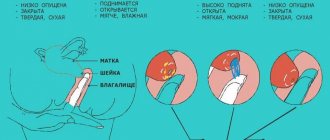
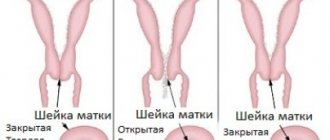
Normally, it is completely closed; towards childbirth it becomes softer and shorter. Its canal gradually expands and, when fully ripe, begins to let the finger inside. Such maturity of the uterus indicates the imminent onset of labor. During the birth of a child, the cervix shortens and smoothes, and directly opens by 8-10 centimeters.
In a healthy woman, the cervical canal remains closed until the onset of labor. However, in some cases premature disclosure occurs. This happens with the development of a pathology such as isthmic-cervical insufficiency. It can occur as a result of injuries caused by previous abortions, surgeries, ruptures in previous births, and for other reasons.
Usually, the cervix begins to prepare for labor gradually, 2-3 weeks before it begins. Signs of preparation are the presence of training contractions and the release of the mucus plug covering the cervical canal. As a rule, first-time women notice the presence of these symptoms earlier than with repeat births. The opening and smoothing of the cervix can begin directly in the child.
Determining on your own whether disclosure has begun is quite difficult. This can be done by the attending physician during a gynecological examination. Based on the results of the examination, he can judge the woman’s readiness for the birth process.
How to give birth without gaps: preparation
If by 38 weeks the cervix is not yet ready for the birth of a baby, medications are often used to soften it. The use of any medications should be carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor. An obstetrician-gynecologist may prescribe the use of antispasmodic drugs in the form of tablets or suppositories that relieve muscle tension, as well as prostaglandins that promote rapid maturation, and physical stimulation.
You can start preparing the cervix and perineum for childbirth at. 4 weeks before the expected birth, gynecologists advise women to actively engage in sex without a condom. Due to natural massage during friction, contractions of the uterus during orgasm and the influence of prostaglandins contained in male sperm on the woman’s body, the cervix softens. However, sexual intercourse is possible only in cases where both partners are healthy.
Evening primrose oil is recommended to be used internally from 36 weeks, one capsule, and from 38 - two capsules. It should be taken before meals and washed down with plenty of water. The fatty acids contained in the oil increase the production of prostaglandins, but you should consult your doctor before using it.
Eating oily fish also helps prepare the cervix for childbirth. This method has no contraindications.
Gentle massage of the nipples with oil or baby cream stimulates the production of the hormone oxytocin, which is necessary for the contraction of the uterus and the onset of labor. This procedure is recommended to be carried out from 38 weeks twice a day for 5-10 minutes.
You can use a decoction of raspberry leaves. Place two tablespoons of dried crushed leaves in an enamel pan, add a liter of water, bring to a boil, strain and cool. From 38 weeks, before each meal you need to drink 100 ml of the resulting decoction.
At 36 weeks, you can start taking rosehip infusion, which not only softens the cervix, but also saturates the woman’s body with useful vitamins and microelements. For 150 grams of dried berries you need a liter of boiling water. Take 200 ml infusion on an empty stomach every morning.
Hawthorn tincture will prepare the cervix for childbirth. Thanks to the use of 10-15 drops of tincture dissolved in water at dinner, the pregnant woman’s sleep will also become more restful.
Strawberry decoction is very useful. It is made from fresh berries, leaves and water. From the 37th week of pregnancy it can be consumed in unlimited quantities instead of tea.
Perineal massage with baby oil or a special cream helps to avoid ruptures during childbirth. It is performed daily before bed with your fingers for 3-5 minutes, starting from the 36th week of pregnancy.
It should be remembered that it is undesirable to carry out artificial stimulation of labor without medical indications, as this may have negative consequences: painful contractions, oxygen starvation of the fetus, the risk of uterine rupture along the scar in previous births, and unpreparedness of the fetus. Artificial stimulation may be necessary in cases of postterm pregnancy, large fetus, hypertension in a woman, or prolapse of the umbilical cord, but the decision on stimulation in any case must be made by the attending physician. Preparing the uterus for childbirth and stimulating labor are completely different things. If in the first case you can safely use most folk remedies at home, then in the second all procedures should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of medical staff.
09-09-2006, 22:06
What am I talking about? Most often, the body itself knows what it is doing! I understand that it's different for everyone. But why do doctors always talk about this neck... Well, if she’s not ready, she’ll have to get ready :)) Delov then: fifa: I didn’t prepare her on purpose, she did it all herself :) Do these predictions agree with everyone? Have an easy birth everyone! :flower:
09-09-2006, 22:19
A week before giving birth, it was deaf, like in a tank :). They sent us out for a walk and a walk. A week later in the morning I decided to give birth, arrived at the maternity hospital with good dilatation, and gave birth quickly. But this is the second birth. At first, she didn’t want to open up for a long time. And the preparation did not help - I was in prenatal care.
09-09-2006, 23:58
10-09-2006, 00:36
Something came over me to tell... Many people here are complaining, the doctor said that the cervix is not at all ready, etc., etc.... They told me that too and said that I would be giving birth for a long time, since at 40 weeks the cervix doesn’t even think about childbirth... And my pelvis narrow and what didn’t they tell me…. Even a midwife with extensive experience looked at me 9 hours before the birth and said that this was not labor, the cervix was not ready at all: 004: 4 hours before the birth she said that the cervix was softening a little - you would give birth in 3 days: ded: And when you arrive in 3 hours - she grabbed and dragged me to the maternity hospital, since it was already a FULL opening...
Oh, right about me! Only it was not the midwife who looked at me, but the very experienced Gleim L.I. And she yelled at me at the top of her lungs because I didn’t cook the neck, so and so. If only you knew how much I ate no-shpa and used up belladonna candles. And no matter what I did, the cervix did not open. As a result, I barely crawled to the birth center, waiting for contractions after 3 minutes, and they opened my cervix with my hands.
And then I had a question that still torments me to this day. Well, the doctor has been working for N number of years, has he never met a woman in labor whose cervix did not dilate at all??? Am I the first and only one in the whole world to get caught????? Am I the only one???
10-09-2006, 09:20
On Tuesday the doctor looked at me and said: “Well, there’s still a week left,” but from Wednesday to Thursday contractions began and on Thursday I gave birth.
Identically! Even by day of the week :)! Only my water started to break, and not contractions. Everything went great.
♠Marxie♠
10-09-2006, 09:44
For me it was the other way around - one finger dilated - the next day you’ll give birth (a week passed), then two fingers dilated - well, you’re about to give birth (another week passed). Then, of course, I gave birth. Like this…..
10-09-2006, 13:04
At the 40th week (August 25) at 13.00 the doctor looked at me and said - quietly in the forest... :) For about 10 days you can still walk calmly without twitching, this will not be a post-maturity... We went to the dacha to soap ourselves... And at 19.00 the contractions began... Immediately there was such a super opening... On the morning of August 26 at 9.50 I already gave birth.:004: The doctor said that the birth process is started by the child, and only he knows when to give the command to the cervix to open... It’s another thing when it doesn’t obey... But that’s another thing .
10-09-2006, 13:32
And then I had a question that still torments me to this day. Well, the doctor has been working for N number of years, has he never met a woman in labor whose cervix did not dilate at all??? Am I the first and only one in the whole world to get caught????? Am I the only one??? Yes, the birth was exactly at 40 weeks.
Apparently I'm the same. True, the birth was already at full 42 weeks. On the eve of the promised stimulation, because it was no longer possible to wait, and the gel did not help, the waters broke at night. Before that, irregular contractions were going on for 24 hours, they looked at the chair three times: “The cervix is not effaced, there is no dilatation In general, these are harbingers." When the waters broke, there was nowhere to go, and the cervix was still not prepared. Injected with Promedol. After 4 hours, she gave birth. All 4 hours, lying on her back (this is terrible!!!). Anyone lying during contractions will understand me. .At 7cm they opened it with their hands. I’m just sure that all this is because I was kept VERY actively throughout my pregnancy.
10-09-2006, 14:50
I had an examination at 40 weeks, the doctor is also experienced, he said that the cervix was not ready and the baby’s head had not even dropped, judging by the state of my pregnancy at 38 weeks, they decided to wait another week, and then we will stimulate, in principle he did not insist. I had to decide. I also eat the fucking no-shpa as I’m supposed to. In short, at exactly 41 weeks I came to the maternity hospital to give up, because... Nothing has changed for me, and after examining me the day before, the doctor said that the baby’s heartbeat began to fluctuate a little, which indicates that it’s time for him to be born. They put me on a drip, I lay with it for 2 hours and there were zero results, then the doctor punctured my bladder and they took me to a caesarean section, just like that.
10-09-2006, 15:34
I was prepared for 1.5 weeks in prenatal care and was told that I could give birth at any moment. The birth began unexpectedly (as it always happens =)), with a softened (not very much true) and not dilated cervix (well, it was 2 cm). So, IMHO, you can’t predict anything in advance and you can’t really predict anything by looking at the neck =)
10-09-2006, 21:23
Likewise. :)) We came to see the doctor during the day. The PDR was supposed to be the next day. The doctor examined me and said that you should be fine for another two weeks. Since there is no opening, the neck does not even let half a finger through, but it is already soft. And at three o’clock in the morning my water broke aaaand…. away we go. The baby himself knows when it’s time for him. Mine was struggling a lot that evening and night before giving birth. As a result, we were born right in the PDR. :004: The report is on the website.
Collapse
In order for labor to begin, a woman's cervix must be well dilated. Sometimes a woman in labor is told that she has an immature cervix. What to do in this case and what does this mean? This cannot be done without additional help; medical workers use various methods of stimulation. Only a doctor can choose the appropriate one after examining the patient.
The structure of the cervix and the entire organ and their role in pregnancy and childbirth
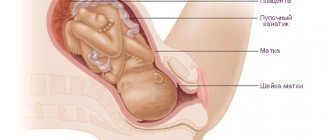
The uterus is the female reproductive hollow organ in which the fetus develops from conception to birth.
The shape resembles an inverted pear, and consists of a bottom (widened upper part), a body and a neck. It is connected by the cervix to the vagina, and on the sides to the fallopian tubes. In the body it is located in the pelvis, behind the bladder and in front of the rectum. It has three layers: perimeter, myometrium, endometrium.
Its position depends on the state of the digestive and urinary systems, and may shift slightly during the day.
The cervix looks like a light pink ring of muscles and consists of an isthmus, cervical canal and vaginal part. On both sides, the cervix is limited by pharynxes - external (vaginal) and internal (uterine).
During pregnancy, the cervix produces a special secretion to protect the fetus and uterus from infection, and maintains the uterus in the desired position at the required level.
Functions of the cervix during pregnancy and childbirth:
- production of mucous secretion to protect against viral, fungal, and bacterial infections;
- keeping the fetus in the proper place;
- informational - the gynecologist confirms the fact of pregnancy during a vaginal examination, based on the appearance of the cervix - the color changes from pink to bluish-purple and increases in size. Shortly before birth, the cervix becomes soft, the organ prepares for labor. During the process of childbirth, the gynecologist assesses the degree of dilation, and this indicator is used to guide the process.
Ways to stimulate the cervix
What to do if a woman’s cervix is completely ready for childbirth, but contractions still don’t start? Only a woman's doctor can tell you the answer - it is he who will select all the necessary medications and suggest home remedies to help stimulate labor.
There are a number of medications designed to activate the process of dilation of the cervix and intensify labor. Such medications are injected into the cervical canal, the effect can be expected within 2-3 hours.
Treatment of a narrowed cervical canal is carried out using kelp, a medicinal product that comes in the form of sticks. Such sticks, saturated with moisture, are introduced into the cavity of the cervical canal, where, under the influence of time, they begin to gradually swell and increase in size, leading to an expansion of the canal. As a rule, 3-5 hours of using kelp is quite enough to prepare the cervix for childbirth.
Prostaglandin in the form of a gel or suppository - within a few hours the woman’s body is completely ready for childbirth.
In the most severe cases, an amniotomy can be performed in a hospital hospital setting - this procedure is a medical puncture of the amniotic sac. In this case, the water breaks, the baby’s head drops, and labor accelerates.
Non-medicinal methods of activating labor activity of the uterine cervix:
- sexual intercourse - just one sex can provoke a noticeable contraction of the muscle fibers of the uterine organ, which activates labor;
- cleansing enema - has an activating and irritating effect on the walls of the uterus, provoking accelerated contraction of the organ;
- physical activity - of course, no one forces the expectant mother to do strength training; it is quite enough to constantly walk around the ward or in the corridor of the maternity ward.
The cervix and indicators of its maturity play an extremely important role in the process of childbirth. If the uterus is ready for childbirth, but there are no contractions, various methods of quickly stimulating labor are used. These include medications as well as other methods. All this will help the birth of a healthy and active baby.
Video: 40 weeks. Induction of labor naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xyy_PaBD3gs
Video: how to induce contractions?
Causes of cervical dilatation
Labor that begins at 37 weeks or later is considered normal.
During this period, the cervix independently opens to one finger, which indicates the physiological maturity of the uterus. She begins to contract, and her body becomes smaller. The pressure of the fetus on the birth canal increases and its opening occurs.
Before birth, amniotic fluid is divided into the upper and lower poles of the amniotic sac.
The lower part enters the cervical canal and also helps to open the cervix.
Towards the end of pregnancy, the amount of the pregnancy hormone progesterone decreases and this marks the beginning of labor.
Dilation may be premature and occur long before the due date. The main reason is hormonal deficiency.
Dilation of the uterus after 28 weeks leads to the birth of a viable baby.
If the opening occurs earlier, its causes may be infections, placental abruption, inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system, or lack of progesterone.
Childbirth
is an event that cannot always be predicted down to the day. In a full-term pregnancy, they occur at 38-40 weeks.
Of course, all expectant mothers look forward to meeting their baby and begin to listen to themselves long before labor begins. As a rule, childbirth does not come as a complete surprise. There are several signs that determine the readiness of the female body for this sacrament. They are also called harbingers.
Whenever normal birth occurs
, they are preceded by complex preparation with the participation of many physiological mechanisms. Today, no one can say for sure what exactly triggers the onset of contractions. In the time of Hippocrates, it was believed that labor is provoked by the fetus itself: when it reaches the required degree of maturity, it pushes away from the fundus of the uterus and independently tries to get out, which causes delivery. Now this concept seems obviously incorrect and simplistic, but one thing about it is completely true: normal labor begins only when the baby is ready for it. It is he who triggers a chain of complex biochemical reactions that cause changes in the mother’s body. As a rule, all these changes begin 2-3 weeks before birth, as indicated by the precursors.
One of the most important signs of readiness for childbirth
- prolapse of the abdomen. This sign is widely known and always portends the imminent birth of a baby. Omission occurs for several reasons. The baby's head enters deeper into the pelvis, pressing against the outlet of the uterus, which, under the influence of pressure and hormones, becomes more relaxed and pliable. At the same time, the abdominal muscles relax, so in the lower part it looks more convex. Prolapse can be noticed not only by the obstetrician-gynecologist, but also by the pregnant woman herself, and one should focus not only on the shape of the tummy. If you place your hand below the sternum, then the palm will fit freely between the chest and the bulge of the abdomen, when, as in earlier stages, it bulges just under the chest. At each visit to the antenatal clinic, the height of the uterine fundus is measured; on the last visits its size becomes 2-3 cm smaller; this also speaks of prolapse and imminent birth. As a rule, this sign appears first, 2-3 weeks before the birth of the child, but in some cases it can appear within a few days, and sometimes even remain almost invisible.
As the abdomen descends, the center of gravity shifts. The protruding uterus pulls forward, so to maintain balance when walking, a woman has to lean back, moving her shoulders and head back a little. Because of this, there is a change in the usual posture and gait, which becomes a “proud walk.” Another symptom of approaching labor is a larger-than-usual protrusion of the navel. Due to the fact that increased pressure is placed on the lower part of the uterus and abdomen, it bulges forward more.
The next precursor is physiological weight loss
. Typically, pregnant women weigh themselves often enough to monitor their weight gain. If you carry out this procedure daily or at least every other day, you will notice that 2-3 days before the onset of labor, the weight decreases by about 2 kg (on average - from 1 to 3 kg, depending on the initial figures). This is explained by the fact that before childbirth, the body gets rid of some of the fluid that it accumulated to increase tissue elasticity.
Shortly before an exciting event, many women experience a change in their psychological state. Some women become more nervous, excitable and irritable than usual, and this is caused not so much by fear as by physiological changes in the nervous system that occur during the hormonal surge that precedes childbirth. Others, on the contrary, complain of drowsiness and fall into an indifferent, apathetic state. There is a certain protective mechanism in this: the body prepares for the upcoming load, resting before childbirth. As a rule, such mental changes begin 3-4 days before contractions.
Detachment and calm
can apply not only to a woman who is about to become a mother, but also to a child. Doctors notice that in many pregnant women, a few days before giving birth, the fetus begins to move less actively than before. However, a significant portion of those who gave birth claim that they did not notice a decrease in the baby’s activity, while for some, the child, on the contrary, began to move more often. Like all other precursors, this sign is not observed in all cases.
Some experts consider Braxton-Hicks contractions to be a warning sign of labor.
, or training contractions. They can begin within 2-3 weeks before birth, but sometimes occur earlier, from the 34th-35th week of pregnancy. These contractions do not cause labor and are painless, irregular contractions of the uterus of varying duration. A woman who has already undergone childbirth will never confuse training contractions with the real ones during her second pregnancy. The latter occur with more or less pain and appear regularly - at certain gradually decreasing intervals and with increasing duration. Therefore, if there is any doubt about the origin of contractions, it is enough to measure their duration and the periods after which they repeat over a period of 30-40 minutes.
A few days before giving birth, a woman may be bothered by vague, weak pain of an aching, pulling nature, mainly in the back, sacrum and lower abdomen. They are not regular and usually do not bother you much. Their appearance is caused by muscle stretching and divergence of the pelvic bones.
INTERESTING
According to the legislation of our country, childbirth is considered to be the birth of a child after 28 weeks of pregnancy. An earlier delivery is called a miscarriage. In Western medicine, where care for premature babies is better developed, childbirth means the birth of a baby from the 22nd week, when it weighs only about 500 g.
Finally, the last sign of readiness for childbirth, which the pregnant woman herself can notice, is the release of the mucus plug.
. During pregnancy, the plug, which is the secretion of the cervical glands, is located in the cervical canal. It plays a protective role, isolating the uterus and fetus from infection that can enter there from the vagina. The plug comes off at different times: sometimes 2-3 weeks, sometimes no more than a few hours before the onset of contractions, and sometimes even with the onset of labor. For first-time mothers, it is quite difficult to determine the passage of the plug. It may look and feel different. Most often, the plug looks like a clot of mucus - transparent, sometimes with a greenish-brown tint or streaks of blood. When parents are asked to make a comparison that everyone can understand, they usually talk about its resemblance to an undercooked egg white or garden slugs. You should not be afraid of small red or pink inclusions - this is blood from the capillaries of the cervix, which expands before childbirth. On the contrary, you can even be happy about such a plug: if it comes off in the form of a transparent clot, it means that labor will most likely begin in a few days, and if it contains elements of blood, there are almost certainly only a few hours left before the birth of the child.
The mucus plug may come off completely or in parts. In the latter case, the woman either sees separate fragments of it, or notes that there is more vaginal discharge than usual. If the plug is mixed with blood, then sometimes it becomes noticeable in the form of spotting, which sometimes frightens pregnant women. If a woman expecting childbirth is not sure that the blood is a passing plug, she should immediately consult a doctor.
In addition to the listed signs of readiness for childbirth, there is one more - the degree of ripening of the cervix. It can only be assessed by an obstetrician-gynecologist during a speculum examination. As you prepare for childbirth, the cervix becomes softer, shortens, smoothes and opens its lumen, which before birth can reach 2 cm. Speaking about the degree of maturity of the cervix, the doctor can roughly judge when labor will begin. Typically, maturation begins 2 weeks before the onset of labor, but sometimes faster, literally 2-3 days, less often - a few hours.
Assessing precursors is an important step in monitoring pregnancy. It allows you not only to calm and prepare a pregnant woman, but also to provide certain information to doctors.
New materials
- Succession period - 06/28/2013 04:41
- The period of expulsion of the fetus is 06/28/2013 04:40
- Periods of childbirth. Cervical dilatation period - 06/28/2013 04:38
Old materials
- Pregnancy with anemia - 06/28/2013 04:26
- Pregnancy with liver diseases. Hepatitis - 06/28/2013 04:26
- Pregnancy with liver diseases. Intrahepatic cholestasis - 06/28/2013 04:24
How to prepare the cervix for dilatation
It happens that labor has begun, but the cervix is not ready - it is hard and does not open. In this case, there is nothing left but to speed up the dilation of the cervix before childbirth.
If you do not stimulate, tissue ruptures will occur during childbirth, the process will be delayed and you will have to resort to a caesarean section.
The cervix is prepared for dilatation in case of post-term pregnancy, and the need to induce labor ahead of time - in case of gestosis and fetal hypoxia, and other indications.
Disclosure is helped by:
- gynecological examination;
- taking antispasmodics;
- Sinestrol injections intramuscularly - soften the uterus and do not cause contractions;
- Enzaprost intravenously - contains prostaglandins and speeds up the labor process;
- prostaglandins - under their action, the cervix softens. Produced naturally by massaging the cervical canal, or gels containing prostaglandins are introduced intravaginally;
- Laminaria seaweed is introduced into the vagina in the form of sticks 3-4 mm thick. A humid environment causes them to swell 10 times, the cervix stretches, softens, and training contractions begin. Algae comes out along with mucous secretions. There are also vaginal suppositories with kelp;
- sex - mechanical stimulation and prostaglandins, which are part of sperm, help. Orgasm, with a sufficient degree of readiness, can become the beginning of labor;
- physical activity - cleaning before childbirth better prepares the cervix. Walking, going up and down stairs, squatting (for example, when washing floors) are useful;
- herbal medicine - raspberry and strawberry leaves, rose hips help the neck to ripen.
Medication methods are used only in a hospital; the use of drugs speeds up labor.
Usually, closer to childbirth, if the course of pregnancy is favorable, the gynecologist explains to the pregnant woman how to prepare for childbirth and open the cervix at home.
If the cervix opens prematurely
The opposite situation also happens, when the cervix begins to open and prepare for childbirth ahead of schedule. This is usually associated with a pathology of the cervical canal called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. It lies in the inability of the cervix to properly contain the fetus. It shortens and opens early, which often leads to spontaneous abortion.
The presence of this pathology is indicated by the length of the cervical canal at 20–30 weeks of less than 25 mm.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can develop due to trauma to the cervix, hormonal disorders, or excessive load on the cervix during pregnancy. In this situation, measures should be taken aimed at maximizing the prolongation of pregnancy:
- Bed rest (usually in a hospital setting).
- Prescription of tocolytics, antispasmodics and sedatives.
- Emotional peace.
- Stitches are placed on the cervix, which are removed at 37 weeks.
In addition, treatment is carried out to promote the rapid maturation of the fetal lungs in case labor begins prematurely. Before childbirth, the cervix changes so much that it allows the baby to be born unhindered.
The gradual dilatation of the cervix before childbirth is almost unnoticed by the woman herself.
Therefore, visits to the gynecologist in the third trimester should be regular and accompanied by a vaginal examination, which allows you to assess the degree of readiness of the body for childbirth. This is especially true for those women who already feel other warning signs. If the due date has already approached, but cervical maturity has not yet arrived, then there is no need to be afraid of stimulation. Sometimes delay can cost the lives of both mother and child.
Symptoms of disclosure
Inexperienced women are concerned about the dilation of the cervix at which labor begins.
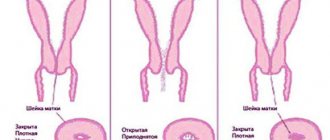
Normal labor begins with the cervix dilating by 1 cm. After the mucous plug comes off, it dilates by 2 or more fingers - up to 10-12 cm, sufficient to pass the baby’s head.
The opening is accompanied by contractions varying in strength and frequency. The neck becomes short, about 1 centimeter.
In women giving birth for the first time, dilation begins from the internal os, and the cervix resembles a cone with a base at the uterus.
In multiparous women, both pharynxes open simultaneously, and this happens faster.
The main sign of dilatation is contractions. At first they occur at intervals of 20-30 minutes, then they become more frequent and occur with a break of 5 minutes or continuously.
After opening by 2 fingers, its speed is 1 centimeter per hour.
Conclusion
Why is the cervix not ready for labor? The answer to this question will be given by an obstetrician-gynecologist after examination and examination. Diagnostics will show when to give birth in one case or another, because there are situations when you cannot delay.
Special exercises, kelp sticks, herbal decoctions and infusions, as well as medications will help prepare the immature cervix for delivery. Medicines are used in the form of gels, tablets, suppositories and injections. The doctor will decide what is most suitable for a woman. Self-medication in this case will not only be inappropriate, but also life-threatening for the pregnant woman and her baby.
←Previous article Next article →
It's no secret that you need to prepare for childbirth. This preparation includes not only “raids” on stores with children’s things and a psycho-emotional mood. You also need to prepare for childbirth, in which your little one grows and develops for 9 months. In principle, nature itself made sure that all female organs “ripe” as much as possible before childbirth and do not fail at the right moment. However, not everything and does not always go according to plan.
Periods and phases of cervical dilatation
Dilatation is the first and longest stage of labor.
This period is divided into three phases:
- Latent - the initial phase of disclosure, lasts six or more hours. Symptoms at this stage are absent or mild. The opening of the neck reaches four centimeters - two fingers.
- Active - within four hours the cervix dilates to 6-8 centimeters, at the end of the phase an outpouring of amniotic fluid occurs in a volume of approximately 200 ml. The woman in labor experiences pain, distension in the lower abdomen, and aching in the lower back. When walking and other physical activity, the process accelerates. At this time, the baby is involved in labor - his head reaches the pelvic floor.
- Transition – This phase is also called the deceleration phase. In multiparous women, it may be absent or go away very quickly. Women giving birth for the first time go through this phase in varying amounts of time - usually from an hour to two. At this time, the greatest dilation of the cervix of 10-12 centimeters occurs.
The opening period is divided into two stages:
- disclosure - lasts from the beginning of the process, when the pharynx is opened by 4 centimeters and until full disclosure. The amount of full dilatation is individual for each case and is about 6 centimeters for a premature pregnancy, 10-12 cm for a normal pregnancy;
- maximum dilation - from full dilation to the birth of the child, and then the placenta.
Normal cervix during pregnancy
Cervical dilatation is the first stage of labor. The cervix should be closed before birth; under the influence of contractions, the uterus tenses, then relaxes, and at the moment the muscle fibers contract, their relative position changes - that is, the cervix opens.
The moment of dilatation of the cervix also occurs with the help of the amniotic sac. With its weight and downward pressure it helps to open.
The cervix has an internal and external os. There are differences between the primiparous and multiparous cervix. In a primigravida, the internal cervical os first opens, which takes the shape of a funnel, and then the outer os stretches. It is easier for multiparous women to dilate the cervix, since the external os is often already open by 1 finger at the end of pregnancy. When the cervix of a multiparous woman dilates, the external and internal os open almost simultaneously.
The cervix dilates by 1 finger, then by 2 fingers, gradual expansion occurs. Full dilation is 10 - 12 fingers or 10 - 12 cm. At this degree, the pharynx allows the fetal head and torso to pass through.
When does the water break and the amniotic sac ruptures? During contractions, the baby in the amniotic sac presses on the cervix; the place where the baby's head encircles, in contact with the lower segment of the cervix, is called the contact belt. This contact zone divides the amniotic fluid into anterior and posterior. Almost when fully dilated, the bladder bursts and the anterior amniotic fluid drains.
After the baby is born, the posterior amniotic fluid leaves. When the waters break when the cervix is not fully dilated, this is an early release of the waters; if the waters break before the onset of labor, then such a departure will be called premature. When the amniotic sac is very dense and does not rupture on its own, it is ruptured by an obstetrician.
The cervix of the uterus in primiparous and multiparous women is different; subsequent births usually occur easier and faster than the first. Many people are interested in how to give birth without ruptures, how not to tear the cervix? In many ways, a good gynecologist who delivers the baby will help you give birth without ruptures and without tearing the cervix. The birth canal and perineum will depend 80% on it.
Yes, it is possible to give birth without cervical ruptures or perineal ruptures, but if there are already existing ruptures or sutures in the intimate area, as well as with a narrow pelvis, it is difficult to avoid ruptures.
Monitoring the cervix before childbirth and at the moment of dilatation is the job of specialists; for a woman in labor, the main thing is to find one and fulfill their requirements.
We will be very grateful if you evaluate the usefulness of this article. Your opinion is very important to us
Just before childbirth, the cervix changes dramatically. A pregnant woman does not feel these changes, but the unborn child gets a chance to be born naturally. So how exactly does this reproductive organ change and when is medical attention needed to improve the dilatation of the uterus? We are looking for answers to these and other similar questions.
The parameters characterizing the state of the uterus before childbirth are its location in the pelvis, state of softness and length. The softening of the cervix to the point where it can allow 1-2 fingers of the doctor inside indicates the readiness of the birth canal for the process of delivery. Such changes are accompanied by the removal of the mucous plug. That is, the sooner the cervix begins to dilate, the sooner the woman in labor notices this sign of the onset of contractions.
Before childbirth, the cervix shortens. According to medical statistics, its length is about one centimeter. If we talk about the location, then it becomes in the center of the small pelvis, while during pregnancy the cervix is tilted back.
Doctors evaluate all of the above parameters on a five-point scale. A score of 5 indicates that the uterus is ideally ready for childbirth. This condition is called a mature uterus.
The above are excellent prenatal parameters. But in practice, this does not always happen, and doctors resort to stimulating the process of cervical dilatation.
If a medical examination shows that the cervix is not mature, and you are due to give birth soon, then it is quite acceptable to speed up this process and perform stimulation. Not using it sometimes means dooming the baby to oxygen starvation, given that before birth the placenta ages and cannot cope with its functions as before.
Administration of Enzaprost intravenously. This drug also contains prostaglandins. Thus, the period of contractions is reduced in time.
Sometimes women use self-induction of labor.
- Enema. After it, the mucus plug comes off - and the cervix becomes mature. The procedure can only be used by women who have already reached their due date, that is, the baby is full-term.
- A warm bath is not recommended for loose plugs and waters. The procedure is also dangerous for women with high blood pressure.
- Sex acts as a medical stimulant. After all, sperm contains prostaglandins. That is, it promotes the maturity of the uterus. But pregnant women whose plug has already come out should not have sex. After all, there is a possibility of contracting an infection in the uterus.
- Physical activity. This could be a brisk walk, washing the floors, or cleaning. Women with hypertension do not need to overdo these methods.
But such methods can be fraught with dangerous consequences.
When registering for pregnancy, a woman must undergo a series of diagnostic procedures to determine her health status and ability to bear and give birth to a baby. The greatest importance is attached to the examination of the internal genital organs, especially the condition of the cervix.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the dynamics of pregnancy with twins by week
What it is?
The cervix is the most important part of the female organ, associated with the process of childbirth, affecting both the course of pregnancy and the birth process. It is a small tube, approximately 4 cm by 2.5 cm, connecting the uterus and vagina. The cervix is divided into the upper - supravaginal part, located above the vagina, and the lower - vaginal part, which protrudes into the vaginal cavity.
Additionally, in the center of the lower part, the cervical canal opens in the form of an internal pharynx (entrance to the uterine cavity). The surface of a healthy cervix is pale pink, shiny, smooth and elastic, and from the inside of the cervical canal the color becomes more intense, and the surface is loose and velvety.
July 21, 2015
The cervix is the lower segment of the organ and is a continuation of the body of the uterus. The isthmus is the boundary between the body and the neck.
Walls
The wall of the cervix differs from the wall of the uterine body in the presence of more collagenous connective tissue fibers and, to a lesser extent, elastic smooth muscle fibers. The mucous membrane of the cervix is located directly under the connective tissue membrane, represented by columnar epithelium.
Columnar epithelium consists of tall cells capable of secreting mucus. Nabothian glands are derivatives of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. At the point where the cervix enters the vagina (the vaginal surface of the cervix), there is a zone where the columnar epithelium is replaced by stratified non-keratinizing epithelium.
The cervix (photo presented later in the article) anatomically consists of: the isthmus, supravaginal and vaginal parts.
- Vaginal surface of the cervix.
- Supravaginal segment of the cervix.
- External os of the uterus.
- Internal os of the uterus.
- Cervical canal.
The vaginal part is the lower part of the uterus. It is in this area that there is a transition zone of the epithelium, which is diagnostically significant for the doctor at the time of the examination. Normally, the entire surface of the vaginal part of the cervix is covered with stratified non-keratinizing epithelium, like the surface of the vagina.
Schematic photo of the cervix
When the transition zone shifts, part of the vaginal surface is occupied by columnar epithelium, which is not normal. In this case, we should talk about pathological changes - the formation of pseudo-erosions or erosions. On the vaginal surface there is an external os, which is limited by the anterior and posterior lips of the cervix.
Between the posterior lip and the vaginal wall there is a “pocket” - the posterior vaginal fornix, and between the anterior lip and the anterior wall - the anterior fornix. These anatomical structures are the site of punctures performed by a doctor for diagnostic purposes. The supravaginal part of the cervix is its upper segment, located between the vaginal section and the isthmus.
The cervical canal is the connection between the vagina and the uterine cavity. The anatomical unit begins with the internal os in the cavity of the body of the uterus, passes into the cervical canal proper of the cervix and exits through the external os into the vagina. Glands that produce a significant amount of mucus form a mucus plug in the canal, preventing foreign infection from entering.
Ligaments and muscles
The ligamentous apparatus is represented by a complex of muscles, ligaments and fascia that perform supporting, fixing and suspending functions.
| Function | Ligaments that perform the function |
| Suspension (attachment of the uterus to the wall of the pelvic ring) |
|
| Fixing (providing the necessary mobility to the pregnant uterus) |
|
| Supportive (separation and support of the pelvic organs in their anatomical position) |
|
The ligamentous apparatus of the cervix includes all 3 functions, but not all ligaments are involved in its attachment.
Normal functioning of the cervix is ensured by:
- wide paired and circular ligaments, which perform a suspensory function;
- the main uterine ligament that performs fixation;
- muscle fibers with a fascial membrane as a supporting apparatus.
Based on the anatomical features of the cervical wall (the predominance of collagen fibers of connective tissue), such a section is not able to fully stretch and return to its original position. The main task of the cervix is to support the fetus during pregnancy inside the uterus, to prevent foreign infection from entering the uterine cavity and to ensure the natural birth canal at the right time.
In teenagers
Sensations of a woman in labor during dilatation of the cervix
All births are individual, and the same woman experiences different sensations during repeated births.
The fetus presses on the lower abdomen, the pain is characterized as bursting. Pulls the lower back and lower abdomen. At the beginning of labor, it is similar to the sensations of painful menstruation; after the contractions increase, the pain intensifies.
Often, shortly before childbirth, contractions subside and the pain goes away. After a short rest, contractions resume, usually more intense.
The opening of the cervix at the last stage, before pushing, is the most painful in the entire birth process.
Uterus unprepared for childbirth
The “house” of your belly is an elongated organ, which consists of muscle and fibrous tissue - the uterus, which ends in the cervix in the lower part. As soon as labor occurs (researchers, by the way, still cannot figure out why labor occurs at one time or another), the uterus begins to contract, that is. During contractions (the first stage of labor - dilation), the uterus should fully open and release the fetus. At this time, incredible events occur in the still pregnant body: the uterus, contracting, seems to “slide” from the fertilized egg, rising upward, and the fetus itself descends into the cervical canal. Full dilatation of the cervix is recorded when the baby’s head can “crawl” through it. As soon as this happens, the second stage of labor begins - expulsion and pushing, which ends with the birth of the baby.
To be born, the child has to go through a very difficult path, but the belly-dweller stops at nothing. For example, if the cervix does not allow it, it still climbs, and this results in ruptures, which are frequent accompaniments of childbirth. It is easy to guess why exactly this complication occurs - due to insufficient elasticity of the muscle tissue of the perineum. It is clear that there are other reasons for ruptures during childbirth, but nevertheless, the elasticity of the uterus is a prerequisite for successful childbirth.
It is interesting that during pregnancy the uterus independently prepares for the upcoming birth. In the last trimester of pregnancy, muscle tissue is very actively replaced by collagen fibers, which provide it with the ability to stretch. Doctors call this condition “maturity of the uterus and its cervix.” Typically, the attending physician determines this “maturity”, at which the length of the cervix should be up to 2 cm, its “consistency” should be soft, one transverse finger should pass beyond the area of the internal pharynx (this is the result of shortening of the cervix) and the cervix should be located in the center of the vagina.
Deviations from these norms (the cervix is too long, its consistency is dense, the cervical canal is closed and the external os) indicates the immaturity of the cervix, that is, the body is not ready for childbirth and needs “recharge.” Doctors call an immature neck an “oak neck.” You should not hope that a uterus that is ready for childbirth will ensure that there are no ruptures, but its “maturity” will greatly reduce their likelihood. Therefore, you should not neglect preparation.
Degree of cervical dilatation
Dilation of more than 8 centimeters cannot be determined during a vaginal examination - the edges cannot be palpated. Therefore, the question of how many fingers should be open is not entirely correct.
They focus not only on the degree of opening, but also on the structure of the tissues and the placement of the cervix.
During pregnancy, the external os is tilted back, and during childbirth it is turned straight.
The degree of cervical dilatation corresponds to the following indicators:
- 1 finger - 2 cm;
- 2 fingers - 4 cm;
- 3 fingers - 6 cm;
- 4 fingers - 8 cm.
The degree of dilatation is also assessed based on the condition of the cervix:
- not flattened or opened;
- completely smoothed out;
- dilated 6 cm;
- fully opened.
Diagnosis of cervical diseases
The doctor may suspect some pathological conditions of the cervix during a gynecological examination (examination of the organ in the speculum). Such a diagnosis is informative only for diseases affecting the vaginal part of the cervix. The cervical canal is inaccessible at this stage.
To clarify the diagnosis, the gynecologist resorts to the Schiller test - the use of iodine to identify pathological areas. Healthy cervical cells will intensively absorb iodine, turning brown, and areas of the lesion where there are no such cells will become pale.
Ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs is informative in severe conditions - cancer, endometriosis. Such an examination is carried out in order to exclude damage to the body and fundus of the uterus, as well as the spread of the disease to neighboring organs.
Colposcopy makes it possible to evaluate the morphology of cells, thanks to the magnifying ability of the colposcope. Taking a biopsy is an extreme diagnostic measure, which the gynecologist resorts to if previous methods are not informative.
The purpose of a biopsy is to take tissue at the border of a healthy zone and a lesion for cytological examination in order to determine the presence of cancer cells in the biomaterial. Sometimes doctors use CT scan data to detect metastases (distant cancer cells) in other organs and systems.
How is the degree of cervical dilation determined?
The degree of dilation is determined by vaginal examination of the cervix before birth.
The middle and index fingers are inserted into the vagina. Then the inspector moves them in different directions until the edges touch.
The resulting distance in centimeters is the desired value. The meaning is subjective.
The mature uterus is soft and loose to the touch. To determine maturity, they use the concept of cervical effacement, which means its thinning, and softening of the cervix before childbirth.
During pregnancy, the cervix is dense; closer to childbirth, it becomes thinner. Measured as a percentage. 90% effacement indicates readiness for childbirth.
To determine the degree of disclosure, external methods are also used. During labor, the uterus forms a contraction ring.
Using the Schatz-Unterberger method, the distance from the pubis to the groove of the ring is measured in centimeters.
This distance is equal to the size of the opening of the internal mouth.
How is the cervical examination before childbirth?
Every woman in labor wants to know how a prenatal examination takes place. In principle, this procedure is practically no different from operations that are performed during a preventive visit to the gynecologist.
As a rule, it is carried out at the final stage of pregnancy (several days before birth). During this procedure, the woman sits on a gynecological chair in a horizontal position.
The doctor always performs this procedure wearing disposable sterile gloves. The inspection algorithm is as follows.
- First, the gynecologist examines the condition of the external genitalia, paying special attention to the labia majora and minora.
- Then begins the so-called examination of the cervix before childbirth in the speculum. With the help of these devices, the doctor determines the maturity of the cervix and its readiness for childbirth. Indicators of the optimal condition of the cervix are its short length (no more than 2 cm), sufficient width of the cervical canal (a finger should pass through it freely), and a centered location of the cervix (it should be in the central part of the small pelvis).
A similar examination of the vagina also takes place in the initial stages of labor. Thanks to it, the condition of the birth canal is diagnosed, the presenting part of the fetus passing along these paths is determined (this can be the pelvic end or the head).
In addition, during such studies, the doctor looks at the dynamics with which the cervix dilates and observes the progress of the presenting part of the fetus.
When conducting such examinations, the gynecologist also carries out the following actions:
- the condition of the amniotic sac is studied (its integrity, the degree of tension, and how much water it is filled with are determined);
- the degree of smoothness of the uterus is revealed;
- check how open the uterine pharynx is (optimal indicators are 10-12 cm);
- the condition of the edges of the pharynx is studied (they can be soft or dense, thick or thin).
During the active stages of labor, an examination is carried out if:
- rupture of amniotic fluid occurred;
- the woman in labor began to struggle; as a rule, such attempts are similar to the urge to defecate (emptying the rectum);
- any complications have arisen (the vagina is bleeding, the condition of the mother or fetus has noticeably worsened, labor is too weak).
Prenatal examination of the cervix before childbirth should always be carried out with the utmost caution, because there is a high probability of pathogenic microbes entering the vagina.
To protect the woman in labor from possible complications, the birth canal must be treated with an antiseptic before the procedure begins.
Many women (especially those experiencing their first pregnancy) are interested in the question of whether such examinations are painful.
There is no clear answer to this question. It all depends on the condition of the cervix and the presence of certain problems. During a normal pregnancy, a woman may feel only slight discomfort.
Consequences and possible complications during disclosure
A long and dense cervix before childbirth is a pathological condition and often becomes the cause of labor complications. In this case, complications are possible:
- perineal rupture;
- cervical rupture;
- uterine rupture;
- long painful labor;
- fetal hypoxia.
The duration of labor directly depends on the degree of readiness of the cervix. Since the preparation of the uterus is asymptomatic, sometimes pathology is detected when the body is already involved in childbirth.
In this case, urgent stimulation with medications or mechanical stimulation is carried out - during contractions, the pharynx is expanded manually.
Premature dilatation can cause the birth of a premature baby or fetal death.
Too early shortening of the cervix often indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This pathology is one of the main causes of spontaneous miscarriages.
Author: Irina Petrovna, obstetrician Specially for the site kakrodit.ru
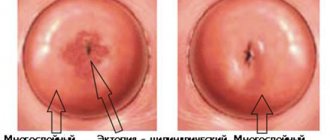
Erosion during pregnancy
Very often, a pregnant woman finds out that she has been diagnosed with cervical erosion. Erosion either forms during pregnancy or existed before its onset. Erosion is a common disease common to all ages; it is expressed in a defect in the mucous membrane of the cervix. The cause of the pathology is previous inflammation, trauma, birth control pills, hormonal imbalances, infectious diseases, previous births or abortion. Ill-conducted douching and excess weight also cause erosion.
Erosion is divided into true and ectopia (pseudo). True erosion is an extremely rare and serious disease. Among patients and doctors, when talking about erosion, they often mean pseudo-erosion - ectopia, which looks like a slight redness on the mucous membrane. According to statistics, about 70% of women have encountered the concept of erosion in all its manifestations.
The gynecologist discovers erosion during examination and sends the patient for colposcopic examination. Symptoms of erosion include bleeding and pain after intercourse. Such signs occur with advanced erosion; if this is the initial stage, then there are no special symptoms. Previously, erosion was treated by cauterization; today this method is considered undesirable for nulliparous girls. After cauterization, a scar may appear, the cervix before childbirth
cannot open normally, rupture is possible. Non-pregnant patients are usually treated with laser.
If erosion is detected in a pregnant woman, it is usually treated after childbirth. In exceptional cases, when the deformities are significant, individual treatment is prescribed. This treatment will not affect the child. But after childbirth, treatment should definitely continue to improve if the erosion does not go away spontaneously (this happens quite often).
You can share the article with friends via social media. networks: