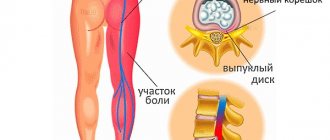
A high heart rate is called tachycardia. There are two types of this deviation from the norm. The sinus type is represented by a disruption of the natural pacemaker. The paroxysmal type is caused by the formation of new foci of electrical activity.
An increased heart rate can be completely physiological: the distribution between natural and pathogenic causes is presented as 30% to 70%.
The phenomena that cause acceleration of heart rate are multiple. Therefore, diagnosis is accompanied by certain difficulties. A research team is required. Even in this case, distinguishing one condition from another is problematic.
The phenomenon is complicated by the fact that the cause does not always lie in cardiac pathologies. Neurogenic, endocrine or hormonal factors are possible.
Recovery in most cases is carried out on an outpatient basis. Severe diseases are treated in a hospital, under the supervision of cardiologists. Eliminating the root cause is the main task.
What numbers are we talking about?
Depends on the type of pathological process. An accelerated heart rate is considered to be over 90 beats per minute. This is no longer the normal state of affairs. Further levels vary.
Against the background of standard sinus tachycardia, the contraction frequency rarely exceeds 150. Options are possible. This type of condition does not pose a danger to life or health as such.
Paroxysmal varieties give up to 250 beats per minute, perhaps a little more. They feel like intense short contractions that are relatively weak. This process is much more dangerous, as it is fraught with sudden cardiac arrest. Recovery and resuscitation measures will have no effect.
The last possible option is ventricular or atrial fibrillation. They increase heart rate to 300-400 beats per minute. Subjectively, the changes are not felt at all.
These are not full-fledged movements of cardiac structures, but minor twitching of muscle fibers. They are recorded only on the ECG, give a typical clinical picture and pose a colossal danger to the patient’s life.
Each specific case needs to be examined separately. The question of the origin and type of the pathological process is determined by objective diagnosis in several ways. 24-hour monitoring and electrocardiography are indicated. It's minimum.
Causes of elevated heart rate
Multiple. They are divided into two groups. Cardiac diseases are especially common, but an indirect cause of the pathological process is possible.
Strict classification does not have much clinical significance. The issue of origin is resolved on the spot, during diagnostic measures.
Approximate list of diseases:
Arterial hypertension
Both of symptomatic origin and actual independent diagnosis. The essence of the deviation is the increase in pressure. Normal blood pressure levels range from 100 to 139 at 60-89 mmHg. Anything more is inadequate indicators.
The higher the pressure, the greater the risk. There is no direct conditioning, however, both the increase in tonometer numbers and the acceleration of heart contractions are due to the same factor.
A change in the pulse rate is detected in the process of increasing blood pressure.
Relieving the underlying condition does not always give a full effect. Therefore, the use of a group of medications is indicated.
Anemia
Iron deficiency, megaloblastic, not of great importance. The essence of the pathological process is always the same - a sharp drop in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood.
It occurs as a result of a deficiency of microelements, vitamin B12, prolonged bleeding in small amounts and other issues.
As a result of the prolonged existence of the pathological process, a violation of myocardial contractility occurs. The conductivity of the His bundle decreases, and partial blockade of the pathways is observed.
Hence the formation of abnormal electrical impulses in the atria and ventricles. This is an extremely dangerous condition. It is often combined with typical sinus tachycardia. Urgent treatment is required.
The duration of anemia management is minimal: about 3-4 weeks, sometimes less, depending on the severity of the process.
Anorexia
Malnutrition. Most often it has psychopathological roots. There is still no consensus on whether it is considered an independent diagnosis.
The second possible option is a physiological inability to eat or a significant limitation of the process. For example, as a result of Crohn's disease, stomach cancer, operations on the digestive tract, Alzheimer's and others.
Poor nutrition leads to exhaustion or cachexia. The body utilizes itself, first fat reserves are used, then muscles.
Stable tachycardia almost always occurs. Especially against the backdrop of a running process. The body intensifies its own activity in order to somehow provide the tissues with energy by releasing it from accumulated reserves.
Heart defects
Congenital or acquired. They constitute serious violations.
The most common options are mitral valve prolapse and aortic valve stenosis, aneurysm of the interatrial septum, and abnormal development of vascular structures. A strong pulse is caused by disruption of the sinus node and His bundle conduction.
Recovery is possible not only with medication, but also with surgical methods. Other than an increased heart rate, there may be no symptoms. Such clinical variants are detected at later stages or during autopsy.
Myocarditis
Inflammation of the muscle layer of the heart. An increased pulse is a typical symptom of damage to cardiac structures and is observed on an ongoing basis. The patient cannot rest even at night due to intense beating in the chest.
This is a worrying sign. An urgent diagnosis is required. Without treatment, cardiac arrest or tissue destruction is likely to occur. Prosthetics will be required.
Inflammation of the pericardium
Pericarditis (inflammation of the pericardial sac). It is a hollow formation that holds the organ in one position. The danger is not only an increase in heart rate, but also possible complications such as tamponade (compression) of the heart muscle.
Obesity
Body weight itself is not considered a factor in the development of the pathological process. We are talking about lipid metabolism disorders. It is the metabolic deviation that is to blame.
A common factor in the development of the problem is the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the coronary arteries. A high heart rate at rest and during physical activity is the result of increased heart function.
This is a compensatory mechanism. The body seeks to correct insufficient nutrition by increasing the number of contractions per minute in order to somehow increase the volume of blood output. But it only gets worse.
A constantly high pulse becomes chronic and over time the patient ceases to notice the symptom.
Hyperthyroidism
As a result of disorders of the thyroid gland. From hypertrophy, inflammation to cancer processes.
An increase in the concentration of specific hormones is just a consequence. The basic condition needs to be corrected. Symptomatic therapy is a secondary measure.
The reasons for the high pulse in this case are the result of the stimulating influence of T3, T4, and partially TSH. The decrease in indicators is characterized by a momentary reduction of tachycardia, which directly indicates an endocrine state.
Lung pathologies
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma and other diagnoses of this kind. The intensification of cardiac activity is due to impaired myocardial nutrition and oxygen starvation. Other organs also suffer.
Infectious diseases
Including colds, ARVI. Why a high pulse in this case is quite understandable: an increase in body temperature, an increase in the load on the heart as a result of intoxication with waste products of bacteria, fungal or viral agents.
Angina pectoris
In a word - coronary insufficiency.
Why is this condition dangerous?
Rapid heartbeat, occurring spontaneously, periodically or lasting a long period of time, cannot spontaneously disappear or pass without a trace for the body. The heart muscle suffers the most from high heart rate - it quickly wears out and copes with its functions worse and worse. And this, in turn, leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to organs (ischemia), which threatens the development of:
- IHD;
- atrial fibrillation;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart failure;
- cardiomegaly (increase in the mass and volume of the heart);
- myocardial infarction.
Therefore, you should not look for ways, if your pulse is high, what to do at home, this is not a situation where you can experiment. Look for a better opportunity to visit a doctor.
Controllable reasons
In addition to the indicated, actually pathogenic reasons, there is a group of subjective points. If desired, the patient can adjust them on his own.
- Smoking. Provokes stenosis of the coronary arteries. The result is a decrease in nutrition of cardiac structures. The action and degree of the negative effect of tobacco, tar and other harmful substances depend on the individual resistance of the body. For some, a cigarette is enough, for others, even a pack is not enough. But sooner or later nature will take its toll. It is the matter of time.
- Alcohol abuse. The process is identical to that of smoking. Only the speed of development of negative phenomena is many times higher. All claims about the benefits of alcohol are false. As practice shows, only high-quality red wine, in quantities of up to 50 ml per week, has a positive effect. That is, strictly therapeutic doses.
- Too much caffeine-containing drinks. You should not drink, including tea, if you are prone to disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- The cause of increased heart rate may be long-term use of diuretics. Diuretics provoke the excretion of potassium and magnesium. Hence the instability of the myocardium. The typical condition, early ventricular repolarization syndrome, is of metabolic origin.
The question of why the pulse increases is best addressed to a doctor: identifying the causes requires diagnosis, at a minimum, electrocardiography and ultrasound examination of tissues (ECHO-CG), as well as daily Holter monitoring.
What can you do at home?
Since there are many reasons for a high heart rate, there is a risk of making a mistake. Even doctors are not able to navigate the situation by eye. What can we say about people without special training?
Therefore, the first thing that is recommended is to call an ambulance. The task before the team arrives is to stabilize the patient’s condition and partially relieve the attack of increased heartbeat. But do this with great caution.
An approximate algorithm is:
- Sit the patient on a chair or sofa, put a soft cushion of clothes or blankets under his back. Any available materials will do. The main thing is not to lie down, otherwise blood circulation will be uneven. On the one hand, this will lead to an acceleration of the heart rate, on the other hand, breathing will be impaired, and the risk of pulmonary edema will increase. It can all end in the death of the patient.
- The arms and legs should be lowered so as not to create excessive peripheral hemodynamics. You should sit in this position the entire time.
- Move less. All movements are fraught with an increase in heart rate, and cardiac arrest is possible.
- Open a vent or window to provide fresh air into the room. This partially compensates for hypoxia.
- Give the patient an Anaprilin tablet, 50 mg, no more. If the symptom is not very pronounced, half is enough. You can no longer take a beta blocker.
- Additionally, you can take motherwort (1 tablet), or valerian (1 tablet), you can also use Corvalol.
- The use of a special folk remedy is allowed: the herb of yarrow, calendula, anise and peppermint is mixed in equal proportions and poured with boiling water (500 ml). Drink in any quantity.
- In case of disturbances of consciousness, the use of ammonia is indicated. But don't shove the bottle in the patient's face. Moisten the cotton wool and bring it to the nome at a distance of 5-7 centimeters. Otherwise, you can cause respiratory arrest or chemical burns.
Next, you need to wait for the doctors; you can’t do anything else on your own, and it’s not worth it, it’s dangerous. The issue of transporting the patient to a cardiology hospital is decided on the spot.
All controversial cases require urgent qualified assessment. You should not refuse; the process will probably worsen or relapse in the near future.
What you definitely shouldn’t do: engage in physical activity, drink drugs other than those described, sit in the bath, douse yourself with cold or warm water, eat, turn to dubious folk recipes. Many “grandmother’s” drugs are downright dangerous.
Symptoms
Failure of the heart rhythm necessarily affects the general condition of the human body. In parallel, the following may occur:
- pulsation,
- dizziness,
- weakness,
- darkening of the eyes and noise in the ears.
But if these manifestations are repeated repeatedly, they can lead to loss of consciousness and the development of heart failure.
What should be done?
First, you need to see a doctor. Sometimes this is a symptom of very serious disorders that occur inside the body and have not yet revealed themselves. To determine the disease, you need to consult an endocrinologist, take tests and undergo an ultrasound examination. After this, the doctor makes a diagnosis.
First of all, treatment of the disease begins with eliminating the cause of tachycardia. For example, if the cause of tachycardia is hidden in anemia, thyrotoxicosis or a septic process, then treatment must be used to solve these problems. If there are diseases of the endocrine system, it is necessary to eliminate these disorders.
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia begins with taking medications to calm the nervous system or antidepressants. If the disease was detected in time, then Valerian, Diazepam or Persam will help well. They will help partially normalize the functioning of the heart.
When to call an ambulance
According to clinical recommendations, you need to call the emergency room if an elevated pulse persists for 20 minutes or more. 90-120 - acceptable indicators. The remaining options are already dangerous.
In addition to changes in heart rate, other symptoms may be present:
- Panic attack. The patient feels intense fear, rushes about, cannot find a place for himself. The reverse process is possible. The patient completely loses interest in the world and is indifferent to external stimuli. Both are bad.
- Pressing pain in the chest. They indicate an ischemic process, which in itself is extremely dangerous. Perhaps we are talking about an attack of angina or a heart attack.
- Fibrillation, extrasystole. Subjectively, it feels like missing beats in the chest, slowing down activity, tying a knot.
- Dyspnea. Against a background of complete peace. The patient cannot not only engage in physical activity, but also simply lie down.
- Headache, dizziness, neurological signs. They develop as a result of insufficient blood circulation in cerebral structures.
- Weakness, drowsiness, general malaise.
The patient feels an increased pulse even at night, which prevents him from sleeping normally. A decrease in blood pressure is objectively detected.
What examinations are recommended?
A visit to a cardiologist is indicated on a planned or urgent basis. An approximate list of diagnostic measures:
- Oral questioning of the patient. Interested in complaints, as well as the frequency of tachycardia attacks. How long ago did the process begin, how much does it interfere?
- Anamnesis collection. Interested in lifestyle, family history, past pathological processes, current diseases.
- Measurement of blood pressure, heart rate. Both are outside the normal range. Blood pressure is below adequate levels, heart rate is higher.
- Daily monitoring. Using a special automatic tonometer. To assess the condition
- health over time. Electrocardiography. Functional features are subject to research. This is a specialized technique for identifying arrhythmias of various types, including combined ones.
- Echocardiography. Ultrasonic method of tissue visualization.
- General blood test, hormones and biochemical.
Basically this is enough. An MRI may be ordered as needed.
How to measure?
To find out your pulse, you need to know how to take measurements correctly. This can be done at several points on the body:
- wrist;
- whiskey;
- neck;
- heart area.
Using two fingers, the main artery is felt in one of the indicated areas, on which it is best possible to record the pulse. The procedure can be performed with any fingers, with the exception of the thumb. This is due to the fact that it has its own pulsation, which does not allow you to accurately measure your heart rate. The blows are measured for 15 seconds, after which the resulting number is multiplied by 4. The resulting indicator must be checked against normal values. If they are more than the norm, then contact a doctor who will help bring down the high pulse.
Treatment
Conducted by a specialized specialist. Three tasks are solved: eliminating the root cause of the condition, relieving symptoms and preventing dangerous complications for health and life. The main method is medication.
List of drugs:
- Beta blockers. Anaprilin, Carvedilol, Metoprolol.
- Antihypertensives as needed.
- Cardiac glycosides. Increase myocardial contractility. Digoxin will do.
- Antiarrhythmic. Amiodarone or Quinidine. Other drugs are strictly not suitable. The work of the muscle organ is likely to stop.
- Tranquilizers. Diazepam and others, as part of extended therapy.
- Sedatives of plant origin. Valerian, Motherwort, but only in tablets.
- Medicines based on magnesium and potassium. Asparkam and others.
Surgical treatment is prescribed when cardiac malformations are detected. The usual tactics are valve replacement, expansion of the affected vessel. Also, advanced atherosclerosis is eliminated in this way.
It is possible to implant a pacemaker and cauterize abnormal foci of signal formation using the radiofrequency method (ablation).
Lifestyle changes play a big role. It is mandatory to give up smoking, alcohol, and excessive physical activity. Stress should be avoided whenever possible.
The diet is also subject to correction. It is recommended to create a menu in accordance with treatment table No. 10; it meets all the needs of heart patients. Whenever possible, you should contact a specialized nutritionist.
Folk remedies can be a good help, but not the main way of therapy. The use of lemon balm, peppermint, anise, motherwort, valerian, and yarrow is indicated. Dry raw materials, it is better to brew and drink like tea.
A mixture of lemon, cinnamon and honey has a good therapeutic effect. Grind the ingredients and mix them. The resulting gruel should be eaten one tablespoon 3 times a day.
What you should definitely not take is the tincture. Alcohol has an extremely negative effect on the health of the core.
The use of folk recipes
- Combine 2 tablespoons of freshly squeezed carrot juice and the same amount of alcohol, 3 tablespoons of cranberry juice, 1 tablespoon of chokeberry and squeezed lemon juice.
- You need to take 1 teaspoon each of celandine and dried hawthorn. Fill with hot water and boil a little. Leave to brew overnight in a dark, warm place.
- A very intensive remedy helps restore heart function. For this you will need apricot kernels, lemons and honey. Clean the seeds and turn into a paste using a blender. Lemons also need to be grated. Combine all ingredients.
- Mint and lemon balm. Add two ingredients in equal quantities and add boiled water. Take as tea. This remedy has a preventive and therapeutic effect.
- Hop cones have a good healing effect. This drink should be consumed every day in the form of tea.
It becomes dangerous for the body if a rapid heartbeat occurs for more than one day. This may indicate serious problems.
If you have a rapid heartbeat after taking certain types of medications (pills), this may be a side effect.
Other causes of tachycardia:
- Oncology education.
- Adrenal gland dysfunction.
- Sudden changes in pressure.
- Meteosensitivity.
- Allergic reaction of the body.
- Insomnia.
- Excess weight.
- Constant overwork.
- Excessive coffee consumption.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Insufficient amounts of microelements.
- Age-related changes.
- Temperature increase.
- Infectious diseases.
- Adrenal cancer.
- Problems in the endocrine system.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Toxification of the body.
That is, the reasons that lead to a rapid heartbeat are very diverse. The first thing to do in this case is to consult a doctor so that he can establish a diagnosis and determine the necessary therapy.
How else can you help yourself?
The first thing to do is to take a comfortable position for relaxation; lying on the bed is best. It is advisable to drink 1 glass of water. For better relaxation, you need to take a deep breath and exhale. The use of a contrast shower is good for normalizing the heartbeat. It is necessary to drink from the following medications:
- Anaprilin,
- Corvalol,
- Validol or motherwort tincture.
If the cause of rapid heartbeat lies in insufficient amounts of microelements, then you can consult a pharmacist.
Taking vitamins such as Magnesium B6 or Omega-3 may be a good option. To improve the functioning of the heart muscle, additional dietary nutrition is necessary. A large amount of fatty and fried foods will further aggravate the situation.
If the reason for the increase in the number of heartbeats is the presence of hemorrhage, then you must immediately go to the hospital. The presence of ulcers in the stomach or duodenum is especially dangerous for the body. In the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, nausea and vomiting may occur in parallel. An additional feeling of panic arises. It is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with sedatives to resolve this disorder.
Sometimes the reason is not so dangerous to health. For example. Such manifestations can occur after intense physical activity or stress. Sometimes intense stress occurs due to overeating. The most dangerous for the body will be disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, the thyroid gland, and infectious diseases.