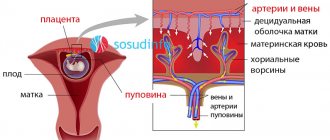
Fibrinogen is a special biological protein that is part of human blood. Its main biological role is to ensure blood clotting. The level of this substance is very important during pregnancy, as well as during the delivery process.
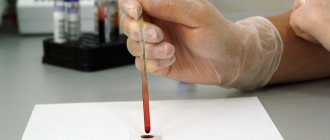
To determine it, a special research technique is used - a coagulogram.
A change in the amount of fibrinogen content, both downward and upward, is extremely undesirable for a pregnant woman.
What is fibrinogen during pregnancy
Fibrinogen is a protein substance that is part of blood plasma.
This is a soluble substance. This blood component is synthesized in the liver and then transported into the bloodstream.
When a vessel is injured, fibrinogen, under the influence of a special enzyme thrombin, is transformed into an insoluble substance - fibrin.
It plays a direct role in the formation of a blood clot or thrombus.
The level of fibrinogen in the blood plasma can change both up and down. This depends on the general condition of the body and the presence of concomitant diseases.
What are the reasons for increased protein?
It should be noted that protein levels may often not coincide with the norm - they may rise, not only due to inflammation in the body or infections. The reason for this may be a well-known disease - thrombophilia. This disease is characterized by increased blood clotting. Such a pathology in the body of a pregnant woman must be detected in time, otherwise it will have a very negative impact on the course of pregnancy, as well as the development of the fetus. If an expectant mother is diagnosed with thrombophilia, she must be registered with a hematologist, undergo tests and follow instructions throughout all three trimesters. If the doctor finds out about the problem in time, he will be able to adjust the fibrinogen level with medication and help him cope with carrying the child to term.
There are other reasons why protein in a woman’s blood may increase. This:
- any injuries, burns;
- rheumatism;
- pre-infarction state and the infarction itself;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- hepatitis, more precisely, its mild forms;
- tuberculosis;
- oncological diseases;
- diabetes.
The nutrition of the expectant mother, its quality and regimen, and the conditions in which the woman lives have a huge impact on the level of protein in the blood. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with any of the above, she must take special care of her health.
We also recommend reading: Urinary incontinence after childbirth
How to treat the problem of high protein in the blood?
When a woman finds out that there is elevated protein in her blood, she panics. But what to do in this case? You can’t do anything on your own, but quickly contact a specialist so that he can prescribe the necessary therapy.
In most cases, specialists prescribe treatment with medications such as beta-adrenergic receptor blockers and fibrinolytics. These may be Cyclopidine, Oxypentiphylline and other drugs. The substances that these medications contain can lower fibrinogen levels. But they cannot be taken on their own, as the consequences can be unpredictable. If the case is more severe, then perhaps outpatient treatment with injections.
What measures need to be taken?
After you are examined and the specialist prescribes treatment, you must strictly adhere to all his instructions. You need to take medications on time and adjust your food intake and nutrition itself. Every day, be sure to eat more of those foods that can reduce protein levels, namely:
- bitter chocolate;
- natural cocoa;
- freshly squeezed beet juice and beets themselves;
- cranberry juices;
- weak green tea;
- fresh vegetables;
- raspberries;
- seafood and seaweed;
- garlic.
It is also good to drink decoctions from the roots of Kalanchoe and aloe to reduce protein levels.
Factors influencing changes in fibrinogen levels in pregnant women
The fibrinogen content in the blood may deviate from the normal value.
Under the influence of a number of factors, its amount can either increase or decrease. Reasons for increased levels of fibrinogen in a pregnant woman:
- Inflammatory processes in the body of a pregnant woman;
- The presence of infectious diseases;
- Severe manifestations of toxicosis in pregnant women;
- High level of physical activity;
- Increased anxiety in women and stress.
Reasons for low fibrinogen levels in a pregnant woman:
- Insufficient nutrition of a pregnant woman;
- Presence of diseases of the digestive system;
- The presence of tumors in the body, both benign and oncological;
- Diabetes.
It should be noted that the situation when fibrinogen is reduced occurs much less frequently than pathological conditions associated with its increase.
This deviation option is no less dangerous for a pregnant woman.
How to get your numbers back to normal
A gynecologist or hematologist should tell you how to bring the indicators back to normal. They will outline a regimen for taking the necessary medications that will help reduce or increase fibrinogen in the blood.
Promotions
There is an algorithm of actions on how to lower fibrinogen during pregnancy that a woman will need to implement.
If a pregnant woman has elevated fibrinogen levels after taking the test, she will be asked to undergo additional examinations to establish the cause and other abnormalities.
Such analyzes include:
- D-dimer level test;
- for the time of blood clotting;
- by the number of specific bodies.
If the indicators are not critically inflated, then such a pregnant woman is most often simply taken under observation.
She is prescribed medications containing folic acid, acetylsalicylic acid in small doses, B vitamins, antiplatelet agents, after a course of which a control analysis is carried out.
If it is discovered that fibrinogen is increased during pregnancy in the first or second trimester, then with this treatment and the use of appropriate products it can be brought back to normal. Foods that lower fibrinogen levels include: beets, pomegranate, dark chocolate, raspberries.
If, after additional tests, a number of significant hemostasis disorders are discovered, and the level of fibrinogen is off the charts, then the gynecologist is obliged to give the pregnant woman a referral for consultation with a hematologist.
Find out whether pregnant women can eat grapes, ice cream, strawberries, garlic, watermelon, mint, parsley, tomato juice, and rose hips.
The tactics of pregnancy management and the prescription of treatment in the future will be jointly carried out by these two doctors. If the pregnant woman’s condition and fibrinogen levels cannot be stabilized before childbirth, she should give birth in special conditions with the participation of experienced doctors and midwives.
Diagnosis of the level of this protein
Throughout pregnancy, a woman’s blood levels of this protein are monitored.
A coagulogram analysis is mandatory, which is taken 3 times during the entire period of gestation - once per trimester.
There is another type of blood test for fibrinogen - a hemostasiogram, which is more detailed.
In order to obtain a reliable research result, it is very important to prepare for it correctly.
- The analysis is given only on an empty stomach. It is advisable to stop drinking even liquids an hour before donating blood;
- At least 2 hours before the analysis, it is very important to reduce the level of excitement and anxiety, because in this condition, the amount of fibrinogen increases.
A blood test for fibrinogen is taken from a vein. The resulting biological fluid is treated with a special saline solution and the plasma is separated.
Fibrinogen can be isolated from it in a variety of ways:
- Fibrinogen according to Claus or optical;
- Colorimetric or method for determining fibrinogen by color;
- Gravimetric - a method for determining fibrinogen by its specific gravity;
- Immunochemical.
Based on these indications, it is possible to determine the content of fibrinogen protein in the blood of a pregnant woman.
Tests to determine fibrinogen levels
A coagulogram test is performed in the first week of each trimester. This study gives a general picture of blood clotting and allows timely detection of hemostasis disorders.
If a change in the fibrinogen indicator is detected, to clarify the diagnosis, the woman is prescribed:
- color chromic study;
- immunochemical diagnostics;
- weight determination of a substance;
- optical method of element counting.
We recommend: Progesterone norms during pregnancy, table by week, causes of deviation and treatment.
But before prescribing additional diagnostics, the pregnant woman is recommended to take a coagulogram again to exclude an erroneous result.
The reason for receiving inaccurate data may be:
- laboratory reagents;
- equipment malfunction;
- improper preparation for the study.
The last external reason is quite common. A pregnant woman should visit the laboratory on an empty stomach and avoid physical and psychological stress in the morning. Often, expectant mothers neglect the basic rules, and as a result, they get a reason for unnecessary worries about their health.
Level indicators and their significance at normal levels of fibrinogen in pregnant women
The level of fibrinogen in the blood during pregnancy differs from that during the normal period.
In women who are pregnant, this protein is slightly elevated and this is acceptable.
The level of its content depends on the stage of pregnancy.
Fibrinogen standards during pregnancy by trimester:
- 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) 2.98 g/l;
- 2nd trimester (14-27 weeks) 3.1 g/l;
- 3rd trimester (from 28 weeks until birth) 4.95 – 6 g/l.
The amount of fibrinogen in the blood plasma increases with increasing pregnancy. Its maximum content is observed in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
If these indicators change both up and down, this is a signal about the development of pathology.
What function does fibrinogen perform and how to determine its level?
Fibrinogen is a specific protein that is synthesized by liver cells. It is directly involved in the construction of fibrin, a component that promotes thickening and normal blood clotting. A sufficient amount of fibrin in the body is necessary for every person, and especially for expectant mothers.
It is known that during labor a woman loses a considerable amount of blood. If there is not enough fibrinogen in the body, blood loss may be too heavy.
Also, the growth and development of the unborn child and the characteristics of pregnancy directly depend on the amount of fibrinogen in the body, since the blood clotting process has a direct impact on the functional activity of the placenta. If the level of fibrinogen is decreased or increased during pregnancy, the appearance of pathological conditions in the woman’s body and delays in the development of the fetus cannot be ruled out.
In the event of a significant fluctuation in fibrinogen levels, down or up, doctors make assumptions about the presence of a pronounced inflammatory process or necrotic tissue changes in the expectant mother’s body.
Nature has foreseen in advance possible problems associated with pregnancy and childbirth. To prevent serious bleeding during childbirth, the amount of fibrinogen in the blood of the expectant mother increases.
If in women before pregnancy the level of fibrinogen in the blood is considered normal at 2-4 g/l, then after conception this figure increases to 6 g/l, which is also considered normal. Typically, the level of fibrinogen during pregnancy is significantly increased in the 3rd trimester, when the body begins active preparation for the upcoming birth.
Even though an increase in fibrinogen during pregnancy is the norm, it also has its own limit values, the excess of which indicates the formation of a pathological process. In this situation, the doctor usually prescribes an extensive blood test - a hemostasiogram. Read more about performing a hemostasiogram during pregnancy→
Increased fibrinogen during pregnancy in the 1st trimester indicates the presence of a focus of inflammation in the body. To clarify the situation, the doctor writes the patient a referral for additional laboratory tests. It is important to do this in a timely manner, since any infectious or inflammatory process that occurs in the body of a pregnant woman negatively affects the development of the fetus.
From approximately the 13th week of pregnancy, many women experience symptoms of toxicosis, their well-being noticeably improves, against which the results of blood tests return to normal.
If, despite this, fibrinogen remains elevated, it can be assumed that blood clots are likely to form. This pathology is dangerous during pregnancy because it interferes with normal nutrition and oxygen supply to the fetus, which negatively affects its growth and development.
Additional reasons for increased fibrinogen in the 2nd trimester may be:
- disruption of the functional activity of the thyroid gland;
- pneumonia, pneumonia;
- the formation of benign or malignant tumors in the body.
Tests and a comprehensive examination of the woman will help to find out what exactly caused the high level of fibrinogen.
If fibrinogen during pregnancy is increased in the last months of gestation, this may indicate pulmonary pathology in the body of the expectant mother. In the 3rd trimester, the body intensively prepares for childbirth, so there is a physiological increase in fibrinogen to 6 g/l.
If the indicator is exceeded, pulmonary thrombosis becomes a dangerous complication of this condition, provoking placental abruption and premature labor. All this can be fatal for the expectant mother and child.
Women whose fibrinogen is increased during pregnancy are under the supervision of a specialized doctor until birth.
An insufficient level of fibrinogen in the blood contributes to its thinning and impaired viscosity due to deterioration of coagulation. This is fraught with premature placental abruption, disruption of its functional significance, hypoxia and malnutrition of the fetus.
Women with low fibrinogen levels may have the following diseases and conditions:
- hepatitis;
- acute lack of vitamins B2 and C;
- gestosis;
- DIC syndrome.
Most often, fibrinogen deficiency in the body is explained by the development of late toxicosis of pregnancy - acute gestosis.
This is a dangerous condition, which is characterized by increased blood pressure, headaches, and disruption of the general well-being of a pregnant woman. Preeclampsia negatively affects the development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy. Read more about gestosis→
First of all, it is important to understand that there can be no talk of any self-medication for disturbances in the level of fibrinogen in the body. This is a serious condition in which the expectant mother must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
If fibrinogen is increased during pregnancy, treatment includes the prescription of medications selected by a specialist based on the clinical situation, the causes of the pathology and the patient’s condition. The only thing a woman herself can do is to review her diet and, if necessary, make appropriate adjustments to it.
Lemon, garlic, raspberries, strawberries, beets, tomatoes, cucumbers, green and cranberry tea will help lower the level of fibrinogen in the blood.
Among the medicinal herbs, aloe juice, decoctions based on chestnut and peony root are recommended. Quitting smoking and alcohol will also help normalize the amount of fibrinogen in the blood, if the expectant mother has not yet done so.
Serious complications due to abnormal fibrinogen levels in the body can be prevented if you follow all the recommendations of your doctor. Modern medicine and progressive methods of treating women during pregnancy guarantee a high chance of a safe birth of a healthy baby.
Author: Olga Rogozhkina, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Based on materials from mama66.ru
What does an increase in fibrinogen levels mean and what is dangerous?
It is very important to understand the dangers of increased fibrinogen during pregnancy.
With the development of this pathological condition in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriage or intrauterine fetal growth may occur.
Also, a high level of fibrinogen before the 12th week of pregnancy can provoke the development of intrauterine fetal abnormalities, thrombosis and placental abruption.
The most dangerous consequence is pulmonary artery thrombosis, which almost always ends in the woman’s death.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, increased fibrinogen may indicate the following pathologies:
- Infectious diseases of women;
- Intrauterine diseases of the fetus of infectious and inflammatory nature;
- Inflammatory processes in the body of the expectant mother.
Reasons for the downgrade
It was discussed above what function fibrinogen performs to protect the body from blood loss. A strong decrease in the indicator leads to the fact that the blood becomes less viscous. The reasons for the decrease during pregnancy are often:
- vitamin deficiency (lack of vitamins B and C);
- inflammatory processes in the liver;
- gestosis;
- DIC syndrome.
The decrease does not have a negative effect on the development of the fetus, but with a lack of fibrin, the risk of heavy blood loss from minor injuries increases. Of particular danger is a decrease in fibrinogen in the 3rd trimester: low blood clotting causes postpartum hemorrhage.
If the level is low
Another type of disorder that is associated with the level of fibrinogen is its low level in the blood.
In most cases, the cause of this pathology is very severe toxicosis in a pregnant woman.
Also, the causes of low fibrinogen include disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome and vitamin deficiency.
Reduced fibrinogen is no less dangerous than its excess content.
If fibrinolytic activity is reduced during pregnancy, the following complications may develop:
- Intrauterine death to the fetus;
- Embolism or entry of amniotic fluid into the bloodstream of a pregnant woman;
- Premature placental abruption;
- Decreased uterine tone;
- Increased blood pressure of mother and child.
Decreased fibrinogen
Obstetrician-gynecologists rarely encounter a decrease in fibrinogen levels in pregnant women. One of the most common causes of low fibrinogen is severe vomiting of a pregnant woman (up to 20-25 times a day) in the early stages. This condition is called severe toxicosis and requires treatment in the pregnancy pathology department. Another extremely serious reason for the decrease in fibrinogen is the last stage of DIC syndrome (disseminated intravascular coagulation), when the body has used up all its coagulation factors, including fibrinogen. DIC syndrome develops against the background of:
- Massive bleeding;
- Severe intoxication;
- Traumatic operations;
- Burns;
- Infections;
- Amniotic fluid embolism;
- Eclampsia;
- Errors during blood transfusion.
Such patients develop severe external and internal bleeding, the fight against which is often doomed to failure. Fortunately, such complications in obstetrics are rare, and a team of resuscitators and transfusiologists is involved in saving the lives of such patients.
Compliance by a pregnant woman with all recommendations of an obstetrician-gynecologist and hematologist minimizes the risk of severe complications. A huge amount of knowledge and skills of modern doctors helps babies to be born even in hopelessly difficult cases. Expectant mothers should remember that their happiness and health are the key to the happiness and health of their children.
Correction of fibrinogen levels in pregnant women
If there is a change in the fibrinogen content in the blood of a pregnant woman, the doctor prescribes the necessary measures to correct this condition.
You can change the amount of this protein in the blood plasma in the following ways:
- Medication;
- With the help of certain foods;
- Using medicinal herbs.
Medicines that increase blood clotting include:
- Thrombin;
- Fibrinogen;
- Vikasol;
- Phytomenadione.
To reduce the amount of fibrinogen, your doctor may prescribe:
- Nattokinase;
- Curcumin;
- Serrapeptase;
- Bromelain.
The necessary therapy is prescribed by the doctor after collecting a complete history of the woman’s condition.
In most cases, to normalize fibrinogen levels, it is enough to adjust your diet.
Foods that increase fibrinogen:
- Oats;
- Wheat;
- Buckwheat;
- Greenery;
- Potato;
- Cabbage;
- Liver.
Some herbs also have enhancing properties.
These include:
- Yarrow;
- Stinging nettle;
- Arnica.
Foods that lower fibrinogen:
- Corn;
- Kelp or seaweed;
- Green tea;
- Strawberries;
- Raspberries;
- Bitter chocolate;
- Oranges and other citrus fruits.
This also includes herbs:
- Motherwort;
- Rose hip;
- Aloe.
Decoctions are most often made from medicinal herbs.
It is not recommended to use alcohol tinctures due to the negative effect of alcohol on the development of a child.
You should not self-medicate. Correction of nutrition and prescription of medications is prescribed only by a doctor.
If you self-medicate incorrectly, you can only aggravate the condition and cause even more harm to yourself and your child.
The level of fibrinogen protein in the blood of a pregnant woman is a very important indicator. The successful course of pregnancy and the health status of mother and child depend on its quantity.
Even if during the tests a deviation of this indicator from the norm was diagnosed, with timely and correct therapy the risks of complications can be minimized.
Monitoring your health, proper nutrition and following the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle are the best prevention of diseases.
The importance of fibrinogen and its indicators during pregnancy
A protein produced in the kidneys that affects blood clotting is called fibrinogen. Due to its vital functions and activity, it turns into fibrin and becomes the basis of a blood clot. From the first days of pregnancy, changes occur in a woman’s body, including in the functioning of the circulatory system, which in the future will make it possible to control bleeding. Therefore, it is important to monitor fibrinogen levels throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
It is easy to check the amount of fibrinogen in the female body - a coagulogram is used for this. To compare the results of different examinations, it is worth donating blood in the same place.
On a note! The frequency of monitoring during pregnancy is determined by the supervising gynecologist. Taking into account the peculiarities of the course of pregnancy and the indicators of the first examinations carried out during registration, the doctor decides which health parameters should be checked more often and which less often.
Table: fibrinogen indicators - normal and its violations
| Normal value for an adult | 2–4 g/l |
| Normal for a pregnant woman | up to 6 g/l |
| Exceeding the normal indicator | over 6 g/l |
| Reduced rate during pregnancy | less than 3g/l |
With the onset of pregnancy, the amount of fibrinogen increases, this will ensure the necessary blood clotting process. The increase in the indicator occurs gradually. In the first trimester, it may not exceed 3 g/l, especially if the pregnant woman suffers from toxicosis.
In the second trimester, test results should show 3.2–3.6 g/l. And by the end of the third trimester, the amount of fibrinogen will reach 6 g/l. Such values are normal and indicate a normal process within the circulatory system.
The effect of fibrinogen on pregnancy
Elevated fibrinogen levels during pregnancy are common. This is how the body prepares for future childbirth, because some blood loss is inevitable.
How does fibrinogen affect pregnancy:
- The increased amount is due to future blood loss of up to 500 ml - this is how the body protects itself from the development of pathologies. After childbirth, the indicators return to normal.
- Due to an increase in this protein, the fetus may experience oxygen starvation, placental abruption ahead of schedule, and death is possible. Blood clots that appear due to fibrinogen during pregnancy are able to move into the vascular system of the placenta, forming an insufficient blood supply.
- A high concentration can cause pathologies in the mother’s body, leading to thromboembolism of the arteries of the lungs (risk of death due to the impossibility of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange).
- Decreased or hypofibrinogenemia causes bleeding, which can form in any of the organs of a pregnant woman. Bleeding in the uterus leads to possible termination of pregnancy.
How to lower fibrinogen levels during pregnancy
However, there may be a disruption in the functioning of this organ and problems with the baby’s intrauterine development.
A woman who has been diagnosed with low fibrinogen may be diagnosed with the following disorders in the body:
- Acute deficiency of vitamins C and B2;
- Hepatitis;
- DIC syndrome (active neutralization of thromboplastic substances in the blood);
- Complicated late toxicosis (preeclampsia).
In most cases, low fibrinogen in the blood of a pregnant woman is due to acute gestosis. This is a negative condition in the later stages, in which the pregnant woman suffers from headaches, high blood pressure, “fly spots” flashing before her eyes and overall poor health.
Preeclampsia has many causes and can negatively affect the condition of a developing child.
What to do if fibrinogen is increased during pregnancy
The level of fibrinogen in the blood ranges from 2.0 to 3.5 g/l. At different stages of pregnancy, the content of this protein changes. At the beginning of pregnancy, its amount in the blood may be lower than normal values or correspond to them (1.8-2.2).
Fibrinogen is reduced during pregnancy in the following cases:
- hormonal changes during pregnancy;
- an increase in circulating blood volume due to the enlarging uterus and developing fetus.
As the concentration of this protein decreases, the blood becomes less viscous and its rheological properties improve. Such changes in a woman’s body occur to ensure the normal functioning of the placenta and adequate blood supply to the growing fetus.
There is a concept of hyperfibrinogemia during pregnancy - what does it mean? Fibrinogen levels often increase significantly from the 7th month of pregnancy.
The norm after 35 weeks of gestation is 6.5 g/l. This can be regarded as a physiological mechanism that protects a woman from blood loss during and after childbirth.
Pathological reasons can lead to a decrease in the amount of this protein in the blood of a pregnant woman:
- chronic diseases of the liver and kidneys, often aggravated during pregnancy;
- unbalanced diet with insufficient intake of protein and vitamins;
- diabetes;
- oncological diseases;
- immunodeficiency states.
A low concentration of coagulation protein in the blood of a pregnant woman leads to dangerous consequences. Possible complications: internal bleeding due to gastric ulcer, exacerbation of chronic colitis.
These diseases can lead to the development of serous-fibrinous peritonitis with perforation of a stomach or intestinal ulcer. In this case, serous fluid with a large amount of fibrin accumulates in the peritoneal cavity, which is prone to the formation of films.
This condition requires immediate hospitalization. Emergency conditions include hemorrhagic stroke, hemorrhage into the ventricles of the brain.
The development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome is very dangerous due to the imbalance of the hemostatic system. Premature placental abruption is possible. For the fetus, a decrease in fibrinogen in the blood can result in developmental defects, malnutrition and death.
Fibrinogen is a protein liquefied in the bloodstream and produced in the liver. Experts also call this element “the first clotting factor” or “factor I”.
With the help of fibrinogen, blood is able to form clots and cover open wounds with a hard crust. Fibrinogen in the body performs the following functions:
- participation in the process of clot formation;
- regulation of the duration of wound healing;
- influence on the duration of blood clot elimination;
- stimulation of the renewal of blood vessels and capillaries;
- ensuring interaction at the cellular level;
- regulation of inflammatory processes;
- influence on the intensity of erythrocyte sedimentation.
Without fibrinogen, blood loses its ability to clot. New protein is produced every 3–5 days. The element is activated by thrombin, forming together with it insoluble fibrin. Fibrinogen in the blood is examined in the presence of the following indications:
- pregnancy and analysis of the mother's condition after childbirth;
- preparatory measures before surgery and postoperative monitoring;
- pathological conditions of the heart and blood vessels;
- clarification of the diagnosis when identifying inflammation in the body;
- liver diseases;
- low clotting rate;
- intense bleeding of unknown etiology;
- suspicions of pathological changes in the hematopoietic system.
Inconsistency of fibrinogen levels with the norm poses a danger to the health and life of the expectant mother and child. As protein increases, the blood becomes thicker, and the delivery of oxygen and beneficial elements deteriorates.
The consequences of fibrinogen levels above and below the permissible level are similar in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd periods of pregnancy. The table describes what pathologies occur if protein levels are increased or decreased.
| Fibrinogen level abnormalities | Consequences depending on the trimester of pregnancy | Regardless of gestational age | ||
| First | Second | Third | ||
| Promoted |
|
|
|
|
| Demoted | fading pregnancy | placental abruption |
|
|
Fibrinogen is a protein substance that is part of blood plasma. This is a soluble substance.
This blood component is synthesized in the liver and then transported into the bloodstream.
When a vessel is injured, fibrinogen, under the influence of a special enzyme thrombin, is transformed into an insoluble substance - fibrin.
It plays a direct role in the formation of a blood clot or thrombus.
The main function of this protein is to ensure the process of blood clotting. The level of blood loss during childbirth depends on this.
Fibrinogen is also extremely important for a child. It is involved in the work of the placenta.
The level of fibrinogen in the blood during pregnancy differs from that during the normal period.
In women who are pregnant, this protein is slightly elevated and this is acceptable.
MORE ABOUT: Falls during pregnancy - Pregnancy
The level of its content depends on the stage of pregnancy.
Fibrinogen standards during pregnancy by trimester:
- 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) 2.98 g/l;
- 2nd trimester (14-27 weeks) 3.1 g/l;
- 3rd trimester (from 28 weeks until birth) 4.95 – 6 g/l.
The amount of fibrinogen in the blood plasma increases with increasing pregnancy. Its maximum content is observed in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Another type of disorder that is associated with the level of fibrinogen is its low level in the blood.
In most cases, the cause of this pathology is very severe toxicosis in a pregnant woman.
Also, the causes of low fibrinogen include disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome and vitamin deficiency.
Reduced fibrinogen is no less dangerous than its excess content.
If fibrinolytic activity is reduced during pregnancy, the following complications may develop:
- Intrauterine death to the fetus;
- Embolism or entry of amniotic fluid into the bloodstream of a pregnant woman;
- Premature placental abruption;
- Decreased uterine tone;
- Increased blood pressure of mother and child.
It is this element that serves as the basis of a blood clot - a thrombus. During a natural, physiological birth, a woman loses about 250-300 ml of blood, and during a caesarean section - up to 700 ml.
If doctors talk about a pathological condition and complicated childbirth, the inability of blood to clot normally, or an abnormal level of blood clots that develop due to increased/decreased levels of fibrinogen, death of the mother and fetus is possible.
A high level of fibrinogen protein produced by the liver may indicate the course of a variety of pathological processes in the mother’s body. Therefore, this deviation, as well as a reduced protein level, should not be ignored.
Causes
Speaking about the reasons that can provoke a decrease in fibrinogen levels, doctors identify the following:
- The course of an acute infectious disease. Most often, the protein level increases during the course of the inflammatory process, the focus of which is localized in the gastrointestinal tract, damage to the blood or heart.
- In the case of a burn of various origins, in which the release of plasma proteins by the liver sharply increases.
- Malignant neoplasms that can provoke significant changes in the levels of clotting substances in the blood, disrupting the natural course of pregnancy.
Treatment
In case of a slight increase in fibrinogen levels, the doctor prescribes a course of general medications:
- taking folic acid;
- B vitamins;
- blood thinning drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- in the case of oncology – a course of anti-cancer therapy.
An important aspect of therapy is a review of your own diet. The menu should include products that thin the blood - sunflower seeds and corn, chocolate and citrus fruits, seaweed, raspberries and strawberries, as well as green tea.
Low levels of fibrinogen are less common than high levels, but this does not reduce the risk of pathology. The main thing a woman should remember is that she should not self-medicate, so as not to aggravate her own situation.
Causes
Doctors list the following factors as reasons that can reduce fibrinogen levels:
- The course of a woman’s severe form of toxicosis - the stronger the toxicosis, the lower the protein level will be.
- Lack of vitamins that are actively involved in the process of hemostasis. First of all, such vitamins are vitamins B12 and C.
- Diagnosis of stage 2 or 3 DIC syndrome in a pregnant woman, leading to severe blood thinning, caused by congenital/acquired pathologies.
In each individual case, the root cause of the pathological decrease in fibrinogen levels is determined by a gynecologist based on the results of laboratory tests and examination of the patient.
Treatment
In this case, the doctor prescribes treatment depending on the cause that provoked the pathology - it is important to undergo an examination and consultation with a gynecologist and hematologist.
- Anticoagulants - they inhibit the activity of protein coagulation and prevent the development of thrombosis. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Heparin or Enoxyparin.
- A course of taking antiplatelet drugs - they are prescribed to prevent thrombophlebitis and related complications.
- Vitamins of group P - it strengthens the walls of blood vessels and reduces the activity of fragments that disrupt the level of blood clotting.