Hip dysplasia is a congenital pathology characterized by a violation of the formation and development of the anatomical structures (muscles, ligaments, bones) that form the hip joint. As a result of such disorders, the femoral head is displaced relative to the articular surface of the pelvic bone.
In Russia, hip dysplasia (HJD or DTS) is detected in 2–4% of newborn children, 80% of them are girls. Damage to the left joint is more common - in 60% of cases. The hip joint (HJ) is formed by the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone. A cartilaginous rim runs along the edge of the acetabulum, which limits the mobility of the joint.
The head of the femur is spherical and covered with articular cartilage. The head is connected to the body of the bone by the femoral neck - a section of bone with a smaller diameter. The femoral head is attached to the edge of the acetabulum with the help of an articular ligament, which contains the neurovascular bundle that supplies the joint. The ligament is also needed for shock absorption. Externally, the joint is protected by an articular capsule (bursa), which is attached along the edge of the acetabulum, and on the femur, covering the head and neck of the femur.
Causes of dysplasia
Hip dysplasia in children occurs due to a number of reasons:
- Hereditary burden. In almost a third of patients, cases of the disease can be identified in close relatives.
- Breech presentation. With this position of the fetus in the uterus, THD occurs several times more often.
- Malnutrition of the mother during pregnancy. The lack of sufficient amounts of essential microelements and vitamins leads to pathology in the formation of the joint apparatus in the fetus.
- Early toxicosis.
- Taking medications during pregnancy.
- The mother has gynecological diseases.
- Birth trauma (more often when the fetus is large).
- Ecology. In areas with poor environmental conditions, cases of dysplasia are recorded 4–5 times more often.
Prognosis and complications
If treatment is not started immediately after the baby is diagnosed, then as the child grows older, when the child begins to stand on his feet, the load on the joint will be distributed incorrectly. In severe cases, joint dislocation occurs, even if the baby initially had an initial degree of dysplasia.
In this case, surgical intervention will be required to improve the patient's condition and regain mobility of the joint. The joint will no longer be completely healthy.
Interesting!
Some experts believe that about 50% of adults who experience osteoarthritis have suffered from undiagnosed hip dysplasia since childhood.
Lack of treatment for hip dysplasia in infants is dangerous; the following complications may occur:
- Scoliosis,
- Flat feet,
- Necrosis of the tissues of the femoral head,
- Osteochondrosis,
- Pathologies of the spine, legs and pelvis that interfere with the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment of hip dysplasia in babies under 3 months is the most effective, with more than 90% of cases of complete restoration of joint function. If therapy is started after six months, the chances of recovery become much lower.
Classification
Acetabular dysplasia - developmental disorders affect only the acetabulum of the joint. Epiphyseal dysplasia. This type changes the angle at which the femoral neck connects to the shaft of the femur. Stiffness of the joints leads to deformation and pain. Rotational dysplasia. It is characterized by a violation of the configuration of structures in the horizontal plane, which leads to displacement of the femoral head relative to the acetabulum.
According to the severity of manifestations of THD, they are distinguished:
- Mild degree – pre-dislocation. The muscles and ligaments are of normal structure, but hypermobility of the femoral head is noted.
- Medium degree – subluxation. This degree is manifested by incomplete displacement of the femoral head in relation to the acetabulum. The femoral head does not extend beyond the joint. The ligaments and joint capsule are stretched.
- Severe degree - dislocation. The articular surfaces of the femoral head and acetabulum are completely displaced relative to each other. The femoral head leaves the joint cavity, and the articular cartilage enters the joint capsule.
Therapy methods
Even if the joint defect is not too significant, therapy should be started immediately. Pre-dislocation can turn into dislocation.
In addition, treatment for a baby up to six months will be quick and effective; for the youngest, it is enough to undergo therapy for two months. The disease in children takes much longer to treat after a year.
Therapy
The therapeutic technique depends on the degree of neglect of the dysplastic process.
| Method of therapy | How is it carried out? | At what age is it effective? |
| Wide swaddling | A folded diaper 16–21 cm wide is placed between the legs, bent at an angle of 90 degrees. | From birth to three months. |
| Pillow (feather) Freyka | A special roller, secured to the baby’s body with straps, secures the hips in an extended position. Like the previous method, it helps only in the mildest cases. | From birth to three months. |
| Becker's pants | Panties with a felt or metal insert in the gusset prevent the legs from being pulled together. They come in different sizes. | From one to nine months. |
| Pavlik stirrups | A bandage made of soft fabric, also secured with straps, provides a therapeutic effect on the problem area without limiting the baby’s movements. | From the second month to a year. |
| Sling and ergo backpack | They allow the baby to be in the correct and comfortable position. | A sling - from birth, an ergo backpack - from five months. |
Pavlik stirrups
In serious cases, fixing spacer splints are used. These can be elastic Vilensky and Volkov splints or plaster analogues with a distraction system. This therapy is intended for children under 3 years of age. Individual options are also used for older children, but usually as a safety net after surgery.
Closed reduction of a dislocation in the pelvic joint is performed in difficult cases in children under 6 years of age. For those who are older, such therapy will only do harm. Skeletal traction can help with severe pathologies in preschool children up to 7 years old.
The operation can be open or endoscopic - it depends on the severity of the disease. Usually, if treatment for dysplasia is started on time, it is possible to manage with conservative methods.
The risks associated with surgery (bleeding, infection, and those associated with anesthesia) are minimal. However, when performing surgery on children, orthopedists do need to take extra care to avoid a condition called avascular necrosis, in which the head of the femur (the ball of the hip joint) does not receive enough blood, a condition that can lead to abnormal bone growth.
Gymnastics for hip dysplasia is aimed at flexion-extension, adduction-extension of the legs. Exercises can be performed at home, but exercise therapy should be recommended by an orthopedist, based on age and severity of the pathology.
Physiotherapy will reduce inflammation and pain, improve cell regeneration in tissues. The most effective procedures of this kind include:
- Electrophoresis;
- Paraffin applications;
- Amplipulse therapy;
- Ultrasound;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Hyperbaric oxygenation;
- Acupuncture;
- Mud therapy.
Massage for hip dysplasia in newborns will strengthen the muscles and joint capsules. It must be done regularly six times a day before feeding. The newborn lies on his back, and the adult spreads his legs bent at the knees as far as possible and alternately straightens and bends them eight times.
Experts divide treatment of hip dysplasia in newborns into several groups:
- orthopedic;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical.
The choice of treatment method depends on the characteristics of the development of the pathology and the degree of its severity. In any case, it is necessary to carry out physical therapy and massage for hip dysplasia in newborns. Follow the link to find out how to treat an inguinal hernia in a child and how this disease is diagnosed.
The main goal of orthopedic therapy for the disease in infants is to center the femur in the joint and “build up” its roof. The hips are given a “forced” position using devices:
- Freik's pads;
- diverting pants;
- Vilensky outlet bus;
- Koshlya outlet bus;
- Mirzoev outlet bus;
- Volkov outlet bus;
- Pavlik stirrups;
- Gnevsky's apparatus.
The choice of device and its fitting are entrusted to the orthopedic surgeon. It is strictly forbidden to select and select a device on your own, because you can not only slow down recovery, but also cause additional harm to the baby’s health. The doctor will provide a consultation on how to care for the child in the device and how to remove it.
Orthopedic devices must be worn around the clock. Its removal is possible only during water procedures, massage and physical therapy. For mild dysplasia or during the final period of therapy, the device is worn only at night.
Dysplasia in a newborn responds well to physiotherapeutic methods. One of the main ones is electrophoresis with medicinal substances. Wet plates - electrodes with Eufillin solution (most often) are applied to the diseased area. Electrophoresis for hip dysplasia in children has a minimum of contraindications.
Another method of physiotherapy is heat therapy, or rather paraffin therapy. Exposing the affected areas to white paraffin helps warm them up. For newborns, it is the white type of paraffin that is used, since it does not contain any harmful substances or impurities.
Magnetic therapy is also often prescribed. A magnetic field is applied to the affected area, which helps speed up metabolic processes and blood microcirculation. Such processes help accelerate the development of tissues (muscle, cartilage, connective tissue).
Increased excitability, nervousness and hyperactivity in infants can be reduced using hydrotherapy. The main advantage of the method is the ability to use it at home. For example, decoctions of medicinal herbs or sea salt are added to the bathtub.
Physiotherapy can be supplemented with gymnastics, which gives good results for hip dysplasia in newborns. Exercise therapy for hip dysplasia in children is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the development of the pathology.
Signs
Depending on the severity and type of dysplasia, as well as the age of the child, the disease will manifest itself differently.
DTS in newborns
With grade 1 or 2 dysplasia, the symptoms of the disease in the first days of life are almost impossible to determine. But a severe degree of dysplasia can be detected in a baby while still in the maternity hospital. The following symptoms are possible: difficulty in spreading the legs bent at the knees and abducting the hips, asymmetry of the kneecaps, which indicates shortening of one leg; when the child’s legs are spread, he cries, visible asymmetry of the hip.
Signs of dysplasia in children under one year old
In addition to difficulties in hip abduction, the following symptoms can be identified in infants under one year of age. Asymmetry of the folds that are located under the buttocks, under the knees and in the groin. But this symptom can be assessed only after 3 months, because in a baby at an earlier age, asymmetry of the folds is the norm. "Snap" syndrome. This is one of the most reliable signs of THD. During the examination, the orthopedist bends and abducts the child’s legs in a special way so that the joint returns to its normal position. At this time, a characteristic click is heard.
Signs of dysplasia in children after one year
If THD was not detected in time and the child did not receive treatment, then children experience difficulty walking. When you try to move, pain appears, and later an inflammatory process may occur in the joint. With bilateral dislocation, the gait takes on a characteristic appearance - the so-called duck gait. If the dislocation is unilateral, then lameness is observed on the affected leg.
Possible complications
With a long course of the disease without proper treatment, certain complications arise in an older child, which are expressed in the following:
- lameness when walking,
- pain when moving a joint, pain in the knees,
- amyotrophy,
- poor posture,
- shortening of one leg.
Severe defects in dysplasia may subsequently require surgical intervention, which is an undesirable consequence for a small organism.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis, especially in infants, is not always an easy task. With mild and moderate dysplasia, clinical signs are mild. The first examination of the baby is done by a neonatologist in the maternity hospital. Subsequently, the child is observed by a pediatrician. At one month, three and six months, children are routinely examined by a pediatric orthopedist.
When making a diagnosis, not only the results of the examination are taken into account, but confirmation is also necessarily carried out using an x-ray method or ultrasound diagnostics.
X-ray examination is carried out for children older than 3 months (at earlier times this method is not informative). An x-ray can determine the type of dysplasia, the severity of the disorders and the presence of concomitant pathology. In children under one year of age, the ultrasound diagnostic method is predominantly used. It is also highly informative and does not carry additional radiation exposure.
The ultrasound method of hip joints is absolutely safe even for newborns
Symptoms
In the first months of a child’s life, you can detect symptoms of an anatomical defect on your own, but it is important to contact a pediatric orthopedist as soon as possible.
Among the main signs indicating dysplasia are the following:
- pronounced asymmetry of skin folds on the baby’s buttocks and hips,
- different knee heights when bending the child’s legs,
- incomplete hip extension (normally, both legs of the baby should be spread evenly),
- different leg lengths,
- the appearance of a click in the joint during its movement.
Already in the maternity hospital, the newborn is tested for these signs; in the future, the baby must regularly visit an orthopedist to exclude pathologies.
Treatment
Treatment of predislocation and subluxation of the hip joint in young children, as well as most cases of dislocation, is carried out conservatively.
Wide swaddling
Coxitis of the hip joint in adults
This method is used for both preventive and therapeutic purposes. The essence of the method is that it allows you to hold the child’s legs in a position separated by 60–80 degrees. To do this, 2 diapers, folded in several layers, are placed between the child’s legs, and the third diaper secures them to the belt.
This type of swaddling is recommended to be used:
- Children at risk for THD.
- If a child has an immaturity of the hip joint on ultrasound.
- For joint dysplasia, when it is impossible to use other correction methods.
Application of orthopedic structures
During the study of THA, many devices were designed to correct congenital hip dislocation without surgery. Among them are tires from Vilensky, Volkov, and Freik. They are used for grade 2-3 dysplasia. If the child is already older than six months, then more rigid plaster spacers are used.
Pavlik stirrups are called the gold standard of pediatric orthopedics. They were developed by Czech professor Arnold Pavlik. If THD was diagnosed before the age of six months, then the effectiveness of therapy with Pavlik stirrups reaches 95%. Stirrups are chest and ankle braces connected by special straps (straps). This design allows you to securely fix the joint while maintaining the mobility of the child’s legs.
Pavlik stirrups for hip dysplasia
Massage
Therapeutic massage is prescribed for all types of dysplasia. It can also be done in the presence of orthopedic structures without removing them. The massage should be performed by a pediatric specialist. During the procedures, blood circulation improves, muscles and ligaments are strengthened. The massage therapist works not only the thigh area, but also the neck and back.
Physiotherapy
It is prescribed for almost all types of dysplasia. The doctor selects a set of therapeutic exercises for the child, which are performed every day or at intervals of two to three days. First, the physical therapy instructor performs the exercises with the child, and after mastering this technique, the parents do the exercises.
Electrophoresis
The method of choice for physiotherapeutic treatment in young children is electrophoresis with calcium, phosphorus or iodine. This method helps to quickly deliver medications to the joint area, improves local blood circulation and trophism (nutrition) of tissues.
Surgery
Currently, this correction method is used quite rarely. Indications for surgery are:
- Severe degree of dislocation.
- Late diagnosis of pathology.
- Ineffectiveness of conservative therapy.
- Infringement of cartilage in the joint capsule.
Preventive measures
Treating a disease is always more difficult than preventing it. Prevention of hip dysplasia in infants includes simple manipulations that will prevent the development of pathology.
Pregnant women should carefully consider their health status, plan their diet wisely and take vitamin supplements. After birth, the child should be examined by specialists in order to notice the disease at the earliest stages.
It is necessary to avoid tight swaddling, which can aggravate joint problems. For hip dysplasia in infants, Dr. Komarovsky recommends wearing the baby in a sling facing the mother.
Be sure to perform special gymnastics and massage aimed at improving joint function. But you cannot “rush” the baby: put him on his feet at an early age, sit him down before he himself begins to learn these movements.
Having understood what hip dysplasia in newborns is, it becomes clear that this is a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment. The first symptoms in a baby can be noticed by maternity hospital doctors or parents; the diagnosis is made at the age of 3-6 months. The therapy used helps prevent the deterioration of the young patient’s condition, improve the quality of life and prevent the development of complications in later life.
Consequences
If dysplasia is not treated in infancy, then undesirable consequences may occur in the future, such as:
- Muscle atrophy in the affected leg. On the healthy leg, on the contrary, the muscles hypertrophy compensatoryly.
- Lameness occurs.
- Due to the displacement of the fulcrum, curvature of the spine occurs.
- Formation of a “false joint”, accompanied by shortening of the limb and impaired muscle function. This complication can only be corrected surgically.
Hip dysplasia in adults
Mild degrees of joint underdevelopment may remain undiagnosed in childhood and will manifest themselves over the age of 20 years. Manifestations of the disease are most often triggered by pregnancy (due to changes in a woman’s hormonal levels) or a significant decrease in physical activity.
At the initial stages, massage, special gymnastics, and physiotherapeutic methods are used for correction. To relieve pain, the doctor prescribes drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nise, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide). However, often such patients quickly develop progressive arthrosis.
In adults with progressive arthrosis, they resort to endoprosthetics
Symptoms in newborns and infants
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
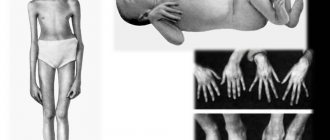
It happens that when examining her own baby, a young mother notices some oddities: the knees are not at the same level, the folds of the buttocks and hips are asymmetrical. If you place such a baby on the table, bend his legs at the knees and spread them in different directions, he will not be able to touch the table.
The main thing to do in this situation is to show the baby to a pediatric orthopedist as quickly as possible. Most likely, the baby has dysplasia - underdevelopment of both or one of the hip joints. Depending on the severity, dysplasia can manifest itself as a subluxation, preluxation or dislocation of the joint, differing in the degree of displacement of the femoral component of the joint relative to the pelvic cavity.
The corresponding signs of a sprained leg can be seen with the naked eye.
You need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Additional fold in the leg area;
- One leg is smaller, and the other is long;
- Asymmetry during leg abduction;
- Asymmetry of the buttocks, as well as gluteal, femoral and inguinal folds;
- A clicking sound that occurs when bending the legs;
- Legs bent at the knees cannot be completely retracted.
If these signs are detected, then it is necessary to immediately show the baby to an orthopedist.
Try to eliminate the negative impact on the fetus during pregnancy and cure your diseases promptly. Monitor the condition of your baby and do not neglect visiting specialists.
To ensure that the baby’s joints develop correctly, experts recommend extensive swaddling or avoid swaddling completely. Never swaddle tightly, otherwise the newborn's legs will straighten out due to the tight diaper. Congenital dislocation of the leg occurs quite rarely in regions where tight swaddling of children is not accepted (Vietnam, Africa, Korea).
Try using special carriers, backpacks, car seats and slings. Choose models that allow your baby to hold on with his legs spread as wide as possible.
Komarovsky is a doctor who has conducted a series of studies and a whole video on hip dysplasia in children. What is the essence of the problem and will swaddling with a “soldier” protect you from crooked legs? Recognizable Uncle Doctor will tell you how to prevent dysplasia and how to cure it.
One of the little participants in the program described hip dysplasia as a disease in which the bones become stuck. The child's worldview outlined the problem more clearly and simply. With dysplasia, underdevelopment of cartilage, the bones in the joint will actually “seize”, and the following discrepancies are likely:
- pain in the joint;
- subluxation, dislocation;
- the risk of developing coxarthrosis and other pathologies;
- lameness.
Dysplasia can be severe and mild, it can appear in a newborn right away, or maybe only after a few months the joints in infants will lag behind in development.
Fact! The diagnosis of hip dysplasia is suspected in every 2 newborns.
They began to look at the problem in the video with Komarovsky using the example of a 5-month-old baby. Immaturity of the hip joint in a baby can be suspected by the following signs:
- dissymmetry of folds on the back of the thighs;
- during charging, the thigh is tightly abducted;
- When abducted, clicks are heard.
If there is a problem in one joint, the ancestors may notice a difference in the length of the legs; the limb with an underdeveloped joint will be smaller.
Fundamentally! After only a year, a child with an underdeveloped joint may begin to limp and complain of pain.
If we talk about the reasons for the appearance of dysplasia, then there may be several of them - scientists still have not recognized the clear conditions preceding the pathology. Only approximate causes of risk can be named:
- 1st birth;
- large fruit;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- difficult childbirth, fetal injuries during the process;
- polyhydramnios.
Girls are 5 times more likely than boys to develop underdevelopment of the hip joint. The more causes are identified in newborns, the higher the risk of developing pathology ( “” (from the Greek
).
For reference! The condition and development of joints is often monitored once every 3 months.
The joints of newborns do not have a strong structure - the skeletal system is not yet fully developed. The pelvic bones, which have not yet fused, have not become stronger and cannot perfectly hold the femurs in any position. The best option is the frog pose, which is loved by all children.
When tightly swaddling with strictly straightened legs, as great-grandmothers taught, the hip joint is strained to the limit. If there is dysplasia ( abnormal development of tissues, organs or body parts
) – the head of the leg is not yet the same size or the joint is strengthened by a weak ligamentous apparatus, the possibility of dislocation, the emergence of the femoral head from the acetabulum, is more than 90%.
An ordinary disposable diaper will help prevent hip dysplasia - thanks to the absorbent substance that does not allow the child to bring his legs together.
Healing
Treatment of dysplasia is carried out depending on its degree of regression. Komarovsky says that healing rarely lasts more than 3-4 months; the sooner it starts, the more effective it will be.
Extensive swaddling can be used from the first minutes of a baby's life. Swaddling is to fix the baby's legs in a spread state.
To do this, use an ordinary diaper, which is rolled up and placed between the baby’s legs, then with the help of another diaper or a pair they secure the entire homemade structure. Thanks to this swaddling, the hip joint will always be in a suitable position.
For reference! Instead of wide swaddling, if the baby is more than 3 months old, you can use ordinary baby slings made of hard material.
If the situation is severe, and dysplasia is expressed to degree 3, then orthopedic devices are used, which are put on the baby by an orthopedist. These designs will help you cope with the problem:
- Pavlik stirrups;
- Freyk's pad;
- Vilensky tires;
- Becker trousers;
- corsets.
A cast may be applied from time to time. These devices differ in the degree of fixation and time of implementation. Freik's pad can be removed for several hours a day; Pavlik stirrups are not recommended to be removed for 3 months.
The people were taken aback! Joints will recover in 3 days! Attach...
Few people know, but this is exactly what heals joints in 7 days!
Exercise therapy and massage
Regular massage sessions and physical exercises are effective at any stage of dysplasia. Only a specialist should massage the lumbar and buttocks area. The same goes for exercise.
After a couple of sessions, the parents can experience a massage without the help of others, but under the supervision of a specialist. Massage and exercises should be performed up to 5 times a day for no more than 5 minutes.
For reference! In difficult situations, electrophoresis may be used; the number of procedures is chosen personally.
If the situation is so advanced that the doctor diagnoses a congenital dislocation of the leg, it will be reduced to the child ( in general, a person during childhood
) you will need to wear special fixing corsets so that the joint can be strengthened with the help of ligaments.
In cases where the child was born with severe disorders, or dysplasia was discovered late, surgical intervention is used - open reduction of the head of the leg at the desired angle. After this, restorative healing is needed.
Additional measures
Caring for a child with hip dysplasia must be special. In order for the healing to be of higher quality, parents should adhere to the following rules:
- Make sure that the baby's legs are always spread apart ( part of the fruiting body of the cap-footed mushroom
). To do this, you cannot dress him in tight pants, or put him in a car seat that is not his size or his age. - You can stand on your legs only with the permission of an orthopedist. In some cases, doctors prohibit placing a baby before 12 months.
- If the child is always in the mother's arms, you need to choose a method of carrying the baby in which he will wrap his legs around the mother.
Komarovsky says that hip dysplasia is in no way a disease, and healing as such is not required, you just need to correct the position of the bones in the joint and help them align correctly.
Parents should be sensitive to the health of the baby. In order to prevent their baby from becoming disabled later, they need to follow the advice of a pediatrician and orthopedist.
→ Necessary information → The baby has hip dysplasia
Abnormal structure and improper functioning of bones ( male Russian personal name of Latin origin; goes back to Latin constans (genitive case constantis) - “constant, persistent”
) pelvis - these are the first signs of hip dysplasia in infants.
This is the most common type of pathology of the musculoskeletal system in children ( in the main sense, a person during childhood
) in early childhood.
According to statistics, such a disease develops in 2.5% of newborns. In regions where poor environmental conditions are observed, the indicator can increase significantly. In addition, experts note that the disease more often affects girls than boys.
According to medical terminology, hip dysplasia is a pathology in which unformed parts of the joint are observed:
- ligaments;
- cartilage tissue;
- bones;
- muscle tissue;
- nerves.
Some experts call this a disease ( this is a condition of the body, expressed in disruption of its normal functioning, life expectancy and its ability to maintain its homeostasis
) – congenital dislocation of the leg. Doctors distinguish three stages of development of pathology in children:
- Stage 1 – osteochondral tissues are not formed, muscles and ligaments are usually developed. Differences between the head ( the name of a number of rounded individual objects or the ends of objects of a more complex shape
) of the leg bone are not observed; - Stage 2 – against the background of the abnormal structure of the osteochondral parts, a displacement of the head of the bone appears upward and outward.
- Stage 3 is the most severe type of pathology. There is no contact of the femoral head with the acetabulum.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the medical picture of the disease, specialists identify several forms of pathology in newborns:
- acetabular – an incorrect structure of the acetabulum is observed. The head of the leg ( a part of the body (limb) that is a load-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape
) presses on the cartilage and deforms it. Ossification of cartilage tissue and displacement of the head of the leg occurs; - epiphyseal – diagnosed when the mobility of the pelvic joints is impaired and pain occurs;
- rotational – incorrect placement of the pelvic bones is observed. The baby has a club foot.
Reasons for development
Incorrect formation of the hip joints in infants occurs against the background of disturbances in the intrauterine development of the embryo. Most often, development ( this is a type of movement and change in nature and society associated with the transition from one quality, state to another, from old to new
) this pathology begins at 4-5 weeks of pregnancy. Experts identify several reasons that have a negative impact on the development of the musculoskeletal system in the fetus:
- a genetic mutation caused by a disorder in the primary formation of pelvic joints;
- the effect of bad substances on the embryo (chemicals, poisons, toxins, certain groups of medicinal products, etc.);
- large fetal size;
- breech presentation, stimulating damage to the pelvic bones during delivery.
- intrauterine infections or renal deficiency in the fetus ( the final stage of development of a flower modified during the process of double fertilization; the generative organ of angiosperms, which serves to form, protect and distribute prisoners
). Against the background of such deviations, a violation of water-salt metabolism is observed.
Prevention
To prevent incorrect formation of the hip joint, the following simple measures must be observed:
- At the stage of bearing a child, a woman should eat well, with a sufficient amount of protein, Omega-3, polyunsaturated fatty acids, calcium and other microelements in her diet.
- Avoid tightly swaddling your baby. For children at risk, it is better to use wide swaddling.
- Comfortable position for the baby when feeding and in the arms of an adult. There is no need to press the baby's legs too tightly against you.
- Do therapeutic exercises and massage.
- Visit an orthopedist regularly.
A timely diagnosis and timely treatment lead to the correct formation of the joint, and in the future the person lives a full life.
Advice from Doctor Komarovsky
Children's doctor Komarovsky advises mothers and fathers not to panic if their baby shows signs of hip dysplasia. Characteristic symptoms may also be present in healthy children; a final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after additional ultrasound examination and x-rays. Moreover, according to Komarovsky, in most cases in babies the pathology goes away on its own and does not require medical intervention. However, if the orthopedic doctor nevertheless prescribed treatment, Evgeniy Olegovich does not advise parents to refuse it, because the lack of therapy will not always have a positive effect in the future; advanced cases of dysplasia can even lead to disability.
The famous children's doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky advises treating mild forms of pathology at home with the help of wide swaddling, gymnastics and massage.
For more complex forms of the disease, orthopedic devices, for example, Pavlik stirrups, will be effective.
Dr. Komarovsky does not consider the disease to be congenital, since in a newborn all the elements of the joint are in place, and the softening and stretching of the ligaments is most often caused not by a structural defect, but by the hormonal background of the mother. X-rays are not recommended before 4 months; ultrasound can provide the necessary results without significant harm to the baby’s health. The earlier the problem is detected, the more effective the treatment will be.
The doctor notes that a child diagnosed with hip dysplasia should not be put on his feet too early; it will be much more useful if he learns to crawl steadily. Any treatment will be effective up to the age of 1 year; after 5 years, the disease can only be eliminated by surgery.