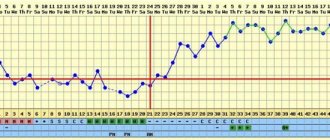
What does the core temperature curve indicate?
Pregnant women keep basal temperature charts, focusing mainly on obstetric dates, which are calculated from the beginning of the cycle, so they are 2 weeks longer than embryonic periods.
Using the graph, you can track whether ovulation has occurred and suggest possible fertilization if in the second phase the temperature rises or remains stably at a high level (from 37°C) for at least 14-18 days.
Many pregnant women note on their basal temperature chart during pregnancy before the delay a one-day decrease in internal temperature on the 7th - 10th day from ovulation (implantation retraction). This moment is associated with the attachment of the embryo to the uterus and the hormonal changes occurring in the body. Often, at the moment of consolidation of the fertilized egg, slight bleeding is observed for 1-2 days, nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Then, during the normal course of pregnancy, BT should stably exceed 37°C. It may rise slightly by 2-3 tenths of a degree on the day of the delay (but not for everyone).
When is a basal temperature chart necessary?
Keeping a graph of basal temperature allows you to determine the correct functioning of the female ovaries and identify a number of problems that affect the ability to conceive a child.
Using the graph you can determine:
- egg maturation time;
- the presence of ovulation in a particular cycle or its absence;
- favorable and unfavorable days for conception;
- presence of hormonal problems;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- the reason for the delay of the next menstruation.
The measurement results will be informative only if the graphs were kept for at least three menstrual cycles.
Some gynecologists monitor the dynamics of basal temperature for at least six months in order to accurately make a diagnosis. For correct interpretation, correct measurement of basal temperature is necessary. Otherwise, the graph data will not be indicative.
Norm
Examples of graphs of basal temperature for pregnant women who successfully carried and gave birth to a child may differ slightly in digital values, but they show a pattern: BT in the second phase of the monthly cycle should be at least 0.4 - 0.5 ° C higher than in the first . For some women, the internal temperature in the first phase may be consistently low (for example, 36.2 ° C), then it is not scary if after ovulation it does not rise above 37 degrees. Sometimes, even after fertilization, as well as during pregnancy, BT does not rise above 39°C, and women endure pregnancy without complications.
According to the basal temperature chart during pregnancy, the norm after ovulation and conception is considered to be 37.1-37.4 °C. This is exactly what an ideal BT is, when the fertilized egg is fixed in the uterus and progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin begin to be intensely secreted, the content of which in the body determines the onset of pregnancy.
The upper temperature limit is 38°C, the lower one is 37 – 36.9°C. If BT in pregnant women, especially in the first weeks, significantly decreases or increases, these temperature fluctuations can pose a threat to pregnancy. At the same time, a one-day temperature jump does not mean anything, since it may simply be the result of incorrect measurements or other factors.
The so-called “pregnant” basal temperature charts on forums are presented in various variations with different cycle lengths and average temperatures. Women share not only their schedules, but also their feelings during each period of gestation, as well as comments on them.
The normal graph of internal temperature after fertilization, starting from the 3rd week, should differ from the usual two-phase graphs, when conception does not occur and menstruation begins.
Pregnant women should not experience a premenstrual drop in temperature if progesterone levels are normal.
Their “pregnant” graph visually resembles a monotonous straight line with a temperature of 37°C and above.
Pregnant chart like a fence
Our rulers of planners.
Try it and express your opinion!—> * Dear friends! Yes, this is an advertisement, you have to spin like that!
This month's schedule is like a fence. Ovulation is usually on days 19-20 of the cycle. Will she be there this month?
Eternal, you very often feel unwell in this chart - hence the “fence”. This happened to me in October: I was sick twice during the cycle and the schedule jumped. There was no ovulation. Most likely you won’t have it this cycle either. But you can and should hope for a miracle! Good luck.
And your chest always hurts from the very beginning of the cycle.
No, my breasts start to hurt about 3 weeks after my period. And first the nipples, then the next day one breast, the next day the other. 2 days before menstruation, the pain goes away as if by hand.
It’s something this month that my breasts are constantly hurting and I feel sick often... So I’ll put it that I’m not feeling well, right now I actually have a little cold, but I don’t have a fever.
Hello! So my graph is like a fence, but according to the ultrasound at 13 DC the dominant follicle is 26.3 mm, free fluid, i.e. ovulation most likely occurred ().
Girls, I actually have some kind of nightmare. Here's today's ultrasound. Ultrasound results (21 dts) M-echo: 6mm (the doctor said this is normal) LA: dominant follicle-19. 5x19mm (was 23x21mm at 16 dts.) decreased, PJ: dominant follicle - 22x17. 4 mm (there were 2 pieces of 10 mm at 16 dts.) from two grew 1. Lord, why not Oh? And the schedule is something! What do you say?
Judging by the protein secretions, ovulation is on the 14th or 15th day.
Oh, I wrote this for Chaffinch... Sorry!
Irina, you have noted a lot of poor health, on such days the chart is not at all indicative! And by the 19th everything can still get better, by the way!
Yuata, at 15dc and 17dc according to O tests, there were //very bright stripes. And today at the ultrasound they said that there was no O.
Finch, of course, it’s hard to argue with an ultrasound... Every healthy woman has 1-2 cycles a year without ovulation, nature rests. Especially in the autumn-winter period.
Yuata, Well then, let’s rest and not worry about this cycle.
Chaffinch, about “not worrying” - that’s a very good idea! Read here:
Princess, by the way, my chest starts to hurt immediately after M, does this mean something? Don't you know?
You must register or log in to be able to comment.
Our rulers of planners. Try it and tell us your opinion!—>
* Dear friends! Yes, this is an advertisement, you have to spin like that!
Girls, I’m new here, I built the first graph in my life. I don’t like that the temperature fluctuations in the second phase average two tenths of a degree. I see that in pregnant charts the fluctuations in the second phase are not so strong, rather there is a gradual increase. What can such jumps mean? In addition, I also had a terrible jump in the first phase! Actually, I managed to get pregnant before (the first time 5 years ago, the pregnancy was normal), and the second time 5 months ago (the pregnancy had to be terminated due to a chromosomal disorder in the fetus). I’ll make a reservation: my cycle is usually 25-26 days, but this is only the second cycle after the interruption, ovulation was late, so I’m counting on at least 28 days. I'm terribly psychotic right now, it seems to me that a late-term abortion would have catastrophic consequences. Is my schedule weird or not? Please take a look!www.my-bt.ru/gr/133002
It seems to me that your schedule is good and gives hope. The fact that there was a jump in the first phase for 1 day does not mean anything, it’s just that on that day, for some reason, the BT could have been unremarkable. The difference between the phases is good, but what jumps a little in the second phase is hormones.
Malinka, thank you for your feedback, it’s very encouraging. Perhaps the physical and psychological state also affects hormones. Still, only 2 months have passed since this horror ((
What’s also strange is that my hair almost stopped coming out this month (it had been growing quite a lot all my life, except for the second half of pregnancy 5 years ago). I’m happy for my hair, of course, but these are clearly hormonal changes, and I’m afraid that these changes will prevent me from getting pregnant. Maybe the body still thinks that it is pregnant (I would now be in the second half of my pregnancy if it had not been terminated). Well, probably, it was necessary to create a separate topic on this issue.
Coco, such “fences” are only due to hormonal imbalances. Get tested for hormones.
Nata, I’ll probably call the doctor as soon as M starts and schedule an ultrasound and tests somewhere in the middle of the cycle. Now I have a glimmer of hope that suddenly M will not start...
Coco, I’m also happy for your hair, but this is not an indicator of hormonal changes, before you say this, you need to get tested. Don’t beat yourself up and don’t think about the bad, I’m trying to understand you, because you’ve been through a terrible thing, but! - it’s all behind us - and we look forward, and there’s only good. God helps us with this. And on you I will do-A-PCHHI-I-I! Good luck!
Good schedule, wait a couple more days and do the test, good luck to you!
Deviations
The most common pregnancy schedule is BT with low temperature. On various forums, women express their concerns and ask for advice regarding low internal temperature during pregnancy. If you go to such a forum, the graph of basal temperature during pregnancy for many women who have given birth may differ from normal. Benchmarks. But this is not necessarily a sign of irregularities. In principle, BT in pregnant women is always elevated, since after conception the corpus luteum does not dissolve, but continues to promote the production of progesterone until the placenta is fully formed, and this occurs until 12–16 weeks.
Let us recall that after 12-16 weeks, BT measurement data are no longer so informative, since during this period it is not the corpus luteum, but the placenta, that is responsible for the production of hormones. Therefore, if you find that after the 14th - 16th week the basal temperature decreases, this can be explained by hormonal changes and there is no need to panic.
Core temperature during gestation can be compared to normal second phase levels or slightly higher. The norm is individual for each woman; it may not reach the required minimum – 37°C. Or it can be very elevated. Thus, in 25% of pregnant women, BT is 38°C.
But in most cases, an abnormal basal temperature chart during pregnancy is a cause for concern and a possible sign of pathology. This is especially true for women who have already had problems with pregnancy (early involuntary abortions, missed abortion). Let's consider possible deviations from the schedule and their reasons.
How to measure BT?
How to measure basal body temperature? To do this, you need to stock up on a separate thermometer, preferably a mercury one. BT is measured in the mouth, vaginally and rectally. The latter method is considered the most preferable, since the results of such measurements are the most reliable due to the minimal influence of external factors. BT is not measured in the armpit. You only need to choose one method, without changing it throughout the entire diagnostic period, which is at least 3 months. Measurements should be taken in the morning, after at least 6 hours of sleep, without getting out of bed, preferably at the same time.
Women with menstrual irregularities and pregnant women monitor changes in basal temperature. BT charts for planning girls will become indispensable assistants in determining favorable days for conceiving a child.
You need to start recording BT indicators on the first day of menstruation (the beginning of the cycle) in order to obtain complete information for the monthly period. Pregnant women should maintain BT schedules regularly throughout the first trimester.
It is recommended to record the results immediately after the measurement, since an error may affect the diagnosis and decoding of the indicators. In addition to indicating the temperature itself, it is necessary to indicate the day of the cycle, the number of days of menstruation. It is extremely important to note additional factors that may affect measurement results: taking medications, lack of sleep, illness, stress, physical activity, sexual intercourse on the eve of measurements, consumption of spicy foods and alcohol. The BT schedule for a pregnant woman, in addition to the above factors, should reflect the woman’s well-being and sensations.
Types and causes of deviations
Examples of graphs of basal temperature during pregnancy with deviations towards increasing or decreasing BT are associated with the following groups of reasons.
- A decrease in core temperature to 36.8 ° C or lower is often associated with a lack of hormones necessary for normal gestation (especially progesterone). In such cases, the risk of fetal development faltering or involuntary abortion (miscarriage) increases. Often in such cases, when there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, the woman has pain and pulling in her lower abdomen, and bleeding is observed.
- An increased BT is not as dangerous as a decreased one. But it cannot be ignored, since a prolonged increase in indicators to 37.9 – 38°C can be interpreted in different ways:
- as a sign of any inflammation;
- as a symptom of the attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterus: sometimes elevated internal temperature during gestation is associated precisely with the threat of ectopic pregnancy, especially if alarming measurement data is accompanied by acute pain in the lower abdomen.
In any case, elevated internal temperature readings, constantly recorded, can interfere with the normal development of the fetus.
It was said above that the temperature chart must be compared with BT indicators in the post-ovulation phase during previous cycles. For example, if the norm for a woman in the second phase is 37°C, and during pregnancy this figure jumped to 38°C, then this is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist (provided that all measurements were taken correctly). It is possible that a temperature that is very high compared to the individual norm indicates an inflammatory process of a local or general nature.
Such examples of basal temperature charts during pregnancy are available on the forum of expectant mothers.
If before conception a woman had a consistently high temperature in the second half of the cycle, not associated with any disease, then there is hardly any need to worry.
Non-pregnant BT values
Normal non-pregnant BBT curve readings suggest that at the end of each monthly cycle the readings will have a biphasic division. That is, in the first half of the cycle, before ovulation, the temperature is not higher than 36.8 degrees , and in the second half of the cycle the temperature will increase to 37 degrees . Moreover, before ovulation, BT decreases sharply by at least 0.4 degrees .
After ovulation, the indicators increase for 14 days, after which they decrease again at the beginning of the next cycle.
It is worth remembering that there are some factors that influence changes in BT . They should be taken into account and indicated in the schedule:
- stress;
- fatigue;
- climate change;
- colds with fever;
- drinking alcohol;
- sexual intercourse several hours before measuring BT;
- short sleep;
- non-compliance with the rules for measuring BT;
- taking contraceptives;
- using a new thermometer.
Diagnosis and treatment
If you detect the slightest deviations in the graph from the norm or a strong difference from individual indicators in the 2nd phase of the cycle, just in case, show your notes to the doctor. You may have to undergo tests, a pelvic ultrasound and other examinations.
If low temperature during pregnancy is associated with a lack of hormones, timely treatment by taking synthetic replacement drugs can help save the child.
In case of a frozen pregnancy, it will not be possible to normalize the further development of the fetus. In this case, drug therapy will not help - you will have to do curettage. But such a diagnosis must be verified using ultrasound.
Thus, the graph of internal temperature during pregnancy (after conception and implantation retraction) should look like a more or less straight line with readings of 37 ° C and above. If the graph is zigzag, with temperature jumps, perhaps you are simply violating the rules for measuring temperature. Consistently underestimated or overestimated indicators are a reason to consult a doctor. Particularly dangerous during pregnancy are low temperatures (below 36.8°C) and a prolonged increase in BT over 38°C against the background of other symptoms.
Temperature when taking Duphaston and other drugs
There is an opinion that some medications taken before pregnancy may affect changes in BT. Questions often arise when taking synthetic progesterone.
Duphaston is a fairly well-known drug with artificial progesterone . Its effect on changes in BT schedules is not clear and has not been fully studied .
According to reviews of some women, when taking Duphaston and other similar drugs, the BT schedule is reversed. That is, at those moments when the temperature should increase, it decreases and vice versa. Doctors explain such phenomena as:
- individual characteristics of the body;
- irrationality of Duphaston's appointment.
In the first case, it is assumed that changes in BT schedules are an individual feature of the body of this particular woman. In the second case, the reason for the change in the basal temperature chart is the incorrect prescription of the drug. This is often the case with both some inexperienced doctors and women who self-medicate.
In addition to Duphaston, changes in BT can be caused by drugs such as:
- Utrozhestan;
- Ingesta;
- Triderm;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Tri-regol;
- Nasonex;
- Rigevidon;
- Noretin;
- Lokoid;
- Diana is 35;
- Climodien;
- Yarina;
- Janine;
- Marvelon;
- Nuvaring;
- Gyneprison;
- Femiwell.
However, in addition to drugs with artificial progesterone, changes in BT can be affected by painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, some psychotropic and hypnotic drugs .
When monitoring basal temperature, it is important to take all measurements at the same time without changing your position after sleep, without going to the toilet or eating. This is the only way that all changes are considered correct and, based on them, you can monitor the current pregnancy or plan it.