity of symptoms and establish the stage of the pathology.
The second step of diagnosis is laboratory tests, which are limited to performing a general and biochemical blood test, which will indicate a change in its composition, characteristic of such a disease.
The final stage of diagnosis is the implementation of instrumental examinations, including:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- gastroscopy;
- radiography using a contrast agent;
- CT and MRI - to identify lesions of internal organs.
Gastroscopy
Anorectic drugs for obesity
Anorectics are a group of pharmaceutical drugs aimed at reducing appetite. As a result of their intake, the parts of the brain responsible for the feeling of fullness while eating are blocked.
The action of the drug is based on the following principles:
- increased thermogenesis, which helps activate metabolism,
- blocking receptors responsible for appetite,
- decreased ability of the intestines to absorb fats.
Initially, anorectics were part of sports nutrition. They helped saturate the body with nutrients during increased physical activity. Later, medications began to be used for rapid weight loss in case of serious health problems.
After stopping the treatment course, you should adhere to proper nutrition. Otherwise, the lost kilograms will return. The medicine is taken in accordance with the prescribed dosage.
The most common drugs in this category include:
- Sibutramine,
- Lorcaserin,
- Cabergoline.
Treatment
The fight against abdominal obesity is complex and takes a fairly long period of time.
Complex therapy consists of:
- lifestyle changes;
- maintaining a gentle diet;
- performing gymnastic exercises;
- taking medications;
- treatment of concomitant pathologies.
The following medications are considered the most effective:
- "Orlistat" - reduces the absorption of fat in the intestine;
- "Sibutramine" is an antidepressant that reduces appetite;
- "Rimonabant" - belongs to the category of antagonists, reduces appetite and promotes rapid weight loss;
- "Metformin";
- "Pramlintide" - creates a feeling of saturation;
- "Exenatide Baeta."
The diet and complex of therapeutic exercises are compiled individually for each patient, which depends on the severity of the disease. However, in any case, therapy should take an integrated approach.
If conservative methods are ineffective, as well as in severe stages, the treatment of abdominal obesity in both sexes involves surgery. The intervention is aimed at partially removing the intestines or reducing the capacity of the stomach.
It is worth noting that in this case, folk remedies do not give a positive result, and sometimes they can aggravate the problem and lead to complications.
How to deal with the disease?
Only when you reach stage 4 obesity will surgery be required. Before this, everything can be solved with nutrition and physical activity.
To overcome excess weight, you need to combine a strict diet and strength exercises. It is necessary to follow all medical recommendations thoroughly, completely eliminating all kinds of indulgences and temptations, for example, an occasional piece of cake. This is the only way to cope with this difficult task.
Diet and basic principles of nutrition
All meals recognized by world nutritionists include a number of similar features, for example:
- the daily diet should not exceed 2000 kilocalories;
- fats and carbohydrates should be close to zero (it is recommended to replace them with fiber);
- protein maximum 400 kcal (found in fish, meat, chicken eggs, etc.).
Protein foods have a beneficial effect on the body, help to gain a feeling of satiety, and energy is spent on proper absorption. It is important to remember that the transition to a different diet should be smooth so that the body can get used to it and there are no sudden disruptions due to unexpected changes.
Approximate weekly diet
Possible complications
Abdominal obesity is a dangerous disease that can lead to a large number of dangerous consequences. The list of the dangers of the disease includes:
- malignant arterial hypertension;
- inability to have children;
- secondary diabetes mellitus resulting from insulin resistance;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- atrial fibrillation;
- stroke;
- cardiac ischemia;
- fatty liver degeneration;
- calculous cholecystitis;
- susceptibility to oncology and inflammatory processes;
- accumulation of large amounts of cholesterol in blood vessels, which disrupts the nutrition of internal organs;
- heart failure;
- salt deposits in joints.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the development of abdominal obesity, you should adhere to the following simple rules of prevention:
- lifelong cessation of bad habits;
- healthy and nutritious nutrition;
- maintaining a moderately active lifestyle;
- constant strengthening of the abdominal muscles;
- adequate use of medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- avoiding emotional stress;
- Regularly undergoing a full medical examination with visits to all specialists.
The prognosis of the disease depends entirely on several factors - the severity of its course, the age category of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathologies and conscientious adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician.
Fat and carbohydrate blockers
Male type obesity is often eliminated using carbohydrate and fat blockers. They are divided into two main groups. The first includes drugs that slow down the process of lipase formation. The second group includes medications that interfere with the digestion of fat.
There are many drugs available on the pharmaceutical market that interfere with the absorption of carbohydrates. Initially they were intended for people suffering from diabetes. Glucobay is considered a prominent representative of such drugs.
It lowers sugar levels in the body by preventing carbohydrates from being absorbed into the lining of the small intestine. The drug is taken immediately before meals.
The dosage depends on the purpose of use. Normally, it should not exceed 600 mg.
Fat blockers act on the principle of sorbents. They bind fat molecules and remove them from the body. The effectiveness of drugs is observed only when following a low-calorie diet. Otherwise, treatment will be inappropriate.
The advantages of drugs in this group include the ability to rid the body of toxins. Among the disadvantages is the removal of micronutrients, which are necessary to maintain the life support of the entire body. The most common fat blocker is Chitosan in drop format.
Among the medications that slow down lipase synthesis, Orlistan is distinguished. It does not have a systemic effect on the body. The drug is active only within the digestive tract.
Side effects of the drug include:
- flatulence,
- dysmenorrhea,
- headache,
- loose stools,
- feeling of weakness.