Causes of JVP
With the development of dyskinesia, the motility of the gallbladder and biliary tract changes. As a result, the flow of bile into the duodenum is disrupted, which inevitably affects the functioning of the entire digestive tract. In this case, both a noticeable lack of bile in the intestinal lumen (hypokinesia) and its excess (hyperkinesia) are possible. Any of these conditions disrupts the functioning of the duodenum and prevents the normal digestion of incoming food.
Factors provoking the development of ADHD:
- gallbladder diseases;
- congenital malformations of the biliary tract;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- metabolic disorders.
The psychological state of a woman plays an important role in the development of dyskinesia. Often this disease occurs after suffering stress and is a kind of reaction to negative events. Impaired motility of the biliary tract may also be associated with the constitutional characteristics of a woman or be a consequence of poor nutrition.
Pregnancy itself is a risk factor for the development of ADHD. In anticipation of the baby, the smooth muscles of the bile ducts relax. Their motility is impaired, which naturally leads to insufficient or excessive flow of bile into the intestines. All these processes occur under the influence of progesterone and other hormones that regulate the course of pregnancy from conception to childbirth.
Another reason for the development of GIB during pregnancy is the pressure of the growing uterus on the gallbladder and all organs of the digestive tract. Constant compression of the bile ducts leads to impaired motility and improper secretion of bile. It is no coincidence that the disease most often occurs in the third trimester and shortly before childbirth.
Diagnostics
Cholestasis during pregnancy is accompanied by jaundice, which often manifests itself in other pathologies of the hepatobiliary system. To identify disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and the cause of bile drainage failures, a pregnant woman undergoes the following examinations:
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound, MRI or CT scan of the liver and gallbladder;
- liver tests.
In ambiguous situations, the bile ducts are examined using endoscopic cholangiography. Its essence lies in an X-ray examination of the bile ducts with direct injection of a contrast agent into the biliary system.
The classic methods remain urine tests, blood tests and ultrasound. Most often, the disease manifests itself in the second half of pregnancy, after the twenty-sixth week.
Cholestasis during pregnancy is differentiated from viral hepatitis, cholecystitis, and steatosis. Based on the diagnostic results, the cause of the disease is determined and an adequate treatment regimen for pregnant women is drawn up.
Main manifestations
Typical symptoms of ADHD include:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- a feeling of heaviness and pressure in the projection of the gallbladder;
- belching;
- nausea;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- bloating;
- decreased appetite.
The pain with biliary dyskinesia is dull, aching, not too intense. The disease develops gradually, and for a long time a woman may not notice the characteristic symptoms of the pathology, attributing them to normal manifestations of pregnancy. In the early stages, dyskinesia is often disguised as prolonged toxicosis.
Exacerbations of the disease occur after stress and due to errors in diet. Some expectant mothers develop a picture of a vegetative crisis. Pain in the heart, tachycardia, shortness of breath, increased sweating and numbness of the extremities - all these signs complement the typical symptoms of ADHD. Insomnia develops throughout the entire period of exacerbation of the disease.
Choleretic for cholestasis
Disruption of the processes of formation and secretion of bile is called cholestasis, or stagnation. The pathology is manifested by unpleasant sensations in the right hypochondrium, significant itching of the whole body (especially the palms and feet), fatigue and even jaundice of the skin. Cholestasis is often confused with manifestations of allergies due to the similarity of symptoms. The difficulty of diagnosing the disease leads to the fact that it is detected only after special tests (biochemistry) to detect the level of bilirubin and transaminase. An ultrasound examination of the liver is also indicated.
Cholestasis is usually detected in late pregnancy, which is associated with compression of the internal organs by the growing fetus. Women who have a hereditary predisposition to the disease can also suffer from the pathology. Therefore, it would be useful to ask your relatives if similar troubles have happened to them.
If the presence of the disease is confirmed, the doctor prescribes choleretics, drugs that increase the production of bile secretions, or cholekinetics that stimulate the outflow of bile.
You should definitely check for gallstones before taking this group of medications. When bile production is stimulated, they can move and block the ducts.
Among the natural-based drugs recommended:
- Holosas, Holos, Holemaks (extract from rose hips).
- Peridol, Insadol (extract from corn silk).
- Hofitol, Holebil (artichoke extract).
- Flamin (extract from immortelle flowers).
- Tanacehol (tansy extract).
These medicines are based on plant extracts, so pregnant women can take them calmly, remembering to consult a doctor.
Treatment methods
The main goal of treatment for DVT during pregnancy is to relieve pain and eliminate unpleasant symptoms of the disease. In many cases, full treatment of the disease is possible only after the birth of the child. During pregnancy, the list of approved medications is very limited.
Non-drug treatment
A balanced diet is of great importance in the treatment of ADHD. Pregnant women should adhere to the following principles:
- Meals should be small and frequent, 5-6 times a day.
- Portions should be small (up to 50% of the usual volume).
- Light snacks are allowed throughout the day.
- Fried, spicy, salty and spicy foods are excluded.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
When the disease worsens, the following foods are completely excluded from the diet:
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- strong meat and fish broths;
- egg yolk;
- baked goods;
- nuts;
- raw vegetables and fruits.
All these dishes contribute to contraction of the gallbladder, which in turn disrupts the motility of the biliary tract and worsens the condition of the pregnant woman. When the symptoms of the disease subside, the diet expands to include vegetable dishes, fresh fruits (melon, watermelon), dried fruits (raisins, dried apricots, prunes). These products restore the functionality of the biliary tract and also prevent the development of constipation.
In case of a hypomotor form of GIB, accompanied by an insufficient supply of bile, it is recommended to gradually introduce cottage cheese, sour cream, cod, weak meat and fish broths into the diet. These dishes stimulate the production of bile and ease the course of the disease. The use of mineral water with high mineralization also relieves the symptoms of the disease. In case of hypermotor variant of JVP, when there is already too much bile, it is recommended to drink mineral water of low mineralization (Essentuki 17 and others).
All pregnant women with PVD are recommended to lead an active lifestyle. Regular walks in the fresh air and swimming in the pool are the best way to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and prevent relapse of the disease. From the second trimester of pregnancy, you can do therapeutic exercises or yoga in special groups.
Drug treatment
Choleretic drugs are actively used for the treatment of ADHD. Priority is given to herbal preparations (choleretic collection and others). These remedies usually include immortelle flowers, yarrow, corn silk, dill seeds, mint, rose hips and other plants. The course of treatment lasts at least 2 weeks and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Self-administration of herbal preparations during pregnancy is not recommended.
In the treatment of the hyperkinetic form of JVP, antispasmodic drugs are used. These drugs normalize the flow of bile, relax sphincters and stabilize the digestive tract. To treat the hypokinetic form, cholekinetics are used, taking into account the duration of the current pregnancy.
Biliary dyskinesia does not have a negative effect on the course of pregnancy and fetal development. This disease is not an obstacle to vaginal delivery. In most cases, biliary motility is restored within 4 weeks after birth. If the symptoms of the disease have not subsided within the specified period, you should definitely see a doctor.
At first glance, biliary dyskinesia that occurs during pregnancy seems harmless, but in fact this disease develops an inflammatory process and promotes stone formation in the gallbladder. The biliary system and other digestive organs are carefully interconnected, and the work of one organ depends to one degree or another on the work of the other.
Natural choleretic agents
It is believed that the use of traditional medicine recipes is the safest method of treatment. Medicinal herbs can really help solve gallbladder problems. Choleretic infusions are widely used, which include immortelle flowers (sandy cumin), peppermint, and coriander fruits. As an addition, they include yarrow or trefoil herb.
Helichrysum is used as an effective natural remedy that stimulates bile secretion and increases bilirubin and cholate levels. The active substances of the plant - flavonoids - have an antispasmodic effect on the walls of the gallbladder and extrahepatic ducts. Peppermint herb reduces inflammation, reduces muscle tone, and has a calming effect. Yarrow enhances the antispasmodic effect, while simultaneously relieving inflammation and increasing gastric secretion.
Never change the dosage of medicinal preparations and decoctions recommended by your doctor. Many herbs have toxic properties in large quantities, so they must be taken exactly as prescribed.
A good remedy that promotes the outflow of bile is corn silk extract. The oils contained in the herbal preparation enhance the motility of the gallbladder, dilute the bile, and relax the ducts.
Expectant mothers can brew teas from herbs that promote bile secretion. All herbal preparations are prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. spoon per glass of boiling water.
The following herbs can be recommended:
- Garden dill. Raw materials are prepared from ripened fruits. Take half a glass up to 4 times a day.
- Creeping wheatgrass. In the fall, the roots are harvested, thoroughly washed and dried. The decoction is taken 4 times a day, half a glass.
- Rosehip (fruit). The dried raw materials are brewed and allowed to brew. Take half a glass three times a day.
- Immortelle (tsmin sandy). The collected herbs are dried and brewed according to the recipe. Take before meals three times a day.
All manipulations must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Based on the collected history, he will recommend the best option.
Treatment of biliary dyskinesia during pregnancy
How to treat biliary dyskinesia?
When a pregnant woman develops symptoms and signs of biliary dyskinesia, the first step is to normalize the flow of bile and prevent it from stagnating. As a rule, the doctor prescribes complex treatment for this disease. First of all, the pregnant woman will be advised to follow a proper diet of 5-6 meals a day. The diet for the treatment of dyskinesia should consist of foods and dishes that promote contraction of the gallbladder. If you strictly follow the doctor’s instructions, then after treatment the pregnant woman will very soon restore her body and enjoy her pregnancy.
Cholelithiasis.
Cholelithiasis, calculous cholecystitis, is a disease that occurs with the formation of stones in the kidneys or gall bladder. Doctors say that during pregnancy, when great changes occur in a woman’s body, this disease can worsen significantly.
To treat this disease, you should use choleretic drugs, as well as adhere to proper nutrition. If severe pain occurs, then drugs with an antispasmodic effect should be used, such as analgin, no-spa, papaverine, hydrochloride, baralgin.
Relatively recently, drugs appeared on the pharmacological market that have the properties of dissolving stones. They contain cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids. It is worth noting that a pregnant woman should not use such drugs, as they can negatively affect the fetus. It is also strictly forbidden to take stone crushing agents, such as shock wave lithotripsy.
During pregnancy, only as a last resort, namely when the common bile duct is blocked by a stone, surgery is performed. This may be removal of the gallbladder or laparoscopic intervention.
This option is often used because it is not necessary to completely open the abdominal cavity. All necessary manipulations are performed using surgical instruments through the navel and small side incisions under the ribs. After this, not even a scar remains, and the recovery period lasts only three days.
Pregnancy in the presence of diseases of this type does not require termination. It is worth noting that during exacerbations that last quite a long time and are accompanied by severe colic in the abdominal area, surgical intervention should be performed immediately, since cholecystitis can manifest itself in the form of jaundice.
Symptoms of biliary dyskinesia during pregnancy
How do you know if a pregnant woman has dyskinesia? As a rule, this disease has a number of symptoms and signs, and if all of them are pronounced, then most likely the pregnant woman is suffering from dyskinesia.
Signs of biliary dyskinesia
As a rule, with dyskinesia, a pregnant woman suffers from the following symptoms: a dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of heaviness, and an immediate loss of appetite. And if pain occurs, a woman may experience nausea, bitterness in the mouth, belching, heartburn and even bloating. In this case, with each movement of the fetus, the pain in the right side may intensify.
Pain in this area can occur immediately after a heavy meal, or due to nervous fatigue. In this case, pain may appear not only in the right hypochondrium, but also in the heart area. Additional symptoms of dyskinesia include increased heart rate, headache, sweating, numbness in the limbs, and poor sleep.
Very often during pregnancy, women complain of pain. They can appear on various parts of the body and can indicate certain diseases. If a pregnant woman notices the appearance of pain in the right hypochondrium, and the pain only increases every day and sometimes becomes unbearable, then most likely the pregnant woman has dyskinesia of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Symptoms of pathology
At the initial stage, impaired motility of the biliary tract occurs with minor symptoms that bother the woman little and do not attract much attention. Gradually, the manifestations of the pathology intensify and force you to consult a doctor. The signs of different types of dyskinesia differ.
Our regular reader recommended an effective method! New discovery! Novosibirsk scientists have identified the best remedy for restoring the gallbladder. 5 years of research!!! Self-treatment at home! After carefully reviewing it, we decided to offer it to your attention.
Signs of hypomotor dyskinesia: bowel problems such as prolonged constipation, deterioration or loss of appetite, weight loss, feeling of fullness or.
Symptoms of hypermotor dyskinesia:
- frequent attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- stool disorders in the form of diarrhea;
- change in appetite;
- weakness, headache;
- paroxysmal pain in the right hypochondrium during physical activity;
- heartburn, bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowish coating on the tongue.
Manifestations of mixed dyskinesia combine symptoms of hypertensive and hypertensive variants of the pathology, which alternate. For example, prolonged constipation can be replaced by diarrhea, the pain is either paroxysmal or aching.
Causes of biliary dyskinesia during pregnancy
Why does a pregnant woman develop biliary dyskinesia?
- During pregnancy, a woman's hormonal levels change, which can lead to disruption of the functioning of internal organs. Also, immediately after conception, a woman’s body produces a large amount of the hormone progesterone, its volume increases in the second half of pregnancy. The main task of this hormone during this period is to relax the uterus in order to prevent miscarriage, as well as premature birth. But along with the muscles of the uterus, other smooth muscle organs also relax, and the gallbladder is no exception. Due to such changes, the functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts weakens. The gallbladder is not emptied enough, which leads to its stretching, which in turn causes pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Also, biliary dyskinesia during pregnancy can occur mechanically, because not only the growing uterus, liver and gallbladder, but also the organs of the thoracic cavity put pressure on the organ, so the normal process of bile secretion is disrupted.
Diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia
To diagnose the disease and begin treatment for dyskinesia, the doctor first sends the pregnant woman for an ultrasound of the gallbladder, and be sure to measure its size. Thanks to an ultrasound examination, a specialist can determine whether there is stone or sand in the gallbladder, or inflammatory changes.
Sharashkina N.V. Therapist Center for Immunology and Reproduction
Pregnancy is a wonderful time of waiting for a baby for any woman. Unfortunately, not every day you can feel comfortable: nausea, drowsiness, frequent mood swings and other “troubles” often become companions of your “tour” of 9 months.
One fine day you begin to suffer from a pain of unknown origin somewhere in the right hypochondrium. You come to your doctor and it turns out that you have dyskinesia of the gallbladder and bile ducts. What it is? Is this diagnosis dangerous? So, let's try to calm down and figure it out.
A little theory. Biliary dyskinesia
– a disease based on impaired motility of the gallbladder and biliary tract without signs of organic damage. Dyskinesia is a syndrome that occurs in various diseases: chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, after surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy), pathology of the stomach and duodenum, and liver. In the absence of concomitant diseases, the cause of dyskinesia may be congenital anomalies in the development of the gallbladder (kinks, constrictions).
Symptoms:
—
this is pain and dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, feeling of heaviness in the abdominal cavity, unstable stool).
—
dull, prolonged pain in the area of the right hypochondrium without clear irradiation, and short-term, cramping pain.
Biliary dyskinesia is one of the most common diseases found in women of reproductive age. Pregnancy and accompanying hormonal changes are risk factors predisposing to the development of the disease. For example, in the second half of pregnancy, a woman’s body produces large amounts of progesterone.
. Progesterone is called the pregnancy hormone, as it reduces the contractile activity of the smooth muscles of the uterus, preventing miscarriage and premature birth. Therefore, as pregnancy progresses, the motor activity of the gallbladder decreases, the release of bile is delayed, and the rate of emptying of the gallbladder decreases.
Remember that the diagnosis of dyskinesia is established on the basis of the clinical picture and ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity (ultrasound). Very often, structural features of the biliary tract or gallbladder are the direct cause of dyskinesia.
And yet, what to do if the diagnosis is confirmed? The treatment of pregnant women with biliary dyskinesia is based on an integrated approach. The main goal of treatment is to restore the normal flow of bile through the ducts. This means that measures are being taken in several areas: restoring normal routine and nutrition; elimination of hypovitaminosis and intestinal dysbiosis, drug therapy.
"You are what you eat"
Therapeutic nutrition should be chemically, mechanically and thermally gentle.
Let's crush!
Pregnant women should eat up to 5-6 times a day with a relatively even distribution of food throughout the day to ensure rhythmic secretion of bile.
Let's not escalate!
Extractive substances should be excluded from the diet: peppers, onions, garlic, radishes, smoked meats, mushrooms.
Let's soften it up!
You should not consume refractory fats, since the digestion of fats during dyskinesia is difficult due to the irregular flow of bile into the intestines and a decrease in the activity of pancreatic enzymes.
Let's cajole!
It is preferable to use vegetable oils (sunflower, olive), since their processing does not require a significant amount of bile and enzymes.
What do we treat?
The choice of drugs to restore the functions of bile formation and bile excretion depends on the type of dyskinesia.
For concomitant pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, therapy is based on the treatment of the underlying disease.
- In cases of severe pain, antispasmodic and painkillers are indicated: no-spa, papaverine hydrochloride, mebeverine, baralgin and others.
- In the treatment of biliary dyskinesia, a special role belongs to choleretic drugs. Choleretic herbal remedies can be taken in the form of a choleretic tea or tea. Its composition most often includes immortelle flowers, yarrow herb, coriander fruits, corn silk, tansy, and rose hips. Prescribe 1/2 glass 2-3 times a day in between meals.
- Choleretic drugs also include choleretics, drugs that enhance the formation of bile: allochol, hofitol, cholenzyme, holosas and other drugs with bile acids, valerian preparations, mineral water (increasing the secretion of bile due to the water component).
- Cholekinetics promote the release of bile from the bladder into the intestinal lumen. These include: magnesium sulfate, sorbitol, xylitol, antispasmodics, aminophylline (relaxes the sphincters of the biliary system). They have not only a choleretic, but also a laxative effect, and can also be used in pregnant women as a laxative.
However, biliary dyskinesia does not have a negative effect on the development of pregnancy and fetal formation. However, if symptoms increase or severe pain occurs, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo an examination to rule out a more serious pathology. After childbirth, the gallbladder and ducts restore their tone during the first month. Have an easy pregnancy!
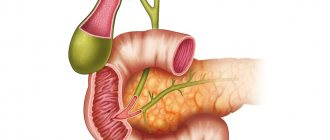
To explain what this means, one cannot do without a basic excursion into anatomy.
The biliary system includes the gallbladder, bile ducts and three sphincters (physicians call a sphincter a circular muscle that narrows or closes one or another opening in the body during contraction). Two sphincters are located in the neck of the gallbladder, and the third is in the duodenum, at the “exit” of the common bile duct, through which bile enters the intestine. The formation of bile in the liver is a continuous process, and its entry into the duodenum occurs mainly during digestion. The gallbladder in humans undergoes vigorous contractions during digestion. The release of bile into the intestine occurs with active contraction of the walls of the bladder and simultaneous relaxation of the so-called sphincter of Oddi (located in the duodenum); relaxation of the gallbladder is accompanied by the closure of this sphincter and the cessation of bile secretion. So, under dyskinesia
in relation to the biliary system, uncoordinated, excessive or insufficient contraction of the gallbladder and sphincters is understood. Pain occurs due to a violation of the sequence and coordination of contraction and relaxation of the gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts.
Biliary dyskinesia is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance, since it contributes to the development of the inflammatory process and stone formation. And on the contrary, dyskinesia can be one of the manifestations of cholelithiasis, chronic cholecystitis, and anomalies in the development of the biliary tract.
There are various anatomical, functional and hormonal connections between the biliary system and other digestive organs; they have a significant impact on the activity of this system. For example, the entry of food into the stomach not only causes mechanical irritation of the stomach receptors, but often also increases bile formation and motor activity of the bile ducts.
The motor function of the gallbladder and bile ducts largely depends on the state of the nervous system: for example, dystonia of the autonomic nervous system
may disrupt the coordination of contraction of the gallbladder muscles and relaxation of sphincter tone and cause a delay in bile secretion.
Psychogenic factors
can also play an important role in the occurrence of dyskinesia , since it is often a consequence and one of the clinical manifestations of general neurosis.
Muscular weakness of the biliary tract is sometimes constitutional (associated with body type) in nature, sometimes provoked by an unbalanced diet or may be a consequence of hormonal imbalance.
Why can dyskinesia develop during pregnancy?
Pregnant women are characterized by hypomotor (i.e., associated with a decrease in motor activity) dysfunction of internal organs caused by a general change in hormonal levels
. In the second half of pregnancy, a woman's body produces large amounts of progesterone. The main physiological meaning of the action of progesterone during this period is to relax the uterus, preventing miscarriage and premature birth. However, “at the same time” other smooth muscle organs, including the gallbladder, also relax. Hypomotor dyskinesia is based on weak, insufficient emptying of the gallbladder, leading to its distension and pain.
The occurrence of dyskinesia can also be associated with purely mechanical reasons: the growing uterus presses, “squeezes” the organs of the chest cavity, including the liver and gall bladder, as a result the normal process of bile secretion may be disrupted.
Diagnosis of dyskinesia
Typically, a woman is bothered by dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium (which can spread to the epigastric region), a feeling of heaviness, a feeling of pressure in this area, often accompanied by a lack of appetite, nausea, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, belching of air, heartburn, and bloating. The pain may intensify with fetal movements, depending on its position in the uterus.
Excessive emotions, nervous fatigue, and sometimes errors in diet increase or provoke pain and a feeling of fullness in the hypochondrium. Pain in the heart area, palpitations, headache, numbness of the limbs, sweating, sleep disturbances may occur - doctors call these symptoms a picture of a vegetative crisis.
In the diagnosis of dyskinesia, the leading place is given to ultrasound examination of the gallbladder. By measuring its size before and after a choleretic breakfast (usually 2 raw egg yolks), the doctor makes a conclusion about the nature of the motor disorders and the type of dyskinesia. In addition, the method allows you to reject or confirm the presence of stones (stones, sand) and inflammatory changes in the gallbladder.
Treatment of biliary dyskinesia
The goal of therapeutic measures for biliary dyskinesia is to normalize the outflow of bile and prevent its stagnation in the gallbladder. Treatment should be comprehensive and include a number of measures:
- Proper nutrition
is absolutely necessary . First of all, it should be fractional, food should be taken at least 5-6 times a day, the diet must include foods and dishes that help reduce the gallbladder: weak meat or fish broths, soups, cream, sour cream, soft-boiled eggs, butter and vegetable oil, rosehip decoction. Healthy foods include cottage cheese, protein omelet, cod (they are rich in substances that prevent fatty liver), as well as foods rich in plant fiber, magnesium salts (bran, buckwheat porridge, carrots, cabbage, apples). - It is also recommended to take choleretic drugs
, and preference should be given to those that are more conducive to bladder contraction.
Choleretic herbal remedies are often prescribed in the form of a so-called choleretic tea
or tea.
The composition of the choleretic collection most often includes sandy immortelle flowers (4 parts), yarrow leaves or herbs (3 or 2 parts), coriander fruits (2 parts). You need to take it like this: brew a tablespoon with two glasses of boiling water, leave for 20-30 minutes, strain. Take 1/2 cup 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Choleretic tea
contain corn silk, tansy, and rose hips. Prescribe 1/2 glass 2-3 times a day in between meals. - To combat bile stagnation, you can, in consultation with your doctor, carry out a “blind” probing
, or
tubage
, with one of the following components: -
vegetable oil
(30-40 ml of corn or olive oil);
— Carlsbad salt
(1 teaspoon per glass of water);
- sorbitol or xylitol
(1 tablespoon per glass of water) - in the absence of edema -
mineral water
(500 ml warm). To carry out tubage in the morning on an empty stomach, you need to drink one of the above remedies and lie down in a warm bed on your right side for 1.5-2 hours. It is not necessary to use a heating pad for a pregnant woman. You should not be alarmed if tubage has a laxative effect. - In addition, in the second half of pregnancy, when it is necessary to strictly take into account the amount of fluid consumed, if edema develops, it is convenient to use Flamin
(dry concentrate of immortelle flowers) - 1-2 tablets 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals or
Holosas
(rose hip syrup) - 1 teaspoon 2-3 times a day.
Biliary dyskinesia does not have a negative effect on the development of pregnancy, the formation of the fetus, and is not an obstacle to childbirth through the natural birth canal. Usually after childbirth, the gallbladder and ducts restore their tone within the first month. However, if pain persists despite the therapy described above, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination to rule out a more serious pathology.
Choleretic for cholecystitis
In the last trimester of pregnancy, against the background of late gestosis, a woman may develop cholecystitis. Usually it occurs if the pregnant woman had prerequisites for this or previously suffered from this pathology. With the intensification of all processes in the body, increased inflammation of the gallbladder may also appear. In the third trimester, the uterus rises high and compression of the internal organs occurs. The liver secretion ceases to be normally pushed out of the ducts, stagnates and provokes the formation of stones.
Many women pay almost no attention to the symptoms of cholecystitis - pain, nausea, belching - associating the painful manifestations with pregnancy. And only when an exacerbation begins, women consult a doctor. If toxicosis continues until the 30th week, this directly indicates liver problems. The seriousness of the situation is confirmed by symptoms such as yellowing of the skin and discoloration of stool. Cholecystitis is very easily diagnosed through a doctor’s examination, palpation, and ultrasound.
Exacerbation of cholecystitis is fraught with the spread of inflammatory processes throughout the entire abdominal cavity.
If toxicosis continues until the 30th week, then you should definitely seek the help of a specialist, since the operation is contraindicated for pregnant women.
After the tests, the doctor will recommend a suitable diet and choleretic agent:
- Kholosas (alcohol-free rosehip syrup);
- Chophytol (tincture of field artichoke water);
- Tanacechol (tansy extract);
Severe attacks of pain can be relieved by using antispasmodics:
- Drotaverine;
- Convaflavin (lily of the valley extract);
- Baralgin.
Choleretic tea, which contains herbal ingredients, is used as an affordable natural remedy.
But even with herbal medicines you need to be careful: they can cause allergic reactions or nausea. Surgery for cholecystitis is resorted to only in very threatening cases: when the diagnosis of purulent inflammation is confirmed or when stones are stuck in the bile ducts.