In most cases, the reason a woman does not become pregnant is gynecological diseases. Endometritis provokes infertility and impairs reproductive function. The pathology mainly affects women of childbearing age. To prevent inflammation of the uterine mucosa from disrupting the functioning of the reproductive system, treatment should be started on time. If therapy is started in a timely manner, the disease will not lead to infertility. How to recognize the disease, is it possible to get pregnant with endometritis?
Chances of pregnancy
There are statistics that in 14% of cases of various pathologies during pregnancy, the “culprit” is chronic endometritis. Experts say that a viable fertilized egg along with a healthy, functional endometrium are the deciding factors when trying to conceive. The fertilized egg is looking for a safe haven for further development, and only the uterus is suitable for this role. But if its tissues are damaged, then the blastocyst cannot take root. This is exactly what happens in chronic endometritis, when the affected uterine tissue cannot create conditions favorable for the development of the fertilized egg.
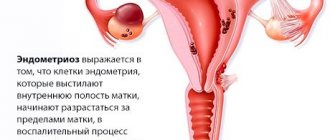
Endometritis is an inflammation of the uterine mucosa, as a result of which the (internal mucous membrane) becomes covered with adhesions and scars, thickens and hardens. It is almost impossible to get used to such armor, and the egg that makes an unsuccessful attempt is mercilessly rejected - a miscarriage occurs even in the early stages. Very often, a woman does not even suspect that conception has taken place, since menstrual-like bleeding occurs.
Endometritis develops as a result of a violation of the integrity of the uterine endometrium when mechanical damage occurs. Abortions are especially common causes of endometritis; the disease can also develop after childbirth or surgery. Sexual infections also contribute to the disruption of the integrity of the uterine mucosa.
Untreated or untreated endometritis becomes chronic. It not only causes discomfort with its systematic manifestation (signs of endometritis include acute pain in the lower abdomen, purulent discharge from the genital tract, chaotic uterine bleeding, menstrual irregularities), but in many cases, as we have already said, it becomes the cause of infertility and.
Forecasts during pregnancy
In rare cases, a woman manages to become pregnant against the background of chronic endometritis, but almost always such a pregnancy is doomed. If the egg manages to implant into the uterus affected by endometritis, it will persist throughout the entire gestation period. Other disorders and complications will also always accompany such a pregnancy. In addition, endometritis will spread, affecting the tissues of the fetus, which will ultimately lead to fetal death.
Symptoms of chronic endometritis
After acute endometritis becomes chronic, its symptoms subside. The woman believes that she has recovered and does not see a doctor. From time to time she experiences yellowish vaginal discharge, but it does not cause any significant discomfort.
Symptoms of chronic inflammation of the endometrium of the uterus include pain that occurs during sexual intercourse. However, most women ignore them because they are not very intense. As the pathology progresses, disruptions occur in the menstrual cycle. At first the menstruation is scanty, and then it becomes profuse.
The most significant symptom of endometritis is infertility. It is after long and unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child that women finally turn to a specialist.
How to get pregnant and give birth?
Yet chronic endometritis and pregnancy are not mutually exclusive. We have painted a rather gloomy picture just so that you understand that we are talking about serious things. This is your health, your life and the fate of your future children. If you are unsuccessfully trying to get pregnant, be sure to undergo a full examination, including checking the condition of the uterus. If the diagnosis of chronic endometritis is confirmed, you will have to undergo the entire course of treatment, including antibacterial, physiotherapeutic, immunostimulating therapy, taking oral contraceptives, sedatives and vitamin preparations, and treatment of concomitant diseases. Recently, modern methods of treating chronic endometritis have been increasingly used - laser therapy, magnetic therapy, infusion therapy, ozone therapy and others. Let us immediately note that chronic endometritis is a serious pathology that takes quite a long time to be treated. But without this, it is vain to hope for a successful pregnancy and safe gestation. Completely cured endometritis does not pose any danger to future pregnancies.
In some cases, when pregnancy took place against the background of chronic endometritis and it was detected early, treatment can be carried out with minimal risk to the child.
Do not despair if you are diagnosed with chronic endometritis. In fact, today women are being diagnosed with this more and more often. And this does not prevent in the future, after completing the treatment course, from giving birth to healthy children, many healthy children. Often (but not necessarily!) doctors resort to and, but the main thing is that everything is possible! And everything will be fine with you too - you’ll see!
Especially for
— Elena Kichak
From Guest
I am 33 years old. Patients with endometritis are referred for IVF. My preparation for IVF included 6 injections of alloferon. The gynecologist convinced me to try adding this immunomodulator. Studies were conducted in Samara that showed very good results.
From Guest
I treated endometritis for a long time, after an unsuccessful pregnancy and miscarriage I managed to get pregnant on my own without the help of IVF, the pregnancy was quite difficult, but it was worth it, I gave birth to a son and am very happy! I am undergoing treatment again, preparing for the next pregnancy! Do not despair if you have been diagnosed with this, with proper treatment and under the supervision of a qualified gynecologist, everything is possible! 
From Guest
I am 35 years old, I have secondary infertility and chronic endometritis (two ectopic pregnancies), I have been living with this diagnosis since 2004. I treated endometritis many times, but it subsided for a while and then reappeared. Two IVF attempts in 2012 and 2013. The first attempt was unsuccessful, but the second attempt was successful. In July 2014, I gave birth to my son. I was monitored throughout the pregnancy, it was not easy, but it was worth it. Don't let go and believe your dreams come true!!!
Among the reasons causing difficulties with conception and pregnancy, endometritis is not the least important. Indeed, in 90% of cases, the disease is detected in women of reproductive age. But are endometritis and pregnancy really incompatible? By no means, doctors do not put an end to the reproductive capabilities of patients even with such a serious illness.
Read in this article
Is it possible and how to conceive a child after treatment?
It is believed that pregnancy and this disease are not very compatible. Endometriosis can disrupt the processes of egg maturation and release , which affects the possibility of conception.
In addition, the risk of infertility increases if adhesions form in the genitals. They pose a danger in the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
But the disease is not a guarantee of absolute infertility . There are situations when this disease is detected in women who have not had problems conceiving.
And after treating the disease, many women finally manage to get pregnant. Is pregnancy possible with endometriosis?
Although the chances of getting pregnant are reduced, they remain if fertilization does occur and the egg can implant.
Although experts often advise planning pregnancy after treatment of the disease, interrupting it can worsen the course of the problem and provoke new lesions.
Therefore, if you do not want to get pregnant, with this diagnosis you need to carefully monitor contraception. Endometriosis poses a danger when bearing a child . But how it will influence it can only be explained in each case by a specialist.
The proliferation of endometrial tissue increases the risk of spontaneous abortion and miscarriage. There is a risk of severe uterine bleeding.
Therefore, if you have endometriosis, before planning a pregnancy, you need to undergo an examination and consult with a specialist. If we talk about the genital appearance of the disease, then it is quite compatible with pregnancy. One of the dangerous complications of the disease is frozen pregnancy.
As we have already understood, you can get pregnant with this disease, but you can encounter a number of obstacles and undergo treatment. Age plays a role. With this diagnosis, it is better to plan conception no later than 30 years.
The threat of miscarriage when the endometrium grows is high , therefore the expectant mother should be under the close supervision of a specialist from the first weeks of pregnancy and use medications to prevent miscarriage.
But any mother should be reassured by the fact that the disease does not affect the development of the child.
If you are less than eight weeks pregnant, your doctor may prescribe hormonal medications. Physiotherapeutic measures may be indicated.
In any case, it is important not to engage in amateur activities and follow the scheme prescribed by a specialist.
Read the article about how endometriosis is treated after 40 years, what treatment features are provided at this age. Read in this publication how endometriosis is treated with hormonal drugs and how these drugs affect the female body.
In this review, we will talk about the symptoms of atrophic colpitis in women, and whether it can be treated with folk remedies.
A little about endometritis
Endometritis is the result of the destructive work of viruses and bacteria on the inner lining of the uterus. They cause an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane, interfering with its proper development.
The acute form is easy to detect due to severe symptoms. If the wrong treatment is chosen to eliminate the disease, or it is not completed, it turns into a more hidden form. This is also facilitated by the persistence of disease-provoking factors.
The chronic form may not make itself felt with tangible signs. But one of them is the inability to conceive and bear a child, since the inflamed mucous membrane is unable to hold the embryo. Chronic endometritis and pregnancy are practically incompatible things.
Causes of endometrial inflammation
The main culprits of endometritis are pathogens. The uterine mucosa is normally sterile. It is closely connected with other parts of the reproductive system, so there are several ways for pathogenic bacteria to penetrate it:
- through blood or lymph with long-term infection in other organs and systems;
- ascending, when the vagina and other external reproductive organs become inflamed first.
Damage to the uterine mucosa by bacteria or viruses can occur as a result of:
- incorrect invasion of the organ cavity during a hysteroscopic examination or a simple gynecological examination;
- medical abortion;
- diagnostic or therapeutic curettage;
- transmission of sexually transmitted infections;
- protection;
- sex during menstruation.
Is it possible to get pregnant with endometritis? Of course, but only after his treatment.
Who is at risk of developing the disease?
Under all of the above circumstances, women are at greater risk of developing endometritis:
- leading a too free lifestyle with frequent changes of sexual partners;
- having ;
- suffering from bacterial;
- having or ;
- ignoring hygiene rules, especially on critical days;
- those with weakened immunity (this includes not only women who are often ill, but also those who have recently given birth);
- having diseases of the fallopian tubes, vagina (inflammation of the cervix of the organ is especially dangerous);
- often resort to abortion;
- using douching without a doctor’s prescription;
- recently freed from a sexually transmitted infection.
Symptoms of the disease are determined by its form. In acute endometritis the following appear:
- Abdominal pain of varying intensity, similar to menstrual pain. They become more noticeable when pressing on the abdominal wall in the area of the uterus.
- Severe loss of strength, chills.
- Temperature up to 39 degrees.
- Copious discharge (transparent, yellow, brown, but always with an unpleasant odor).
In chronic endometritis, all signs may be present, but less pronounced:
- low-grade fever;
- weakness, desire to lie down;
- periodic abdominal pain, always occurring after sexual intercourse or physical activity;
- small discharge mixed with pus, blood, and an unpleasant odor.
But its main symptoms are related to menstrual function:
- appear due to insufficient development of the uterine layer affected by the disease, in some menstruation stops altogether;
- menstruation becomes noticeable and lasts longer than usual;
- spotting is noticed outside of menstrual periods;
- Menstruation becomes much more painful.
What is endometritis
The inner surface of the uterus is covered with a mucous membrane - the endometrium. A number of pathological reasons can lead to the formation of an inflammatory process on it - endometritis, which can be acute or occur in a chronic stage.
Penetration of infection through the ascending tract into the uterine cavity can be provoked by the following circumstances:
- Childbirth, postpartum surgical procedures;
- C-section;
- Miscarriages or induced abortions;
- Consequences of a general infectious disease of the body with transmission of infection through blood or lymph;
- Diagnostic or therapeutic medical manipulations with penetration into the uterus;
- Sexual activity during menstruation;
- Use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- Sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Have you heard about bacterial vaginitis? A fairly common disease today, details here.
Acute endometritis
It is simply impossible not to notice the onset of this disease - it is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature, chills, and sharp pain in the lower abdomen. Often the pain is also felt in the groin or sacral region. There is serous-purulent discharge from the vagina, with a strong unpleasant odor, sometimes mixed with blood.
Diagnosis of endometritis
Even the acute form of the disease cannot be diagnosed by a specialist only based on the signs listed by the patient. They are too similar to the manifestations of other pathologies. Hardware methods and laboratory tests will help make a diagnosis, including:
- general blood test, which also reveals ESR;
- Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages;
- flora smear to determine the composition of bacteria in the vagina;
- hysteroscopy to obtain organ tissue for examination;
- sowing material to determine the type of pathogens;
- blood test for antibodies to rule out or confirm the presence of viral infections;
- PCR diagnostics, which makes it possible to identify all microorganisms involved in the occurrence of the disease.
Some women also need a blood test for hormones to understand how much endometritis has disrupted the functioning of the reproductive system as a whole. Disorders in this area become a serious obstacle to conception. And to the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with uterine endometritis, the doctor will answer only after a complete diagnosis of the expectant mother’s body.
An acute form of endometritis forces a woman to see a doctor. But in chronic conditions, her state of health is such that she may not associate the malaise with the disease, but blame fatigue and nerves. This allows endometritis to destroy the lining of the uterus for a long time. The inflammation can progress further, affecting the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Naturally, you can get pregnant with endometritis, but only in the initial stages of the disease. The progression of the disease results in:
- lack of ovulation;
- impossibility of implantation of the fertilized egg;
- pregnancy fading;
- miscarriages.
That is, the general result of chronic endometritis is infertility.
Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia
What priority research is carried out for a woman with suspected endometrial hyperplasia and complaints of infertility?
The thickness of the endometrium is assessed by the anteroposterior size of the M-Echo. Normal indicators change in accordance with the phases of the menstrual cycle.
Norms of endometrial thickness on different days of the cycle
Ultrasound signs of endometrial hyperplasia:
- Increasing M-Echo values.
- Heterogeneity of the structure, unevenness of the boundaries of the endometrium.
- The presence of echo-positive and/or echo-negative inclusions in the endometrium.
Hysteroscopy is a visual examination of the uterine cavity using special equipment. This procedure confirms or excludes the diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia. Curettage is performed under her control
uterine mucosa - surgical removal of altered endometrium.
Histological analysis of endometrial samples.
Pipelle biopsy for endometrial hyperplasia
The final diagnosis and form of endometrial hyperplasia, as well as individual treatment for the patient, are determined after histology - examination of the removed endometrial tissue under a microscope.
Sometimes tissue samples from the uterus are obtained not by curettage, but by using a Pipel curette (biopsy). This method is less traumatic, but less informative. It is used in nulliparous women or to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for hyperplasia.
Treatment of endometritis
Considering the culprits in the development of the infection, therapy should be directed primarily against them, that is, contain antibacterial drugs:
- “Amoxicillin”;
- “Ciprofloxacin”;
- “Cephalexin”;
- “Gentamicin.”
In addition to injections and tablets, vaginal suppositories will help, including Ternidazole, Nystatin, Niomycin, Prednisolone, Betadine.
The doctor may add to these:
- antimicrobial drugs “Tinidazole”, “Ofloxin 400”;
- antiviral “Atskilovir”, “Zovirax”, “Virolex”.
In addition to the direct effect on pathogens, you will need the following:
- diclofenac, ibuprofen, analgin to relieve pain and inflammation;
- suprastin, tavegil, claritin to eliminate edema;
- kipferon, vitamins to stimulate the immune system;
- hemostatic agents “Vikasola”, “Tranexama”;
- hormonal drugs “Duphaston”, “Utrozhestan” to normalize the cycle and development of the endometrium.
In case of severe bleeding, curettage is performed, but conservative treatment is not canceled. The choice of drugs is up to the doctor; a combination of several antibiotics in different forms is possible. It is important to complete the entire course without giving up medications when you feel better.
Planning pregnancy after getting rid of endometritis
In order for endometrial function to be fully restored, treatment must be brought to its logical conclusion. The test results become the point:
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- endometrial tissue biopsy;
- smear on vaginal microflora;
- blood tests for hormones.
If the doctor is convinced that they are satisfactory, nothing prevents the woman from starting to plan a pregnancy.
Many people are sure in advance that there is no possibility of getting pregnant naturally with chronic endometritis. But if the disease, even becoming chronic, has not existed without treatment for years, the chance of conceiving without the use of medical technologies remains.
Some people succeed in this in the first cycle after stopping hormonal medications. Others are prescribed a course of progesterone drugs that promote the development of the endometrium for 3-6 months, after which the mucous membrane acquires a thickness normal for each stage of the cycle. It is good to supplement it with physiotherapy using UHF, magnetic waves, and calcium chloride. This will help restore the endometrium and prevent the formation of adhesions in the uterus, which will subsequently interfere with pregnancy.
Pregnancy after endometritis is quite possible, but treatment should be a mandatory part of planning. To restore the proper functioning of a woman’s reproductive organs, the use of drugs will also help:
IVF increases the chances of pregnancy after treatment of endometritis. The method allows you to “unload” the female body, helping the process of bringing the egg and then the embryo to the desired state.
But pregnancy through IVF does not eliminate possible difficulties with pregnancy. A woman should especially carefully monitor her well-being, not lift heavy objects, eat right, and take vitamins. It will be necessary to take progesterone medications to maintain the thickness and friability of the endometrium necessary to retain the fertilized egg.
And some women have to spend a significant part of the time of gestation in a horizontal position.
If endometritis develops during pregnancy, you will have to be under constant medical supervision without IVF.
The disease, despite the absence of obvious signs in its chronic course, can leave consequences for life. Therefore, it is better to start treatment as early as possible, then the chances of getting pregnant after endometritis are higher.
The appearance of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs is quite common, statistics remind us of this. According to her data, such a problem occurs in every tenth woman. And if some, fearing for their health, immediately go to the doctor, undergo the prescribed course of therapy and do not remember the disease for a long time, then others prefer restraint, self-medication, which is inappropriate in this case, and risk the appearance of serious complications.
A visit to a qualified specialist when symptoms of female diseases appear is a must. Moreover, sooner or later this will still have to be done, since there will be a need to plan a pregnancy.
Chronic endometritis is one of the most common diseases of the female genital area. This disease is an inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the inner cavity of the uterus. It can be very difficult to detect and often happens that this occurs only after a miscarriage or long-term infertility.
What is the main danger of uterine endometritis during pregnancy? And which activities will be most important in planning? This is what we will talk about.
Is it possible to get pregnant with endometriosis?
How can you get pregnant with endometriosis?
It is impossible to get an exact answer to this question. Sometimes a woman can conceive and give birth normally, sometimes miscarriages occur, but more often than not it is not possible to become pregnant at all. During such an illness, conceiving a child is not as difficult as carrying one. This depends on the fact that the cells that have grown in the endometrium do not allow the child to fully develop.
Risks:
- failures in ovulation;
- sperm die while still in the uterine cavity;
- the egg cannot pass into the uterus due to adhesions;
- if the fundus and cavity of the uterus were affected, then the patient is at risk of cervical implantation of the embryo after a miscarriage.
Still, is pregnancy possible with endometriosis? The best way to achieve this is to get treatment immediately after diagnosis. And the sooner you do this, the greater the chances of getting pregnant and giving birth to a healthy child.
If an adhesive process is carried out, it is necessary to undergo a procedure of laparoscopic removal of adhesions, and only then plan the conception of the fetus.
If you do get pregnant with endometriosis, you need to support her with medication and monitor hormonal changes. It is best if the first 4 months of pregnancy proceed under the supervision of doctors in a hospital.
If the treatment is completed successfully, then the possibility of getting pregnant with endometriosis increases significantly, but there is no need to rush. It would be best to delay pregnancy for some time so that the internal organs return to a normal functional state.
If pregnancy has not occurred and the doctor has not diagnosed infertility, you will need to undergo a series of tests and establish a true diagnosis of the problem, rather than using folk remedies.
Dear ladies, if you don’t know how to get pregnant with endometriosis, you have discovered symptoms of the disease, or your intuition tells you something bad, go to the doctor and make sure everything is okay.
Endometriosis and conception are completely compatible concepts if everything is done in a timely manner and correctly! And remember: only a professional doctor knows how to cure endometriosis!
First of all, you need to contact an experienced doctor who will examine you and select an individual treatment method, be it drug therapy, surgery or a combination of both.
Comprehensive and timely treatment of endometriosis is the key to recovery. To do this, hormonal agents need to suppress menstrual function in order to restore the functioning of all affected organs and systems. Hormonal therapy allows the ovaries to rest, and after it ends, they begin to actively produce follicles.
After the first stage of hormonal treatment, laparoscopic microsurgeries are performed, during which endometrioid lesions are removed and the integrity of the fallopian tubes and their patency are restored.
Surgical treatment of endometriosis helps restore a woman’s reproductive function.
In the postoperative period, the second stage of hormonal therapy is carried out.
When carrying out hormonal therapy, the following drugs are used:
- combined contraceptives - Zhanine, Novinet, Diane-35, Regulon, which are used for a long period in a cyclical or continuous course;
- drugs based on norsteroids - the Mirena intrauterine device, which contains the hormone Levonorgestrel and is installed for 5 years;
- progestins - Depo-Provera, Utrozhestan, Duphaston;
- drugs that suppress the function of the reproductive endocrine glands - Danazol, Gestrinone;
- gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists – Zoladex, Buserelin;
To influence the mechanisms of development of endometriosis and to eliminate the manifestations of the disease, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is prescribed - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, enzyme preparations, immunomodulators, hemostatics, antioxidants, vitamin therapy.
Important! It is rarely possible to become pregnant with endometriosis, which was advanced due to delays in seeking medical help. In such cases, artificial insemination is resorted to.
Interesting! Of course, getting pregnant with endometriosis is difficult, but it is still possible. Treatment or assisted reproductive technology can help you experience the joys of motherhood.
The path to recovery is long and difficult, but pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby are worth it.
Despite the fact that the disease is quite difficult and long to treat, under some circumstances the birth of a healthy child is possible. It is very important to diagnose the disease at an early stage and begin treatment immediately. To do this, it is important to contact an experienced specialist and complete the entire therapeutic course, following the doctor’s instructions.
The classic treatment option includes a combination of drug therapy and surgery. Initially, with the help of hormonal drugs, the menstrual cycle is suppressed so that all affected systems and organs can gain strength rather than lose them.
The next stage is micro-surgery, which is aimed at removing foci of the disease in the tissues. Often this is enough to restore a woman’s reproductive function and the ability to bear a child.
After some time, the second stage of the course of hormonal therapy is applied. The main focus in the treatment of this disease is the patency and integrity of the fallopian tubes. Among other things, it is equally important to restore the full functioning of the ovaries.
In advanced cases of the disease, when the fallopian tubes are affected and adhesions form in them, it will be difficult to get pregnant with the standard option. The problem is that the egg cannot be fertilized by sperm due to the closure of the fallopian tubes.
In this case, you can only get pregnant using artificial fertilization methods, for example, the in vitro option. It is very complex and expensive, but possible.
Endometriosis is a leading problem in modern reproductive medicine. According to statistics, 40% of women cannot become pregnant on their own with this disease. Most often this is due to advanced adhesions in the abdominal cavity or fallopian tubes.
Early diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis are of great importance in pregnancy planning. Unfortunately, this pathology in most cases is diagnosed late or accidentally during a woman’s long and unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant.
Postponing childbearing until later after diagnosis of endometriosis and delaying treatment can cause severe infertility and the inability to become pregnant on your own in the future.
The best natural way to treat endometriosis is pregnancy itself!
Pregnancy with endometriosis is possible, despite the unfavorable prognosis of its occurrence in this disease. More than half of women have a high chance of becoming pregnant and bearing a healthy child.
The difficulty is presented by advanced cases aggravated by the adhesive process, however, even in such situations, modern medicine helps women experience the joy of motherhood.
Pregnancy is impossible only in extreme situations, when endometriosis has caused the removal of the uterus and ovaries.
With endometriosis, tissue similar to the endometrium of the uterus grows cyclically outside the uterus itself. Endometrioid areas go through all the stages of formation, like the endometrium, so on the days when it is rejected and a woman begins menstruation, endometrioid areas also bleed.
Endometriosis affects young women of reproductive age from 20 to 40 years (sometimes older). Foci of endometriosis can be genital (located in the ovaries, vagina, fallopian tubes, peritoneum) and extragenital (on the surface of the intestines, eyes, lungs).
Constant dishormonal changes in areas located in atypical places lead to the formation of an adhesive process.
The causes of endometriosis are not fully understood, but there are two theories regarding its development.
According to the first theory, the cause of endometrioid ovarian cysts or peritoneal endometriosis is the retrograde movement of menstrual blood, in which endometrial particles are displaced and attached to another place (ovaries, peritoneum), after which they grow and form endometriotic areas. A similar problem is observed during medical procedures (uterine curettage, cesarean section).
According to the second theory, endometriosis is caused by a genetic factor. Changes in this case occur in a female fetus even at the stage of intrauterine development. It is impossible to influence the genetic factor.
We invite you to read: The best cosmetics for newborns: rating and list of essentials
What are the causes of problems with conception with endometriosis? A long-term inflammatory process in the ovaries, tubes and abdominal cavity eventually leads to the formation of adhesions - dense strands of connective tissue that prevent the movement of the egg through the internal genital tract and reduce the contractile function of the fallopian tubes.
The second reason for the impossibility of conceiving with endometriosis is a hormonal imbalance, in which a lot of estrogen is synthesized and little progesterone. As a result, the endometrium of the uterus is too thin, and a fertilized egg cannot implant into its thickness and develop normally.
If a woman suffering from endometriosis does become pregnant, she has certain risk factors, these include the following conditions:
- Ectopic pregnancy requiring emergency surgical removal of the fertilized egg;
- Hormonal imbalance associated with low progesterone concentrations, which can lead to miscarriage in the 1st and 2nd trimesters. To avoid this, progesterone analogues are prescribed;
- Uterine rupture due to severe thinning of the muscle layer in the later stages. In such cases, a caesarean section is performed.
- Decreased elasticity of the cervix. For this reason, independent delivery becomes impossible, the cervix does not dilate, and a caesarean section becomes necessary.
A pregnant woman suffering from endometriosis should be under the supervision of a doctor throughout her pregnancy.
Endometriosis is most often diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound scan, which reveals ovarian cysts.
What causes the appearance of chronic endometritis?
Since adolescence, every woman knows that every month, under the influence of hormones, a number of changes occur in her body that are necessary for successful conception and bearing a healthy baby.
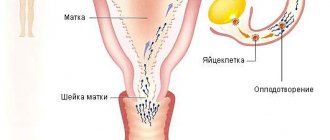
It is also no secret that implantation and subsequent growth of the embryo occurs in the uterus, and its inner lining is ideal for this: it is sterile, rich in all necessary nutrients and is capable of sensitively responding to all sorts of changes in the hormonal background, creating all the conditions for normal fetal development.
But if infectious inflammation occurs in the vagina or on the cervix, viruses and microorganisms can ascend into the uterine cavity.
Poor immunity, lack of treatment or incorrectly selected therapy allows the infection to penetrate the endometrial cells and become its “resident”. And under the influence of bad habits, stress, hypothermia or other negative factors, the disease begins to constantly “disturb” the woman’s immunity and sooner or later becomes chronic.
As a result of ongoing inflammation, the mucous membrane in the endometrium, as a rule, begins to be replaced by connective tissue, resulting in poor circulation and decreased sensitivity to hormones. And this can lead to improper attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus.
All these reasons invariably indicate that treatment of chronic endometritis should be carried out before pregnancy. Otherwise, there may be difficulties with conception, insufficiency of the 2nd phase of the cycle, miscarriage or its “fading” in the initial stages.
The main factors provoking the appearance of endometritis are:
- any surgical interventions in the uterine cavity (abortion, hysteroscopy, curettage, endometrial biopsy, etc.);
- infectious diseases of the external genitalia, vagina or cervix;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- radiation therapy;
- intrauterine devices;
- various complications after pregnancy or childbirth.
How does gestation proceed?
Despite the fact that pregnancy and endometrial disease are not very compatible, the occurrence of the former is still possible, even if the disease is not treated.
Usually,
treatment is not carried out during pregnancy , but is done after childbirth.
An exception, however, is when a pregnant woman is diagnosed with an endometrioid ovarian cyst.
If there is a risk of torsion or rupture, surgery is needed , which is usually performed at a period that is safe for the fetus - 16-20 weeks.
A pregnant woman with this diagnosis needs to be especially careful about her condition, regularly visiting a doctor.
Since there are risks of miscarriage with endometriosis, hormonal support for pregnancy is often needed. With endometriosis during pregnancy, the risks of miscarriage are especially high in the first and second trimester.
After all, a woman’s body may lack progesterone, which helps ensure the proper development of pregnancy and suppress contractions of the uterine muscles.
Once the placenta is formed, the risk of abortion is reduced. Endometrial disease no longer threatens the fetus and does not affect its development.
On our portal you will also learn about the symptoms and treatment of hypothyroidism in women, how dangerous this disease can be! In the following material, read about measures to prevent chronic cystitis in women, how to treat the disease in the acute stage.
Do you know what a pituitary adenoma in women is? Find out about diagnostic methods and treatment methods here: .
Planning pregnancy: how to get rid of the disease in time
It is necessary to treat chronic endometritis when planning pregnancy in a comprehensive and step-by-step manner. The main goal of therapy should be both restoration of the endometrium and normalization of reproductive function in general.
The first stage includes
antibiotic therapy.
Only the attending physician should prescribe this or that antibacterial drug and only after conducting laboratory tests to determine the causative agent. It is also possible to prescribe intrauterine infusions of drugs.
From the very first day of the cycle, the use of immunostimulants should be indicated to strengthen the body's immune forces. But before this, the doctor must check the woman’s interferon status (i.e., the state of her body’s innate nonspecific defense) and determine sensitivity to interferon inducers.
The second stage is divided into:
- Metabolic therapy. It is aimed at improving the supply of oxygen and glucose to the endometrium and increasing local immunity.
- Physiotherapy. It is usually prescribed taking into account all gynecological pathologies of a woman. It has a resolving effect, increases blood circulation and also increases local immunity.
If necessary, hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed.
In general, treatment for endometritis takes three to four months. The effectiveness of the treatment measures taken is determined 2 months after the end of therapy. After such treatment of chronic endometritis, women can plan both natural pregnancy and with the help of assisted reproductive technology (ART) programs.
Features of pregnancy with chronic endometritis
Cases when a woman manages to become pregnant against the background of a progressive disease are quite rare and such a pregnancy is usually considered doomed. If the egg was able to implant in the affected uterus, then the threat of miscarriage will persist throughout the entire period of gestation. However, other complications may accompany such a pregnancy.
Endometritis is a chronic disease of the female reproductive system that is asymptomatic. The pathology occurs in women of childbearing age; the disease is especially dangerous at the age of 25-35, when a girl faces the question of pregnancy.
Modern scientific research in the field of medicine shows that women with chronic endometritis as a concomitant disease suffer from infertility, undeveloped pregnancy and recurrent miscarriage in almost 100% of cases. Traditional treatment methods are not always able to cope with this pathology, which attracts the close attention of gynecologists. This article will discuss the possibilities of pregnancy and gestation for women with chronic endometrial pathology.
Pregnancy with chronic endometritis
Pregnancy with chronic endometritis is possible in the early stages of the disease. During this period, the mucous layer of the uterus still retains areas where the embryo can attach and begin to grow. However, gynecologists stop patients from such a rash step.
The danger to the health of women and children is too high. Pregnancy can end in miscarriage, stillbirth, or early placental abruption. The baby may be born with developmental abnormalities.
It is very important to get examined before planning to conceive. Even if pregnancy occurs with endometritis, there will be a high probability of miscarriage during gestation.
In 10% of cases, chronic endometritis causes absolute infertility. This happens when the deep layer of the uterus, the myometrium, is involved in the inflammatory process. To prevent this serious complication, you need to start treatment on time.
Causes of infertility and miscarriage
The uterus is the main organ of the reproductive sphere, where all stages of conception and implantation of the embryo, and then the development of the fetus, take place. The inside of the uterus is lined with a layer of epithelium - the endometrium. In accordance with the phase of the menstrual cycle, the thickness of the endometrium changes due to active regeneration. The greatest thickness of the endometrium corresponds to the middle of the menstrual cycle, when the egg is released and the woman’s body prepares for conception. A regenerated thick layer of the endometrium is the main condition for successful implantation of the embryo into the mucous wall of the uterus and further development of the fetus.
In chronic endometritis, endometrial regeneration does not occur due to the inflammatory process. With endometritis, the processes of fibrosis (proliferation of connective tissue at the site of inflammation), disruption of hormonal regulation at the local and systemic level, as well as disruption of the normal flora and cellular composition of the uterine mucosa predominate.
Thus, infertility and miscarriages with endometritis occur for several reasons:
- Violation of the morphology of the endometrium with replacement by connective tissue. As a result, the fertilized egg cannot implant in the uterus and is released along with vaginal discharge. In this case, the woman does not even suspect that she was pregnant.
- Progesterone synthesis disorders. Progesterone is the only hormone of the reproductive system that maintains pregnancy, maintaining it for a long time, by reducing the tone of the inflamed uterus. In chronic endometritis, progesterone is not produced, since the synthesis of inflammatory mediators predominates, which is manifested by termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
- Pregnancy with endometritis does not occur due to the inactivation of male sperm already at the stage of conception. In the process of inflammation, phagocytic cells take an active part: macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells. They destroy foreign antigens, including sperm. When male germ cells enter the uterine cavity, they are phagocytosed and destroyed by inflammatory macrophages and neutrophils.
It is important to know! Chronic endometritis is often asymptomatic. For its timely detection, women need to undergo annual preventive medical examinations with a gynecologist. This way you can significantly reduce the risk of infertility in the future.
The connection between endometritis and infertility
To prevent endometritis from becoming a surprise, pregnancy should be planned in advance. To do this, a woman must undergo examination by a gynecologist. As you know, a child grows and develops in the uterus. Therefore, the health of the fetus depends on the condition of the organ, as well as whether the egg can even attach to the endometrium. For this to happen, it must have a certain thickness and structure. Endometritis causes the inner uterine layer to undergo pathological changes, causing a woman to develop infertility.
Several reasons why pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child with endometritis are impossible:
- The mucous layer of the uterus, affected by the inflammatory process, will not be able to accept the fertilized egg. It thickens, becomes dense, and its normal cells are replaced by connective tissue. Therefore, even if all conditions are met (fertilization of the egg, patency of the uterine appendages, etc.), attachment of the embryo becomes impossible. In addition, against the background of endometritis, polyps, cysts and adhesions often begin to grow in the uterus. This further aggravates the pathological process.
- Provided that the fertilized egg has found a suitable place for attachment, the likelihood of successful completion of the pregnancy is extremely low. An enlarged and inflamed uterus will not be able to provide normal nutrition and blood supply to the embryo. Therefore, most women have a miscarriage.
- Pregnancy against the background of endometritis is dangerous because the pathogenic flora that caused inflammation of the mark can penetrate the fetal membrane. Bacteria can cause irreparable harm to the embryo, disrupting its growth and development.
What you need to know about treatment when planning pregnancy
- Follow your doctor's recommendations. Find an experienced gynecologist who has repeatedly treated endometritis.
- If possible, see a fertility specialist to check your chances of pregnancy.
- During the therapeutic course, use contraceptives so as not to deplete your body with abortions.
- Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are used for treatment. Physiotherapeutic procedures have a great effect in the treatment of endometritis: UHF exposure, massage.
- To restore hormonal levels, psychotraumatic influences are excluded and sedatives are prescribed.
- Heavy physical and mental labor is not recommended during this period of time. It is important to create a favorable atmosphere around yourself.
Important information! Before a course of treatment, a woman needs to be patient. Treatment lasts from 4 to 6 months, and pregnancy itself occurs 2-4 months after it.
Also, do not forget that after the last miscarriage, at least six months must pass before the onset of a new pregnancy. This is why it is so important to use contraceptives during treatment, especially if the woman has previously had spontaneous abortions due to endometritis.
Treatment of endometritis during pregnancy planning
To begin treatment of endometritis, it is necessary to establish which flora provoked inflammation of the uterus. This analysis is performed at the diagnostic stage. Most often, the doctor recommends that a woman take broad-spectrum antibiotics, which will be harmful to most representatives of the microbial flora. To increase the effect of the therapy, immunomodulatory drugs are used. If the inflammation was caused by viruses or protozoa, then taking antiprotozoal and immunomodulatory drugs is indicated.
First you need to completely cure endometritis, and then get pregnant.
To prevent inflammation from leading to the formation of adhesions, absorbable agents can be used. Oral contraceptives allow you to regulate hormonal levels. Most often, hospitalization is not required. Only those patients whose endometritis has led to severe complications and need the help of a surgeon are admitted to the hospital.
You cannot plan a pregnancy while you are treating the disease . It is allowed to start trying to conceive only after completing the treatment course. The fact is that the drugs that a woman takes can harm the embryo.
Course of pregnancy
Numerous reviews from women and doctors indicate that after treatment of endometritis, pregnancy occurs with a probability of up to 90-100% and ends in childbirth in 60-70% of cases. A pregnant woman should be regularly observed at the antenatal clinic, at least 2 times a month.
If there are signs of a threat of miscarriage, progesterone drugs (preserving pregnancy) are prescribed. When pregnant, it is advisable to take vitamin complexes, after consulting with your doctor.
A pregnant woman is at high risk of miscarriage, so it is necessary to limit physical activity and stress. Heavy lifting is strictly prohibited.
In general, 60-70% of pregnancies end in childbirth; most women carry and give birth to a second child without problems.
IVF after endometritis
Modern reproductive technologies have brought into our lives the possibility of in vitro fertilization. In cases of recurrent miscarriage and infertility, this procedure is often the only chance to have children. However, there are nuances here.
Difficulties with IVF are associated with endometrial restructuring. If the patient cannot become pregnant and carry a fetus to term, this means that the endometrium is not ready to accept the embryo and preserve it. With IVF, the egg is fertilized outside the uterine cavity, after which the embryo is artificially implanted into the mother, but there is a high risk that the endometrium will not accept this embryo either.
Research shows that only a small percentage of women with chronic endometritis carry and give birth to children after in vitro fertilization. To increase efficiency, it is better to use several attempts at embryo transfer with a short time interval.
What to do if endometritis is detected
First of all, when diagnosing endometritis, do not despair. If the disease is detected early, everything can be corrected. Mild forms of pathology can be treated in a timely manner, which increases the likelihood of pregnancy after a therapeutic course.
Difficulties arise with advanced forms of endometritis and purulent forms of the disease. In this case, treatment is lengthy and complications often occur. With a prolonged and purulent course of the disease, the endometrium undergoes a complete morphological restructuring, which creates serious obstacles to pregnancy in the future.
Important tip! There is no need to delay treatment and consider its feasibility if a woman plans to have children in the future. So the chances of conceiving and bearing a child are reduced by 2-3 times. After a timely therapeutic course, 60-70% of women carry and give birth to healthy children. With complicated forms of the disease and prolonged treatment, this percentage drops to 10-20%.
Symptoms and treatment
Endometritis in acute form is usually manifested by fever, vaginal discharge, pain with localization of pain in the lumbar region or lower abdomen. Sometimes cycle disorders are observed. During an objective examination, the doctor discovers an enlarged uterus, painful upon manual examination.
At the same time, in the chronic form of the pathology, pronounced symptoms may be absent. Body temperature is usually within normal limits. There is no discharge at all, or it is small in quantity and mucopurulent in nature. Diagnosis is difficult because the patient usually does not see a doctor.
There may be no symptoms at all. In this case, chronic inflammation in the uterus is detected during diagnosis for other diseases.
Treatment of endometritis has several goals. But the main one is the destruction of pathogenic microbes. For this, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics.
In parallel, anti-inflammatory and symptomatic therapy is used.
Typical and specific symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is largely determined by the specific localization of pathological foci of the endometrium and the general health of the woman. In some cases, the disease is asymptomatic, especially at the initial stage. In this case, endometriosis can only be detected during a regular preventive examination or when visiting a gynecologist due to difficulties conceiving a child.
As the pathological process develops, the following characteristic signs appear:
- Painful sensations in the pelvic area. This symptom is observed in 16–24% of patients. The pain syndrome is constantly present, having a clear localization or, conversely, diffuse character.
- Cyclic pain associated with menstruation. Occurs in half of patients. Particularly severe pain is observed in the first three days of menstruation and is associated with factors such as:
- spasms of uterine vessels;
- effusion of blood from the affected areas into the peritoneum;
- increased pressure and blood flow into the cyst.
- Unpleasant and even painful sensations during sex. More often they appear when affected areas appear in the vaginal epithelium and on the ligaments of the uterus.
- Changes in the normal course of the monthly cycle:
- prolonged and too “strong” menstruation;
- weak brown discharge before and after menstruation;
- short menstruation;
- bleeding in the middle of the cycle.
- Problems with conceiving and bearing a child. This symptom is observed in 25–40% of sick women. Possible causes of infertility include ovarian dysfunction, low immunity and ovulation disorders.
In addition to the characteristic signs of endometriosis, in some cases specific symptoms appear, such as:
- bloody discharge in stool and urine;
- defecation disorder;
- hemoptysis;
- bleeding from the navel;
- bloody tears.
These signs are rare (or extremely rare) and depend on the location of the areas affected by the endometrium in the female body.