Is it possible to determine pregnancy using a general blood test?
A general blood test is a typical laboratory test performed as part of planned or separately prescribed activities. It is taken regardless of age, gender and the current state of the body, and allows you to basicly determine the main blood parameters.
As part of the natural process of pregnancy, the indicated parameters change due to changes in the body, modification of the hormonal profile, and other circumstances within normal limits.
Typical changes in general blood test parameters during pregnancy:
- Decrease in hematocrit and hemoglobin levels at the end of the second trimester;
- An increase in the level of leukocytes from the second half of pregnancy until the last month.
The indicators of red blood cells, reticulocytes, platelets, basophils, neutrophils and other components fluctuate within the normal range for women of the corresponding age who are not carrying a fetus.
However, despite the fact that changes in the above parameters are characteristic of the normal course of pregnancy, they are never taken as confirmation of the current condition.
The main reason is the absence of an obvious marker indicating the launch and development of the basic process. Such fluctuations are characteristic of a wide range of physiological conditions, internal diseases, and the external influence of a huge number of factors. The main test to detect pregnancy is a blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin.
Clinical blood test during pregnancy: how much, when and why?
Blood is a liquid tissue of the body, which consists of plasma, consisting of 90% water and 10% proteins, trace elements and blood cells (leukocytes, platelets, red blood cells). A general clinical blood test is an important test during pregnancy to monitor the condition of the expectant mother, as it quickly reveals changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
At an early stage during registration, a blood test can identify changes in a woman’s body that existed even before pregnancy, which can have an adverse effect on the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. For example, a low hemoglobin content in a woman’s blood, detected early, very often leads to disruption of the proper development of the placenta and fetal growth retardation. At 18 weeks, a clinical blood test shows how much a woman’s body is adapting to the changes caused by pregnancy. Most often, by taking the test within these periods, it is possible to assess the initial changes and begin treatment in a timely manner if necessary. If any deviations are detected, the frequency of this analysis is increased to assess the dynamics in the patient’s condition and the effect of the treatment.
Blood collection for analysis can be done in two ways. The most common is to take blood from the fingertip. For this, a special needle is used - a scarifier. It allows you to make a neat, almost painless puncture, from which blood is drawn with a special tube. The second method is to take blood from a vein. This method has recently begun to be used much more often in adults. This is explained by the fact that to perform analysis on modern, more accurate instruments, you need a larger amount of blood than can be drawn from a finger. In this case, blood is usually drawn into a vacuum tube containing a special preservative for transporting the blood sample from the collection site to the laboratory where this analysis will be performed. It must be remembered that the standard indicators for taking blood from a vein and from a finger may differ slightly.
To obtain more accurate results, it is best to take a blood test in the morning on an empty stomach; at least 8 hours should pass after the last meal.
A clinical blood test allows you to get an idea of the quantity and quality of cells contained in the blood, and to assess the ratio of blood cells and plasma.
Blood test during pregnancy: red blood cells and hemoglobin
Erythrocytes are so-called red blood cells filled with iron-containing protein - hemoglobin. The main function of these formed elements is to transport oxygen to tissues. They are formed in the red bone marrow and live in the bloodstream for about 120 days. The normal number of red blood cells is 3.9–4.7 x 1012 per 1 liter of blood (normal values may vary slightly in different laboratories). During pregnancy, serious changes occur in a woman's cardiovascular system. First of all, there is a significant increase in circulating blood volume, which begins already in the first trimester of pregnancy, reaching its maximum by the 36th week. This occurs mainly due to an increase in blood plasma volume (by 35–47%), although the number of circulating red blood cells also increases (by 11–30%). Since the percentage increase in plasma volume exceeds the increase in the number of red blood cells, so-called physiological anemia of pregnancy occurs. The number of red blood cells in the blood of pregnant women usually varies depending on the trimester: for example, in the first trimester the normal value is 4.2 x 1012 per 1 l, in the second trimester it can decrease to 3.5 x 1012, in the third trimester the average normal value is 3 .9 x 1012 in 1 liter of blood.
Hemoglobin is a protein contained in red blood cells and performs the so-called respiratory function. Hemoglobin, binding oxygen, transfers it to organs and tissues, taking carbon dioxide from them. The normal hemoglobin content in the blood of a healthy woman is considered to be 120–150 g/l. During pregnancy, there is also a slight physiological decrease in hemoglobin levels. So, in the first trimester, its level can be 115–135 g/l, in the second – 112–130 g/l, in the third, a decrease in hemoglobin level to 110–125 g/l is considered physiological.
Red blood cells and hemoglobin: possible deviations from the norm
Most often, a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a decrease in the number of red blood cells and the hemoglobin content in them. This condition is called anemia. Anemia can exist before pregnancy (in this case it is diagnosed in the early stages) or develop during it, which is manifested by a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells, determined in the 2nd or 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. Most often, the cause of anemia during pregnancy is an increased consumption of iron reserves, insufficient intake of iron from food or a lack of vitamins that improve the absorption of iron - folic acid, vitamin B12, B6, C. The diagnosis of true anemia is confirmed by detecting red blood cells of altered size in a blood test (anisocytosis ) and form (poikilocytosis). If anisocytosis is an early sign of anemia, then poikilocytosis is observed in moderate and severe cases. In mild anemia, hemoglobin decreases to 90 g/l, moderate anemia - to 80 g/l, a decrease in hemoglobin below 80 g/l is a severe degree of anemia. Iron deficiency anemia can lead to miscarriage, premature placental abruption, intrauterine growth retardation, fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen), labor abnormalities, and massive bleeding in the postpartum period. Other forms of anemia, for example, due to massive destruction of blood cells or general inhibition of the hematopoietic system, are much less common and are not associated with pregnancy. If anemia is present, a clinical blood test is examined once a month. In addition, if anemia is detected, the doctor must prescribe a biochemical blood test, evaluate liver function and the concentration of iron in the blood, as well as proteins involved in iron metabolism.
An increase in the number of red blood cells in the peripheral blood occurs when the body is dehydrated, for example, with severe vomiting during pregnancy, with diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, kidneys, and with diseases of the blood system. In addition, a slight increase in the number of red blood cells may occur in professional athletes and residents of high mountain areas, where the concentration of oxygen in the inhaled air is reduced.
Blood test during pregnancy: leukocytes
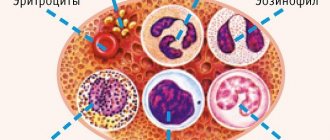
Leukocytes are so-called white blood cells that play a major role in protecting the body from infections, participate in the neutralization of microbial agents, and protect the body from its own damaged cells. White blood cells vary in structure and purpose. Among them are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils), as well as lymphocytes and monocytes. The percentage of individual types of leukocytes in the peripheral blood is called the leukocyte formula. It is calculated per 100 leukocytes. The leukocyte formula allows the doctor to visualize which leukocytes are numerous and which are few. This makes it possible to determine the presence and severity of the inflammatory reaction in the body, the presence of diseases of the blood system.
Normally, the number of leukocytes is 4–9 x 109 in 1 liter of blood. During pregnancy, due to the restructuring of the immune system, the number of leukocytes can gradually increase (this is called physiological leukocytosis) up to 10 x 109 in the second trimester and 10-13 x 109 in the third. The increase in leukocytes occurs mainly due to neutrophils, which will affect the ratio of cells in the leukocyte formula.
Use the new convenient service “List of tests during pregnancy”
Leukocytes: possible deviations from the norm
A significant and sharp increase in the number of leukocytes is observed in infectious diseases. This may be an acute infection or an exacerbation of a chronic disease during pregnancy. Therefore, an increased number of leukocytes in a blood test alerts the doctor and forces him to carefully look for the cause of this increase. In this case, the leukocyte formula is also necessarily assessed. An increase in the number of lymphocytes indicates a current viral infection or diseases of the blood system; a decrease in the level of lymphocytes may indicate a severe viral infection or cancer. Neutrophils increase during infections caused by bacteria, stress, poisoning, and a decrease in their number in a blood test indicates the presence of a viral, fungal or chronic bacterial infection.
An increase in the number of monocytes in the leukocyte formula indicates the presence of a viral or bacterial infectious process; their number may also increase in diseases of the blood system. A decrease in their level occurs with long-term treatment with glucocorticoid hormones.
An increase in the number of eosinophils most often indicates a current allergic process or helminthic infestation. A low level of eosinophils occurs in cases of heavy metal poisoning, severe purulent infections, and injuries.
An increase in the number of basophils is also observed during allergic reactions, some infectious diseases, and pathologies of the blood system, and a decrease can occur with excessive thyroid function, stressful situations, and pneumonia.
A decrease in the number of leukocytes in the peripheral blood is observed with anemia, exhaustion, viral infections, tumor diseases of the hematopoietic system, while taking antibiotics and drugs that inhibit the growth of tumors.
Blood test during pregnancy: platelets
Platelets are blood cells involved in clotting processes. When tissues are damaged, they “stick” to each other and stick to the site of damage to the vascular wall, forming a temporary clot. In addition, they secrete special substances - blood clotting factors, which trigger further processes to stop bleeding. The lifespan of a platelet in the bloodstream is 7–10 days. The normal platelet level is 180–320 x 109 in 1 liter of blood. During the first trimester of pregnancy, there may be a slight increase in platelet counts. This occurs due to the activation of some parts of the blood coagulation system at the stage of attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity; in the second and third trimesters, it can decrease due to physiological dilution of the blood to 150–160 x 109 in 1 liter of blood.
Platelets: possible deviations from the norm
A general blood test may reveal a decrease in the number of platelets. Typically, this disease is hereditary or associated with changes in the body’s immune system and most often begins before pregnancy, but can be first identified during examination of a pregnant woman when she is registered at a antenatal clinic. In addition, a decrease in platelet count can be caused by certain medications, infections, allergic reactions, and diseases of internal organs. Since platelets are involved in the hemostasis system (stopping bleeding), when their number decreases, there is a danger of massive bleeding.
An increase in platelet count is rare and can be observed against the background of iron deficiency anemia, infections, malignant tumors, and hereditary diseases. When the number of platelets in the blood increases, there is a risk of blood clots (blood clots) forming in the vessels of the placenta and other organs of the pregnant woman.
If the number of platelets changes, an additional analysis of the activity of the blood coagulation system is performed.
Blood test during pregnancy: hematocrit
Hematocrit is the proportion of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets) to the total blood volume, expressed as a percentage. In non-pregnant women, the hematocrit is normally 36–42%; in pregnant women, by the third trimester it can decrease to 31–39.5%.
Hematocrit: possible deviations from the norm
A decrease in hematocrit occurs with anemia, with an increase in the concentration of proteins in the blood. An increased value of this indicator can be observed with dehydration and diseases of the blood system.
Blood test during pregnancy: ESR
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a laboratory indicator that can change under various pathological conditions. Since the weight of red blood cells is higher than the weight of blood plasma, under the influence of gravity they settle to the bottom of the test tube with the added anticoagulant solution. Normally, ESR is 2–15 mm/h in non-pregnant women. Changes in the protein composition of the blood during pregnancy lead to an increase in ESR during this period. In pregnant women in the first trimester, ESR increases to 13–21 mm/h, in the second to 25 mm/h, in the third it can reach 30–35 mm/h.
ESR: possible deviations from the norm
The sedimentation rate depends on various factors, for example, on the number of red blood cells or proteins that make up the blood plasma. During inflammatory processes in the body, an increase in the concentration of inflammatory proteins in the plasma leads to an acceleration of the process of erythrocyte sedimentation. A decrease in ESR is possible, for example, during fasting, but since the ESR rate is counted from 0, it is impossible to track the decrease.
Thus, a general clinical blood test is considered one of the most important diagnostic methods of modern medicine. It is a necessary study for all pregnant women, allowing the attending physician to promptly notice adverse changes in the body of the expectant mother, prescribe the necessary treatment in a timely manner and prevent serious complications from the health of the expectant mother and her baby.
What is hCG?
A universal, accurate and modern laboratory test that allows you to confirm pregnancy is a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
HCG is a specific hormone produced by syncytiotrophoblast, a component of an already fertilized egg.
The hormone consists of two types of units and is necessary to stimulate the active growth of the placenta through a complex effect on the woman’s body.
The hormonal effect of hCG is based on accelerating the production of progesterone and estrogen from the first weeks after fertilization, the protective function of the corpus luteum, and correction of the immune background for normal acceptance of the fetus. In addition, human chorionic gonadotropin activates the adrenal glands and gonads in the fetus.
The essence of the analysis is to identify a unique hCG in biological fluid. The designated component is de facto produced from the first hours after successful conception, but cannot be immediately detected by available modern methods. In the blood, hCG is determined 6-8 days after fertilization. Up to 9-11 weeks of pregnancy, its concentration increases rapidly, after which it gradually decreases and disappears 5-7 days after birth.
When can a human chorionic gonadotropin test show pregnancy?
With the current technological level of modern medicine, an analysis for the presence of hCG in the blood allows one to determine the presence of pregnancy 6-8 days after successful fertilization.
It should be noted that in such an early period the chances of a false negative result are quite high, since the intensity of hormone production depends on a number of factors, including the current state of immunity, hormonal levels and other circumstances, both internal and external.
With a high degree of probability, pregnancy is detected 10-12 days after fertilization.
Up to 10-11 weeks, the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin increases rapidly. The hormone supports the functioning of the corpus luteum until the planet begins to independently produce estrogen and progesterone. From the 12th week, the growth of the parameter stops , and it gradually decreases until delivery, remaining to circulate in trace quantities for another 1 week after delivery.
You will find a detailed explanation of the analysis for hCG during pregnancy in this article.
How to prepare for research?
No special preparation is required for the test for human chorionic gonadotropin. General recommendations:
- Eating stops 10 hours before taking biomaterial . Most often, venous blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach;
- 12 hours before the test, any physical and emotional stress is excluded;
- Fluid intake is limited 3-4 hours before blood sampling;
- If possible, you should temporarily stop taking any medications , especially hormonal drugs (48 hours before the test). If this is impossible, you should definitely report the problem to the gynecologist who referred the woman for analysis.
As part of the hCG test procedure, a specialized specialist may prescribe a series of studies in which biological material is collected 3 times within 48 hours. This procedure allows you to track changes in hormone concentration over time. Accordingly, the above recommendations should be followed taking into account the indicated time interval.
Indications for use
An hCG test is carried out at the beginning of the first trimester, from the very beginning of a missed period. If a woman has no suspicions of pregnancy, rapid tests show a negative result and no changes in her health are observed, you can postpone going to the clinic.
In addition to mandatory studies, an hCG test may be prescribed in the following cases:
- suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy;
- suspicion of multiple pregnancy;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- the woman is at risk of having a child with Down syndrome;
- increased risk of miscarriage or missed pregnancy;
- the woman was exposed to radioactive radiation.
If these indications are not available, the hCG level can be determined at 10 weeks of pregnancy. If the pregnancy is progressing properly, a later analysis may be performed at 15–17 weeks. In this case, an examination is carried out to confirm the absence of pathologies in the fetus. This blood test is called a triple detailed test. With its help, you can find out not only the level of chorionic hormone, but also the content of gonadotropin, estriol and AFP.
Decoding the analysis results
Direct examination of the collected venous blood is carried out using the method of enzyme immunoassay of the serum of the obtained biomaterial.
The results of the procedure are actually available 1.5-2 hours after the procedure is completed , however, the final timing is affected by the distance of the material collection point from the laboratory, the issuance regulations (via the Internet or paper forms), and so on.
Most domestic laboratories measure the concentration of hCG in mU/milliliter. Summary average results of potential gestational ages:
- Absence of pregnancy – 0-5;
- From 3 to 7 days – 5-25;
- From 1 to 2 weeks – 25-150;
- From 2 to 3 weeks – 100-4500;
- From 3 to 4 weeks – 1100-31000;
- From 4 to 5 weeks – 2500-82000;
- From 5 to 6 weeks – 23000-150000;
- From 6 to 7 weeks – 27200-230000;
- From 7 to 11 weeks – 29000-290000;
- From 11 to 16 weeks – 6200-102000;
- From 16 to 21 weeks – 4700-80000;
- From 21 to 39 weeks – 2700-78000.
The indicated parameters of potential concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin are averaged. Specific values and units of measurement may vary depending on the calculation methodology, equipment and other factors in the laboratory.
False positive hCG result
False-positive laboratory test results for human chorionic gonadotropin occur in the vast majority of cases in various pathologies. The most typical cases:
- Active processes of formation of malignant or benign tumors. We are talking about both women and men. In the absence of pregnancy and a high concentration of hCG in the blood, underlying problems are most often found in the testicles, uterus, lungs, and kidneys. In addition, such findings may indicate choriocarcinoma;
- Recent miscarriage. If fertilization is successful, but the fetus subsequently dies, the hormone circulates in the blood for some time, identifying a false positive result;
- Bubble drift. As part of the pathology, the product of conception does not develop, and the chorionic villi grow in the form of specific round formations filled with liquid;
- Sharp fluctuations in hormonal levels. Occurs in all women of reproductive age and adolescence.
Why do pregnant women have special norms?
When a girl's uterus is fertilized, the amount of hormones produced (chorionic gonadotropins) increases significantly in the first two weeks. At the same time, beta globulin appears in the body.
Together they affect not only the circulatory system, but also the entire body of the expectant mother.
The readings of an ordinary woman and a pregnant woman in the early stages will differ, although the difference in some points is insignificant.
What increases in the blood during pregnancy
The most important point is to increase its total volume in the body.
Accordingly, because of this, the percentages of various microelements change dramatically. Changes in hormonal levels affect the production and enlargement of red cells.
During pregnancy, almost all indicators of blood components increase slightly.
Doctors have already managed to establish certain patterns, so the conditions for a pregnant woman make it possible to establish acceptable values. The absence/presence of a specific disease is determined by changes in indicators.
False negative test response
A false-negative human chorionic gonadotropin test result usually indicates that testing was performed too early. Despite the fact that modern diagnostic methods make it possible to detect the hormone 1 week after fertilization, when using outdated equipment as part of the study of biomaterial, it sometimes leads to negative indicators.
Other reasons:
- Taking hormonal medications. When using oral contraceptives, “emergency” drugs for early termination of pregnancy and other medications, the risks of a negative result increase;
- Failure to comply with preparatory measures or errors in collection/transportation/storage of biomaterial. The sample may be spoiled by externally indicated circumstances;
HCG is elevated: reasons and what to do
In some cases, with a successfully diagnosed pregnancy, confirmed by an examination by a gynecologist and an ultrasound scan, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin is significantly higher than it should be when actually calculating the age of the fetus. Possible factors that can provoke abnormal results:
- Toxicosis in the active phase;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Background activation of diabetes mellitus in a expectant mother;
- Regular use of synthetic gestagens;
- Incorrect calculation of the timing of actual pregnancy;
- Various pathologies of fetal development;
- Formation of a hydatidiform mole, benign or malignant neoplasm.
Regardless of the circumstances, the gynecologist should be familiar with the test results. He will refer the patient for additional examination and, if necessary, prescribe corrective therapy.
Causes of low hormone levels
A decrease in the level of human chorionic gonadotropin as part of the natural process of bearing a baby can be caused by the following reasons:
- Initially incorrect determination of the timing of the actual pregnancy;
- Retarded embryonic development;
- Complex placental insufficiency;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Risk of miscarriage;
- Fetal death.
If there is a significant decrease in the concentration of hCG, it is necessary to urgently contact a gynecologist, who will prescribe an unscheduled ultrasound, conduct a direct examination and other measures, if necessary, in order to accurately identify the type of pathology and develop an individual plan for further actions.
After a positive hCG became negative: reasons, what to do
Changes in the level of hCG in the blood have a clearly visible trend - a dynamic sharp increase in concentration up to the 11th week of pregnancy, followed by a slow decrease until childbirth. A significant discrepancy with such a scheme may be caused by the following reasons:
- False positive result of the first test;
- Fetal growth retardation;
- Ectopic or frozen pregnancy;
- Threat of miscarriage, death of embryo.
If a woman has previously been diagnosed and confirmed pregnant, she should immediately contact a gynecologist - most likely, urgent hospitalization will be necessary.
In the same case, when the test was taken for the first time, but pregnancy was not confirmed, it is worth undergoing a comprehensive examination to make sure there are no tumors or to identify a potential hormonal imbalance.
What is a general blood test?
Blood tests during pregnancy are a mandatory procedure that can be performed in every hospital.
This moment does not require special expensive equipment or qualified specialists, and needles in the 21st century do not cause pain.
To do this, just go to the nearest hospital and make an appointment.
The process itself takes a few minutes, and the results are sent to the doctor the next day.
Why is a general blood test prescribed during pregnancy?
A general blood test during pregnancy will help to promptly detect diseases that are in the early or late stages. In this case, in the practical majority of cases, the cause becomes known, that is, treatment will be quick and effective.
The examination is based on the natural characteristics of cells (number of platelets, leukocytes, red blood cells, hemoglobin level). Based on it, many conclusions can be drawn, including about the condition of the unborn child.
How much does it cost and where can I get tested for human chorionic gonadotropin?
Analysis for the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in venous blood is carried out both in government institutions (hospitals, clinics, maternity hospitals, etc.) and in private centers.
HCG testing is included in the compulsory health insurance policy and is performed free of charge at government institutions. Private laboratories set a price tag of 500 to 1000 rubles for a one-time collection of material with interpretation of the results. The dynamic procedure will cost 1500-3000 rubles.
Conducting and transcribing the study
The material is submitted for research in the morning. It is recommended to give up breakfast, drinking alcohol, smoking, tea or coffee. The last meal should be in the evening, no later than 20-21 hours. To get tested, you must contact the laboratory, saying the name of the study. How long will it take for the result to be ready and whether it can be obtained urgently depends on the laboratory in which it is carried out.
You can get tested in any city, be it Krivoy Rog or St. Petersburg, in a private laboratory. No one will forbid you to go to the laboratories of a public clinic. But there are often long queues in public clinics, so it is important not to miss the deadline for the test indicated in the referral by the obstetrician-gynecologist who is observing the woman.
The cost of the test depends on the level of the laboratory and the speed of the result. In any case, its price is not high relative to its great information content and importance.
The results of the hCG test are interpreted using special tables that indicate the normal level of hormones by week of pregnancy. This table shows whether conception has occurred if the test is carried out in the early stages, and also whether the fetus has developmental pathologies if the test is carried out in the 2-3 trimester.
Other ways to determine pregnancy
In addition to the hCG blood test, there are other methods for detecting pregnancy. The most effective:
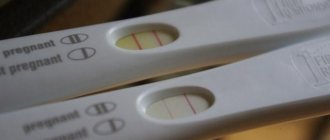
- Express tests. They are sold everywhere through pharmacy chains and used at home. Identical to the basic blood test, the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin is also detected, only in the urine. Modern means have a factual reliability of 85-90 percent, but it should be borne in mind that the hormone appears in the designated biological fluid later than in the blood - on average 2-3 weeks after successful fertilization;
- Physical examination by a gynecologist. A classic technique that allows you to detect pregnancy with a high degree of reliability if a specialized specialist has the appropriate level of qualifications. Allows you to diagnose the presence of a fetus 1.5 months after fertilization;
- Ultrasound. The main instrumental way to confirm and track the current level of fetal development. The fertilized egg is detected 5 weeks after fertilization. The embryo itself is in 7 weeks.
Pregnancy hormone detection
The first signs indicating conception appear 13–15 days after fertilization of the egg. If the monthly cycle is not disrupted, menstruation should begin at this time, but during pregnancy there is a delay. As medical practice shows, rapid tests often show a false result.
That is why, if there is a suspicion of an “interesting situation,” it is wiser to immediately go to the clinic and take the appropriate test. Many girls do not know what a blood test for pregnancy is called. In clinics and hospitals it is called a hCG test. The abbreviation hCG stands for human chorionic hormone.
This specific protein begins to be produced by chorion tissues after conception; its level begins to increase already 6–8 days after fertilization of the egg. Human chorionic hormone synthesizes the production of other biological components that help the body maintain pregnancy. It is by its quantity that pregnancy can be determined.
Protein chorionic hormone contains 2 components: beta and alpha. In the early stages of pregnancy, only the alpha component, which has a unique composition, is studied. In a non-pregnant woman, its level does not exceed 5 mU/ml. But if fertilization has occurred, its concentration will be increased, and it will increase every 2-3 days.