What does low protein mean during pregnancy?
Content
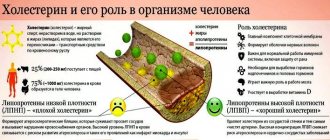
The term “total protein” refers to the total concentration of globulin and albumin in the blood.
Total protein in the body performs the following functions:
- participates in immune processes;
- participates in the process of blood clotting;
- performs the transport function of blood.
Thanks to proteins, blood has a certain fluidity, viscosity and a certain formed volume in the vascular bed, so we can say that protein reflects the state of homeostasis.
During pregnancy, a woman needs to undergo many different examinations. The most effective diagnostic method is a urine test, as it shows the functioning of the urinary tract. It is this analysis that helps prevent possible deviations during pregnancy. 120 mg. — daily norm of protein content in urine. Fluctuations in this indicator may be associated with physical activity and stress.
An increase in the level of protein in the urine during pregnancy indicates symptoms of nephropathy (preeclampsia). This disease is a pathological process in the kidneys that occurs only during pregnancy. Swelling and high blood pressure are also symptoms of gestosis. If this disease is detected in time, it helps to avoid the future occurrence of diseases such as eclampsia and preeclampsia (convulsions, development of cerebral edema). For this reason, protein levels must be checked throughout pregnancy.
The protein norm during pregnancy is from 63 to 83 g/l. A decrease in its level in the blood is not a pathology; an increase in the concentration of protein in the blood serum indicates that the blood is thickening in the body and dehydration is occurring. Low protein during pregnancy indicates the presence of diseases that occur with a decrease in overall nutrition, which is a dangerous phenomenon for a pregnant woman. A sufficient presence of protein during pregnancy ensures: optimal functioning of the anticoagulant and coagulation systems, development and growth of the baby, uterus, mammary glands, placenta, and immune defense of the body.
It is important! The metabolism of protein in the body directly depends on its intake from food. Therefore, pregnant women really need to eat properly and nutritiously. The health of her unborn child depends on what and how a pregnant woman consumes.
What is proteinuria and what are the reasons for its development?
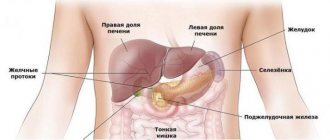
Urine is a filtrate obtained by the passage of blood through the urinary system, namely the glomerular filters and renal tubules.
Every woman during pregnancy, according to established standards, must regularly undergo a urine protein test to determine the functional capacity of the kidneys. The amount of protein that is considered normal is 0.033 g per liter of urine. If the indicator exceeds this value, what does this mean? This means that there are certain causal factors. A high protein ratio in the urine is called proteinuria.
The increase in protein particles in the urine is due to “renal” reasons:
- Pathological changes in the walls of blood vessels of glomerular filters, as a result of which the membrane allows large molecules, including protein particles, to pass through.
- A decrease in the intensity of blood supply to the kidneys for any reason also contributes to stagnation of blood in the glomeruli, which causes the presence of protein in the urine.
- Tubular pathology of the kidneys, when the reabsorption of protein is impaired.
Significant loss of protein along with urinary fluid can lead to the following consequences:
- Decrease in the content of blood protein fractions (normally, blood protein (total fraction) should be no less than 65 and no more than 85 g/l, and the albumin fraction should be from 35 to 50 g/l);
- Increased blood pressure due to increased levels of antidiuretic hormone and aldosterone in the patient’s blood;
- Fluid is retained in the body, the permeability coefficient of the vascular walls increases, resulting in the development of edema syndrome;
- The level of various lipid fractions increases significantly (hypercholesterolemia);
Protein in the urine during pregnancy may appear due to the development of gestosis. With severe gestosis, atrophy of the epithelial layer occurs in the renal tubules and membranous nephropathy develops (as with glomerulonephritis).
However, pregnancy cannot be the only cause of proteinuria. The appearance of protein in the urine of pregnant women is explained by the presence of any abnormalities in the functioning of the urinary system.
There is an established norm for protein in urine during pregnancy, information is given in the table below.
| Protein in urine during pregnancy: norm, table | |
| Morning urine | Up to 0.033 g/l or complete absence/traces of protein |
| Urine collected per day | From 0.025 to 0.150 grams in the daily urine volume |
If an increase in protein concentration in the urine of a pregnant woman is initially detected, another urine sample should be taken for repeated laboratory analysis. Why can proteins appear transiently and insignificantly in the urine? Failure to follow certain rules when submitting material for analysis may cause a false positive result.
How to properly collect urine (morning):
- Immediately after sleep, empty your bladder; urine should be collected in a clean container (all of it!);
- First, you should wash the external genitalia with clean water and cover the vagina with a cotton swab;
- Then you should pour 100-150 ml of urine into a special plastic container;
- Urine must be delivered to the laboratory within 2-3 hours after collection.
Low protein in the blood
Hypoproteinemia (low protein levels in the blood) indicates the following changes:
- increasing blood volume in the body;
- pregnancy;
- prolonged immobilization;
- lactation period.
Hypoproteinemia can also be observed in the following cases:
- liver diseases that provoke disruption of protein synthesis (parenchymal hepatitis, metastases, carcinomas, tumors or cirrhosis of the liver;
- problems of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, enterocolitis);
- cancerous formations;
- thermal burns leading to protein breakdown;
- a large amount of water in the body;
- Diets, fasting, refusal to eat are the reasons for insufficient protein intake in the body;
- inflammatory bowel diseases, which result in a decrease in the digestibility of proteins in the body;
- poisoning;
- surgical interventions and injuries;
- kidney disorders such as glomerulonephritis;
- frequent and/or prolonged bleeding;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland - thyrotoxicosis;
- Hereditary diseases - Wilson-Konovalov disease, etc.
Other proven methods
In addition to diet, there are other ways to adjust protein levels.
Folk remedies
The following can be used as folk remedies to reduce the concentration of protein in the blood:
- consumption of cranberry juice (lingonberries, cherries, red currants are also suitable);
- consumption of infusions of birch buds, parsley, corn cob;
- consumption of fir decoctions, pumpkin seeds;
- consumption of bee products.
If you want to correct the overall blood picture through the use of traditional medicine, it is important not only to take into account all possible individual characteristics and intolerances of the body, but also to seek advice from a general practitioner or nutritionist who is observing you.
The following pharmaceuticals are used as methods of drug therapy:
- intended to lower blood pressure;
- inhibitors in general;
- immunosuppressants;
- drugs to correct sugar levels (for diabetes).
The choice of dosage forms in each specific case should be made exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the individual needs and characteristics of the patient’s body, as well as the nature of each case separately.
Increased protein during pregnancy
Low hemoglobin (protein level in the blood) is a fairly common phenomenon during pregnancy, but what are the dangers of increased protein during pregnancy?
Due to physiological changes in the pregnant woman's body, a gradual decrease in hemoglobin levels occurs.
An increase in protein levels occurs as a result of external, internal, and sometimes hereditary factors. A high level of hemoglobin is observed in women who smoke; for this reason, in order to avoid harmful consequences, when planning pregnancy, it is recommended to get rid of this bad habit several months before pregnancy. Also, an increase in protein levels in the blood can be caused by the condition of the kidneys and heart of the pregnant woman.
With a high hemoglobin level, a woman may experience:
- Visual impairment;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system;
- Drowsiness, fatigue;
- Lack of appetite.
These symptoms are very similar to those observed with reduced protein, so during pregnancy you need to donate blood regularly, since increased hemoglobin affects the thickness and viscosity of the blood.
High hemoglobin levels can lead to fetal death in the first trimester or fetal hypoxia. Thick blood with high protein cannot sufficiently saturate the amniotic fluid with nutrients, for this reason the child dies or slows down its development.
It is important! It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids at the first sign of an increase in protein levels. If it is elevated for a long time, you need to consult a hematologist and undergo a course of treatment.
It is not recommended to take vitamins without a doctor's prescription (they contain B vitamins, folic acid, zinc and copper, which promote the absorption of iron, which leads to an increase in hemoglobin).
Experts have noticed that increased hemoglobin in women in the first trimester of pregnancy leads to fetal birth around the fifth month. Because of this, during pregnancy it is necessary to monitor the level of protein in the blood since it greatly affects both the baby’s body and the mother’s body.
It is important! Self-medication is not the best way out of this situation. At the first signs of changes in hemoglobin, you should consult a doctor; the protein level should be constantly checked.
Due to physiological changes in the pregnant woman's body, a gradual decrease in hemoglobin levels occurs.
Reduced total protein in the blood during pregnancy: the norm, how to increase it
Proteins are high-molecular organic compounds that are called the basis of life. The terms “proteins” and “polypeptides” are synonyms for the concept “protein”. The absence of polypeptides in the human diet causes severe disturbances in his metabolism. If the protein in the blood of the expectant mother is reduced during pregnancy, this can lead to complications in the development of the fetus.
Proteins consist of α-amino acids connected by peptides. There are twenty varieties of amino acids that are significant for people. The absence of even one out of twenty amino acids in a person’s diet can impair his health. Some of them are synthesized by the human body itself, and some can only be obtained from food containing proteins - meat, fish, poultry, nuts, dairy, beans, grains. Fruits, vegetables and berries contain significantly less protein. Mushroom polypeptides are not digestible by humans at all.
In the early thirties in the USA, laboratory studies of plasma osmotic pressure in pregnant women showed its relationship with the amount of protein consumed by women. Scientists M. Strauss and R. Ros, who conducted the research, found that the threat of eclampsia and miscarriage increases significantly if protein levels in the blood of pregnant women do not correspond to the norm. Later, the results of the scientists' research were tested and confirmed - the dependence of the normal development of the fetus on the level of protein in the blood of the expectant mother became a medical fact.
Include cottage cheese in your diet
Curd cheese is a delicious product that is also rich in protein. One serving (225 grams) contains about 25 grams of protein and 220 calories. A 2020 study found that cream cheese makes you feel as full as eggs.
What's more, the fatty variety is an excellent source of healthy cholesterol and can help with weight loss and lead to improvements in body composition.
One experiment was carried out on women who ate a lot of protein and dairy products, while exercising and trying to eat fewer calories. They lost more abdominal fat and gained more muscle mass than women with average protein and dairy intake.
Curd cheese is delicious on its own. You can try it with nuts or seeds, cinnamon, stevia or another sweetener for a quick breakfast. Plus, a small amount of cream cheese is a great snack.
Protein as a medical indicator
You can find out the protein level using a general blood test by looking at the “hemoglobin” column, but this type of analysis is not very informative when it is necessary to more thoroughly understand the health status of a pregnant woman. In such cases, a special blood test is used, aimed at determining the amount of key types of protein - a proteinogram.
The proteinogram shows indicators for the following types of polypeptides:
- Albumin
- Globulins (alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, beta 2, gamma)
The proteinogram column “total protein” shows the total level of albumin and globulins in the blood.
Interpretation of results
Normally, the concentration of protein C in the blood depends on age and is:
| Patient age | Protein C (%) |
| Up to 5 days of life | 17–53 |
| 5-30 days | 20 – 64 |
| 1-3 months | 21 – 65 |
| 3-6 months | 28 – 80 |
| 6-12 months | 37 – 81 |
| 1-6 years | 40 – 92 |
| 6-10 years | 45 – 93 |
| 10-16 years | 55 – 111 |
| > 16 years old | 70 – 140 |
Note:
in newborns and preschool children, low concentrations of protein C are due to the physiological immaturity of the liver.
Normal protein level
The calculation of the protein indicator is based on the weight, age and gender of a person and is on average 65-85 g/l. In men, the total polypeptide content is slightly higher than in women, but with age the gap becomes smaller and, in general, the level of polypeptides decreases.
The indicator of normal protein content in a pregnant woman is different from that of a woman in a normal state. During pregnancy, the norm for a woman’s total protein content is 60-75 g/l. If proteins are below 60 g/l, this is considered a sign of “low protein”, if above 75 g/l - “high”. As pregnancy progresses, protein levels drop, which is especially noticeable in the third trimester. This is due to an increase in the cost of proteins in the maternal body, which act as building materials in the development of the fetus.
Important! The figures given in this section are given as an example and cannot be a direct basis for drawing conclusions about a person’s health status. There is a direct relationship between the weight, age of the expectant mother and the level of protein in the blood. Racial, regional, individual characteristics, as well as the woman's history of illnesses may also be taken into account. The correct calculation of the normal level of proteins in the blood for a particular person is carried out by a specialist.
Snack on cheese
Snacking is a good way to get some extra protein into your diet, as long as you choose the right options. Many popular snacks contain little or no protein. These include chips, pretzels and crackers.
For example, 28 grams of chips contain 137 calories and only 2 grams of protein. In contrast, the same amount of cheddar cheese contains 7 grams of protein, yet has twenty fewer calories and four times the calcium. In addition to this, cheese does not particularly raise cholesterol levels even in those people who suffer from it.
Protein deficiency in pregnant women - causes and signs
A low blood protein level during pregnancy is not necessarily a sign that the woman is sick or that the fetus is at risk. But, as you know, a pregnant woman should pay attention to any, even minor, changes in her health, therefore it is important to diagnose low protein in time and know the possible causes of this phenomenon.
Signs of protein deficiency
- Insufficient weight gain in a woman during pregnancy, especially during the period from the end of the second and beginning of the third trimester.
- Increased hemoglobin (above 120 g/l) in the third trimester.
- Reduced intrauterine development of the fetus. During pregnancy, protein is used by the female body as a building material for the fetus, and the lack of its development indicates a protein deficiency.
- High blood pressure. Red blood cells are blood cells that transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. This becomes possible thanks to the protein – hemoglobin. If there is little hemoglobin in the body, then the body is forced to increase blood flow by increasing blood pressure.
- Increased production of enzymes by the liver.
- Eclampsia (complication of gestosis).
Causes of protein deficiency
- Psychological (I don’t want to eat) or physiological (I can’t eat) dietary restrictions. Psychological reasons can be due to personal motives, stress or depression, and physiological reasons can be due to disability, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system.
- Nervous shocks and stress. Intense nervous activity requires a large expenditure of energy. The source of energy is proteins and carbohydrates. With a lack of carbohydrates, the body begins to burn proteins. Protein reserves are restored worse than carbohydrate reserves, and therefore protein deficiency quickly occurs in the body.
- Food with a low content of amino acids necessary for humans can reduce the content of polypeptides.
- A woman is carrying twins or triplets. Pregnancy with two or more children increases the burden on the female body.
How to increase protein content?
Increasing the level of polypeptides in the body of a pregnant woman depends primarily on the woman herself - on how seriously she takes her health, as well as the health of the unborn child. You need to constantly monitor your well-being, take all the necessary tests on time, and be attentive to the words of your doctor. It is necessary to balance your diet, do not give up food rich in protein, eat vegetables, fruits and cereals, drink enough liquid (at least 1.5 liters per day). It is imperative to eliminate bad habits - alcohol and smoking! We must take good care of our psyche, try to avoid stress and nervous shock, and always remain calm if possible.
If these tips do not help increase blood protein, you should immediately seek the help of a qualified specialist.
Increasing the level of polypeptides in the body of a pregnant woman depends primarily on the woman herself - on how seriously she takes her health, as well as the health of the unborn child. You need to constantly monitor your well-being, take all the necessary tests on time, and be attentive to the words of your doctor. It is necessary to balance your diet, do not give up food rich in protein, eat vegetables, fruits and cereals, drink enough liquid (at least 1.5 liters per day). It is imperative to eliminate bad habits - alcohol and smoking! We must take good care of our psyche, try to avoid stress and nervous shock, and always remain calm if possible.
Low protein during pregnancy
Minor deviations are allowed due to stressful situations and physical education. Increased protein in the urine is a symptom of gestosis, a kidney pathology that occurs exclusively during gestation. Other symptoms of gestosis are swelling, high blood pressure. The last stage of the disease is cerebral edema and convulsions.
Low protein in the blood during pregnancy A mandatory test during pregnancy is a general blood test. Its composition may change due to processes occurring in the female body. The normal level of protein in the blood of a pregnant woman is 63-83 hl. A slight decrease in the indicator is acceptable. Elevated protein indicates blood thickening and dehydration of the mother’s body. Very low protein in the blood during pregnancy indicates the development of the following diseases:
- liver diseases: protein synthesis is impaired;
- chronic kidney disease, extensive burn: protein levels decrease;
- overheating of the body, thermal burn: protein will disintegrate;
- insufficient intake of protein from foods during diet, functional digestive disorders, inflammatory bowel disease;
- excess amount of water in the body of a pregnant woman.
Menu for low protein during pregnancy
Protein ensures fetal growth, protection of the expectant mother's immune system, development of the mammary glands, and normal functioning of the coagulation system. A woman carrying a child should be careful about her diet. Its menu should be very varied. A pregnant woman's diet requires regular inclusion of cereals in combination with protein-containing foods. Protein in foods for pregnant women::
- cheese;
- fermented milk products;
- milk;
- fish dishes;
- meat food;
- bird;
- legumes
It is recommended to give preference to animal proteins. They contain amino acids that are not found in plant proteins.
Why is low protein in the blood of a pregnant woman dangerous? Low protein during pregnancy often leads to a decrease in body weight, a sharp increase in hematocrit levels, and an increase in hemoglobin. If a pregnant woman's hemoglobin is more than 120 g/l, she needs medical attention. As hemoglobin increases, protein levels decrease. Blood circulation is disrupted and thickening is observed. Protein levels can be normalized. After completing therapy, the pregnant woman will need to take a repeat blood test.
- liver diseases: protein synthesis is impaired;
- chronic kidney disease, extensive burn: protein levels decrease;
- overheating of the body, thermal burn: protein will disintegrate;
- insufficient intake of protein from foods during diet, functional digestive disorders, inflammatory bowel disease;
- excess amount of water in the body of a pregnant woman.
How to increase protein in the blood during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, various changes occur in the body, which a woman can feel in her condition. But much more information is obtained by studying biochemical parameters. A blood test should be performed at every doctor's visit, and even more often if necessary. This allows you to monitor the progress of pregnancy, and if any deviations are identified, then they can be corrected in a timely manner.
One of the important blood indicators is the protein level. It is necessary to carefully monitor its concentration throughout pregnancy. Normally, certain changes in protein metabolism are possible, but they should not go beyond the scope of physiological processes. Otherwise, we have to recognize the appearance of disturbances in the body, which may affect the course of pregnancy.
Every woman should monitor protein levels when carrying a child.
What is protein
Protein is an organic polymer found in human blood, consisting of various amino acids. Its concentration in the blood serum is an important indicator of health, since the protein is “responsible” for the functioning of organs and is involved in many processes occurring in the body. Protein has an effect on blood coagulation, viscosity and fluidity, blood volume in blood vessels, the body's protective functions, the stability of the blood pH value, the transport of pigments, steroid hormones, bilirubin and lipids through the blood vessels to all organs in the body.
General information
Protein is one of the main organic substances, which is an integral part of most structural and functional processes. It consists of a set of different amino acids. The structure of total blood protein is heterogeneous and consists of the total concentration of albumins and globulins. They are in a certain ratio, which can change under the influence of various factors. Globulins have several varieties:
- Alpha 1 (alpha fetoprotein).
- Alpha-2 (ceruloplasmin, haptoglobin).
- Beta-1 (transferrin).
- Beta-2 (C-reactive protein, fibrinogen).
- Gamma (immunoglobulins).
Proteins differ in their structure - size, molecular shape, surface charge - and the functions they perform. We can say that none of the processes can do without the presence of proteins. Their biological role is enormous; it consists in regulating and ensuring many reactions and functions of the body. The most important of them are:
- Transport of substances (hormones, vitamins, fatty acids, microelements, bilirubin, drugs, etc.).
- Providing tissue trophism.
- Maintaining oncotic pressure.
- Formation of immune defense.
- The course of biochemical reactions (enzymes).
- Participation in blood clotting.
- Components of acid-base balance.
Protein substances have a wide range of biological effects, making a significant contribution to ensuring the constancy of the internal environment of the body. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor protein concentrations when carrying a child.
Normal during pregnancy
The content of total protein and its fractions, like many blood indicators, is constant. Any changes must be within clear limits of reference values. Thus, total protein in an adult does not go beyond 65–85 g/l. During pregnancy, its concentration is slightly lower and ranges from 55 to 65 g/l. This is due to several reasons:
- Firstly, during this period a woman experiences an increase in blood volume as a result of fluid retention with increased progesterone levels. This means that the relative protein content decreases. This mainly occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Secondly, the consumption of proteins as a building material for fetal development increases.
If we consider individual protein fractions, they also change during pregnancy. Albumin levels, which normally make up 60% of total protein, also decrease, which is noticeable in the second and third trimester. But the concentration of globulins increases, which applies to all fractions, especially in the later stages.
At the same time, the albumin-globulin ratio gradually decreases relative to the generally accepted norm (1.3–1.35) and before birth often reaches 0.85–0.9. At the beginning of pregnancy, an increase in C-reactive protein may be observed, which is explained by the body's reaction to increased cell division in the fetus.
If the proteinogram indicators are within acceptable values, then there is every reason to believe that the pregnancy is proceeding normally.
There are situations when low protein is noted during pregnancy. Hypoproteinemia is an important indicator that indicates quite serious changes in the body. This phenomenon is observed in various conditions:
- Liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis).
- Kidney disease (glomerulonephritis).
- Severe gestosis (nephropathy, preeclampsia).
- Digestive pathology with malabsorption (pancreatitis, enteritis).
- Diseases of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis).
- Tumor processes.
- Immunodeficiencies.
- Injuries and burns.
- Intoxication.
- Bleeding.
- Starvation.
- Anemia.
Most of them are a dangerous pathology that can lead to undesirable consequences not only for the woman’s health, but also for the unborn child. Therefore, if a reduced concentration of protein in the blood is detected, then it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination to determine the cause of hypoproteinemia.
In order to diagnose pathology in a timely manner, a woman must undergo regular screenings during pregnancy.
There is also the opposite situation - when protein levels increase, which is called hyperproteinemia. This deviation from the norm also occurs during pregnancy and indicates no less danger. The following conditions may be the cause of high protein concentrations:
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases in the acute stage.
- Blood diseases (myeloma, macroglobulinemia).
- Diseases with dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea, polyuria).
- Autoimmune processes (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, hepatitis, glomerulonephritis).
- Severe allergic reactions.
- Pathology of the coagulation system (DIC syndrome).
In this case, an increase in globulin fractions, which are responsible for the occurrence of inflammatory and immune processes, is most often recorded. Often there is an increase in acute phase parameters: C-reactive protein, ceruloplasmin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen.
When an excess of normal proteinogram values is recorded, you should first of all find out what causes such changes.
Most often, women wonder how to increase the protein level in the blood during hypoproteinemia. Since this situation is quite common during pregnancy, you should consider some ways to normalize protein metabolism.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that led to a decrease in proteins. Without this, any measures will have only a temporary effect. The origin of hypoproteinemia can only be determined by a doctor, and taking into account the diagnosis, treatment methods will be recommended.
To normalize protein concentration, it is necessary to increase its intake from food. Therefore, pregnant women should eat properly and nutritiously. The doctor will recommend the most effective methods of dietary correction. In this case, a woman must adhere to the following rules:
When a woman wants to increase the level of protein in her body, a proper diet will be a good help. If during the examination any diseases are identified, then the nature of the diet must be adjusted in accordance with the type of pathology.
Dietary recommendations need to be given special attention during pregnancy.
Drug therapy
Any changes in the proteinogram require correction. But this must be done taking into account the underlying pathology, because a change in protein concentration is only a biochemical marker. Therefore, the prescription of drugs is carried out according to the established diagnosis and condition of the pregnant woman.
In order not to harm the fetus, only those medications that have proven their safety are used. Considering the variety of factors affecting protein metabolism, it is difficult to talk about any specific drugs. Comprehensive information can be obtained by consulting a doctor.
Thus, it is necessary to constantly monitor the protein concentration in the body at all stages of pregnancy. Identification of any deviations from the norm should be the reason for an in-depth examination, the results of which will indicate the need for certain therapeutic measures.
In this case, an increase in globulin fractions, which are responsible for the occurrence of inflammatory and immune processes, is most often recorded. Often there is an increase in acute phase parameters: C-reactive protein, ceruloplasmin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen.
The effect of protein in the blood during pregnancy
Protein in the blood ensures the normal functioning of the body. It consists of fractions of albumin and globulin, thanks to which normal blood circulation is maintained and beneficial substances quickly reach their goal. During pregnancy, a woman regularly undergoes urine and blood tests. If the protein level does not go beyond 63-83 g/l, then this is considered normal.
Elevated values indicate that the blood is thickening and the body is dehydrated. Low blood protein indicates a disease that is associated with poor nutrition and decreased appetite, which can be dangerous for the expectant mother. If the indicators are normal, then the coagulation and density of blood flow is normal, the supply of nutrients reaches the goal and the baby develops without any deviations.
Worth knowing! Total protein and its indicators directly depend on proper nutrition. A complete and balanced diet will help the expectant mother keep her indicators within acceptable limits.
Protein S
Proteins C and S are present in the blood in free and protein-bound form (it is inactive).
Only the free form is able to bind to protein C and limit blood clotting. Damage to a vessel triggers a complex process of stopping bleeding; it consists of a complex of reactions of blood vessels, platelets, proteins - procoagulants and anticoagulants (clotting and liquefying). The goal is to create a clot to prevent blood from leaking out. But the activation of the coagulation system must be limited; a minor injury cannot be allowed to lead to more thrombosis than necessary. Such limiters are the proteins of the anticoagulation cascade, which is closely related to the process of thrombus formation.
Activation of protein C takes place on the surface of the endothelium (cells lining the vessel from the inside), they carry a special protein - thrombomodulin. Thrombomodulin in combination with thrombin (coagulation factor II) converts inactive protein C into active protein, containing sites for contact with protein S and factor V (accelerin) and VIII. Protein S is necessary for the action of protein C; without it, protein C is inactive.
Protein S deficiency increases the risk of thrombosis and is transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner, i.e. all descendants, regardless of their gender. The likelihood of spontaneous thrombosis depends on the form of carriage - homozygous or heterozygous (all or half of the cells carry the defective gene).
The homozygous form manifests itself from birth as fulminant neonatal purpura, DIC syndrome in infancy with high mortality. Symptoms of heterozygous carriage will appear after puberty - a high risk of vascular thrombosis (6 times) and a reduced response to anticoagulant therapy.
Tests for suspected protein S deficiency
type I –
Source
Causes of low protein in the blood
A low level of this substance in the blood indicates hypoproteinemia, which accompanies the following changes in the body:
- increased blood volume;
- pregnancy;
- prolonged immobilization.
And also during breastfeeding.
Hypoproteinemia may occur in the following cases:
- liver diseases;
- diseases of the pancreas and intestines;
- cancerous tumors;
- thermal burns accompanying protein breakdown;
- diets with food refusal;
- in case of poisoning;
- after surgery;
- in case of kidney dysfunction;
- with regular bleeding;
- hereditary diseases;
- disease of the thyroid gland, its hyperfunction, that is, thyrotoxicosis.
What foods contain protein?
- dairy products such as yogurt, cheese, milk;
- legumes: peas, beans, lentils, soybeans, beans, chickpeas;
- fish, seafood (squid, shrimp, crab, lobster);
- poultry: chicken, turkey, goose, Indian duck, quail;
- meat;
- egg.
Worth knowing! The most important amino acids are found in animal products. The daily protein intake is 70 g.
Causes of high protein in the blood
An increase in indicators may occur for hereditary reasons. The increase in protein is especially pronounced when smoking. Therefore, it is worth giving up this habit six months before pregnancy. Also, kidney and heart disease can affect the increase in protein in the blood.
It is also worth knowing that an increase in protein in the blood can be observed during simple physiological processes, which indicates the presence of a pathology due to which increased values are formed. So, this can happen if an infectious disease develops in the body, which can result in consequences such as vomiting, diarrhea and dehydration.
Increasing protein in the body is not a random process, so you need to consult a doctor in time and undergo an examination. He will be able to make an accurate diagnosis, establish the causes and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Main reasons for the increase:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- poisoning, infections accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lymphorganulomatosis;
- chronic hepatitis;
- extensive burns;
- intestinal obstruction;
- allergies;
- diabetes insipidus, etc.