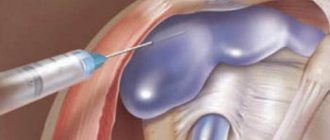
A polyp of the cervical canal is a benign neoplasm that is quite often diagnosed. A fungal tumor, one or several, appears against the background of epithelial proliferation. The only effective treatment option is removal with a laser or radio wave knife. This is a necessary measure to prevent tissue degeneration into cancer.
What is a cervical canal polyp? This is a benign tumor caused by excessive growth of mucous epithelial tissue in the lumen of the cervix. Externally, the neoplasm resembles a mushroom about 5 mm or larger in size, on a thin or wide stalk. Either one or several pieces can form (polyposis of the cervical canal).
The disease occurs in women of all ages, but more often after 40 years. The only treatment is removal. Otherwise, further growth may lead to degeneration of the tissue character.
Characteristics of the pathology
You can find out about serozocervix after an ultrasound diagnosis. With this disease there are no characteristic symptoms, so such a diagnosis comes as a surprise to any woman.
Most often, women have to find out what it is - serozocervix - in the period after the onset of menopause. But sometimes girls who are planning a pregnancy also face this diagnosis. With this disease, serious changes are observed in the cervical canal. Its patency may be impaired. Often, when serozocervix is detected, serozometra is simultaneously diagnosed. This is what gynecologists call a condition when fluid begins to accumulate in the uterine cavity. Initially, serozometra can only be detected by ultrasound, but if left untreated, the disease begins to progress. It is impossible not to notice it, because the uterus increases in size.
With serozocervix, pathological contents begin to accumulate in the cervical canal, provoking the appearance of characteristic changes. In the part that is closer to the vagina, narrowing occurs. This makes it difficult to drain.
Pathology
One of the most important functions of the cervical canal is to maintain pregnancy. If there are any pathologies of such a pharynx in the body of a pregnant woman, there is a high probability of miscarriage or premature birth. To prevent this from happening, you need to regularly visit a gynecologist during pregnancy and monitor the size of the cervical canal.
One of the most common pathologies of the pharynx is isthmic-cervical insufficiency. With this disorder, the opening in the cervix expands ahead of schedule. In this case, the fetus may not be able to stay in the uterus, and premature birth will begin. Most often, this pathology is detected in pregnant women at 19-20 weeks of gestation. During this period, the fetus actively grows and develops, which means it gains weight.
If the cervical canal is enlarged during pregnancy, you should definitely seek help from a doctor. This condition is detected during ultrasound diagnostics or routine examination. The pharynx should not increase in size ahead of schedule.
When the cervical canal of a pregnant woman is so open that the gynecologist’s finger can easily pass through, the patient needs urgent hospitalization. This condition at the 20th week of pregnancy can cause premature birth.
Main reasons
When diagnosing serozocervix, they say that the cervical canal expands due to the accumulation of fluid and the onset of the inflammatory process. Most often, the appearance of pathology is provoked by:
- hormonal imbalance;
- STI;
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and cervix, which are caused by interventions during childbirth, diagnostic curettages, abortions;
- viral infections of the genitourinary system;
- tumors that have affected the uterus or retroperitoneum;
- miscarriages.
If the inflammatory process begins and treatment is not carried out, then there is a high risk of developing serozometra. Fluid begins to collect in the uterine cavity itself. Treatment is prescribed only after the doctor determines the cause of the formation of serozocervix.
If other pathologies are not identified, then there is no need to panic when making this diagnosis. Doctors advise redoing the ultrasound on another day of the cycle. When serozocervix is detected in young women, gynecologists often do not even pay attention to it and do not prescribe treatment. This is not due to their professional unsuitability, but to the fact that in most cases the appearance of fluid is a normal physiological process. As ovulation approaches, hormonal changes occur in every woman's body. Under their influence, the process of maturation and release of the follicle from the ovary is accompanied by the appearance of copious discharge, which in appearance and consistency is similar to egg white. If an ultrasound is performed during the period of ovulation, the cervical canal passing inside the cervix may be slightly dilated due to the accumulation of thick discharge. Usually a few days after ovulation the picture returns to normal. Treatment in this case is not required. You can make sure that the problem is no longer present by re-diagnosis.
In some patients, a picture characteristic of serozocervix may occur before the onset of menstruation. Therefore, each case is assessed individually. There is no standard developed treatment tactic for this diagnosis.
Identification of serozocervix during postmenopause is in most cases a sign of problems. After all, women no longer have any discharge during this period, so the fluid will be a symptom of the inflammatory process.
What changes occur in the cervical canal during pregnancy?
Pregnancy leaves its mark on the condition of various organs and systems. Changes are also observed in the structure of the genital organs, including the cervical canal. What is considered normal and what is pathology? And if the deviations become painful, what can be done to prevent the baby from getting hurt? We'll figure out.
Pregnancy is precisely that state of a woman when she begins to think more about her health, about the structural features of the female organs, designed to protect a new life and raise a little man.
Nature provides everything, down to the smallest detail. In particular, algorithms for restructuring the functions of the genital organs are also laid down. Before you figure out whether the length of the cervical canal changes during pregnancy and its other parameters, it is worth remembering what it is in general, what the dimensions of the canal are in a “quiet” state.
The cervical canal is the small section of the cervix that connects the vagina and uterine cavity. Essentially, this is an opening in which the external pharynx is directed towards the vagina, and the internal pharynx is directed towards the uterus. Epithelial tissue lines this entire canal; it is this tissue that secretes mucus - a special secretion of the epithelium.
Through this section of the cervix, blood enters the uterine cavity into the vagina during menstruation, and through this same opening sperm enter the uterus to make fertilization possible.
The shape of this channel varies, as it depends on a number of factors: hormonal levels, age, number of previous pregnancies, etc.
The secretion secreted by the epithelium creates a so-called mucus plug. The purpose of this substance is to protect the developing fetus from all kinds of infections. The length of the cervical canal in a woman who has not yet given birth is about 4 centimeters. A woman who has given birth or had an abortion will have some deviations from these averages.
But another factor is even more important: what the external os of the canal looks like. If before pregnancy it is pinkish, then after conception it acquires a bluish tint. It is very important that this area of the cervix is not subject to inflammatory processes, otherwise its function of holding the fetus in the cavity and preventing miscarriage may be impaired.
At appointments, the doctor carefully monitors the condition of this organ, which “locks” the uterus during pregnancy.
The length of the cervical canal does not change for a long time during pregnancy. Only just before birth does it shorten a little, “tighten up,” and the cervix itself softens, making it easier for the fetus to pass through it.
On the eve of childbirth, the mucous plug also begins to move, it comes off either a couple of weeks before birth, or even a few hours. It happens that it generally remains in place, then the doctor has to remove it during the birth process itself. But even if everything goes naturally, women do not always record this moment, since the mucus plug can “slip out” during urination. Or it will be released in portions for several days, leaving marks on the underwear similar to discharge during weak menstruation.
At 16-18 weeks, a woman is sometimes diagnosed with isthmic-cervical insufficiency, that is, a condition in which the cervical canal is dilated during pregnancy due to softening of the cervix due to an excess of male sex hormones. Other possible causes: multiple pregnancies, when too much pressure is created on the cervix, or trauma, congenital anomalies. In such a situation, it becomes more difficult to retain the fertilized egg, and there is a risk of miscarriage.
Timely medical intervention will help to avoid a critical situation. The cervix is strengthened with medication or through the installation of a pessary (a special retaining ring), which will be removed only at the 37th week. The last resort is suturing around the cervical canal, but this is too traumatic and poses a risk of infection.
During pregnancy, the cervical canal normally has a width of about 7-8 centimeters. Dilation ideally begins only when contractions occur. The dilation of the cervix is considered complete to 10-11 centimeters, which ensures normal passage of the fetus along the entire length of the birth canal.
Diagnosis of pathology
It is almost impossible to independently diagnose serozocervix. In the initial stages of the disease, even with a routine gynecological examination it is not always possible to detect it. As the situation worsens and serosometers develop, patients begin to complain of:
- pain in the lower abdomen that appears periodically;
- serous vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- general deterioration of health;
- cycle failure, the appearance of liquid discharge with blood or purulent clots during the time between menstruation;
- pain during sexual intercourse, an increase in the volume of liquid discharge after its completion;
- increased pain during menstruation.
Treatment is prescribed after a comprehensive examination of the woman. The gynecologist does not only a standard smear for microflora, he does the following:
- performs colposcopy;
- takes material for cytological examination of cervical tissue;
- sends the woman to the laboratory for general urine and blood tests;
- prescribes studies aimed at determining hormonal levels and identifying sexually transmitted diseases;
- advises donating blood for tumor markers;
- sends for ultrasound and dopplerography.
If serozocervix is detected in a timely manner, the problem can be treated with conservative treatment methods. In advanced forms, surgical intervention will be required.
General information
A diagnosis such as serozocervix often comes as a surprise to women during menopause. The pathology does not have intense and pronounced symptoms. It is installed only when performing a transvaginal ultrasound for preventive purposes or for other disorders.
The disease is characterized by a pathological accumulation of fluid in the cervical canal, resulting in an inflammatory process. Serosometra, in which fluid also collects in the uterine cavity, is also usually diagnosed.
Over time, as the pathology develops, a narrowing and disruption of the patency of the cervical canal is observed. This provokes the development of a number of complications.
Serozocervix is diagnosed more often in patients during menopause, but can also be diagnosed in young girls.
Causes
Experts believe that the main cause of the development of the disease is inflammation, when the pathological process affects the organs of the reproductive system.
Also among the provoking factors are sexually transmitted infections, miscarriages, hormonal imbalance, which can be caused by diseases of the endocrine system.
The pathology is most often diagnosed in women suffering from dry vaginal mucosa, which is observed during menopause.
Microcracks appear on the surface of the internal genital organs, which leads to the spread of the inflammatory process.
On this topic
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
According to research, it has been established that the process of fluid accumulation in the cervical canal can occur due to metabolic disorders in the body or poor nutrition. Long-term use of hormonal drugs, the presence of cysts, polyps or fibroids significantly increases the risk of developing the disease.
According to experts, previously performed curettage or surgical interventions in the genitourinary system can increase the likelihood of developing serozocervix.
One of the possible causes of the disease is viral infection of the reproductive system.
Signs
The symptoms of serozocervix are not pronounced, which complicates diagnosis in the initial stages of its development.
As the amount of accumulated fluid increases and when a concomitant disease such as serozometra occurs, a number of unpleasant signs arise.
Women complain of a slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of yellow vaginal discharge with a grayish tint. They may have an unpleasant odor.
In some cases, there is an increase in body temperature and pain when urinating. During sexual intercourse, discomfort may also occur, and discharge may appear in greater quantities than usual.
On this topic
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
Between menstruation, the appearance of leucorrhoea is observed, which includes blood clots and purulent inclusions.
Common signs include weakness, constant fatigue, a slight increase in temperature, and apathy.
Such signs are not specific and do not always indicate the presence of serozocervix. But if they appear, you should consult a gynecologist.
Diagnostics
The specialist prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods to the woman in order to establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the method of therapy.
First of all, a gynecological examination is carried out, based on the results of which a preliminary diagnosis is established. During the procedure, a smear from the vaginal mucosa is necessarily taken for microflora.
Colposcopy
The examination is carried out using a colposcope. This is a special device that allows you to enlarge the tissues of the cervical canal and study their structure.
How to prepare for the procedure
At the preparation stage, the following studies are prescribed:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- blood tests for syphilis, HIV infection, viral hepatitis;
- coagulography;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- analysis of the flora of a smear from the urethra and cervical canal;
- analysis for the degree of vaginal cleanliness.
After an examination and consultation with an anesthesiologist, a decision is made on the use of local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
Treatment methods
The treatment tactics are determined by the attending physician based on test results and instrumental diagnostic methods.
In cases where a small amount of fluid is noted and the cervical canal is narrowed slightly, physiotherapeutic methods, vitamin complexes and drugs to stimulate the blood circulation process are prescribed.
If significant changes are present, medications are used or surgery is prescribed.
Drug therapy
In order to dilate the cervix, the gynecologist may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs that also have an analgesic effect. The most commonly used are Naproxen, Indomethacin, or diclofenac-based products.
When the cause of the disease is an infectious lesion, based on the results of a laboratory test, the doctor selects an antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drug.
Effective antibiotics for establishing serozocervix are Valprafen, Amoxicillin, Ornidazole or Moxifloxacin.
For the purpose of the regenerating process in the mucous membrane of the uterus and cervical canal, hormonal suppositories are used. They are administered intravaginally and allow you to quickly restore normal microflora and relieve inflammation.
Surgical intervention
In severe cases, when diagnostic results reveal the presence of a large amount of fluid, surgery is prescribed. The procedure can be carried out in two ways
Laparoscopy
To remove accumulated fluid in the abdominal cavity, the specialist performs several punctures. An endoscope equipped with a camera and lighting device is inserted through them.
The procedure is carried out under the control of an ultrasound machine, which allows the operation to be performed accurately.
The advantages of the method are the absence of large scars on the skin and a short rehabilitation period.
Removing fluid through the incision
The technique is used in cases where serozocervix develops against the background of cysts, fibroids and other formations. During the procedure, the specialist has the opportunity to remove not only fluid, but also tumors of various types.
On this topic
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
The disadvantages of the method are long-term rehabilitation, the presence of scars and cicatrices.
Regardless of the method used to remove accumulated fluid, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is carried out after surgery. This reduces the risk of complications and consequences.
Treating the disease using traditional medicine methods is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to aggravation of the disease.
Features of the procedure
To carry out bougienage, special Hegar dilators of different diameters are used. The patient is located in a gynecological chair. Her external genitalia and vagina are treated with antiseptic agents. After exposing the cervix in the speculum, the anterior lip of the external pharynx is grabbed with bullet forceps, and the first bougie is inserted into it.
The expansion is carried out gradually. Bougies are successively replaced one after another, starting with small sizes and ending with the required diameter. Everything is done carefully, without excessive effort. Depending on the location of the pathological narrowing, the dilator is inserted to the depth of the internal pharynx or moved a little further beyond it. Each bougie remains in the neck for 30-60 seconds, is removed and replaced with the next largest one.
At the end of the procedure, hemostasis and antiseptic treatment of the cervix are performed. The patient receives medical recommendations regarding further behavior, hygiene and treatment procedures. The doctor decides on the advisability of prescribing antibacterial therapy.
Possible complications
The lack of therapy when diagnosing serozocervix causes complications of various types.
When the cause of the disease is pathologies of the reproductive system of an inflammatory nature, the risk of the pathological process spreading to the uterus and fallopian tubes increases.
In addition, serozocervix is characterized by narrowing of the cervical canal, which leads to the absence of a desired pregnancy, miscarriages and premature birth.
According to the results of the research, it was found that in patients with a diagnosed disease, the risk of developing sexually transmitted infectious diseases and cancer tumors significantly increases.
Norm and deviations
Using an ultrasound, a doctor evaluates the length of the cervical canal during pregnancy. The norm directly depends on the gestational age. The number of fetuses that a woman is currently bearing is of no small importance.
Normal indicators for a singleton pregnancy by week are as follows:
- If the measurement is made in the middle of the second trimester, then the length of the canal should be between 45 and 40 mm. However, at week 24, a significant decrease in this indicator to 37 mm can be observed. At the end of the third trimester, a decrease in length of up to 35 mm can be recorded. After 32 weeks of pregnancy, the figure will drop to 30–35 mm.
- If a woman is carrying one child, then the length of the cervix should be more than 30 mm. In this case, the risk of having a child is extremely low. It is only 1%.
- A short cervical canal is noted if the value is between 25 and 30 mm. The woman will need to undergo repeat cervicometry. Based on it, it will be possible to create a complete picture of the course of pregnancy.
- The risk of premature birth increases significantly if the length of the cervix is between 15 and 25 mm. A woman is diagnosed with PPI. You will need to undergo further examination by a specialist in the field. Based on this, the tactics for the further course of treatment will be chosen. It is not recommended to refuse it. The life and health of the child is at stake, so parents must do everything for his well-being.
- If the length is less than 15 mm, the woman should be hospitalized urgently. Typically, 30% give birth within the next 7 days at this rate. However, with the right course of treatment, half of them manage to carry the baby to 32 weeks.
- For multiple pregnancies, there are other indicators of normality. An emergency length is considered if its value is 25 mm. This is the first signal that a woman will give birth much earlier than her due date. However, there are a number of measures that will allow you to achieve normal pregnancy.
Prevention measures
There are no special measures to prevent serozocervix. Gynecologists recommend following general rules:
- To live an active lifestyle. When you stay in one position for a long time, stagnant processes occur, against the background of which inflammation can appear.
- properly . The diet must include vegetables and fruits. Cereals and steamed dishes will bring health benefits. You should not eat fast food products. They contain a large number of dyes and preservatives that negatively affect the body.
- To refuse from bad habits. Drinking alcohol and smoking are considered the most common triggers for many diseases. Alcohol and tobacco smoke contain carcinogens that negatively affect the functioning of all systems and organs.
- Before using hormonal medications, consult your doctor. Such funds should be selected individually.
- Avoid abortions and miscarriages.
- Promptly treat diseases of an inflammatory or infectious nature, especially those in which the pathological process affects the organs of the urinary and reproductive systems.
- Have preventive examinations with a gynecologist twice a year. It is especially important to monitor your health before and after childbirth.
If signs of the disease appear, you should consult a specialist to establish an accurate diagnosis and cause of development.
Serozocervix is a common disease that is most often diagnosed in women during menopause. But it is important to monitor your health at any age.
Lack of therapy can lead to the development of dangerous complications and consequences. The disease can be easily treated with drug therapy in the initial stages. But in advanced cases, surgical intervention is used.
What is the cervical canal and what is it for?
Doctors also call it the pharynx.
Considering where the cervical canal is located, it is worth noting that this is the segment that connects the uterus and vagina. The diameter of the pharynx does not exceed 3 mm. In a girl who has not given birth, when examined by a gynecologist, this canal resembles a small dot. But a woman who already has children has a small gap.
The length of the pharynx in a woman who has not had a child is 4 cm, in a woman who has given birth it is up to 8 cm.
In women giving birth for the second time, it is quite normal if, during examination, the pharynx can allow a finger to pass through.
At the same time, the length of the cervix should not exceed 2 cm.
Features of examination of the uterus using ultrasound
Due to the peculiarities of the structure of a woman’s reproductive system, when undergoing ultrasound diagnostics, it is necessary to adhere to some rules that will allow you to obtain more accurate results: cleansing the esophagus, taking carminatives and other manipulations that help facilitate the examination.
During the first examination of the uterus, the cervical canal is examined, which indicates the presence of pregnancy in the early stages. At the same time, they monitor the presence or absence of serious pathologies, the place of attachment of the embryo and other features that are important during the course of pregnancy.
In rare cases, fluid may be found in the uterus.
This is a very unpleasant sign, indicating an ectopic pregnancy, or the absence of a plug in the cervical canal.
Such a plug should form during ovulation and protect the fetus in the future. In the absence of a plug, the uterus is quite susceptible to the influence of external factors.
Changes in the cervical canal after fertilization
After successful fertilization and throughout pregnancy, the shade and structure of the cervical canal changes. The mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint. Many women consider such a change as a sign of pregnancy and can actually see it, because the blue discoloration can be seen not only on the cervix, but also on the labia.
Significant changes also occur inside the cervical canal. From the moment of pregnancy, a mucous plug begins to form in it, which will protect the fetus from external factors. The production of bactericidal mucus is ensured by the endocervix. That is why the absence of discharge during the first two weeks after expected fertilization may be considered a less accurate sign of pregnancy.
The width of the lumen of the cervical canal is approximately 3-8 mm. In women with a history of childbirth, such a hole has a slit-like shape, and in nulliparous women it has a pinpoint shape. If you suspect the development of pregnancy, you should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will be able to see signs of successful fertilization even with a minimal delay.
Attention! Such changes are natural and occur almost painlessly.
At the 4th obstetric week of pregnancy, you can undergo an ultrasound examination, which will confirm that the fetus is successfully attached to the wall of the uterus. At this time, you can see and evaluate the condition of the cervical canal, as well as detect signs of miscarriage or missed pregnancy.
During the normal course of the gestation process in the early stages, the ends of the pharynx should close tightly. The length of the cervical canal during pregnancy should be about 40 mm. The doctor can predict the imminent onset of labor or identify the risk of early miscarriage based on the condition of the pharynx.
Cervical canal
The part of the fallopian tubes, which is responsible for the passage of the fetus at the time of birth, has an elastic structure that allows it to stretch. There are parameters that are measured during ultrasound diagnostics to determine the possibility of spontaneous childbirth.
- Color of the cervical canal: usually pink or pale whitish. After ovulation it changes and acquires a blue tint. This is what allows us to judge pregnancy at the first examination.
- Dimensions. In the first trimesters of pregnancy it should reach 4-6 centimeters. In the last trimester they should expand to 10 centimeters. If this does not happen, a caesarean section is recommended to facilitate labor. However, even with an unopened canal, spontaneous childbirth is possible. But, at the same time, there is a high risk of rupture of the fallopian tube, which can lead to the death of the woman in labor.
- Presence/absence of polyps in the canal. If they are detected, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination (cervical biopsy).
If ultrasound diagnostics show problems with the cervical canal, treatment can be carried out directly during pregnancy. Although, if the polyp is benign, treatment may be delayed until the postpartum period.
Cervical canal - everything a pregnant woman needs to know
With the onset of pregnancy, the work of the entire female body is rebuilt in a new way.
The most important thing is to protect the unborn baby and create the most optimal conditions for its normal development. And and prepared everything for this
Before pregnancy, a woman does not think about how her body works, what the cervical canal is for, where it is located and what functions it performs. But pregnancy radically changes the attitude towards your own body and organism.
The cervical canal is the section of the cervix that connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. Simply put, this is an opening, the internal pharynx of which is directed towards the uterus, and the external pharynx is directed towards the vagina.
It is through this opening that during menstruation, blood from the uterine cavity enters the vagina, and it is through this opening that the sperm enters the uterus during sexual intercourse.
The cervical canal is lined with epithelial tissue, which secretes a special secretion (mucus).
Those pregnant women who have already given birth once know what a mucus plug is. It is located in the cervical canal.
The mucus plug is formed from the secretion secreted by the epithelial cells of the cervical canal and protects the fetus from unwanted infections.
It is by the external os of the cervical canal that the doctor can determine pregnancy in the early stages. With the onset of pregnancy, the external pharynx becomes bluish in color. But the length of the hole does not change.
From the moment of conception, the cervix performs an obturator function, keeping the fetus in the uterus for all 9 months, preventing miscarriage. The cervix is a muscular ring that closes tightly at the beginning of pregnancy and remains in good shape until the due date.
And here you can find out how labor begins.
During the appointment, the gynecologist carefully examines the woman, especially the cervix, and, assuming pregnancy, prescribes
an ultrasound and tests .
After receiving the examination results, the doctor can draw conclusions about whether there is a pregnancy and how it is progressing. At the first ultrasound, not only the position of the fetus, its size, place of attachment, but also the length of the cervical canal , since this indicator may indicate a threat of miscarriage in the early stages.
Normally, the length of the cervical canal in a pregnant woman should be 3.5-4 cm, the internal and external os of the opening are tightly closed. It is by the condition of the cervical canal that the moment of birth is determined.
The mucus plug that closes the canal protects the baby from various infections. Some time before birth, it most often goes away.
A woman may notice a clot of mucus on her underwear, possibly streaked with blood, this is a mucus plug. But most often the plug comes off at the moment of urination, then the woman will not see anything at all, but may feel that something has fallen out from inside.
If the mucus plug comes off gradually , in small parts, then brownish marks can be seen on the underwear within 1-3 days.
During pregnancy, the cervical canal shortens closer to childbirth , and the cervix becomes soft.
With the onset of regular contractions, the lumen of the canal increases by 2-3 cm, then more. When the opening expands to 10 cm (full dilatation of the cervix), and the uterus and vagina become a single birth canal, we can talk about the beginning of the second stage of labor - expulsion of the fetus.
In this article you will find out whether pregnant women can smoke.
And here you will read about the benefits of grapes for pregnant women.
An ultrasound or examination may reveal that
the cervical canal is dilated - isthmic-cervical insufficiency, that is, the cervix is not able to perform its functions, retain the fertilized egg, and already in the early stages of pregnancy there is a threat of miscarriage.
Most often this happens at 16-18 weeks, when the baby is growing rapidly and is also actively moving.
There are other causes , for example, developmental anomalies and injuries of the cervical canal.
With timely treatment, termination of pregnancy can be prevented. To do this, it is best to continue observation in the hospital.
In an inpatient setting, after a thorough examination, several ways can be taken to prevent the threat of miscarriage .
These may be medications that will strengthen the cervix. Often a pessary is installed (a ring that is removed only at 37 weeks).
The cervix can also be sutured , that is, stitches placed around the cervical canal. Such operations are performed in a hospital setting under anesthesia, usually at 16-18 weeks of pregnancy.
This method has many disadvantages , for example, infection and disruption of the integrity of the amniotic sac are possible. Therefore, they use it only in the most extreme cases.
Often during pregnancy, a woman may hear a very scary diagnosis -
cervical canal polyp .
But this only sounds scary, in reality everything is much simpler. When such a diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes colposcopy and conducts cytological and histological examination.
All this is in order to identify the nature of the origin of the polyp and understand whether it is a true polyp or a decidual pseudopolyp (a polyp-like formation that occurs during pregnancy and disappears in the postpartum period).
Most often, a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a decidual polyp , which can be caused by a hormonal disorder during pregnancy.
In this case , you don’t have to worry, the polyp is not removed or touched , only local anti-inflammatory treatment is carried out. This polyp may fall off on its own during childbirth or begin to develop in the opposite direction in the postpartum period.
Pathologies of the cervical canal
In addition to the presence of polyps, ICN may be detected during examination. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is a sufficient reason for termination of pregnancy and subsequent suturing of the uterus. Due to the expansion of the uterus as a result of ICI, fluid is formed in the cervix, which can lead to miscarriage and death of the mother.
There may also be an abnormal increase in the size of the canal, which will lead to closure of the cervix and the inability to become pregnant. This is usually one of the most common causes of infertility. However, it is quite easy to treat and is detected on ultrasound.
However, the biggest danger for a woman is the discovery of cervicitis. This disease leads to complete fusion of the canal and subsequent inability to give birth.
The cervical canal is open during pregnancy
A slight opening up to 1 cm in diameter is not dangerous for the pregnant woman and the fetus. Provided that the length of the cervical canal is at least 30 mm. In this case, the change is not considered a pathology, but the woman needs constant monitoring; perhaps the doctor will recommend going to the gynecological department for preservation. Therapy consists of using progesterone drugs and antispasmodics to eliminate tone.
Those at risk for enlargement include:
- multiparous women;
- girls with multiple pregnancies;
- patients with elevated testosterone in the blood.
A more significant expansion may indicate the development of serious pathologies that interfere with the normal process of gestation.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
A similar diagnosis is given to women if the cervix dilates and softens prematurely. However, she cannot hold the fetus in the uterus. The disorder is often diagnosed in the second trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus rapidly gains weight in the womb. Pathology is diagnosed during a gynecological examination and ultrasound examination.
The problem is significant due to the growing risks of spontaneous abortion and premature birth. It is difficult to accurately determine the causes of the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency; doctors often rely on hormonal imbalance and the predominance of testosterone in the hormonal background of a pregnant woman. Male hormones do affect the cervix and can cause it to soften prematurely.
Attention! ICI can occur due to abnormal development of the female genital organs. Often the cause is surgical abortion, resulting in cervical injury.
If pathology is detected in a timely manner, the risks present can be minimized. Operational tactics are often used. During the intervention, sutures are placed on the tissue around the cervical canal to prevent premature opening. They are removed several weeks before the expected date of birth, when the risks to the fetus are minimized.
In some cases, they resort to installing special obstetric devices (rings or pessaries). They are used after 24 weeks with diagnosed minor dilation. It is believed that suturing is a more reliable technique.
Polyps
Neoplasms on the cervix appear in women due to hormonal imbalance. This pathology does not prevent delivery, but requires constant monitoring. It is mandatory to undergo an examination to eliminate the risk of developing cervical cancer. Sometimes a biopsy is recommended.
You shouldn't worry too much about this. A polyp is a benign neoplasm, for which a woman will have to provide treatment after childbirth. In some cases, it resolves on its own, without the use of surgical or medicinal tactics.
Endocervicitis
Endocervicitis is an inflammatory process occurring in the cervical canal. Pathology can also be considered as one of the causes of noticeable enlargement, but it is not the main problem. The risk is that the causative agent of the pathology in the vast majority of cases is an infection, the treatment of which must be provided during pregnancy. The patient must undergo a smear of the cervical canal, based on the results of which the gynecologist will select the necessary treatment.
Attention! Against the background of endocervicitis, a woman experiences pain in the genital area.
Fluid behind the uterus on ultrasound diagnostics
During ultrasound diagnostics, in addition to the cervical canal, the uterus is also examined for the presence of fluid in the early stages. If it is detected, the doctor indicates inflammatory processes at the initial stage.
Also, fluid in the uterus may indicate:
- Endometriosis.
- Adnexitis and salpingitis. The last two diseases cause inflammation and can lead to fusion of the uterus. Therefore, it is important to diagnose these diseases at an early stage.
- Ectopic pregnancy: the uterus fills with fluid from the placenta when the embryo is not implanted correctly.
- Opening of the cervical canal and the subsequent occurrence of infection.
An ultrasound scan for the presence of fluid in the uterus is performed at the 5th week, if at least one of the following signs is present:
- history of urinary tract infections;
- current diseases of the genitourinary system;
- polyps in the cervical canal detected earlier.
Sometimes fluid accumulates in the cervix for a long time. Its accumulation can be asymptomatic, so it is important to regularly undergo ultrasound diagnostics, especially in cases where there are problems in the female part:
- uneven and unstable menstrual cycle,
- pain in the pelvic organs,
- suspicion of pregnancy, etc.
On the issue of ultrasound diagnosis of endometrial and cervical canal polyps
Ultrasound scanner PT60A
Portable device for emergency care, intensive care and sports medicine
. Research of the musculoskeletal system, monitoring of anesthesia, etc.
Endocervical polyp is a focal hyperplastic process, the recurrence rate of which reaches 19%. It can occur at any age, but more often at 40-45 years old. Among the reasons contributing to its occurrence are hormonal imbalances and chronic inflammatory processes. Polyps originate from all parts of the cervical canal, in 43.3% - from the lower third. According to the morphological type, fibrous, glandular-fibrous, and glandular polyps are distinguished. Less common is a glandular polyp of the cervical mucosa [1-5].
Unlike endometrial polyps, some of which are easily diagnosed using transvaginal echography in the middle of the proliferative phase, others are better - in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle [5], recognition of cervical canal polyps, which are almost always asymptomatic and are mostly incidental findings in women during preventive visits to the gynecologist, it is very difficult.
This is partly due to the fact that all variants of cervical polyps are characterized by small sizes and solitary lesions. In addition, for example, glandular polyps are not visible at all during ultrasound scanning due to the fact that not only the echo-negative tissue of glandular polyps merges with the image of the cervical myometrium and can be indistinguishable from Ov. Nabotii (Fig. 1), located next to the endocervix, but also due to mucus in the lumen of the cervical canal. At the same time, an echo-negative image of liquid (mucus) emphasizes the contours of an echo-positive pathological formation, making it clearly visible on the echogram. Since the polyp has intraluminal growth and partially obstructs the cervical canal, mucus may accumulate above or below it, which facilitates the detection of the pathological formation (Fig. 2). In doubtful cases, it is advisable to repeat the study in the periovulatory phase (late proliferative and early secretory), when there is a physiological increase in the amount of cervical mucus and the polyp is more clearly visualized against the background of anechoic contents. The fluid contents sometimes make it possible to visualize the stalk of the polyp as a linear echogenic structure or its base [3, 5]. The diameter of the canal lumen gradually expands during the proliferative phase, reaching a maximum at the time of ovulation (1.1 mm on days 4-7 and 1.8 mm on days 11-14). After ovulation, the lumen of the canal almost completely narrows (to 0.5 mm), and is most active in the early secretory phase [4].
Rice. 1.
Paracervical cysts with contents of various echostructures.
Rice. 2.
Polyp in the lumen of the cervical canal.
During our echometrosalpingography using sterile saline as a contrast, it also becomes possible to visualize small endometrial polyps and intrauterine synechiae (Fig. 3). The acoustic basis for the possibility of non-invasive echohysteroscopy and echocervicoscopy is created by serometra, for example, in the postmenopausal period with obstruction of the external pharynx (Fig. 4) or, as noted above, an increase in the production of cervical mucus at the end of the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle. Due to mucus during this period, in some cases, polyps localized in the area of the external pharynx become accessible for visualization. Hematometra and/or hematocervix are less informative due to the processes of organization of clots, since against this background, fibrin clots and polyps can be difficult to differentiate in the usual B-mode (Fig. 5, 6).
Rice. 3.
A small endometrial polyp against the background of an echo-negative contrast medium (sterile saline solution) during echohysteroscopy.
Rice. 4.
Polyp against the background of serometra in the postmenopausal period with obstruction of the external pharynx.
Rice. 5.
Hematometra.
Rice. 6.
Hematocervix.
 The use of color Doppler mapping and volumetric reconstruction helps to determine the localization of the polyp (Fig. 7)
The use of color Doppler mapping and volumetric reconstruction helps to determine the localization of the polyp (Fig. 7)
Rice. 7.
Vessels feeding the polyp of the cervical canal, in color flow mode.
Rice. 8.
Endometrial polyps. Volumetric reconstruction mode.
Unlike benign endometrial tumors, cervical polyps always have a long stalk, which is due to the peculiarities of their location in the elongated narrow “tunnel” of the cervical canal. When using color Doppler mapping, there is vascularization of the polyp tissue, but more often vessels are found in the pedicle, which does not significantly affect the overall vascularization of the neck [3, 4, 6].
The use of various modes of Doppler and preppler visualization of blood flow does allow identification of the vascular pedicle of the polyp (Fig. 9), unless there is evidence of endometrial desquamation. In this case, the movement of blood in the uterine cavity and cervical canal can imitate the blood flow in the vessels of the polyp leg and be recorded on the device screen in the form of similar color signals (Fig. 10).
Rice. 9.
Vascular pedicle of a polyp of the cervical canal in color flow mode.
Rice. 10.
The movement of blood in the uterine cavity against the background of endometrial hyperplasia is recorded in the color flow mode.
In B-mode during the periovulatory period, it seems to us [7], ultrasound diagnosis of small polyps is somewhat complicated due to the secretory transformation of the endometrium gradually moving from the periphery to the center (Fig. 11).
Rice. eleven.
Condition after ovulation: secretory transformation of the endometrium gradually moving from the periphery to the center.
In the secretory phase, to diagnose an endometrial polyp, the previously described [1] “halo” sign is used - a thin echo-negative rim around it (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12.
The “halo” sign is a thin echo-negative rim around the polyp.
In turn, we use one more sign, the presence of which, if submucous fibroids are excluded, may indicate the presence of a polyp whose size exceeds the thickness of the endometrium of one of the uterine walls. In this case, usually a clearly visible median hyperechoic linear thin structure, obtained by reflection from the border of contact of the compact layers of the endometrium of the anterior and posterior walls of the uterine body, seems to go around an obstacle - a small polyp (Fig. 13, 14) or “interrupts”, “disappears” for polyps of larger sizes (Fig. 15).
Rice. 13.
The median hyperechoic linear thin structure (arrows), obtained by reflection from the border of contact of the compact layers of the endometrium of the anterior and posterior walls of the uterine body, seems to go around an obstacle - a small polyp.
Rice. 14.
Endometrial polyp. The same echographic sign (arrows).
Rice. 15.
The median hyperechoic line is “interrupted” with a fibrous polyp of larger size.
Thus, the most optimal period for simultaneous visualization of endometrial and cervical canal polyps in patients of reproductive age during routine transvaginal echography is the end of the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle.
Literature
- Demidov V.N., Zykin B.I. Ultrasound diagnostics in gynecology. M.: Medicine, 1990. 354 p.
- Medvedev M.V., Mikheeva N.G., Rudko G.G., Lyutaya E.D. Basics of ultrasound examinations in gynecology. M.: Real Time, 2010. pp. 48-49.
- Ozerskaya I.A. Echography in gynecology. 2nd ed., revised. and additional M.: Vidar-M, 2013.
- Bulanov M.N. Ultrasound diagnosis of cervical pathology. Author's abstract. dis. ... doc. honey. Sci. M., 2004.
- Khachkuruzov S.G. Ultrasound in gynecology. Symptoms. Diagnostic difficulties and errors. St. Petersburg: ELSBI, 1999.
- Ultrasound gynecology: a course of lectures: in two parts / M.N. Bulanov. 3rd ed., add. M.: Vidar Publishing House - M., 2014.
- Ryabov I.I. Morphoechographic aspects of two moments of the periovulatory period // Ultrasound in Obstetrics. gynek. pediatrician. 2000. T. 8(4). pp. 325-327.
Ultrasound scanner PT60A
Portable device for emergency care, intensive care and sports medicine
. Research of the musculoskeletal system, monitoring of anesthesia, etc.
Conclusion (video)
Timely detection of fluid accumulated in the uterus is the key not only to health, but also to a woman’s ability to give birth. Since, if timely treatment of the cervix and cervical canal is not carried out, sticking may occur, which will lead to irreversible loss of fertility. Ultrasound helps detect even a small amount of intrauterine fluid, which allows you to get rid of it in the early stages. Also, do not forget that pathological changes in the uterus can lead to ectopic pregnancy, which is so dangerous and undesirable for a woman.
The video shows the results of an ultrasound, by which doctors determine free fluid in the cervix. The video also provides information regarding the main parameters during examination of the cervical canal, pathologies that arise due to the accumulation of free fluid behind the uterus.
Signs of pathology in a pregnant woman
There are no obvious symptoms of ICI. You can find out that a woman has a pathology only after the water breaks prematurely. But it is still worth contacting an obstetrician-gynecologist during pregnancy if you feel heaviness in the lower abdomen, frequent urination and discharge.
The doctor can give accurate information about the condition of the pharynx after examining the vagina and cervix.
What says about the ICN is that;
- the cervix is shorter than normal;
- its walls are thinned and softened;
- the outer edge of the canal is slightly open;
- one or two fingers pass through the canal.
During an examination by a doctor, the amniotic sac may be visible in the mirror.
With endocervicitis, copious discharge is observed, which may contain pus. During the development of this pathology, a pregnant woman experiences itching and burning when urinating. Pain in the lower abdomen may be present.
On examination, endocervicitis is indicated by severe redness and swelling. If the pathology is not detected in time, it can become chronic.