Home / Articles about children / Placenta during pregnancy
The placenta is a unique organ in a woman’s body that develops and exists only during pregnancy. After the birth of the baby, the need for it is lost. The baby's place is separated from the walls of the uterus and comes out with amniotic tissue.
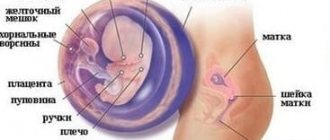
The placenta is formed during pregnancy to connect the intrauterine developing fetus with the mother's body . Formed during conception at the site of implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus, the placenta has an internal and external surface. The first, fruit side, faces the cavity of the fetal egg, the second, or maternal side, is adjacent to the wall of the uterus. The umbilical cord is attached to the inner side, covered with a watery membrane. The outer one is divided into separate parts by deep grooves. Its formation ends by the 4th month of pregnancy. During a full-term pregnancy, the placenta looks like a cake measuring 15 by 20 cm, 2-4 cm thick in the center and weighs about 0.5 kg.
Through the placenta, only in liquid and gaseous states, the baby receives oxygen and nutrients and releases carbon dioxide and metabolic end products into the mother's blood. In addition, during pregnancy, the placenta is an organ of internal secretion; it produces testosterone, serotonin, relaxin , as well as hormones that prevent the release of new eggs and promote the maturation and development of the mammary glands. Performing a protective function, it ensures the development and regulation of the immune system of mother and child, and prevents the occurrence of an immune conflict between them. At the same time, the placenta cannot protect the fetus from drugs, alcohol, nicotine, medications and viruses.
The structure of the placenta during pregnancy depends on its density or level of aging. Doctors distinguish four degrees of maturity, corresponding to a certain period of intrauterine development of the fetus. The normal distribution of the degree of maturity of the placenta by week of pregnancy is:
- Zero – until 27-30;
- The first is from 30 to 34;
- The second - from 34 to 38;
- The third – from 38 onwards until delivery.
The last months are characterized by physiological aging of the placenta, which is accompanied by a decrease in the exchange surface area and the appearance of areas of salt deposition.
What it is
The placenta is an organ of embryonic development of mammalian organisms.
Man also belongs to this group of living organisms, and during pregnancy, this formation is formed in a woman’s body. In everyday life it is called a “children's place” and not by chance. It surrounds a certain area of space inside the mother’s body where the baby’s growth and development will occur.
Protects him and ensures a relationship with his mother.
The quality of the placental membrane determines how the fetus will grow and form. Therefore, it is very important to monitor her condition during pregnancy.
Departure
The birth of placenta after childbirth is a very important and significant issue for any woman. It is the third stage during the birth of a child. When the placenta comes out after the fetus, it is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition. At this moment, doctors assess the extent of blood loss, pay attention to the mother’s pulse and blood pressure, and also closely monitor her general condition.
After two hours, the process is completely completed, but after the birth of the placenta, the woman may still feel blood loss for some time - a volume of 220 ml (anything more than normal indicates a violation). It is very appropriate to ensure that there is no bleeding and the placenta is not retained. If the exit stage has slowed down, you cannot do without outside help. Doctors often have to remove it themselves.
Formation, structure and development
After fertilization of the egg by the sperm, the placenta immediately begins to form.
The place of its initial development is the mucous membrane of the uterus. As a rule, this occurs on the back wall of the muscular organ.
Structure
The amniotic membrane has a very complex structure. There are 8 layers in it:
- decidua - the first layer from the uterine wall, is a modified endometrium that contains a large number of cells with glycogen;
- Langhans layer - consists of a loose type of connective tissue, contains vessels of the circulatory and lymphatic systems;
- trophoblast - a layer that prevents the contractility of arterial vessels;
- lacunae - cavities that are filled with blood;
- multinuclear simplast - a layer of multinuclear muscle fibers;
- cytotrophoblast - a layer of special cells responsible for the secretion of active substances;
- stroma – a connective tissue layer with a large number of vessels;
- amnion is a layer that performs the function of synthesizing amniotic fluid.
For what period and when is it formed?
The completion of the formation of the “baby place” structures occurs at the end of the 4th month of pregnancy, at approximately 15-16 weeks.
A month later, active metabolic processes begin between the placenta and the embryo.
The baby begins to actively receive oxygen and nutrients, and fetal waste products are removed from the amniotic fluid.
From the 22nd week of pregnancy, she begins to actively gain weight. This is due to the child’s ever-increasing needs for nutrition and breathing.
Only by the 36th week of the perinatal period does it reach full maturity.
Development is accompanied by an increase in mass and thickness.
By the 40th week of pregnancy, the weight of the “baby place” is about 0.5 kg. Thickness up to 3 cm.
Inspection
Knowing what is done with the placenta after childbirth and where it is disposed of is extremely useful. The first thing doctors do is submit a sample for histological examination. This is done to check the integrity of the placenta. If even a small particle remains inside, there is a risk of complications in the form of an inflammatory process and dangerous uterine bleeding. Medical professionals examine the appearance of the sample: its structure, size, integrity and general condition of the blood vessels. The shell is examined from all sides very carefully; there should be no torn edges or vascular damage.
There are cases when during the examination it is clear that this organ has not completely come out. Such an incident requires medical attention; doctors usually clean the uterus. This manipulation can be carried out manually or using a special spoon - a curette.
If there are membranes left in the uterus, cleaning is not necessary.
The membranes will come out with lochia (special secretions with blood, fragments of the membrane and particles of the child's place).
What do you do with the afterbirth after childbirth? A mandatory item is weighing the sample and noting the studies performed in the patient’s medical record. Next, the placenta is disposed of.
After examining the child's place, the doctor begins to examine the patient herself. It is very important at this stage to assess the volume of blood lost over time, wash the wound surface with a disinfecting solution, and carefully stitch up all cuts and tears. Next, the young mother goes to the ward, where her health is constantly monitored by experienced specialists. Close attention is provided for 3 hours; this first time carries the risk of complications in the form of uterine bleeding due to decreased uterine tone.
Functions
During pregnancy and fetal development, the placenta plays a very important role and performs a large number of functions:
- ensures the supply of oxygen to the baby and the removal of carbon dioxide from the amniotic fluid;
- transports all the nutrients necessary for the child’s development;
- fetal waste products are removed through the vessels;
- protects the developing baby from attacks by the mother's immune system;
- participates in the synthesis of active biological substances necessary for the proper development of the fetus.
Thus, the placenta provides the functions of gas exchange, excretion, protection, nutrition, as well as the synthesis of substances. Without it, proper development of the fetus in the womb is impossible.
Pregnancy weight by week
The average weight gain during a normal pregnancy is presented in the table
| Gestation period, weeks | Average total weight gain, kg | Average weight gain per week, g |
| First 17 weeks |
During the entire pregnancy, weight gain averages 10-12 kilograms. At the same time, asthenics (thin, tall) can gain about 14 kilograms normally, and for hypersthenics (overweight, or overweight people), the optimal weight gain is about 7 kg.
Mother-placenta-fetus system
After the fusion of the germ cells of the mother and father, the “mother-placenta-fetus” system immediately begins to form. It includes:
- the body of a pregnant woman;
- developing fetus;
- children's place as a connecting link.
The connecting link can be conditionally divided into 2 parts:
- maternal;
- children's room
The maternal part contains a large number of lacunae with blood and vessels. It is a modified mucous membrane. The children's part is represented by the villous chorion.
Blood flow in the maternal part is slow. This makes it possible to thoroughly cleanse the blood that comes from the fetus. In the lacunae, the exchange of substances between the woman’s body and the fetus occurs.
If it doesn't work out
It is difficult to say why the placenta does not come out. Medical workers should be attentive and prompt at this moment. Such a complication can lead to an irreversible outcome and even increase the likelihood of death of the young mother.
Expulsion can be done using different methods:
- light painless massage combined with muscle tension and pushing (Abuladze method);
- without tension on the part of the girl, with impressive pressure and internal movement downwards (Genter method);
- the most effective way: light massage, squeezing, pushing (Crede-Lazarevich method).
Such methods can be used not only for complete expulsion, but also to facilitate the process when it is difficult for the mother to cope on her own and requires outside help. There are also cases during which anesthesia and surgery are required.
Norms for placental thickness at different stages of pregnancy
Thickness is an important criterion for a woman’s pregnancy. During routine ultrasound examinations, this indicator must be monitored.
Deviations in values, both upward and downward, signal possible pathologies and complications.
Thickness is taken into account to determine the degree of maturity of the “children’s seat”.
The first measurement of this value occurs during a routine ultrasound examination at 20 weeks. The thickness norm at this time falls within the range of 16.7 to 28.6 mm.
Until the 36th week of pregnancy, an increase in thickness occurs. This figure increases by about 1 mm per month.
At 25 weeks, normal is considered to be from 20.3 to 34.0 mm, at 30 weeks from 23.9 to 39.5 mm.
Starting from week 36, it gradually becomes thinner. At 40 weeks of pregnancy, normal thickness ranges from 26.7 to 45.0 mm.
Leakage of amniotic fluid
You can determine the leakage of amniotic fluid at home. There is a special test pad for this. The method is quite popular, but such a gasket is quite expensive (400-600 rubles), and the result is not always reliable. So, not only leaking water, but also inflammatory diseases can show a positive result.
The exact result can be obtained in the maternity hospital after examining the discharge.
The most informative way to determine water leakage is amniocentesis. A safe dye is injected into the amniotic sac using a needle, and a tampon is placed in the pregnant woman's vagina. Dyeing the swab will show leakage of amniotic fluid. This method is used in special cases when the child's life is at risk.
Weight gain during pregnancy is an important indicator of the health of a woman and her unborn child. Therefore, at the first visit to an obstetrician-gynecologist, a pregnant woman must weigh herself. Further, the weight is determined at each appearance until the very birth, which is included in the mandatory protocol for examination and management of pregnancy.
information
If a woman has a scale at home, she can weigh herself in the morning in the same clothes before meals and keep a diary of her weight gain.
The most common pathologies
Modern medical science divides all possible pathologies into 3 groups:
- deviation from normal values of size and shape;
- modification and malfunction of the chorion;
- pathological changes in the maternal part.
Pathological changes in size and shape
Normally, the placenta is round in shape. However, it may change under the influence of certain factors.
Causes of deformation:
- the presence of postoperative scars on the uterine walls;
- frequent abortion;
- an increase in the internal uterine surface during pregnancy.
In women, the most common pathology is called placenta accreta.
In this case, the “baby spot” is attached to the uterine walls and is very difficult to remove after the birth of the child.
In addition to changing shape, the placenta can change significantly in size, going beyond the acceptable limits.
Reasons for increasing the “children’s space”:
- the mother has diabetes mellitus;
- tendency to develop edema of varying severity;
- individual characteristics of the expectant mother’s body;
- the presence of infectious diseases during the perinatal period;
- overweight woman.
Causes of thinning:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- maternal hypertension;
- pathologies of kidney function.
Insufficient thickness can cause serious complications in fetal development.
Modification and malfunction of the chorion
Possible pathologies of the children's part:
- inflammatory processes that occur in the chorion;
- development of cysts;
- remnant of the yolk sac from the embryo;
- ingrowth of embryonic hair into the chorion;
- oligohydramnios for a long period.
In obstetric practice, cases of chorionic hemorrhage are often encountered. They provoke complications such as:
- early birth;
- intrauterine developmental delay of the child;
- stopping the child's development;
- internal bleeding.
Pathological changes in the maternal part
The maternal part of the placenta can be subject to such pathologies as:
- hemorrhage;
- placental abruption;
- placental infarction;
- intervillous thrombus formation;
- development of chorioangioma neoplasm.
These pathological conditions can cause the following consequences:
- weakening of the protective function and intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- intrauterine growth retardation and development of the child;
- child hypoxia;
- change in the amount of amniotic fluid;
- increased uterine tone;
- hydatidiform mole.
“Children’s place” is the most important structure during the development of a child. The health of the unborn baby and the condition of the pregnant woman depend on the quality of her work.
To minimize the risk of complications, it is important to regularly monitor the condition of this organ.
The expectant mother should know what the weight of the placenta depends on, what factors provoke the development of pathologies and how to diagnose them in time. As a rule, a timely visit to a doctor makes it possible to freely correct the problem.
Signs of exit
There are a number of signals by which one can confidently determine that the process of separation has begun. An experienced doctor should regularly conduct a personal examination and carefully monitor the patient’s condition in order to notice them. You can talk about the removal of a child's place if:
- Changes in height, shape and uterine structure occur. It becomes flat, deviates to the right and rises towards the navel - Schroeder's sign.
- The end of the umbilical cord, which comes out of the vagina, becomes longer and the umbilical cord itself also lengthens - Alfred's sign.
- The woman feels the urge to push. But this does not happen to all mothers - a sign of Mikulic.
- Elongation of the umbilical cord after such attempts indicates successful separation from the uterus - Klein's sign.
- Pressing with a finger on the suprapubic area provokes elongation of the umbilical cord - the Klyuster-Chukalov sign.
It should be understood that when there is no process of tissue separation, this is natural.
If mommy does not complain about anything and feels normal, she has no bleeding or other signs of abnormalities, there is no reason to panic. Understanding this, doctors can allocate a few more hours (no more than two) while waiting for the process to begin. If such a step does not bring changes or the patient’s condition has worsened significantly, then intervention from medical workers cannot be avoided. Doctors perform surgery under anesthesia or scrape out the cavity manually themselves.
Prevention of complications
If a thickening of the placenta is detected by ultrasound before 20 weeks, there is no need to panic: the doctor will find out the reasons and give recommendations for the prevention of fetoplacental insufficiency. If necessary, treatment will be provided.
The woman herself can contribute well to the prevention of complications:
- You need to be outside more often.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Eat well and eat well.
- Avoid contact with viral infections.
- Treat chronic infections at the planning stage of pregnancy.
- Control your weight and vitamin intake.
- Prevent anemia by getting tested on time.
- Regularly attend an antenatal clinic for early identification of causes that can be eliminated.
If the placenta is too thick and the reasons are clarified, the specialist prescribes therapy in accordance with the period in order to improve metabolism and support the fetus in the current conditions. Timely measures taken significantly increase the chances of giving birth to a normal child, even with significant thickening of the placenta.
The placenta is an important organ of a pregnant woman, which is formed and exists throughout the entire period of fetal growth. After the birth of a newborn, the child's place is rejected. This unique temporary organ connects mother and baby during pregnancy. It is thanks to the placenta that the baby receives the necessary nutrients.
A child's place, like any living organism, forms, matures and ages. Each of these physiological processes must occur at its own time. In this case, the pregnancy will be successful and the child will be healthy. If an expectant mother wants to know what, for example, the degree of maturity of the placenta should be at 33 weeks of pregnancy, she should use a special table with standard indicators. Such a diagram will be given in the article below. Thanks to it, you can find out whether the child’s place is developing correctly.
Fasting days during pregnancy
Fasting days during pregnancy are one of the main non-drug methods for correcting excess weight gain. For this purpose, as a rule, one type of product is used (mono-discharge) with the consumption of 1-1.5 liters of liquid. It is advisable to carry out such therapy no more than 1-2 times a week, especially after holiday feasts. Each woman chooses her own fasting day option. It can be:
- Apple day
(1-1.5 kg of fresh or baked apples divided into 6 meals); - Curd day
(600 grams of low-fat cottage cheese without sugar is also divided into 6 meals); - Rice day
(150-200 grams of boiled unsalted rice, to which you can add 1 apple during the day); - Fermented milk day
(take 1.5 liters of any and drink a little throughout the day); - Vegetable day
(zucchini or pumpkin – 1-1.5 kg. You can add a little sour cream); - Fruit day
(it is better to use apples, but other fruits are also possible); - Meat or fish day
(this should be low-fat varieties of fish or meat, about 400-500 grams, which are divided into 6 servings and washed down with water or unsweetened tea, compote).
Information
You can also use other products for unloading, but you must remember that vegetable or fruit days are the most optimal, since they contain more nutrients.
Thus, timely initiation and correctly selected therapy for pathological weight gain allows, in most cases, to prevent further development of the pathological process. Therefore, weight changes must be monitored throughout pregnancy.