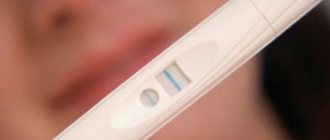
Currently, the use of assisted reproductive medicine methods is becoming increasingly popular. Every year the number of couples diagnosed with various types of infertility increases.
After lengthy preparation, examination and transvaginal puncture, embryos are cultured, which will be transferred into the woman’s uterus from the second to the fifth day. After this long-awaited moment, you need to carefully monitor your health. Discharge is one of the most striking indicators of a woman’s reproductive health, so it is important to know what kind of discharge there should be during embryo implantation.
Physiological state
Under natural conditions, when an egg is fertilized by a sperm, a zygote is formed, which moves through the fallopian tubes directly into the uterine cavity. The onset of implantation is observed from the 8th to the 14th day after conception. The only difference between in vitro fertilization is that the process of conception itself occurs in a special Petri dish, and not inside the woman. After this, embryologists cultivate the embryos until the required day and implant them into the woman. Further development of the embryo occurs under natural conditions.
IVF procedure – click to view
Almost all women experience the formation of objective symptoms of embryo implantation, which manifest themselves in an increase in body temperature, an increase in human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG is a hormone that is the main indicator of pregnancy).
Types of implantation
After ovulation and the meeting of the egg with the sperm, the fertilized zygote begins to move through the fallopian tubes. Its task is to get into the uterus as quickly as possible in order to gain a foothold in the endometrium specially prepared for this. Along the way, the zygote continuously divides and grows. Implantation occurs at the blastocyte stage.
We suggest you read: How to organize a child’s birthday Discussions
Conventionally, we can distinguish between middle, late and early implantation.
- Early. It is quite rare. Usually, implantation that occurs 6-7 days after ovulation is considered early (or 3 dpp - 4 dpp if we are talking about IVF)
- Average. 7-10 days pass between fertilization and implantation (implantation of the embryo after transfer occurs approximately 4-5 days). Doctors say that it takes about 40 hours for morula to penetrate, after which the body begins to produce the hormone hCG in the blood, and the basal temperature rises. Based on this, the so-called embryonic period of development, which lasts until approximately 8 weeks of pregnancy.
- Late. Occurs approximately 10 days after fertilization. This is what always gives women at least a faint hope of a possible pregnancy - even when you can hardly expect it anymore.
If pregnancy does not occur for a long time, then you need to be examined to identify the cause of infertility.
Implantation processes, depending on the period of attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus, can be late, in which it occurs 10 days after ovulation, and early - after 6–7 days. In the case of embryo transfer during IVF, late implantation occurs, since the embryo enters the unusual environment of the mother’s body and needs some time to adapt.
During this period, a woman should take special care to maintain pregnancy, not take a hot bath or any warming procedures, limit physical activity and heavy lifting, follow the correct regimen, devote more time to walks, and eat well. Avoid hypothermia and contact with sick people, do not have sex, and it is best to adhere to bed rest for several days.
Are allocations allowed?
Is discharge allowed after embryo transfer? Most women who decide to undergo IVF cannot conceive a child on their own for a long time, so the appearance of various changes in their body is perceived as a threat. But in reality this is not the case, because there are certain types of mucus that indicate that the implantation of the embryo was successful. To determine, a woman just needs to look at the consistency, color and smell of the liquid. Also an important factor is the time of appearance of the discharge and its quantity.
It is important to know!
It is possible to have mucous discharge from the genital tract, which occurs due to the use of medications or during implantation of the embryo into the uterus. They are not harmful to both the woman and the fetus.
Some women may experience spotting after the transfer, which is accompanied by an unpleasant, nagging pain in the abdomen. These symptoms may be a sign of pregnancy. But it is still necessary to consult a specialist, because this may also be a signal of a threat of miscarriage.
What secretion indicates the process of implantation?
Minor bleeding may indicate the implantation process, during which the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. This is also called implantation bleeding, which is most often observed 7–12 days after the procedure.
But it is worth remembering that such secretion cannot be abundant or have any characteristic odor. Otherwise, one may suspect various disturbances during the implantation process or the presence of concomitant pathologies.
In addition, it is important to remember that brownish or pink secretion after IVF before hCG should stop at 12 - 14 DPP. There is also a possibility of slight pain in the abdominal area, but if they are repeated very often, then the woman urgently needs to see a fertility specialist.
What should be the normal discharge?
What discharge can be considered normal during embryo implantation? It is possible to identify certain criteria that indicate the occurrence of a healthy process. These include:
- characteristic and not pungent odor;
- homogeneous consistency;
- transparency;
- volume within one teaspoon;
- no discomfort.
These are the basic physiological characteristics of discharge that are considered completely normal and safe. It is thanks to these indicators that the vaginal mucosa remains moist and maintains an optimal acidity balance.
However, after embryo transfer, another fluid may be released, which will also not be considered a pathology. The formation of such mucus occurs due to the effects of progesterone, which is contained in the drugs used. As a result, the mucus may acquire a thicker consistency and a white tint. There is also a decrease in fluid secretion.
The appearance of pink or creamy mucus during embryo implantation is also considered normal and occurs due to the effect of hormonal drugs on the woman’s body. However, such discharge should go away immediately as soon as the woman stops taking the medication. Most often, the formation of such discharge occurs after “Utrozhestan” and “Krinon”, which are used as a gel for the vagina.
On days 6–12 after the transfer, the woman begins to experience pale pink or dark brown discharge. Such a change may cause panic, but there is no need to worry ahead of time. This sign appears due to the fixation of the amniotic egg in the uterine cavity. During this process, blood vessels are damaged, which provokes implantation bleeding in 30% of IVF cases. But you should pay attention to the fact that there should be no unpleasant odor and a large amount of mucus.
Tests after replanting
Every woman has a special feeling after embryo transfer. On the second day, unpleasant signs may bother you, but they are a consequence of instrumental interventions and will pass soon. As always, in the second phase of the cycle your breasts may become enlarged and slightly sore.
We suggest you read: What to do if a child refuses to eat formula. An infant refuses formula: reasons and what to do
Implantation of the fertilized egg in a normal cycle occurs on the 8-9th day of its development. One way or another, by day 10 after the embryos are transferred, they will attach to the wall of the uterus or die. The time of cell implantation is determined by the duration of their development in vitro. If three-day periods have been postponed, they will be added to the 7th day. Planting 5 days will result in implantation in about 5 days.
General state
The state after embryo transfer is usually not the most cheerful. Mild malaise, weakness, and increased fatigue appear. On the first day, it is recommended to rest and get enough sleep. Normally, dizziness and discomfort disappear after 1-2 days. The temperature after embryo transfer during IVF may be slightly elevated on the first day, but it should not exceed 37.5 degrees.
After some time, a woman may feel the first signs of pregnancy, which are no different from those that occur during natural conception.
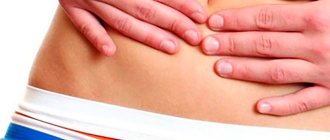
On the first day, a woman’s stomach feels tight and her lower back hurts after embryo transfer. These unpleasant signs are caused by interference in the cavity of the reproductive organ. The cells are delivered to the uterus through a thin catheter that passes into the cervical canal. Minor damage to the mucous membrane leads to spasms and provokes pulling sensations.
Abdominal bloating after embryo transfer is usually caused by taking hormonal medications. To prevent flatulence, you should adhere to your diet and drinking regime.
It sometimes pulls the lower back in women at the time of implantation. When the embryo implants into the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ, minor damage to the blood vessels occurs. This process can manifest itself not only as pulling sensations, but also as discharge.
Discharge
Increased discharge after embryo transfer is a normal condition. It is caused by hormonal changes and an increase in progesterone levels. Taking additional supporting agents helps thicken the vaginal mucus and turn it milky.
Some women experience implantation bleeding 7-10 days after the transfer. It is caused by damage to blood vessels by the attached embryo. Such discharge has a brown or beige tint and goes away on its own after 1-2 days.
After embryo transfer, the patient is prescribed not only hormonal medications, but also additional examinations. Individually recommended blood tests that show the processes occurring in the body.
D-dimer after embryo transfer is given on the 5th day. This study makes it possible to assess the condition of the blood. If there is excessive thickening, the woman is prescribed thinning medications. Often it is thick blood that causes protocol failure. Therefore, timely D-dimer testing increases the chances of a successful outcome.
If the norms for estradiol and progesterone after embryo transfer are determined without deviations, then a successful outcome can be assumed. If underestimated or overestimated values are obtained, corrective medications may be prescribed.
After the transfer, hCG can be taken on the 10th day. During this period, the pregnancy test will not yet show the desired result, but the level of this hormone in the blood can already be determined. It is important to repeat the study after 1-2 days to evaluate the results over time. We should not forget that an hCG injection is given before the puncture. This substance is eliminated from the body in up to two weeks.
The pink area indicates the area when you can start taking a pregnancy test after insemination.
Violet indicates the days when testing can be done after IVF. According to individual indications, a woman may be recommended tests: hemostasis, coagulogram, determination of fibrinogen levels, as well as additional hormonal studies.
Pathological changes
Unfortunately, not all women tolerate the IVF procedure easily. The appearance of a certain type of discharge may indicate an unsuccessful attempt.
Discharge after embryo implantation should not change in color, smell or quantity. If you experience bloody discharge that is greenish, cloudy or cheesy, you should consult a doctor. Watery discharge after embryo transfer may also indicate a pathological condition.
The most dangerous are bloody discharges, which indicate a serious threat to the embryo and are most often formed when:
- detachment of the embryo and its exit from the uterine cavity;
- threat of miscarriage;
- hormonal imbalance;
- insufficient amount of progesterone;
- frozen pregnancy.
Attention!
Unfortunately, in most cases, the appearance of such mucus indicates serious problems due to which it is not possible to save the child.
The second most dangerous is cinnamon discharge, which can turn scarlet over time. Their consistency is very liquid, odorless and varies in quantity. The brown liquid is accompanied by a strong nagging pain.
An ultrasound examination will help you find out exactly the cause of atypical symptoms.
Green, yellow discharge after embryo transfer during IVF indicates the development of a pathological process. In most cases, they are considered a sign of the development of infectious inflammation in the genitourinary system, for example, bacterial vaginosis, which disrupts the vaginal microflora.
Bacterial vaginosis (vaginitis) – click to view
These changes can cause pregnancy to fail or spontaneous miscarriage.
The formation of curdled mucus indicates the development of thrush, which occurs in most women after embryo transfer in a successful protocol. Due to the decrease in mucus acidity, which appears as a result of increased female hubbub, the growth of the fungus is activated. In appearance, these discharges are very similar to cottage cheese and have a sour, pungent odor. Thrush is also accompanied by severe itching and burning. Treatment of this disease is mandatory at any stage of pregnancy, because otherwise the fetus may become infected, which will affect its development.
Thrush (candidiasis) – click to view
What can affect the consistency and smell in the early stages
In addition to individual characteristics (such as microflora and pH), the nature of vaginal discharge is influenced by hormonal changes that occur during the IVF procedure, in particular, taking maintenance doses of progesterone. This hormone causes these effects.
- Suppresses the immune system, which helps the embryo implant into the uterine cavity.
- Suppresses the growth of a new egg in the ovary due to the need to carry an existing pregnancy to term.
- Forms a mucus plug in the cervical canal: a protective barrier against germs that can enter the uterus from the vagina.
Under the influence of progesterone, the discharge becomes whitish and thicker, without being accompanied by the appearance of an odor. Their number is the same as normal, sometimes it even decreases.
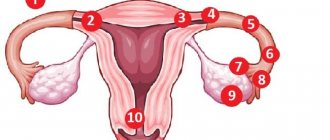
A number of changes in the endometrium, which are caused by the transfer of the embryo, have a great influence on the state of the discharge. During implantation, damage occurs to the upper layers of this mucous tissue lining the uterus from the inside. This is necessary for the firm attachment of the embryo and the appearance of chorion - special villi that contact the mother’s blood vessels and provide the embryo with nutrition until a full-fledged vascular network (placenta) is formed.
Damage to the endometrium leads to changes in the secretion: it becomes thicker, “smearing”, with a reddish or brownish tint. These changes occur only at the moment the embryo is fixed, that is, for 1-2 days. Too much, liquid secretion and the appearance of discharge reminiscent of menstruation indicate the development of conditions that threaten pregnancy and require an urgent call to the doctor.
Discharges that should alert you at any time after an IVF transfer procedure:
- Thick, plentiful, with a yellow-green tint. They often have an unpleasant odor and indicate inflammation in the pelvis.
- In the form of copious curdled leucorrhoea. They talk about candidiasis, accompanied by burning and itching in the genital area.
- Watery, cloudy. Symptom of bacterial vaginosis.
- Heavy bleeding after IVF procedure. It can start any day and is extremely dangerous.
A small amount of bloody discharge is a sign of implantation bleeding. If they started two weeks after replanting, this is evidence of a pathological course of the process. During the examination, the patient may be diagnosed with a frozen pregnancy or hormonal imbalance. Timely medical assistance in many cases will allow you to save your pregnancy.
Brown and dark, almost black discharge is also quite dangerous. Usually their appearance is evidence of an imbalance of progesterone and estradiol. It happens that a woman mistakes such discharge for menstruation and stops taking prescribed medications, which poses a threat to pregnancy. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe and discontinue medications, so they should be taken strictly according to the prescribed regimen.
If implantation is unsuccessful, menstruation occurs 3–12 days after the procedure. Large clots are observed in the discharge, and bleeding may take longer than normal periods. There may be pain and cramping in the lower abdomen. A blood test for hCG shows a negative result, and rapid tests cannot be relied upon in this case.
It is important to remember that in one protocol only 30–40% of women will be successful, and not to despair, but to take measures to restore health. A failed IVF attempt is due to the following reasons:
- medical errors;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvis;
- endometrial thickening (more than 13 mm);
- woman's age over 36;
- blastocyst defect;
- genetic incompatibility of partners.
Another option also happens: the woman already knows about the failure of IVF, but still does not have her period. The cycle will be restored after discontinuation of hormonal therapy. During the year, there may be interruptions in the arrival of menstruation. For example, the first menstruation will come on time, and the subsequent ones will come with some delay. Often, special treatment will be required to restore body functions.
Yellow cloudy discharge is a sign of bacterial vaginosis, which is often diagnosed from 2–4 weeks of gestation. They have an unpleasant odor, can cause discomfort and are never accompanied by groin pain.
Another unpleasant phenomenon after conception is thrush. Its cause is a change in the acid-base balance of the vagina due to hormonal stimulation. The discharge is white, has a sour odor, and has a consistency similar to cottage cheese. They are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, but the woman almost always experiences severe itching in the genital area. Treatment of infection is carried out with antifungal drugs under the supervision of a doctor.
The risk of miscarriage after IVF is much higher than after conception naturally. Its causes in the early stages are as follows:
- stress;
- hormonal dysfunctions;
- violation of doctor's orders;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- insufficient preparation of the uterus for implantation;
- poor absorption of progesterone gels and suppositories.
Frozen pregnancy and miscarriage can happen any day after implantation, so if there is bleeding from the 12th day after embryo transfer, it is important to immediately consult a doctor. It can be spotting, strong, accompanied by nagging or sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
Discharge after IVF must be monitored. For any deviations from the norm, an in-person medical consultation is required. In most cases, the pregnancy can be saved, but for this, the expectant mother must immediately contact a medical facility.
Cryotransfer
Cryotransfer is an additional in vitro fertilization procedure that is used for a number of specific reasons. Most often, freezing is carried out when there are a large number of good embryos on days 3-5; due to the development of hyperstimulation in a woman or other gynecological problems. The IVF protocol allows for the transfer of one to four embryos, but not all take root. The remaining viable embryos are frozen using a special system and stored in liquid nitrogen until the couple decides to make a second transfer.
Note!
By resorting to cryotransfer, most families gain a chance to have another child. The sensations after transfer of a thawed embryo are no different, and the appearance of signs of implantation is the same as during a normal transfer.
In vitro fertilization is becoming an increasingly common method for conceiving a child every day. Many married couples who have been seriously diagnosed with infertility gain the chance to raise their baby. However, not all patients ask reproductive specialists about possible signs of pregnancy, believing that the very first signal will be an hCG test, which is taken 10-14 days after the replantation. But this is not true; in some cases, discharge after embryo transfer can indicate the onset of a desired pregnancy. All that is required of a woman is to carefully monitor her well-being and protect her health, because another person who needs protection may already be living under her heart.
How to behave after the transfer
After embryo transfer, the woman is given individual recommendations.
The main point is post-transfer support. All medications prescribed by the doctor must be taken. The patient should also reduce physical activity in the first few days. It doesn't have to be all the time
, but you shouldn’t play sports either. The diet should be gentle so that bowel movements occur daily and without difficulty. Following a routine after the transfer will help relieve nervous tension and gain a positive attitude.
Why monitor the discharge?
Vaginal secretions, popularly referred to simply as “discharge,” are very important for the normal functioning of the reproductive system. And IVF performed cannot be considered an exception to the rule. A normal vaginal microclimate is important for pregnancy, its maintenance and development. Discharge varies depending on the level of hormones, the day after the transfer, and whether the fertilized egg has implanted or not.
Doctors recommend that women monitor discharge after embryo transfer. It is the change in their character that has important diagnostic significance, which can indicate a successful protocol or failure. It is possible to reliably find out whether the doctors’ efforts were crowned with success only on the 14th day after the transfer, when the woman’s blood is tested for the content of human chorionic gonadotropin.
After embryo transfer, a woman is required to follow the doctor’s recommendations. In addition to a lot of advice on nutrition, intimate life, hygiene and stress, this also applies to controlling the amount, consistency and color of discharge from the genitals. They will most likely differ from the discharge that is observed in a woman after natural conception.
Typically, IVF is carried out after preliminary stimulation of ovarian functions with hormones, so discharge after embryo transfer may seem unusual to a woman. In fact, they are quite understandable - the body has undergone the intake of potent hormones, traumatic puncture of the follicles, which cannot but have consequences.
Even if the embryos implanted in the uterus take root, it is possible that they will be rejected, for example, if the endometrium was not sufficiently ready for transfer or the embryos themselves turned out to be of poor quality and non-viable, which will also be indirectly “informed” by the nature of the discharge. If a woman consults a doctor in a timely manner, the pregnancy can be saved in certain cases.
In order to clearly understand the type, volume and consistency of her own vaginal secretion, a woman after embryo transfer should avoid having sex and not douching. It is necessary to use thin sanitary pads. The use of tampons is strictly prohibited. It can provoke stagnation of vaginal secretion, disruption of its separation and the development of vaginosis.
To facilitate observations, doctors sometimes recommend that a woman keep a special diary, in which she will note the type and color of the discharge every day after the transfer. This will help you notice implantation bleeding if it occurs, as well as timely notice signs of problems in the patient’s condition if they occur.
You can continue to keep a diary during early pregnancy. It will allow you to notice a possible threat of interruption in time and consult a doctor. With timely and early access to qualified medical care, pregnancy can be successfully maintained in most cases.
Dangerous symptoms
The appearance of bleeding on the first day after replantation is considered dangerous. If this happens, you should tell your doctor immediately, especially if the discharge is accompanied by abdominal pain. This does not mean that the protocol is doomed to fail. Various complications are possible, for example, the manifestation of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. But it’s still better to inform the doctor.
The appearance of green or gray-brown discharge 6-8 days after the transfer may indicate a bacterial infection. You should see a doctor as soon as possible to get prescribed medications to treat the infection. A woman could have become infected in the clinic, because, unfortunately, junior medical staff do not always pay sufficient attention to the process of sterilizing instruments.
White, curd-like discharge with itching may be a sign of thrush. By the way, it is the exacerbation of thrush that often indicates the onset of pregnancy in the early stages. But you shouldn’t ignore such an unpleasant vaginal secretion and its accompanying symptoms - you definitely need to start treatment.
On days 11-14, bloody discharge with clots, black liquid discharge may be a sign of rejection of the fertilized egg, if its implantation does take place. You should call an ambulance and get to the hospital as soon as possible, where the woman will be provided with the help necessary in such situations.
There are types of discharge that are considered conditionally normal until a certain period after embryo transfer. We are talking about pink, beige, creamy discharge of a uniform consistency. They should not disturb the woman until 14 days after the transfer.
When to sound the alarm?
If on the seventh day bloody spots are still acceptable, then after 14 DPP such secretion already signals unfavorable conditions for the development of pregnancy. But discharge in the early stages of pregnancy should not be perceived by a woman as unsuccessful in vitro fertilization.
A blood test for hCG will help establish a more accurate picture of the situation. The causes of prolonged brown leucorrhoea may be:
- The embryo no longer develops.
- There is a lack of progesterone.
- The process of rejection of the frozen fertilized egg has begun.
In such a situation, it is necessary to go for an ultrasound so that the doctor can see a picture of what is happening in the uterus. Based on the results of the examination, your doctor will take further actions. Women need to remember that only a doctor can determine which discharge is normal in a given situation and which requires special attention.
In addition, some patients do not have any characteristic leucorrhoea at all, which is also considered normal. Therefore, it is worth monitoring vaginal secretions immediately after the procedure. Its character can change both on the 7th day and two weeks after IVF.
Discharge during IVF stimulation
In order for the female body to produce not one, but several eggs in one menstrual cycle, ovulation is stimulated on certain days (2–7 days of the cycle). A five-day course of special hormones is prescribed, the levels of which are constantly measured and monitored through blood tests for hCG.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HhQlivBzNI8
The course of the procedure may be accompanied by discharge due to an increase in hormone levels or, worse, an infection. This happens infrequently, because the instruments are thoroughly disinfected. The result of medical negligence is a number of complications of gynecological diseases.