Many women dream of conceiving a child and experiencing the joy of motherhood. This requires that ovulation occurs every menstrual cycle. Not every follicle, out of the volume deposited at birth, will participate in this process. Most of them will die. Others become participants in the chain of birth of a new life.
Very often, women are faced with a situation where the desired ovulation does not occur. Everything seemed to be in order. Follicles begin to mature during. A dominant sac grows, in which a mature egg waits in the wings.
And now she is ready to hit the road, towards the sperm, but the capsule does not rupture. Why does such a pathology occur?
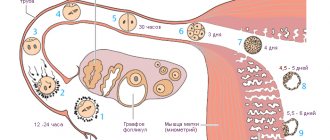
A follicle is a sac inside a woman's ovary. At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the process of maturation of several follicles (up to 25 pieces) begins. At the initial stage, their sizes range from 2-4 mm. And only one, having gone through all stages of maturation, becomes dominant. It grows to 22-25 mm. This is facilitated by follicle-stimulating hormone. Now he is ready to ovulate.
Now the following condition must be met: the bubble must burst and release the mature oocyte. To achieve this, estrogen synthesis increases in the female body. As a result, a rapid increase in luteinizing hormone (LH) begins. Under the influence of LH, the follicle membrane softens and becomes thinner.
At a certain point, it bursts and releases the egg, which goes to the fallopian tube. If within two days she meets a sperm, conception can occur, subject to the fusion of male and female reproductive cells.
Ovulation occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. This process consists of two phases:
- Follicular (the dominant follicle is maturing).
- Luteal (the period from ovulation to the onset of menstruation).
A yellow body forms at the site where the bubble burst. It will synthesize progesterone for some time. After fertilization of the egg, this hormone, when pregnancy occurs, allows the woman’s body to rebuild.
If conception does not occur, progesterone will still be produced, since the corpus luteum will cease to exist only after 12 days.
Then the hormone level begins to fall and a new menstrual cycle begins.
The rupture of the follicle and the release of a mature oocyte is a natural process programmed by nature. This requires a balanced synthesis of various hormones. If there is pathology (the sac does not rupture), conception is impossible. Without finding out the causes of this condition and without timely treatment, this can lead to infertility.
In order to speed up the ovulation process and help the follicle burst, it is necessary to use hormonal therapy. The main condition is that all appointments are made by a specialist.
Causes
The main reasons for this pathology include the presence of a very thick and durable membrane of the vesicle, and hormonal imbalance.
Lack of ovulation can be caused by:
- Violation of the balance of progesterone (especially its deficiency) and androgen.
- Inflammation of the uterine appendages.
- The presence of a cyst in the area of an unruptured vesicle.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the internal (non-genital) organs of a woman. Existing problems of the endocrine system.
- Lack of vitamins, macro- and microelements. They also affect hormone synthesis and help the follicle rupture.
- Great physical activity.
- Stress, depression.
- Uncontrolled diets.
- Irregular sex life.
- Long-term hormonal therapy.
- Uncontrolled intake of hormones, etc.
Normally, after the follicle bursts, the egg travels to the fallopian tube. This does not happen in pathology. The large bubble remains intact. The egg in it overripe and dies, and the follicle itself degenerates into a cyst. Basically, over time, it resolves on its own (if the size of the bubble is < 4 cm). If this does not happen and the follicular cyst bursts, the woman will urgently need surgery.
Relationship between follicle and ovaries
The ovaries are one of the main organs on which the reproductive state of a woman’s body depends. Scientists have found that at the moment when the woman herself was in the intrauterine state, she formed about a million eggs. The older a woman gets, the fewer eggs she contains. Closer to fifty years, the eggs disappear, and menopause occurs. These organs are paired and are connected through the appendages to the uterus. One ovary is slightly higher than the other, and the right organ is slightly heavier than the left. If one of the ovaries is chronically ill, or if it is removed, a woman still has a chance to become a mother; the main condition is the functionality of the remaining organ.
It is in the ovary that the egg is located, which, when mature, breaks out of the follicle and moves towards the sperm. If conception does not occur, the ovaries perform their function again, and this is repeated every menstrual cycle, until the onset of menopause.
The ovaries perform three main functions:
- Vegetative. (Appearance of primary and secondary sexual characteristics);
- Generative. (Egg formation);
- Hormonal. (Production of the following types of hormones: androgens, estrogens and progesterones).
During ovulation, the ovaries increase in size, this is clearly visible on ultrasound images. A woman can, based on her own feelings, find out exactly when she will ovulate:
- Within a few days, mucous discharge of a transparent color appears;
- Slight pain may appear in the lower abdomen;
- On the day when the ovarian follicle ruptures, the basal temperature drops and then rises again;
- When taking a test for the LH hormone, the doctor will notice its elevated level.
Sometimes two follicles mature at the same time. In this case, the woman will have a twin pregnancy if fertilization is successful.
One of the common causes of infertility is immaturity of the follicle. This may happen in the following cases:
- When ovarian dysfunction occurs. In such a situation, the hormonal function of the ovaries is disrupted, and ovulation does not occur. The longer the disease is left untreated, the more the performance of the ovaries decreases.
The main symptoms of dysfunction may be disruptions in the menstrual cycle, lack of ovulation, menstruation is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, the occurrence of amenorrhea, and miscarriage.
The cause of ovarian dysfunction may be: obesity, inflammatory process in the lower genital organs, chronic diseases of the uterus, appendages, cervix, thyroid disease.
To diagnose the disease, you will need to donate blood for hormones, bacterial culture from the vagina, do a biopsy and examine the pelvic organs using an ultrasound machine.
In order to cure ovarian dysfunction, it is first necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease, then adjust the woman’s monthly cycle and hormonal levels.
- In case of malfunction of the endocrine system. At the first complaints about the state of health, the gynecologist should refer the patient to donate blood to determine the level of thyroid hormones. If the test results deviate from the norm, the gynecologist will carry out further treatment together with the endocrinologist.
- During inflammatory processes in the genital organs. The results of blood and urine tests will show whether there is pelvic inflammation. Symptoms may include pain during sexual intercourse, irregular periods, and nagging pain during the menstrual cycle.
- Follicles may not mature in women whose bodies are approaching menopause.
- When benign and malignant tumors occur.
- Long-term depression and frequent nervous disorders can also cause the follicle not to mature.
The appearance of these reasons can become a big problem for a woman’s reproductive function. If there are failures in its development, the follicle may freeze at a certain stage of its development, fail to reach the desired size, fail to rupture, and as a result, the egg will not be able to come out.
Doctors also consider premature or earlier maturation of the vesicle to be a deviation from the norm.
Follicle development occurs in two ways:
- Isolation of one dominant vesicle from the total mass. The monthly cycle is normal, is not accompanied by pain symptoms, and there are no problems with conception;
- Absence of a dominant vesicle. In this case, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, the egg does not mature, and ovulation does not occur. The body begins to produce increased levels of male hormones, and the woman has problems conceiving.
Treatment
If the follicle is not able to burst due to a hormonal disorder and its size is not very large, the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs (progesterone). But when a follicular cyst is detected on ultrasound, various physiotherapy procedures are used aimed at resolving the resulting cyst, improving blood circulation.
A woman also needs:
- Eat right (food should be balanced).
- Visit a psychologist (to normalize your psycho-emotional state).
After undergoing therapy and improving the condition, the likelihood of conception increases.
How much is in the ovary?
Each woman’s follicular reserve is individual, but in medicine there is a concept of an “acceptable norm.”
There should be no more than 30 in both ovaries, otherwise doctors suspect pathology. In more detail, in clinical practice the norm is considered to be the presence of no more than 12-15 capsules in one ovary.
In the first days of the menstrual cycle, there are about 10-12 antral ones on each pair of organs, and by 7-10 days a “graafian vesicle” is already formed, which is ahead of its predecessors in development.
Everyone else regresses and dies. If a woman of reproductive age has an excess or deficiency of cells, then the gynecologist quite reasonably suspects the following pathologies:
- Infertility.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Multifollicular ovaries.
- Low fertility.
- The onset of early menopause.
IMPORTANT! A woman must have at least 5 in one ovary. Otherwise, we can already talk about infertility and serious pathological processes.
Is it possible to get pregnant after ovulation?
The process of ovulation exists to prepare the uterus and ovaries for pregnancy.
The beginning of the luteal phase occurs from the moment of rupture and release of a mature egg, which is ready for fertilization. In this case, after the ovulatory period (7-8 days) is the best time to conceive a child. After the rupture, the corpus luteum appears, which thickens the endometrium.
This promotes gestation of the fertilized egg. During the follicular phase of the cycle, the egg is just maturing inside the follicle, so getting pregnant during this period is extremely problematic. An important condition for conception is the release of the egg from the capsule.
The corpus luteum usually develops approximately 7-8 days after ovulation, and then sharply regresses and disappears. It turns out that in the premenstrual cycle the chances of conceiving a child are also small. In order to make a correct calculation of conception, you need to buy an ovulation test. It will show the concentration of lutein in the urine. This hormone inevitably rises before the rupture of the Graafian vesicle.
REFERENCE! Sperm live in the uterus for 3-5 days, so there is always a chance that they will linger until ovulation occurs and fertilization occurs. This is possible with an unstable menstrual cycle and ovulatory period.
In conclusion, it must be said that the maturation of follicles naturally stops after ovulation. The capsules no longer increase in diameter and remain 5-6 mm in size. Many of them die after the “Graafian bubble” ruptures. This period is considered the most successful for fertilization, but everything depends on the woman’s reproductive health. If there are serious pathologies, then the process of folliculogenesis occurs with disturbances. Conception in this case is unlikely.
Diagnostics
No one knows whether the follicle will burst or not. This amazing vial with a precious female reproductive cell can present many surprises. Neither ovulation tests nor basal temperature will tell you whether a rupture has occurred . This question can only be answered based on the results of folliculometry - ultrasound of the ovaries.
You can clearly see how ovulation occurs in the video below.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Ovarian rupture is a violation of the integrity of the organ, which is accompanied by the release of blood into the abdominal cavity and severe pain. It usually occurs during ovulation or at the stage of formation of the corpus luteum. The disease is not very common, it occurs at a relatively young age, in women under 35 years of age, and occurs extremely rarely at older ages.
Next, we will consider what ovarian rupture is, causes, consequences, symptoms, as well as features of the recovery period.
Diagnostics
If acute pain occurs in the ovarian area, you should not hesitate. It is necessary to contact a medical facility or call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of the disease begins with an analysis of symptoms and palpation. Patients complain of severe pain in the lower abdomen, dizziness, and nausea. With internal bleeding, the pressure usually drops, the pulse quickens, which is why the skin becomes pale.
To make an accurate diagnosis, blood is taken for analysis. When bleeding occurs, the hemoglobin level decreases and the leukocyte (white blood cell) level increases.
Next, a hardware examination is performed - ultrasound. An ultrasound sensor detects the presence of fluid (blood) in the abdominal cavity. In some cases, with mild symptoms, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed - examination of the abdominal cavity from the inside through a puncture in the abdomen.
What happens during luteinization of the follicle?
The process of luteinization involves the formation of the corpus luteum. , in turn, is a temporary gland in the female body. It is formed after and is responsible for the synthesis of progesterone.
The release of an egg from a mature follicle and the formation of a corpus luteum in it (normal).
At the stage of follicle maturation, a malfunction occurs as a result of which it does not burst and the egg, accordingly, does not come out. Nevertheless, all accompanying processes continue to run their course. A corpus luteum forms inside the unruptured follicle, and the hormone progesterone is released into the blood. At this moment, you can observe all the signs of ovulation, but in fact it did not happen.
Important!
Unovulated follicle luteinization syndrome refers to the premature formation of the corpus luteum (luteinization), which occurs without ovulation. This disorder is accompanied by a change in the production of progesterone, as well as untimely transformation of the secretion by the endometrium.
Features of follicle development
Follicles are produced by the ovaries. They include the egg, protective epithelium, and connective tissue. Follicles mature continuously, starting from the prenatal period of a girl’s development and continuing until the end of a woman’s reproductive age.
The birth of a new life depends on the quantity and quality of follicular elements, the place where the egg matures before ovulation. In the follicle, the egg, surrounded by epithelium, is protected by a layer of connective tissue. This protection makes it possible to become pregnant and then bear a child.
Follicles perform another important function - they produce the hormone estrogen.
There are stages of development of follicular elements:
- Primordial . Follicular elements are formed in the body of an intrauterine girl. In this case, the overwhelming number of formed cells die. Size – up to 50 microns.
- Preantral . Cells are formed during maturation. There is an increase in the size of the nucleus. Reach 150-200 microns.
- Antral . There is a sharp increase in growing cells, and estrogens are released. The cell perimeter is 500 µm.
- Preovulatory . The follicle reaches 20 mm. It is where the egg cell is located.
Additional examinations
Anovulatory cycles, when the dominant does not develop, occur several times a year in every healthy woman. This phenomenon is not pathological. During these periods, the ovaries “rest”.
In addition, after 30 years there is a slow but steady increase in anovulatory cycles. Early menopause, which occurs before the age of 45, also guarantees frequent anovulatory cycles. Despite the fact that women at this age rarely plan pregnancy, gynecologists believe that these deviations cannot be ignored and prescribe appropriate hormonal therapy.
If such disorders are recorded in young women of childbearing age every month, this indicates pathological changes that require mandatory treatment.
Why the follicle does not grow or is not able to “release” a mature egg at the time of ovulation, only the attending physician can answer after a series of studies:
- Examination on a gynecological chair;
- Blood tests to detect levels of important hormones at different stages of the menstrual cycle;
- Folliculometry is an ultrasound diagnostic procedure during which the entire process of ovarian function during the menstrual cycle is monitored monthly.
The gynecologist also pays attention to the length of the menstrual cycle. A cycle that is too long or short is often evidence of ovulation disorders.
Most often, the absence of a dominant is associated with hormonal imbalance. The process of proper development of follicles is influenced by several hormones: luteotropic, follicle-stimulating, estrogen and progesterone. Each of these hormones is important at a certain stage of egg maturation. Their insufficient quantity or incorrect distribution leads to problems with the maturation of the dominant.
Objective signs
The changes in a woman’s body listed above can speak not only about the onset of ovulation: pain can be associated with some disease, and an increase in libido can be associated with a corresponding mood. There are more reliable ways to determine the time of egg maturation.
One of the most pronounced and main signs of ovulation is a change in basal temperature. In the first half of the cycle, the basal temperature is about 36 and a half degrees, but a day before the maturation of the egg it decreases, then rises to 37 degrees and remains at this level until the onset of menstruation.
During ovulation, the cervix becomes softer, wetter, and rises higher. But not all women can independently examine the condition of the cervix; this sign is usually observed by gynecologists during examination.
But the most reliable way to determine ovulation is to use test strips that react to elevated levels of luteinizing hormone. Such tests are sold in pharmacies.
Conception occurs due to ovulation. It is provided by one leading follicle, in the depths of which the egg matures. If there is no dominant follicle for several cycles, this indicates infertility.
How the “dominant” develops, why in some cases it does not exist, read our article.
A certain number of eggs are laid in the ovaries of each girl during the period of intrauterine development. Before puberty, they are in a “dormant” state, and with the onset of the menstrual cycle they begin to function.
The growth and death of the follicles in which the egg develops occurs monthly. In this case, follicular development goes through several stages.
At the beginning of the cycle, the growth of several follicles begins, which are of the same size. However, around the 9th day of the cycle, a leader begins to clearly stand out among them: a follicle that is significantly larger than the others in size (it is also called the Graafian vesicle). Its diameter can reach 15 mm. From the moment the dominant is isolated, the remaining follicles begin to regress, that is, decrease in size and gradually die.
Approximately on the 14th day of the cycle, the dominant reaches its maximum size (from 18 to 24 mm) and ruptures, “releasing” a mature egg. Ovulation occurs.
In place of the bursting dominant follicle, a corpus luteum begins to form. Its task is, in case of successful conception, to supply the woman’s body with the hormone progesterone necessary for pregnancy.
A dominant can develop on any ovary. Although most often it is observed on the right. There are frequent cases of the development of a dominant follicle on both ovaries. This mainly occurs after stimulation of ovulation or during artificial insemination. In this case, the chances of conceiving twins or triplets are high. If an ultrasound reveals that there is no dominant follicle in a woman’s ovaries, ovulation, and therefore conception, cannot occur.
Use of medicinal herbs
Sage contains a lot of estrogens, but in order not to harm the body, sage should be taken strictly according to the rules. Pour 250 grams of boiling water over a tablespoon of pharmaceutical sage and leave covered for half an hour. Then strain the infusion and drink a quarter glass once a day for 10 days. You should start taking the infusion on days 5-7 of the cycle. The course of treatment is 3 months. If you add linden to sage, the effect of sage will increase
Important! For polycystic disease, sage is contraindicated
In the second half of the cycle, you can drink boron uterus. This herb contains a lot of progesterone, the infusion is prepared in the same way as the sage infusion, you should drink it a tablespoon a day.
There are reviews that tea made from rose petals also stimulates ovulation, rose petals contain a lot of vitamin E, which is beneficial for the female body, some stimulate the process of follicle maturation with quince, aloe juice, mumiyo, and so on
It is important that herbal treatment is not carried out independently and uncontrolled; before any use of medicinal herbs, you should consult a doctor
Features of the maturation cycle
The number of female germ cells is formed at the stage of embryonic development. They are evenly distributed throughout the body of the ovary and, with the onset of puberty, the girl begins to mature.
The formation of follicles in the ovaries occurs during each menstrual cycle. Gradually, this sac increases in size, and by the middle of the cycle it ruptures, which is accompanied by the release of a mature egg and, possibly, its subsequent fertilization. If conception does not occur, menstrual bleeding is observed. This process is normally repeated every cycle.
When the follicles in the ovary mature, a woman may experience minor discomfort. This is due to an increase in the size of the organ and subsequent rupture of the sac. Initially, several follicles are formed in the ovaries. The quantity norm is up to 10 units per cycle.
By the middle of the cycle, single follicles remain in the ovary. Usually only 1 follicle reaches the end of the maturation cycle. It's called dominant. The remaining formations gradually resolve. If 2 follicles mature simultaneously in one or each ovary, the chance of conceiving twins increases.
Who is at risk?
Many women have experienced hormonal imbalance with the appearance of follicular cysts. Teenagers and mature women often face this problem during menopause. Any girl turns into a girl with the onset of her first menstruation. Changes occur in the body, and because of this, problems with the endocrine system may arise, and such an unpleasant phenomenon as hormonal imbalance may also occur.
During menopause, any woman should visit a gynecologist. Because it may be that the follicle will develop into a cyst, which will threaten the health and life of the patient. A malignant neoplasm can usually be completely invisible at the very beginning of its appearance; a woman may not even be aware of its existence, and the discharge will come less frequently or stop altogether. Therefore, it is very important to see a doctor.
What does the doctor prescribe
Having received the results of tests and ultrasound diagnostics, the gynecologist can prescribe the necessary drug, for example, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the form of injections. That is, a woman’s body lacks such a hormone, and the drug will help stimulate the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. After an injection of hCG, reproductive function can be restored. It is impossible to predict how many days the unruptured follicle will disappear and the ovary will recover. It all depends on the condition of the body.
You can learn more about how to provoke follicle rupture in the article “Stimulating Ovulation”
Symptoms
In the initial stages, the disease is asymptomatic. It is simply physically impossible to feel that there is no ovulation. This sign can only be detected during a gynecological examination, during two-manual palpation of the body or an ultrasound scan. Even after its discovery, the doctor will not rush to make a diagnosis.
In order to correctly differentiate the disease, the patient will be referred for various tests and biopsy (to exclude the risk of cancer). Then you need to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Hormonally inactive small cysts disappear without a trace after 2-3 menstrual cycles (only formations up to 4 cm are considered small). As the cyst grows and develops, the following symptoms may appear:
- increased duration of menstruation with heavy bleeding;
- spotting in pauses between cycles;
- pain during sexual intercourse and spotting after it;
- frequent urination;
- general physical weakness and increased irritability;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, on the right or left side (depending on which ovary the formation appeared in). The pain intensifies after any physical activity, even minimal (simple walking, bending), especially in the second phase of the cycle.
A cyst in the right ovary is similar in symptoms to appendicitis (especially if the ovary ruptures). When the appendix is inflamed, severe pain appears on the right side of the abdomen. A follicular cyst, unlike other types, does not develop into a malignant tumor and does not pose a threat to life (until it ruptures).
Symptoms of a cyst rupture:
- Sharp, piercing, severe pain.
- Severe weakness, dizziness.
- Cyanosis (blue discoloration) and pale skin.
- Sudden drop in pressure.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- State of shock (expressed in blue lips and extreme pallor of the skin, it becomes covered with sticky, cold sweat).
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat due to low blood pressure).
- Fainting.
All these symptoms make it clear that it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible.
The woman herself will not be able to feel the moment of ovulation. Of course, this can be painful, but there are no obvious signs. It is possible to use calculations to determine on which day of the monthly cycle ovulation will occur. However, based on such calculations, it is possible to make a mistake.
Using an ultrasound, a specialist can detect a follicular cyst that develops but does not burst. In order not to remind about the danger of such formations, the doctor determines what dimensions it is, what it contains and why it was formed. If the egg is mature, then usually the follicle will be about 22 mm, no more than 24, and then it bursts. Otherwise, there is a delay on the day of the expected critical days, and the woman may mistake this for pregnancy.
Consequences of ovarian rupture
Any ovarian rupture leads to negative consequences, but timely diagnosis and proper treatment help eliminate or minimize them.
The most dangerous, life-threatening complication of ovarian rupture is considered hemorrhagic shock due to severe blood loss. The sooner a patient is hospitalized in a hospital, the less likely there is a negative outcome. Therefore, it is extremely important that at the first signs of trouble the patient seeks help.
Attempts to independently treat the symptoms of ovarian injury with medication are unacceptable. Taking medications against pain and spasms makes you feel better, creating the impression of improvement, but at this time internal bleeding continues and aggravates the patient’s condition.
The greatest number of negative consequences is observed when trying to conservatively treat mild forms of ovarian rupture.
During surgical treatment, sometimes due to extensive damage to the ovarian tissue, it has to be removed. Therefore, women who have undergone surgery are often concerned about the question of whether pregnancy is possible after rupture of the ovary and its removal. Infertility after an ovarian injury does not develop if the second ovary is healthy and the patient maintains a two-phase ovulatory cycle.
Long-term negative consequences of ovarian trauma are associated with complications after surgery. During internal bleeding, blood accumulates in the pelvic cavity. During the operation they try to eliminate it, but sometimes, with extensive blood loss, this cannot be done. Over time, it can cause inflammation in the appendages, and it also organizes and becomes the source of the formation of the adhesive process.
Ectopic pregnancy after ovarian rupture is associated with inflammatory changes and adhesions in the pelvic area.
If the treatment does not eliminate hormonal dysfunction and vascular pathology, ovarian rupture may recur.
Expert recommendations
After reviewing the results of the tests and ultrasound, the specialist will be able to select the necessary drug for the woman. This means that there is a lack of hormone in the patient’s body, and medications will help stimulate the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg. Is prevention really possible? It is necessary for the follicle to rupture, ovulation to occur and discharge to appear in time. However, there are certain reasons why women aged 18 to 40 may experience problems with ovulation:
- lack of useful components;
- unsuitable diet;
- stressful situations, bad mood;
- bad habits;
- sudden changes in weight;
- irregular intimate life;
- hormonal medications;
- poor nutrition.
Of course, observation by a gynecologist for the sake of prevention is simply necessary to avoid problems with the ovaries in the future. This can be explained like this:
- the more advanced the pathology, the less hope there is for pregnancy in the future;
- the larger the cyst, the greater the danger it poses;
- benign cysts can become malignant tumors;
- with large and multiple follicles, ovarian rupture is possible.