The topic of proper contraception remains relevant for the fair half of humanity at almost any age, but today we will highlight only 1 category - women over 40 years old. After 40 years, a woman’s body undergoes serious changes, including hormonal ones. The process of natural decline in a woman’s reproductive function and ability to bear children begins. The ovaries produce fewer hormones, and the number of ovulations and menstruation is correspondingly reduced. But still, almost 80% of women retain the ability to bear and give birth to children.
Contraceptive pills for women over 40 years of age are an opportunity to avoid unwanted pregnancy, associated complications, health problems in the unborn child, as well as thoughts of abortion. It is for these reasons that this category of women is interested in the question: which birth control pills are best to choose in order to protect themselves from unwanted pregnancy?
There are many modern drugs that you can simply get confused about. This article will help you understand this issue. The article will also provide advice, classifications and types of contraception, and discuss the following questions: what contraceptives should be used after 40 years, which of them are the most effective and safe.
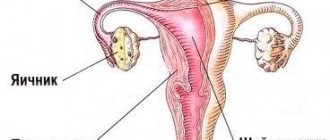
Women's health after 40 years
After 35 years, the natural death of immature eggs accelerates 2-3 times, so after 40 many cycles become anovulatory. Menopause occurs on average at 50-55 years of age, but in some cases menstruation may stop as early as 45 (see pills after 45 years). It is important to choose a contraceptive method that will not harm your hormonal levels.
By the age of 40, diseases that are associated with poor lifestyle, bad habits and gradual aging accumulate in the body. When visiting a doctor, most women find:
- uterine fibroids - according to statistics, taking into account the asymptomatic form, it occurs in 50-70% of women;
- endometriosis – occurs in every 10 women;
- endometrial hyperplasia - according to various sources, is observed in the majority of women with fibroids and endometriosis, the prevalence reaches 60%;
- mastopathy – in various forms occurs in 20-60%.
Metabolic disorders in older age lead to obesity, the development of hyperandrogenism, diabetes mellitus, and thyroid pathology is common. Therefore, many patients complain of irregular menstrual cycles, bleeding and other signs of impaired hormone production.
Sterilization
It is still a little-used way to prevent unwanted pregnancy in Russia. But, it is already gaining momentum, because it provides a 99.9% guarantee. Not everyone can undergo sterilization. You can’t just come and sign up for surgery. In our country, the procedure is allowed only to persons over 35 years of age and with at least 2 children. If such a measure is required for medical reasons, then the patient’s age and the presence of children are not decisive.
Pros:
- does not affect hormonal levels and the menstrual cycle;
- no side effects;
- reliable
Minuses:
- surgical intervention (two micro-incisions);
- there is a possibility of an ectopic pregnancy;
- the procedure is irreversible.
Difficulties in selecting contraceptives for people over 40 are associated not only with concomitant diseases and lifestyle, but also with some illiteracy of modern women in this regard. To prevent such problems from arising, you just need to regularly visit the gynecologist and do not hesitate to ask questions. And following the doctor’s recommendations and competently following his instructions will allow you to enjoy your personal life even after 50 years.
Types of birth control pills after 40 years
Choosing birth control pills after 40 years is more difficult due to the large number of contraindications. But it is impossible to completely abandon birth control methods; few people agree to bear and give birth to a child at this age. Hormonal agents have been developed that are suitable for late reproductive age, which reliably protect against pregnancy and help stabilize the course of diseases associated with increased concentrations of estrogen.
Hormonal agents
Contraceptives for a 40-year-old woman can be produced in various combinations of hormones:
- combined oral contraceptives based on estrogens and gestagens;
- pure gestagenic drugs.
The first group of contraceptives is more popular. Single-phase contraceptives can be used with good control of the menstrual cycle, but microdoses are more often accompanied by intermenstrual bleeding. Therefore, preference is given to low-dose ones with 30 mcg of estrogens.
Hormonal drugs with gestagens after 40 can be prescribed if the estrogen component is contraindicated. More often these are women with hypertension, diabetes and obesity.
Attention! Estrogens increase blood viscosity, so COCs are not recommended for those with a tendency to thrombosis, migraines, and a history of cerebrovascular accidents.
Non-hormonal with phytoestrogens
Some patients are afraid that hormones will make them gain weight or other undesirable effects of oral contraceptives will appear. Therefore, they ask the gynecologist to prescribe herbal remedies with phytoestrogens. These are preparations that contain black cohosh extract. It has been proven that the active substance can replenish the signs of estrogen deficiency and reduce the first manifestations of menopause symptoms, but they do not protect against pregnancy. This is due to the fact that the contraceptive effect is provided by progestins, and their analogues have not been found in plants.
Emergency contraception
After 40 years, you can use an emergency method of birth control, with caution and taking into account contraindications. Birth control medications include levonorgestrel or mifepristone. These substances prevent fertilization or implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine wall, but they are not capable of causing early abortion. There is also a risk of menstrual cycle disruption. Therefore, you need to resort to this method of protection against pregnancy as rarely as possible.
Principles of taking hormonal pills
A course of hormonal pills is prescribed by a doctor on an individual basis. As a rule, they are taken daily at the same time (one at a time, without chewing).
Hormonal contraceptives in adulthood are used not so much for protection, but for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes (for menopause, diseases).
At the same time, it is extremely important to monitor the body’s reaction. If the use of the drug causes side effects, it is better to choose another method of contraception. In addition, after 40, you need to do a hormone test at least once every 3-6 months - this will definitely make sure that everything is in order.
If, soon after the prescription of contraceptives, your health suddenly changes, pain, migraine or other suspicious symptoms appear, immediately contact your treating gynecologist.
Criteria for choosing contraceptives after 40 years
Contraceptives after 40 years are selected based on the patient’s medical history. Absolutely healthy women are prescribed a low-dose drug that contains ethinyl estradiol and any gestagen with low androgenic activity: norgestimate, levonorgestrel, desogestrel, gestodene. In other cases, the following indicators are taken into account:
- for endometriosis - contraceptives with antiandrogenic progestins;
- in case of weight gain, tendency to edema in the second phase of the cycle - contraceptives with drospirenone;
- for controlled diabetes mellitus - a dose of estrogen of 20 mcg, so as not to increase the risk of thrombosis;
- menstrual irregularities when using contraceptives in the past - three-phase contraceptives;
- for dysmenorrhea, dysfunctional bleeding - contraceptives with a pronounced gestagenic effect: Femoden, Janine.
Attention! If you do not follow the recommendations for making the right choice, the risk of side effects increases.
Are modern contraceptives harmful?
If the contraceptive is chosen incorrectly, it can harm the female body. For example, side effects will occur, weight will begin to gain, and hair growth will increase. This applies only to hormonal drugs, which are contraindicated for diseases of the cardiovascular system and diabetes. Even with problems in the liver and kidneys, such drugs are contraindicated. Women who smoke need to choose other contraceptives, since hormonal drugs put a powerful strain on the heart. There is also an increased risk of thrombosis.
According to medical indicators, if you regularly take hormonal drugs for a long time, sexual activity gradually decreases. This is explained by a decrease in testosterone production.
Features of the selection of contraceptive drugs after 40
After 40 years, oral contraceptives are selected taking into account the woman’s age and the likelihood of early menopause. Sometimes menstruation stops as early as age 45, which corresponds to early menopause. If this happens at 40, this is premature menopause.
Premenopausal
You can protect yourself after 40 years with the help of estrogen-progestin drugs, but the dosage is selected carefully. The condition of the mammary gland is taken into account and an ultrasound is performed. If, based on the results, there is a suspicion of a neoplasm, hormones should not be used. They increase the risk of breast cancer progression.
In case of menstrual irregularities, frequent dysfunctional bleeding, it is necessary to establish their cause. After 40, the incidence of cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancer increases sharply . These diseases may be accompanied by acyclic bleeding, but contraceptives are contraindicated.
It is also necessary to take into account the severity of the symptoms of approaching menopause, which is why birth control pills are often used in premenopause as a component of hormone replacement therapy.
During menopause
Menopause is the period in a woman's life after her last menstruation; it is called menopause and is determined retrospectively. If there are no periods during the year, it is considered that menopause has occurred. The function of the ovaries is completely suppressed, they practically do not produce estrogens, and eggs do not mature in them. Therefore, there is no need for contraception.
During this period, hormonal drugs are used for replacement therapy to alleviate the signs of estrogen deficiency. But synthetic ethinyl estradiol is prohibited; natural estrogen is needed. The use of non-hormonal herbal remedies is allowed.
For smokers
After 35 years of age, the risk of developing thrombotic complications increases when using contraceptives. Women who smoke have a significantly higher risk of thrombosis. Therefore, after 40 years of age, methods of contraception without the use of hormones are recommended. These can be disposable condoms, spermicides, but pure gestagens are allowed.
The benefits of oral contraceptives for women over 40
In addition to preventing pregnancy, oral contraceptives also have a positive effect on the female body:
- significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer and ovarian disease;
- normalize the menstrual cycle and reduce the negative symptoms of premenstrual syndrome;
- facilitate a smooth transition to the menopause stage, smoothing out all vegetative manifestations of menopause.
Contraceptive drugs are especially necessary during menopause, when menstruation may not be regular, and it is difficult to track when the next ovulation may begin, which greatly increases the likelihood of an unwanted pregnancy.
Rating of the best birth control pills after 40 years
In the review of contraceptives allowed at age 40, the leading positions are occupied by drugs that help cope with heavy menstruation, regulate the cycle and prepare the body for menopause. But women should be regularly monitored by a doctor, be examined by a gynecologist at least once a year, and have a smear for oncocytology.
No. 1 Klaira
According to many researchers, after 40 years, these are the best birth control pills for mature women. This is the first modern contraceptive drug that contains natural estrogen. Therefore, they provide protection against pregnancy, control the menstrual cycle well, and help prepare the body for the transition to hormone replacement therapy. The price of packaging for 1 and 3 months is 1015-2850 rubles.
No. 2 Janine
The contraceptive drug contains ethinyl estradiol and gestaden. This component has a pronounced progestogenic effect, so the tablets are recommended for women with dysfunctional bleeding, frequent cycle disruptions, and oligomenorrhea. Janine is available in 21 tablets per package, so when using, a break of 7 days is required. Package cost from 940 rub.
No. 3 Mercilon
The tablets are a combination of ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel, which has a weak gestagenic effect. It does not increase the sensitivity of hair follicles to androgens and does not lead to an increase in the concentration of male hormones. Therefore, contraception is recommended for women who develop signs of hirsutism. The cost of a pack for 21 days is from 1300 rubles.
No. 4 Lactinet
These are contraceptives for women over 40 years of age with new generation obesity; they do not increase the risks of vascular complications or thrombosis. Therefore, they can be used in cases where estrogens are prohibited. Contains desogestrel in the minimum dose required to protect against pregnancy. The cost of tablets is 500-750 rubles.
No. 5 Regulon
Contraceptive pills contain synthetic estrogen and desogestrel. It does not have andogenic properties, so it can be used after 40 years for contraception and maintenance treatment for endometrial hyperplasia. Available in 21 tablets in a blister, the cost of one is from 370 rubles.
No. 6 Silest
Birth control pills contain norgestimate, which has a pronounced gestagenic effect. It is necessary in women with dysfunctional bleeding and oligomenorrhea. But it is not recommended if you are prone to hirsutism and acne . But the drug is not popular among doctors and patients, so it is difficult to buy.
No. 7 Tri-regol
A three-phase contraceptive based on ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel. Indicated for women with poor cycle control and signs of estrogen deficiency. Birth control also helps to cope with other signs of estrogen deficiency - decreased libido, vaginal dryness. The cost of packaging is on average 300 rubles.
No. 8 Triquilar
An estrogen-gestagen three-phase contraceptive drug is also recommended for symptoms of female hormone deficiency in women over 40. There are 21 tablets in the package, after finishing it a break of 7 days is required, during which menstrual-like bleeding is observed. The price of a package is on average 600 rubles.
No. 9 Exluton
The tablets are a monocomponent hormonal contraceptive based on linestrenol. This is a gestagen that is recommended for use by women with menstrual irregularities, but without signs of hyperandrogenism, as well as with contraindications to estrogens. The cost of tablets is from 3400 rubles.
No. 10 Yarina
A modern contraceptive drug that contains drospirenone, a progestogen that allows you to control the menstrual cycle, as well as get rid of swelling and weight gain in the second phase. It is recommended for women with signs of hirsutism associated with hyperandrogenism. Packaging costs from 1000 rubles. per month up to 3400 for 3 cycles.
No. 11 Belara
A combination of ethinyl estradiol and chlormadinone, which has an antiandrogenic effect. Birth control pills are recommended for symptoms of excess male hormones and polycystic ovary syndrome. This is a good alternative if the drug with drospirenone or dienogest is not suitable. Price from 600 rub.
CONTRACEPTION IN WOMEN OF TRANSITIONAL AGE
In women of this age, progestogen contraception (mini-pill, injection, norplant) is promising. Surgical contraception could be the method of choice for women of adolescence who have decided on the number of children in the family. Barrier methods of contraception, due to decreased fertility during adolescence, can be successfully used by married couples who consider such methods acceptable.
The menopause in today`s women occurs at the age of 45 – 55 years. There is evidence that ovarian follicles and ova remain during 3 – 5 years, which is attributable to some cases of pregnancy after cessation of menstrual bleeding.
According to the WHO recommendations, women should use contraception right up till the menopause and in the absence of menstrual bleeding for 1 year. For women of this age, gestagenic contraception (minipills, injections, norplant) is promising. Surgical contraception could be the method of choice for women in the transitional period who would solve how many children they could have.
Due to reduced fertility in the transitional period, barrier contraception can be successfully used by a married couple who considers it to be acceptable.
V.N.
Prilepskaya - prof., doctor of medical sciences, head of the outpatient department, N.M. Nazarova - scientific. co-author, Ph.D. Scientific Center for Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology (Director - Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences Prof. V.I. Kulakov), Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow Prof.
VN Prilepskaya, Dr. Sci., Head of Outpatient Department, N.M. Nazarova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Researcher, Research Center of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, (Director Prof.VIKulakov, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences), Russian Academy of Medical Sciences R
The reproductive health of middle-aged and older women receives great attention in many countries around the world. To a certain extent, this is due to the fact that it is this contingent of women that makes up a significant proportion of the economically, culturally, and socially active population. There is no doubt that the reproductive health of women in these age groups is influenced by many factors, such as living conditions, work, reproductive history, exposure to infectious, chemical and other influences, access to qualified medical care, etc. Certain conditions associated with age, menopause and other problems The aging of the body also affects their health. The main difficulties in deciding on contraceptive methods for women of adolescence are associated with a number of features that characterize this period of a woman’s life [1, 2]. The age-related decline in fertility is a generally accepted fact, but the question of when this decline began is still controversial. Literature data indicate the absence (with a regular menstrual cycle) of significant differences in the levels of FSH, LH, estriol and progesterone between women with normal body weight after the age of 45 years and 18 – 30 years [3]. Thus, in late reproductive age, the frequency of ovulatory cycles with a regular rhythm of menstruation is 95% and even with physiological oligomenorrhea - 34% [4]. Thus, there is no doubt that the so-called fertility potential during perimenopause can be preserved. Therefore, the problem of reliable and safe contraception during this period of a woman’s life remains relevant (WHO, 1994). Due to the fact that most women by the age of 40 have already decided on family planning and the number of children in the family, an unplanned pregnancy very often ends in an induced abortion. Abortion ends in almost half of all pregnancies that occur in women over the age of 40 - 45 years, and very often it is complicated by inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, the development of uterine fibroids, endometriosis, severe menopause and, what is most dangerous, in the future it is a background for the development oncological pathology in target organs: the uterus and mammary glands [5 – 7]. Despite the fact that during this period of a woman’s life there is an age-related decline in fertility, cases of children being born over the age of 45 and even after 50 are not so rare. Many women, even at 50 years of age or older, continue to have regular menstruation with a certain number of ovulatory cycles. Thus, according to statistics from Western European countries, 50% of women aged 44 years and 30% aged 45–54 years are sexually active, have a preserved menstrual cycle and are capable of conception, and therefore require contraception until menopause (WHO, 1994 ). Thus, there is no doubt that the main purpose of contraception in this group of women is to prevent abortion and its harmful consequences. Currently, the number of women who, due to certain life circumstances and reasons, are planning the birth of a subsequent, and often first, child after 40–45 years is increasing. Pregnancy in such cases is accompanied by a high risk of miscarriage, a high frequency of gestosis, abnormal location of the placenta, an extremely large number of complications during childbirth and the postpartum period, and high childhood morbidity and mortality. This risk is 20 times or more higher than that of women in the early reproductive period. It has been proven that the health of women after 40-45 years is significantly impaired. Pregnancy and childbirth occur against the background of extragenital pathology, which is registered in 60% of cases, and in 2/3 of patients it is chronic. Most often these are cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the urinary system, liver, digestive organs, etc. As for gynecological morbidity, it is quite high and ranges from 44 to 65% [8]. Among gynecological diseases, chronic inflammatory processes of the genital organs, uterine fibroids, menstrual irregularities, prolapse of the uterus and vagina, etc. predominate. In addition, 10% of women of this age have previously undergone genital surgery.
| According to the literature, menopause in a modern woman, as a rule, occurs between the ages of 45 and 55 years (average age 50 – 52 years). Menopause is preceded by a period of premenopause, characterized by a decrease in ovarian function. The average duration of premenopause is 4 years. The onset of menopause does not mean the complete cessation of ovarian function. It has been proven that follicles with eggs remain in them for another 3 to 5 years, which explains the cases of pregnancy after the cessation of menstruation. In view of this, according to WHO recommendations (1994), contraception is recommended for women until menopause and absence of menstruation for 1 year [9]. |
What methods of contraception can a woman use during this period? Intrauterine contraception (IUC)
occupies one of the leading places in terms of prevalence among the effective and acceptable methods of contraception used.
Intrauterine contraceptives are highly effective, do not have a systemic effect on the body, are accessible, cost-effective, can be used for a long time, and restoration of fertility after removal of the intrauterine device (IUD) occurs very quickly. As for women 45 years of age and older, an IUD is often contraindicated for them due to pathological changes in the cervix and/or uterine body, the presence of endometrial hyperplastic processes, large uterine fibroids, etc. However, it can also be used with taking into account generally accepted absolute contraindications (WHO, 1995) [10], which include: malignant lesions of the reproductive system, conditions after abortion or childbirth complicated by sepsis, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs suffered 3 months before the insertion of the IUD, abnormalities of the uterus, tuberculosis genitals. Preference should be given to hormone-producing IUDs such as Levonova (Finland), which help reduce the volume of menstrual blood and prevent inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. Naval devices such as SiT-380 (Germany), Multiloud-375 (Netherlands) can also be successfully used, i.e. copper-containing IUDs in which the copper surface area exceeds 300 mm. Hormonal contraception
is characterized by high efficiency and pronounced therapeutic properties for a number of gynecological diseases: endometriosis, uterine fibroids, hyperplastic processes of the endometrium and mammary glands.
Patients using hormonal contraceptives are less susceptible to the development of osteoporosis in postmenopause and the incidence of ovarian and uterine cancer. According to WHO recommendations (1995) [10], hormonal contraceptives are absolutely contraindicated in pregnant women, heavy smokers, women with existing or former thromboembolic complications, diseases of the cardiovascular system, severe diabetes mellitus, severe liver diseases, malignant neoplasms of the reproductive organs. systems. It is known that hormonal contraception with estrogen-gestagen drugs is potentially associated with an increased risk of developing vascular and thromboembolic complications in women of adolescence, even when it comes to low-dose drugs of the latest generation. Thus, in women 45 years of age and older, progestogen contraception
(mini-pill, injection, norplant) is very promising.
These drugs do not contain an estrogen component and thus do not cause pronounced changes in blood coagulation factors, lipid metabolism, and do not have a negative effect on liver function [11, 12]. Of the injectable progestin
drugs, the most famous is Depo-provera-150 (DMPA), which has advantages not related to its contraceptive effect - it reduces the risk of inflammatory diseases of the genitals, cases of vulvovaginal candidiasis, does not have a negative effect on liver function, gastrointestinal tract, thereby reducing the likelihood of metabolic changes.
It has been established that Depo-Provera does not cause pronounced changes in blood coagulation factors and lipid metabolism, which determines its advantages over oral contraceptives in terms of the risk of cardiovascular disorders specifically in women after 40 years of age. Research by V.N. Prilepskaya and T.T. Tagieva [7] showed that, taking into account the high contraceptive effectiveness and the peculiarities of the influence of DMPA on hormonal-dependent organs, its use in women of late reproductive age and older age is justified especially in the presence of endometrial hyperplastic processes , uterine fibroids, endometriosis. Most women with endometrial hyperplastic processes experience partial or complete regression. Norplant, a subcutaneous implant
, is also an effective long-acting contraceptive.
Six small soft silastic capsules containing levonorgestrel are implanted under the skin of the upper arm through a small incision under local anesthesia. The contraceptive effect is ensured by the slow continuous release of levonorgestrel into the bloodstream and appears within a day after administration of the drug, persisting for 5 years. When using long-acting gestagens, delayed restoration of fertility is observed - ovarian function may not be restored for a long time (up to two years or more), and in a number of patients over the age of 45, fertility may not be restored and menopause occurs. Currently, surgical contraception
is the most widely used method.
There are female and male sterilization. Female sterilization is a surgical operation in which the patency of the fallopian tubes is disrupted, as a result of which fertilization becomes impossible. There is no doubt that surgical sterilization could be the method of choice for women 45 years of age and older who have decided on the number of children in the family. It is especially indicated for women with various extragenital and gynecological diseases, for whom pregnancy is contraindicated due to their health status. It should be emphasized that for women at increased risk of unwanted pregnancy, there are no absolute contraindications to sterilization (WHO, 1994). Written consent must be obtained from all patients seeking voluntary surgical sterilization to document the existence of an informed and voluntary choice and to give the operation legal legitimacy. Male sterilization
(vasectomy) is a highly effective method that stops a man’s fertile ability without changing hormonal, sexual functions, potency, and does not affect the process of seminal formation, i.e.
male sexual functions remain unchanged. However, in our country, due to the traditional attitude towards surgical intervention as a very complex procedure, surgical contraception has not yet found proper application. In addition, many clinics do not have the appropriate equipment to perform gentle surgery by laparoscopy. Barrier methods
of contraception have low contraceptive effectiveness, but they certainly have advantages in preventing sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
However, due to the decrease in fertility during adolescence, they can be successfully used in married couples who consider such means suitable, especially in the presence of extragenital pathology and gynecological diseases that do not allow the use of other methods of contraception. Barrier methods are divided into mechanical (preventing the progress of sperm - condom, caps) and chemical (affecting sperm, destroying their membrane and reducing their mobility - nonoxynol, benzalkonium chloride). Barrier methods of contraception require proper use and high motivation, which women of this age usually have, protect against STDs, and some chemical spermicides, such as nonoxynol creams, help eliminate vaginal dryness, which is observed in a number of women in menopause. However, the use of Pharmatex may cause a burning sensation in the vagina in some women. A popular method of barrier contraception is condom. Its use is indicated in all age groups, including older married couples. In terms of effectiveness, condom is inferior to modern methods of contraception and its use is directly related to sexual intercourse, which is not always acceptable for a married couple. However, for some couples it is the most acceptable, especially during sexual activity in a long-term marriage. Emergency or postcoital contraception
occupies a very important place in the problem of pregnancy protection, but in women aged 45 years and older, its use is highly undesirable due to the use of large doses of hormones, which can have adverse effects on the body.
It is advisable to recommend emergency contraception as an emergency measure to prevent pregnancy to women who have been raped, or if there are doubts about the integrity of the used condom, under strict medical supervision [13]. The most common means of emergency contraception are combined estrogen-progestin drugs. Prescribe 200 mcg of ethinyl estradiol and 1 mg of levonorgestrel according to the following scheme: within 72 hours after the act, the woman takes the first half of the dose, and 12 hours later - the second. It should be emphasized once again that postcoital contraception is a one-time contraception and its use in women of any age should be carried out according to strict indications and only under the supervision of a doctor. Natural methods of contraception are also very popular among women 45 years of age and older. In first place among them is the method of interrupted coitus
, and this is understandable, since it does not require the use of other contraceptives or planning sexual intercourse.
However, its effectiveness is low, and for some men it is completely unacceptable. For married couples who can tolerate limited sexual activity or who are rarely sexually active, periodic abstinence
, but this method is not suitable for women with irregular menstrual cycles, i.e. oligomenorrhea, which is observed in a number of premenopausal women. During periodic abstinence, several methods are used to determine the so-called fertile phase of the cycle: measuring basal temperature, studying cervical mucus, calendar method, symptom-thermal method. The advantage of periodic abstinence is its safety and lack of side effects. However, the effectiveness of the method depends on strict adherence to the rules of its use. It should be emphasized that intermittent abstinence should be offered as an alternative method to those couples who do not want to use other, more effective methods of contraception for any reason (fear of side effects, religious or religious restrictions). It should be emphasized that the reproductive health of women of transitional age depends, in particular, on the successful use of contraception. When selecting a contraceptive method, it is necessary to take into account the condition and characteristics of the body during this period of life, and the acceptability of a particular method for a married couple. Medical consultation should involve an individual approach to each patient, a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of a particular method. Only such a differentiated approach can provide reliable, convenient and even comfortable protection against unplanned pregnancy and its consequences.
Literature:
1. Oldenhave A, et al. Amer J of Gynecol 1993;168:772–80. 2. World Health Organization. Research of a WHO Scientific Group. Series 866. Geneva 1996. 3. Sherman B J Clin Invest 1985;55:699–706. 4. Schwallie PS. J Reprod Med 1986;(13):113–7. 5. Kulakov V.I., Serov V.N., Vaganov N.N., Prilepskaya V.N. Family Planning Guide. – 1997. – P. 297. 6. Manuilova I.A. Modern contraceptives. – M., 1993. – P. 15–45. 7. Prilepskaya V.N., Tagieva T.T. // Family planning. – 1995. – No. 2. – pp. 37–40. 8. Frolova O.G. // Obstetrics. and gin. – 1997. – No. 3. – P. 45. 9. Outlook 1997;1(4):3–6. 10. Improving the quality of family planning services. Medical criteria for initiation and continuation of contraceptive use. (Based on materials from a WHO meeting). – 1995. – P. 30. 11. Prilepskaya V.N. // Clinical pharmacology and therapy. – 1994. – No. 3. – P. 70–4. 12. Prilepskaya V.N. // Obstetrician. and gin. – 1997. – No. 3. – P. 50–2. 13. Prilepskaya V.N., Rogovskaya S.I., Mezhevitinova E.A. // Vestn. obstetrics gynecol. – 1996. – No. 2. – P. 13–5.
Rules for taking contraceptives after 40 years
Women of older reproductive age must adhere to the general principles of contraceptive use. But for them, a continuous regimen is allowed, when the tablets are taken for 3 months in a row, only after that they take a break for 7 days. Then the course is resumed. This scheme helps to reduce the manifestations of hyperplastic processes and reduce the thickness of the endometrium.
How long you can use birth control pills depends on your overall health. If after 40 years there are signs of imminent menopause, you need to take hormones for no more than 5 years. In other cases, you need to switch to hormone replacement therapy after age 50.
Contraindications and side effects to drugs
When the body begins to age, the number of diseases that lead to the appearance of pathologies of the blood vessels and endocrine system increases. Therefore, you need to be careful about contraindications for using contraceptives:
- arterial hypertension;
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- migraine;
- suffered a stroke, heart attack and other circulatory disorders;
- history of thrombophlebitis;
- bleeding disorders;
- oncological diseases;
- bleeding of unknown origin.
While using contraceptives, undesirable effects may occur that will require replacing the drug or discontinuing it:
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- vaginal dryness;
- decreased libido;
- mood swings;
- weight gain and swelling;
- scanty or heavy menstruation;
- pain in the calf muscles.
A sharp headache, difficulty breathing, stabbing pain in the heart are a sign of severe pathology. This requires emergency medical attention.