Drugs for support after embryo transfer
The range of drugs used in in vitro fertilization is very diverse.
This includes:
- vitamins;
- hormones;
- substances that prevent excessive blood clotting.
Support medications after the transfer are needed to maintain the pregnancy and its normal course. Therefore, their purpose is very important.
The preparations after the transfer include an extensive list of vitamins. Complexes are most often prescribed for pregnant women.
These include:
- Vitrum;
- Femibion;
- Elevit Pronatal.
The doctor can prescribe a vitamin complex himself, but sometimes leaves the choice to the expectant mother. All drugs are similar in composition and action, so there is no significant difference between them.
Vitamins Elevit Pronatal
Important! When choosing a vitamin complex, it is worth taking into account the assortment of pharmacies closest to your place of residence, so that you can always buy exactly the product that was taken earlier. Changing the medication during pregnancy is highly not recommended, especially if there is no allergic reaction or side effects to the prescribed drug.
Support after embryo transfer during IVF involves taking folic acid. It is prescribed in the same quantity as for all pregnant women.
The advantages of this acid are that it:
- prevents pathologies of the fetal neural tube;
- helps the development of all organ systems and tissues;
- prevents spontaneous abortion.
Folic acid can be taken alone or as part of complexes, if the amount corresponds to the prescribed dosage.
Folic acid
Magnesium, which has the following properties, also belongs to support drugs after embryo transfer:
- helps reduce anxiety;
- calm the nervous system;
- prevents the appearance of uterine tone.
It is prescribed in the form of drugs “Magne B6” or “Magnelis”. After embryo transfer, these pills relax the woman’s nervous system and prevent dangerous contractions of the uterine muscles that can provoke the rejection of fertilized eggs.
Vitamins Magne B6
How to maintain pregnancy after IVF
Pregnancy after IVF often occurs with complications. This happens because women with diseases of the endocrine system and reproductive system resort to in vitro fertilization. They often experience miscarriage, toxicosis and other problems that put pregnancy at risk. To prevent this and maintain pregnancy after IVF, you need to be observed in a clinic that has the necessary equipment and qualified specialists working with IVF mothers.
Hormonal disorders during pregnancy after IVF
These problems are caused by the introduction of large doses of hormones during the preparation for IVF, if hormonal stimulation of the ovaries was carried out. For many women, this is a necessity and the only opportunity to become pregnant, since stimulation of the ovaries leads to the maturation of several follicles at once. At the same time, the concentration of estrogen in the blood increases sharply. Hormonal imbalance can cause disturbances in vascular permeability and accumulation of fluid in the lungs and abdominal cavity. Excess moisture prevents a woman from breathing, causes nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite.
Another possible consequence of HS is a slow increase in hCG levels (human chorionic gonadotropin), which is called the “pregnancy hormone”. This hormone should:
- preserve the corpus luteum;
- prepare the woman’s immune system for the upcoming pregnancy;
- stimulate fetal development
With a lack of hCG, fetal growth slows down, which leads to miscarriage and fading of pregnancy.
In this case, pregnancy support after IVF When observed in a specialized clinic, doctors will be able to correct hormonal levels in time, remove swelling and eliminate the threat of miscarriage.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
Women who become pregnant after IVF often suffer from chronic inflammation of the genital organs, which leads to the impossibility of natural conception. Although women are treated as much as possible during the period of preparation for pregnancy, the disease often worsens again. All this affects the functioning of the immune system and reduces the production of hormones responsible for the normal course of pregnancy.
A woman develops a bloody “spot,” indicating a threat of miscarriage. Under these conditions, it is not easy for the fetus to stay in the uterus, so medical support for pregnancy after IVF is required. Medical supervision helps eliminate dangerous inflammatory processes, maintaining pregnancy after IVF.
Maternal problems
IVF is mainly used by women aged 30 years and older. A large percentage of them have various diseases of internal organs (kidneys, heart, liver, gall bladder) and metabolic disorders. All these “sores” are prone to exacerbation during pregnancy, which negatively affects the intrauterine development of the child.
Women who already have health problems may develop gestational diabetes, caused by the pancreas not working properly. The level of glucose in the blood rises, which causes oxygen starvation of the fetus. This complication occurs more often if a woman is carrying twins, which often happens after artificial insemination. If the problems that arise are not treated in time, the pregnancy can be lost. To do this, women, being observed in the clinic after IVF, regularly donate blood for biochemistry and sugar.
Fetoplacental insufficiency
This condition occurs as a result of malformation and or insufficiency of the placenta. Since women who become pregnant after IVF often have problems in the sexual sphere, fetoplacental disorders are not uncommon.
As a result, the fetus suffers, which receives few nutrients and oxygen, which can lead to miscarriage or the birth of a sick child. Periodic Doppler testing, which shows the state of the feto-placental blood flow, can help with this condition. If a pathology is suspected, supporting pregnancy after IVF involves prescribing medications that improve blood circulation in the placenta and help the pregnancy proceed properly.
Multiple pregnancy
During IVF, a woman is often implanted with several embryos at once. If they all take root, a multiple pregnancy occurs. Sometimes twins develop from one egg, as in a normal pregnancy; a woman gives birth to identical twins. Many people consider twins or triplets to be an excellent result after IVF, forgetting that several babies are harder to bear and easier to lose.
Sometimes nature itself regulates the process, and extra embryos stop developing, but often all implanted eggs grow equally. It is possible, of course, to reduce (remove) excess embryos, but parents rarely agree to this.
In women pregnant with twins, toxicosis occurs more often and is more severe. The uterus, growing much faster, puts pressure on the legs, causing them to swell. Pressure on the diaphragm in recent months interferes with the mother’s ability to breathe properly. In the later stages of pregnancy with twins or triplets, an increase in blood pressure is more often observed, which can lead to convulsive syndrome (eclampsia) and premature birth. Since twins are already born with low weight, this can lead to extreme prematurity and death of newborns.
Overstretching of the uterus and increased stress on the body cause:
- bleeding;
- oxygen starvation of the fruits;
- anemia caused by a high load on the mother’s hematopoietic system;
- feto-fetal transfusion syndrome, when one fetus takes more nutrients, inhibiting the development of the second;
- thrombosis of placental vessels. During multiple pregnancies, one or both “baby places” are located incorrectly, which causes premature placental abruption;
- oblique, transverse or pelvic location in the uterus of one or all babies
A woman who has developed a multiple pregnancy as a result of IVF needs special observation and strict control, so she often undergoes an ultrasound to find out how the children are developing.
The condition of babies carried by IVF mothers is monitored using ultrasound and Doppler. Competent doctors working at the Life Line clinic will provide full support for pregnancy after IVF and will help you successfully endure multiple pregnancies and give birth to healthy children. The conscious attitude of a woman and the supervision of experienced specialists allows us to save the majority of pregnancies that occur after IVF.
Progesterone to support pregnancy
Hormonal drugs allow the embryo to become more firmly entrenched in the uterus, as well as the body to adapt to the state of pregnancy. Progesterone has this effect.
Injections after embryo transfer with this drug are quite common. But more often Progesterone is used in two forms:
- a gel that is inserted into the vagina (Crinon);
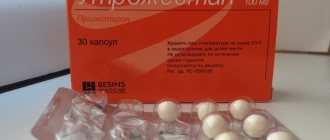
- capsules or suppositories used intravaginally (Utrozhestan).
The choice of dosage form is made by a gynecologist depending on the indications and purpose of treatment, as well as the patient’s condition. Most often, suppositories are prescribed due to ease of use.
Progesterone has several main properties:
- changes the structure of the endometrium, which facilitates the attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus;
- reduces the contractile activity of the uterine myometrium, allowing the cervical canal to close tightly, reducing the risk of spontaneous miscarriage at the beginning of pregnancy.
Progesterone support after IVF is a common method of maintaining a long-awaited pregnancy. The drug is withdrawn gradually from 8 to 20 weeks.
Progesterone in suppositories
The duration of the appointment is determined by the fertility specialist of the medical center performing in vitro fertilization. It is calculated based on the main indicators:
- patient's medical history;
- type of IVF protocol;
- age;
- woman's hormonal background;
- the presence or absence of artificial insemination before this experience and their results.
If a severe allergic reaction or other side effects to drugs that support the luteal phase occur, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
The doctor will select an adequate replacement medication. The drug should be discontinued gradually, reducing the dosage. Abrupt cancellation or skipping of an appointment is unacceptable, as this threatens the safety of the pregnancy.
Stage three: preparing the endometrium for embryo implantation
To successfully place a fertilized egg in the uterus, the expectant mother must have optimal hormonal levels. This is achieved by introducing additional hormones into the body. Lack of progesterone is especially common in women of Balzac age. The line of such drugs includes:
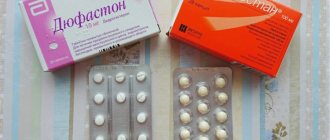
- Duphaston, oral tablets;
- Utrozhestan, capsules;
- Crinon, gel.
Their use helps create favorable conditions for pregnancy. Then the placenta is formed, which produces “its” progesterone in the required concentration. For better blood supply to the uterus and providing the baby with oxygen, doctors recommend medications containing the female hormone estradiol:
- Estrofem;
- Divigel;
- Proginova.
Along with progesterone, the female hormone prepares the endometrium of the uterus for the transfer of an embryo from a test tube, for bearing a child. If fetal maturation is normal, these medications are not prescribed.
Duphaston after transfer
This drug is also an analogue of human progesterone. After embryo transfer, Duphaston helps maintain pregnancy and ensure a successful course. The use of this drug is considered normal for in vitro fertilization protocols. Progesterone increases the chances of successful implantation of an egg into the endometrium of the uterus.
Duphaston belongs to the group of retroprogesterones. These drugs, used to support the luteal phase during in vitro fertilization, have a strong progestational but low androgenic effect.
This gives them a number of advantages:
- lack of feminization of a male child;
- lack of masculinization of the reproductive system organs in a female child;
- does not affect the liver;
- does not affect blood clotting;
- does not cause rashes, hirsutism, change in voice towards a male voice;
- does not affect metabolic processes (does not change the concentration of blood glucose, as well as its lipid spectrum);
- no effect on the pituitary-ovarian system;
- does not provoke adrenal atrophy.
Due to the presence of these properties, doctors actively prescribe Duphaston after transfer during artificial insemination. It is dydrogesterone with a methyl group at position 10 in human progesterone).
Duphaston
This modified structure of the molecule allows Duphaston to be more easily absorbed when taken orally. The use of the drug in a dosage of 20 to 30 mg stimulates the secretion phase in the endometrium. Thus, dydrogesterone supports pregnancy.
The use of the drug begins from the moment of embryo transfer at a dosage of 30 to 60 mg per day. Reception is continued until the 12th week of pregnancy. If there is a threat, treatment is extended to 20 weeks.
Duphaston is absolutely safe for the fetus. The absence of a teratogenic effect has been confirmed by a lot of studies, so the drug is widely used as a support for artificial insemination.
Features of application:
Crinon is a topical drug used intravaginally. It is administered at a dosage of 90 mg every day before going to bed.
Note! The dosage may differ from the stated one, since the doctor, when prescribing the drug, is based on the data obtained as a result of a hormone analysis.
The method of use depends on the form.
More on the topic
Why is Proginova prescribed when planning pregnancy?
Cancellation of Duphaston during pregnancy
Cancellation of Clexane before childbirth
Embryo implantation
Is it possible to avoid toxicosis during pregnancy?
- gel
- Shake the plastic applicator vigorously (just like a mercury thermometer) so that the liquid moves to the bottom.
- Twist the cap or tear it off along the perforations.
- Insert the end of the applicator as deep as possible into the vagina. Move slowly, without causing yourself discomfort.
- Squeeze the container sharply to force the liquid inside.
Reference! It is more convenient to administer Crinon in a lying position, with your knees bent or sitting on the toilet.
- candles
Candles are introduced in the standard manner. The main task is to push the medication deep enough into the vagina.
- side effects
Many drugs that affect hormone production have a number of side effects. Crinon is no exception. Most often, women who underwent such therapy complained of such unpleasant symptoms as:
- attacks of headache;
- increased fatigue;
- drowsiness in the middle of the day;
- chest pain;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody discharge between periods;
- irritation on the mucous tissues of the external genitalia;
- skin rash (in case of intolerance to one or more components).
There have been no cases of overdose with Crinon in medical practice.
- contraindications
The drug is contraindicated for the following ailments:
- bleeding from the vagina of unknown etiology;
- oncological diseases of the mammary glands or genital organs;
- circulatory disorders in the brain;
- frozen pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- intolerance to one or more components of the drug.
Analogs of drugs for maintaining pregnancy
After in vitro fertilization, it is necessary to compensate for the lack of natural estradiol. For this purpose, the drug Proginova is used. It contains synthetic estradiol (estradiol valerate), which allows the fetus to attach itself to the uterine wall.
The dosage form of the drug is tablets for oral administration. The regimen for use is developed individually by a fertility specialist managing the pregnancy, taking into account all contraindications and research results.
Proginova is not prescribed in the following cases:
- with endometriosis;
- if there are malignant liver tumors;
- for diabetes mellitus of any type;
- with increased blood clotting ability;
- if the pregnant woman is overweight.
You cannot stop taking the drug yourself, as this can have consequences including termination of pregnancy. The dosage is reduced gradually, the individual course is calculated by the doctor.
Another progesterone drug is Crinon. It is available in the form of suppositories or gel. Suppositories are most often prescribed; their use is simpler. The drug can be used once a day, which is more convenient for patients than repeated doses.
What do the means have in common?
Both drugs are contraindicated if a woman has the following pathologies:
- Bleeding from the genital tract of unknown origin.
- Acute porphyria.
- Malignant neoplasms of the reproductive organs or mammary glands.
- Intolerance to the composition of the drug.
- Incomplete abortion.
- Thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic pathologies.
- Acute cerebral circulation disorder, including a history.
Both hormonal drugs should not be taken by women who are breastfeeding.
Both medications should be prescribed with caution if a woman is diagnosed with the following pathologies:
- Arterial hypertension.
- Chronic renal and heart failure.
- Migraine pain.
- Depressive state.
- Epilepsy attacks.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Diabetes.
- Increased levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood.
Contraindications and possible side effects after using the drug
Before prescribing Crinon, you should familiarize yourself with the contraindications to its use:
- malignant neoplasms;
- tendency to bleed;
- individual intolerance to the active substance;
- stroke;
- incomplete abortion;
- poor tests indicating blood diseases.
The medication may cause side effects, but they do not necessarily occur:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- drowsiness;
- local irritation;
- bloody issues;
- discomfort in the mammary glands.
Vaginal discharge
A feature of the physiology of the female body is such an arrangement of the genital organs that any administered drug will be released. The first days the gel is released as a small amount of liquid, which has a whitish tint.
Slight brown staining or veining is allowed when implantation occurs. Multiple pregnancies may appear as a short-term black color. With continued use, the drug is released in the form of clots.
The following are not the norm:
- bright, scarlet;
- lasting more than three days;
- accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
If such a situation occurs, you should consult your doctor.