Causes of persistent cough
A persistent cough is repeated frequently and does not go away throughout the day, lasting for several weeks or months. It can be dry or wet, accompanied by temperature or occur without it. The cough reflex does not always occur due to a cold, but still the most common cause remains acute respiratory infection (ARVI) and respiratory diseases.
Constant coughing in the absence of fever or runny nose is a signal of exposure to allergic agents: dust, pollen, pet hair, household chemicals. The problem can even lie in dry air. Another factor that cannot be ignored is alcohol abuse, which results in a decrease in lung volume and swelling.
In addition to the above reasons, the following pathologies can cause the symptom:
- Inflammatory processes (especially chronic) in the throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs.
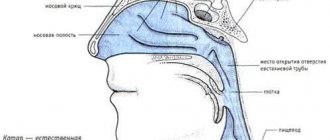
- Pathologies in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: drip syndrome (draining of an increased amount of mucus along the wall of the nasopharynx), chronic sinusitis, deviated nasal septum.
- Heart failure.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Some gastrointestinal diseases.
- Oncology of the respiratory system.
- Autoimmune diseases: tuberculosis, lupus, sarcoidosis.
- Helminthiases: infection with roundworms, lamblia, pulmonary fluke.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Mental disorders, stress. In these cases, the cause of the persistent cough is not in the respiratory tract, but in the brain.
What causes a persistent cough can almost always be determined, with the exception of 2% of cases.
This pathology is called idiopathic cough.
Diseases
The cough reflex manifests itself in certain types of diseases as follows:
- Pharyngitis. The cough is dry, barking, coming from the throat, and may sore the throat. More often appears at night.
- Laryngitis. The reflex is dry, annoying. The voice changes, viscous mucus appears, which is difficult to separate.
- Chronic frontal sinusitis. The persistent cough does not stop even after taking medication.
- Tracheitis is characterized by a dull, dry cough, especially after waking up in the morning and when the patient is in cold air.
- In chronic bronchitis and pneumonia at the initial stage, the reflex is dry, suffocating, barking, and whooping cough. As the disease progresses, sputum appears, which may contain blood.
- Bronchial asthma. The cough is unproductive or wet, often occurring at night. It gets worse in summer, after hard physical work and stress.
- Whooping cough. During the reflex, sounds similar to those of a rooster are made. The cough is paroxysmal, consisting of a series of continuous shocks (from 5 to 15). At first it is unproductive, but then becomes wet, with copious mucous secretions.
- Cystic fibrosis of the lungs. A reflex act with the release of thick mucus cannot be treated and lasts for years. It is so strong that it often causes vomiting.
- Stomach reflux. If the gastrointestinal tract does not function properly, bile enters the stomach from the duodenum. Its acids irritate the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. This leads to a persistent form of pharyngitis or laryngitis and causes a dry, persistent cough.
- Cardiological pathologies. The cough reflex is dry and worsens after exercise. The patient begins to cough when lying down because excess fluid fills the lungs. In a standing position, the reflex act weakens.
- Long-term use of medications. Patients taking tablets to normalize blood pressure (Ramipril, Enalapril) experience frequent coughing and sore throat.
- Tuberculosis begins with a slight cough, which gradually intensifies and becomes paroxysmal, sometimes convulsive. Cough can be both dry and wet. Most often it bothers you in the morning, as with bronchitis, when the patient gets out of bed. In a closed form and in the initial stages, tuberculosis can proceed without it. In some forms of the disease, the patient coughs up blood.
Men are more likely to have a persistent cough, as they are more likely to smoke. In addition, they perform heavy physical work and, to a greater extent than women, are employed in hazardous industries.
Diagnostics
To identify the causes of periodic cough in a child or adult, the doctor first conducts an initial examination to collect a detailed medical history. Depending on the information collected, methods for diagnosing diseases are prescribed:
- X-rays of light;
- analysis of sputum for color and consistency;
- blood test (general and for allergens);
- phonetoscopy;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirogram.
Attention! A chronic cough may cause a physician or pulmonologist to suspect the development of a certain disease. In this case, the doctor prescribes additional examination methods to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
The cause of this problem may be indicated by the time of day when throat irritation increases, the intensity and duration of attacks, the severity of pain in the larynx, as well as the chest.
Treatment methods
They treat not the symptom, but the root cause. To establish it, contact a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer you to specialized specialists: a pulmonologist, gastroenterologist, allergist, otorhinolaryngologist or oncologist. Only the doctor will choose the correct treatment method.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed. Pharmacies now have a large selection of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Other medications are also used, which are prescribed depending on the type of illness. It is useful to do inhalations. They dilate the bronchi, reducing spasms, speed up the liquefaction of sputum, and facilitate coughing. Drugs to strengthen the immune system must be prescribed. Massage and physical therapy are an important component of treatment.
Get rid of cough caused by allergies with the help of antihistamines (Loratadine, Suprastin, Erius). It goes away quickly if you eliminate contact with the allergen. In severe cases, hormonal drugs (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone) are used.
The cough reflex associated with nasal problems (rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis) must be treated with antibiotics and vasoconstrictors. Sometimes they resort to surgical intervention - straightening the nasal septum, removing adenoids, puncturing the paranasal sinuses.
Cough, as a result of digestive disorders, is stopped with the help of a proper diet. Food is taken in small portions, at least 4-5 times. Excluded: fried, salty, spices, alcohol, sweets. Medicines that improve the functioning of the digestive system (Almagel, Omeprazole, Cerucal), decoctions of chamomile, plantain, and marshmallow are prescribed.
To cure a smoker's cough, it is not enough to give up the bad habit. At first, after parting with a cigarette, the cough reflex intensifies, because the lung tissue must be cleared of the accumulation of nicotine toxins in order to recover. Therefore, drug treatment is used. First, medications are prescribed to suppress the cough reflex. When sputum appears, mucolytics and expectorants are used.
To relieve a dry, debilitating cough caused by lung cancer, narcotic drugs are used that reduce phlegm production and suppress the cough reflex. Decoctions of celandine, marshmallow, licorice root, and yellow poppy are recommended. Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used.
The only way to cure a frequent cough that occurs due to medication is to change the medication. If this cannot be done, then the intensity of the reflex is reduced by inhalation, gargling, and lubricating the throat with oil solutions of vitamins E and A.
Traditional medicine methods are used as an addition to drug therapy and only in consultation with a doctor. These include:
- hot foot baths;
- mustard plasters or jars;
- compresses;
- herbal decoctions and herbal teas.
There are many healthy recipes that are easy to prepare at home. They use honey, onions, garlic, milk, butter, animal fats and other products.
If the disease cannot be treated (cancer, lupus, cystic fibrosis), then it is impossible to relieve the patient of the unpleasant symptom, therefore all therapeutic measures are aimed at reducing its intensity.
Traditional medicine to help
A persistent cough can be treated using traditional medicine. The presence of serious pathologies requires the use of complex drug therapy. Herbal recipes in this case are used as a supplement. Traditional methods of treatment help with cough, having a positive effect on the body as a whole.
Painful symptoms will be eliminated by means to alleviate dry cough. Recipes for liquefying and removing sputum are suitable for prolonged productive bronchospasm. Medicinal drinks can be prepared based on rose hips, raspberries, currants, viburnum, and linden inflorescences. Tea with lemon and honey is effective for severe coughs.
Traditional medicine is widely used for the treatment of respiratory diseases, with prolonged severe cough. It is important to consider that plant components, citrus fruits and bee products can cause an allergic reaction. Before using prescriptions, you should consult your doctor.
Dry cough
A cough reflex without the release of bronchial secretions occurs during inflammatory processes of the upper respiratory tract. Several groups of drugs are used to get rid of unproductive cough.
If there is no temperature, medications are used that suppress the reflex act. For inflammatory processes, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. To stop a severe attack, take lozenges (Travisil, Doctor Mom, Doctor Theiss), do inhalations with saline or soda solution, and essential oils. Plenty of fluids, air humidification and regular wet cleaning of the house are required.
A persistent cough is a dangerous symptom that requires competent treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor, and improper use of medications can lead to serious consequences.
Cough in adults at night. How to deal with the problem?
It is impossible to give a definite answer to the question of why a person coughs at night or at other times, since various factors can affect the respiratory system. In some people the cause is a physiological reaction, in others it is a disease. Therefore, in order to provide qualified assistance, it is necessary to carry out a full examination. It is acceptable to use several simple methods to relieve nighttime coughing attacks in an adult, the causes of which have not yet been fully elucidated.
- One of the most accessible methods is warm drinking, which softens and moisturizes the bronchial mucosa. This can be mineral water, decoctions of medicinal plants, or heated milk with honey. When choosing herbs, it is better to focus on linden and chamomile. It is better not to use plants that stimulate coughing, as coughing may worsen during sleep.
- It is necessary to change the horizontal position of the body, because when sitting, sputum is separated much more easily. During an attack, you should bend over a little, then straighten up and stretch, raising both arms up.
- If your body temperature is not elevated, it is advisable to ventilate the room by letting fresh air into the room, or go outside. This will help avoid drying out the mucous membranes and make breathing easier.
- It is necessary to monitor the temperature and humidity in the room. Excessively warm and humid or cold, dry air can irritate the respiratory tract. Comfortable temperature conditions should range between +20…+22°С, permissible air humidity – more than 60%. If the humidity is less than this value, you can increase it using special devices, installing an aquarium in the room, small containers of water, or simply hanging wet towels.
- Another good way is steam inhalation with mineral water or saline solution. Carry out the procedure 1 hour before bedtime. Use medicinal herbs or inhaled medications, as well as antihistamines for an allergic reaction, only after consulting a doctor.
- A good option as an emergency aid would be lollipops that will soften the irritated larynx by activating the secretion of saliva.
- Restore normal breathing by smoothly drawing in air through the nose and just as slowly, effortlessly, exhaling through the mouth.