Sore throat as a reaction to external pathogens or internal pathologies occurs quite often. Almost always it is acute and causes a lot of discomfort. Depending on the degree of damage to the tonsils, it is divided into follicular tonsillitis and lacunar, catarrhal and necrotic. Lacunar tonsillitis is more common in children; sometimes it affects adults. Treatment, in any case, must be comprehensive and adequate, otherwise complications cannot be avoided.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
The disease is diagnosed in adults and children. With this pathology, deep tissue damage to the tonsils along with lacunae is observed. The inflammation is bilateral.
Less often, only 1 tonsil swells. The disease has a specific clinical picture. Symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis include:
- general malaise;
- purulent deposits;
- fever;
- chills;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- pain when swallowing;
- difficulty eating;
- decreased appetite;
- sore throat;
- weakness;
- the presence of seals in the lower jaw or neck.
In most cases, tonsillitis is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Most often it does not exceed 40ºC and lasts for 1-6 days.
This symptom is caused by a violation of the thermoregulation process against the background of the release of various toxins and pyrogenic substances into the blood by the infectious agent. Severe fever is often accompanied by chills.
Acute lacunar tonsillitis is always accompanied by pain when swallowing. The cause of this symptom is considered to be irritation of the nerve endings. A common symptom of the disease is difficulty swallowing food.
This is due to the dilation of blood vessels, increased permeability and tissue swelling. An increase in the volume of the tonsils reduces the diameter of the digestive tube, which leads to dysphagia (swallowing disorder).
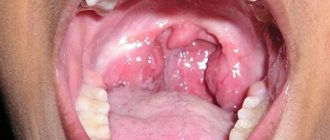
A specific sign of this form of sore throat is a yellow-white coating in the form of foci or a continuous film. If left untreated, it becomes purulent. The plaque is easily removed, and the mucous membrane does not bleed.
This is different from damage to the tonsils due to diphtheria. With angina in children, the following symptoms are possible:
- Abdominal pain.
- Cramps.
- Tearfulness.
- Refusal of food.
- Abnormal stool type diarrhea.
- Vomit.
Purulent plaque due to inflammation of the tonsils is often accompanied by bad breath.
Treatment of a child
How to treat lacunar tonsillitis in a child?
Lacunar tonsillitis in children requires treatment, primarily with antibiotics. As in the case of adult disease, these are amoxicillin drugs:
- Amoxicillin suspension;
- Graximol suspension;
- Ospamox powder for preparing a suspension.
If there is no effect from the drug prescribed by the attending physician, after 3 days from the first dose, you need to inform the pediatrician about this and work together to change the drug. Macrolides are a worthy replacement for Penicillins in the form of:
- Azithromycin suspension;
- Sumameda;
- Azimeda;
- Zitroxa.
Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis in children with topical drugs will not interfere:
- sprays Ingalipt, Kameton and Chlorophyllipt;
- Faringosept (lozenges);
- and if the child has gargling skills, you can use herbal decoctions and infusions.
You can remove high fever, which is so severe and completely undesirable for a child of any age, with the help of antipyretic suspensions, for example Panadol-Baby or Nurofen; if the child feels nauseous or has difficulty swallowing, the suspension can be replaced with rectal suppositories, for example, Nurofen or Cefekon.
To increase immune resistance, the pediatrician may prescribe strengthening medications, such as licorice root powder, Immunal, or a vitamin-mineral complex specifically designed for children.
Causes of the disease
Lacunar tonsillitis in adults and children develops for several reasons. In 90% of cases, the causative agents of the disease are streptococci.
Less commonly, staphylococci, enterobacteria and pneumococci are isolated from the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
Sore throat is caused by the activation of one’s own (opportunistic) microflora or the introduction of bacteria from the external environment.
Risk factors for developing the disease are:
- close contact with people with tonsillitis or a carrier of the infection;
- using sick utensils;
- kisses with carriers of infection;
- eating unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- being in crowded groups;
- contact with coughing and sneezing people;
- inhalation of polluted air;
- dustiness of premises;
- presence of caries;
- drinking cold water;
- general hypothermia;
- presence of chronic runny nose or sinusitis;
- lack of vitamin C;
- weakened immunity;
- poor nutrition.
The causative agent of sore throat can manifest its pathogenic properties when the body's resistance decreases.
This is observed with irradiation, prolonged immobilization, tuberculosis, diabetes, tumors, chemotherapy, uncontrolled use of antibiotics, corticosteroids or immunosuppressants.
The peak incidence occurs in winter and autumn. The reasons are colder temperatures and the formation of groups in schools and kindergartens.
Application of traditional methods
When treating pathology, you should not abandon traditional methods. It is very important that lacunar tonsillitis is defeated as soon as possible, therefore treatment with traditional methods should be supported by folk ones. This will not only give a good effect, but will also help strengthen the immune system and prevent similar situations in the future. Here are examples of the most effective recipes for the treatment of lacunar tonsillitis.
Gargling with beets and vinegar
To reduce inflammation in the tonsil area, use beet juice and vinegar. It is very simple to prepare such a remedy - fresh beets must be grated (or passed through a meat grinder) and squeezed out the juice through cheesecloth. You can cut the beets into small cubes and squeeze the juice through a juicer. For a glass of fresh juice, you need to add one tablespoon of ordinary nine percent vinegar, which is used for canning. Treatment with beets and vinegar is carried out three times a day after meals.
Gargling with Kalanchoe juice
Kalanchoe contains lipids, alkaloids, and steroids that help fight the disease. Thanks to the thick and fleshy leaves, Kalanchoe juice is very easy to obtain, so if this miracle remedy grows in the house, there will be no problems. Those who do not have such a plant can buy Kalanchoe juice at the pharmacy. To rinse the tonsils, you need to dilute the juice with warm water to a uniform consistency in a one-to-one ratio. You can gargle with this remedy every three hours.
Application of propolis
An excellent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory remedy at home is propolis. For treatment, just put a small piece of propolis in your mouth and suck it. If burning and numbness of the tongue occurs, you need to endure this effect of this remedy. It is recommended to take about five grams of the product per day. Real propolis can be bought at a pharmacy or at a trusted apiary where bees do not have infectious diseases. When used correctly, lacunar tonsillitis goes away within three days.
Onion juice for sore throat
The phytoncides contained in onions also help fight sore throat, so onions should not be ignored when choosing a treatment for the disease.
Regular onions must be passed through a meat grinder so that the juice can be squeezed out of the resulting pulp. Drink one teaspoon of fresh onion juice three times a day. For those who refuse to drink onion juice, they offer a different treatment - you can inhale the pulp, spreading it on a saucer. You need to do the procedure for no more than fifteen minutes, since then the healing properties of the onion weaken. Despite the fact that lacunar tonsillitis occurs unexpectedly, and its symptoms worsen by the hour, the patient has every opportunity to minimize the impact of the disease on the body and quickly get rid of the pathology. The key to correct and effective treatment is compliance with the doctor’s instructions, taking all prescribed medications with parallel treatment with traditional medicine.
How is lacunar tonsillitis transmitted?
Sore throat is a contagious disease. The main mechanism of infection transmission is aerogenic (with air). Human infection can occur through airborne droplets, airborne dust, food and household contact.
Bacteria persist for a long time on dishes, toys, towels, and also in dried sputum.
Most often, infection occurs through coughing and sneezing, when, along with tiny particles of saliva and sputum, microbes enter the mouth and pharynx of a susceptible person.
Causes
Why does lacunar tonsillitis occur, and what is it? The main causative agent is streptococci, but it can also be caused by adenoviruses and staphylococci. That is why this disease is considered contagious. It is transmitted by airborne droplets when a sick person sneezes or coughs, or by contact in children - through toys and other contaminated objects.
Also, sore throat can be caused by a variety of surgical interventions in the oral cavity and dental diseases. External factors can also cause the disease. These include hypothermia, drafts, sudden changes in air temperature, dampness, and air pollution.
Lacunar tonsillitis without fever
Lacunar tonsillitis without fever is a rare occurrence. It most often develops in the case of mixed infection and indicates a severe inflammatory process.
This pathology often occurs with gangrene of the tonsil tissue. The absence of temperature indicates a decrease in immunity, since hyperthermia is a response, an adaptive reaction in response to the introduction of a foreign agent.
Sore throat without fever often occurs in weakened people (HIV-infected, drug addicts) and during long-term immunosuppressive therapy.
Treatment
The basis of treatment for lacunar angina is antibiotic therapy; painkillers, antipyretics, antihistamines, immunomodulators, anti-inflammatory drugs, and vitamins are also prescribed.
Antibiotics for lacunar tonsillitis
The course of antibacterial treatment for streptococcal infections is 10 days. When treating lacunar tonsillitis, penicillin antibiotics, carbapenems, and cephalosporins are prescribed.
Mostly, lacunar angina is treated with antibiotics such as augmentin, ampicillin, sumamed, clarithromycin, cefuroxime, cefotiam, ampiox, azicin.
Tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, sulfonamides, and co-trimoxazole are not used in the treatment of lacunar tonsillitis. Tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones do not have sufficient activity against beta-hemolytic streptococcus, and bacteria have become resistant to sulfonamides and co-trimoxazole.
The patient is recommended to gargle up to 6 times a day with furatsilin, gramicidin, chamomile decoction, pink solution of manganese acid.
Washing lacunae
The procedure is used for local treatment of lacunar tonsillitis. Washing lacunae is permitted during pregnancy, for children and adults of any age.
The procedure is performed by an otolaryngologist with a special syringe under visual control. Adults are washed without anesthesia, children are anesthetized with lidocaine.
This method of washing is quite dangerous for the tissues of the tonsil; now the vacuum method of washing lacunae from pus is more often used. The device creates a vacuum, which helps remove purulent plugs, and the additional effect of ultrasound breaks the plug and facilitates the outflow of pus.
Features of treatment of lacunar tonsillitis in children
From the first day, children's temperature can exceed 40 ° C, therefore, in addition to anti-inflammatory treatment, the child is prescribed antipyretic and painkillers. High temperature may be accompanied by convulsions, confusion, and delirium.
It is important to prevent the child from becoming dehydrated, which will aggravate the symptoms of bacterial intoxication. Young children should be offered warm tea, juices other than tomato, milk, fruit drinks, broths
The child needs to drink to soften the throat, as well as to replenish fluid loss in the body due to high temperature and its release through sweat.
Young children should be offered warm tea, juices other than tomato, milk, fruit drinks, and broths. A child needs to drink to soften the throat, as well as to replenish fluid loss in the body due to high temperature and its release through sweat.
Among antipyretics, preference is given to drugs containing paracetamol, ibuprofen, in the form of syrups, and rectal suppositories. Locally irrigate the throat with Hexoral, Givalex, Yox in sprays.
In addition to antibiotic treatment, the child is given lozenges pharyngosept and septolete as a local treatment. It is easier for a child to take medicine in the form of candies for a sore throat than to gargle.
How to treat lacunar tonsillitis
Treatment of lacunar angina is etiotropic and symptomatic. It can't be fast. The main methods of treating the disease are:
- use of systemic antibacterial drugs;
- irrigation of tonsils with antiseptics;
- use of lozenges, lozenges and lozenges;
- taking antipyretic drugs;
- gargling;
- taking antihistamines;
- increasing immunity;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical sparing of the oral mucosa and pharynx;
- taking probiotics.
For inflammation of the lymph nodes, alcohol compresses are indicated. All patients need to remain calm, drink more and ventilate the room several times a day.
To improve immunity, it is recommended to take vitamins. Treatment of lacunar tonsillitis in adults and children begins after examination.
You will need: examination of the oral cavity, laryngoscopy, general clinical tests and examination of a throat smear.
Drug therapy
The basis of therapy for patients with acute tonsillitis is the use of medications. For angina the following are indicated:
- antibiotics in the form of capsules, tablets, powders and solutions;
- local antiseptics;
- antihistamines;
- immunostimulants;
- antipyretics;
- eubiotics.
Antiseptics help cope with pain. These include: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Stopangin, etc. Many drugs have age restrictions.
Patients should gargle. Furacillin has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. A solution for gargling is prepared on its basis.
For lacunar angina, treatment includes the use of systemic antibiotics. The drugs of choice are penicillins (Augmentin, Amoxiclav, Flemoclav Solutab).
Macrolides (Sumamed, Vilprafen) are prescribed less frequently. The duration of antibacterial therapy is about 10 days. In case of severe fever, antipyretic medications are indicated (Paracetamol MS, Efferalgan, Nurofen, Panadol).
To reduce swelling of the tonsils during angina, H1-histamine receptor blockers can be prescribed.
This group includes: Cetrin, Zodak, Claritin, etc. After a course of antibiotic therapy, eubiotics (Linex, Hilak Forte) are often prescribed, which are necessary to restore the intestinal microflora.
Inhalations
An effective method of treating sore throat is inhalation. They help speed up recovery, reduce the duration of drug therapy, alleviate pain, reduce swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, and suppress microbial activity.
Inhalations are often carried out with combined damage to the tonsils and bronchi.
Before introducing the substance into the respiratory tract, you must avoid physical activity. The procedure is carried out at least an hour after eating. Steam inhalations are recommended for adolescents and adults.
They are not recommended when treating preschool children. Antiseptics, saline, mineral water, and homeopathic remedies can be administered by inhalation. Nebulizers are often used to spray substances.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is an auxiliary method of treating angina. The most commonly performed are: magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultraviolet and infrared irradiation.
Physiotherapy can improve immunity, accelerate tissue healing, improve metabolism in the tonsils and eliminate inflammation.
Folk remedies
With the permission of the attending physician, folk remedies can be used for sore throat. These include various decoctions, infusions and tinctures.
It is necessary to use only those plants that do not irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx. Effective for angina:
- soda-based gargling solution;
- warm compotes;
- mineral water;
- infusion based on sage or chamomile.
Folk remedies in the form of herbs used at home do not replace antibacterial therapy.
Nutrition
The treatment regimen includes a diet. If you have a sore throat, you should avoid coffee and other hot drinks, spices, spicy foods and rough foods. It is recommended to avoid drinking milk. Excluded from the menu:
- vegetables and fruits with hard skin;
- seeds;
- nuts;
- mayonnaise;
- sauces;
- spices;
- chips;
- crackers.
It is useful to eat porridge, soups, purees, mousses, drink fruit drinks, green tea, rosehip decoction and jelly.
If there are signs of intoxication, patients should drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day. When treating a sore throat, it is important to strengthen the immune system.
For this purpose, you need to eat more fruits, berries, boiled meat and vegetables. All products must contain vitamins necessary for the body. Sweet juices with pulp are useful for sore throat. They should be drunk warm.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial therapy is indicated for microbial etiology of lacunar tonsillitis. Antibiotics are used as medicines, and sulfonamide drugs are used much less frequently. The purpose of prescribing drugs is eradication (destruction of the pathogen).
The correct selection of antibiotic ensures:
- complete destruction of the pathogen;
- exclusion of side effects from various diseases associated with angina;
- balance between the effect and safety of the antibiotic.
The first-line drugs for purulent sore throat are modern penicillins, combined with components that enhance their effect, since they work best against streptococci. Such medications include Augmentin, Flemoklav, Ecoclave and many others. It is also possible to take penicillins in monoform (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin).
If you are allergic to penicillins, treat with antibacterial drugs from the macrolide group (Sumamed, Azithromycin, Zitrolide, Klacid). Cephalosporin antibiotics are prescribed for recurring tonsillitis or severe disease. These include Cephalexin, Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin, which are often given in the form of injections in the hospital.
It is necessary to take the full course of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor to avoid relapse of the disease and the development of complications. The course of antibiotics for lacunar angina is usually 7-10 days. If you feel better after 2-3 days, and you decide that you are cured, then under no circumstances cancel the prescribed drug.
Lacunar tonsillitis and its treatment.
Lacunar tonsillitis (ICD-10 code - J03) is one of the types of purulent tonsillitis, in which the lacunae in the tonsils become inflamed and filled with pus. Lacunar tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, in particular streptococcus.
By the way, the ICD-10 code is an international list of diseases classified according to their characteristic order. The code consists of a Latin letter and a digital designation of the disease from 0 to 99.
A coding has been created for the convenience of doctors in order to standardize the diagnosis. For example, G00-G99 are diseases of the nervous system, and J00-J99 are diseases of the respiratory system.
Possible complications
With lacunar angina, complications often develop. The most dangerous of them are:
- tissue phlegmon;
- abscess formation;
- swelling of the larynx;
- difficulty breathing;
- oxygen deficiency;
- purulent inflammation of the ear;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- development of chronic tonsillitis.
Negative consequences from internal organs are possible. The spread of microbes often leads to kidney damage such as glomerulonephritis, myocarditis and rheumatism.
The most serious complication of tonsillitis is sepsis. It can lead to shock and multiple organ failure (a combination of failure of several functional systems).
Diagnostics
To correctly interpret the clinical symptoms observed with lacunar angina and to distinguish primary from secondary inflammation, a thorough examination by doctors of various specialties is necessary: pediatrician, internist, otolaryngologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist and nephrologist.
An examination of the pharynx allows one to identify signs characteristic of lacunar tonsillitis: pronounced infiltration and swelling of the palatine tonsils, accumulation in the lacunae of yellowish islands of purulent contents and films covering the surface of the tonsil. When removing the films with a spatula, they come off relatively easily without damaging the underlying tissue or causing bleeding.
To identify the pathogen, it is necessary to examine the contents of a smear from the throat and tonsils by performing a bacteriological or virological analysis. General clinical tests of blood and urine are prescribed, with the help of which the activity of the process is determined (leukocytosis and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate in a blood test) and the presence of complications from the urinary system (leukocytes, red blood cells, protein in a general urine test for nephritis). It is necessary to exclude complications (in particular, rheumatism) when performing a biochemical blood test (changes in the level of C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin-O, rheumatoid factor). Differential diagnosis of lacunar tonsillitis is carried out with other diseases of the ENT organs, secondary processes of an infectious nature (diphtheria of the pharynx, scarlet fever, mononucleosis, etc.).
Prevention
Sore throat in adults and children can be prevented. To do this you need:
- stop drinking cold drinks;
- treat caries, rhinitis and sinusitis;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- visit the dentist regularly;
- brush your teeth and rinse your mouth after every meal;
- eat more fruits and vegetables;
- breathe only through your nose;
- keep your throat warm;
- don't catch a cold;
- harden;
- quit smoking.
If one of the family members is sick, then you are required to wear a mask and use separate utensils. Thus, angina is a common pathology of the respiratory tract.
Symptoms
The incubation period of this disease depends on the type of irritant and can be a couple of days. Symptoms increase very quickly, sometimes within a few hours. Usually the first signs are a sore throat and high body temperature (39-40° with purulent sore throat).
The photo on the right shows the most important symptom of lacunar tonsillitis: purulent plaque on the tonsils
Local status of lacunar angina, patients experience some symptoms:
- redness and inflammation of the palatine arches, tonsils;
- headaches, aching joints, chills, weakness;
- sensation of a lump in the throat when swallowing, sore throat and sore throat;
- sleep disturbance, loss of appetite;
- ulcers on the tonsils;
- children develop digestive disorders, stomach pain, diarrhea, vomiting;
- decreased performance;
- sometimes – tachycardia, tingling in the heart;
- excessive salivation;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In children, the body is weaker than an adult, so acute lacunar tonsillitis poses a serious danger for them. This is due to high fever, severe intoxication and serious complications. But if you know how to treat lacunar tonsillitis at home, the symptoms may decrease within 3-4 days. The duration of the disease is 5-9 days.
The symptoms of lacunar disease are very similar to other forms of tonsillitis, so your doctor will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Symptoms of pathology
The symptoms of tonsillitis in the lacunar form are usually very pronounced, so the disease is difficult to confuse with another pathology. The clinical picture develops within 24 hours. First, the temperature rises to 39-40 degrees, the person feels a sore throat when swallowing.
There is usually no runny nose. The patient has weakness and no appetite, often has a headache, and the lymph nodes become inflamed. If you examine the oropharynx, you will notice swelling of the mucous membranes and hyperemia. In the lacunae there is a purulent plaque of white or grayish color.