What it is
As pregnancy develops, the internal cavity of the baby's membrane is filled with a biologically active fluid called amniotic fluid, which creates a habitat for the unborn child. The interaction of amniotic fluid and the fetus ensures its vital processes in the womb. It performs two main functions.
- Maintaining normal metabolic processes in the development of the child.
- Protective.
The fetal fluid is rich in nutrients; by swallowing it, the unborn baby receives the necessary nutrition for development. In the early stages, this metabolic process occurs through the baby’s skin.
The protective function provides a regime of constant pressure and temperature of the living environment. It also helps absorb external shocks and shocks, which helps to significantly soften their impact. The fetus is protected from noise and loud sounds.
But, perhaps, one of the most important is protection from infectious diseases of the baby. It contains different types of immunoglobulins that provide immune processes. Therefore, the successful course of the entire gestation period will depend on the state of the amniotic fluid.
The physiology of pregnancy is designed in such a way that the fetal fluid of the amnion secretion is replaced every 3 hours. The intensity of its formation depends on the period. In the first trimesters of the perinatal period, its formation is more intense.
As a rule, it is transparent or slightly cloudy because suspended matter appears in it. They consist of:
- epidermal particles;
- hair;
- particles of original substance;
- excess proteins and fats;
- waste products of a small person.
During normal processes during pregnancy, the presence of these echogenic inclusions varies at different times:
- in the period from 32 to 34 weeks - a noticeable amount;
- in the first trimester – slightly noticeable;
- from 14 to 26 weeks – a small amount.
What is amniotic fluid
Experts define amniotic fluid with the term “amniotic fluid” and it is a liquid medium that surrounds the developing fetus. Amniotic fluid plays an important role in the formation and development of the unborn baby:
- is a kind of protective barrier that prevents the penetration of infections to the developing fetus;
- maintains a sterile environment for the baby;
- protects the fetus from the effects of various negative environmental factors.
Amniotic fluid is completely colorless and transparent, but at certain stages of pregnancy it may turn yellowish. One of the dangerous and alarming conditions is the coloration of the amniotic fluid in a pink or bloody color, as this may indicate placental abruption. When diagnosing such a pathology, it is necessary to place the pregnant woman in a medical institution, where, during an ultrasound examination, the degree of placental abruption will be determined.
What is he talking about?
For pregnant women, the question of what amniotic fluid with hyperechoic inclusions is and how dangerous they are is especially relevant.
If their presence was observed sporadically, even with hyperechogenicity, there is no need to sound the alarm. Medical practice states that the appearance of sediment in the fetal fluid in the third trimester is more a pattern than a pathology.
Waste products, epidermal cells and fatty particles of amniotic fluid, against the background of good health, are not indications for an in-depth examination.
Composition of amniotic fluid during normal pregnancy
The water shell of the fetus changes in composition during the pregnancy of a woman, but its main part is always represented by water, which makes up about 98% of the total volume of water. In the initial stages, amniotic fluid resembles blood plasma and contains proteins, fats, vitamin and mineral complexes, as well as hormones, enzymes and other nutrients.
From the moment the second trimester begins, the fluid changes in composition, dying skin cells, vellus-type hairs characteristic of the fetus, its original cheese-like lubricant and waste products appear in it, especially urine (sterile in a child). In this case, the amniotic fluid is changed every three hours.
Causes
Hyperechoic inclusions in amniotic fluid are due to the following reasons:
- infection;
- intrauterine pathologies;
- hypoxia;
- abnormalities in the development of the umbilical cord;
- detachment of the amniotic membranes;
- physiological metabolic processes in development.
All of them are dangerous for the healthy bearing of a child, and sometimes can lead to premature birth.
Diagnostics
All three methods have different indications for use. They are also used for different periods.
- Ultrasound reveals the first signs of the presence of suspension. It is safe and painless.
- Amniscopy is an examination using an amniscope, which is inserted through the cervix.
- Amniocentesis is an internal examination. It is carried out by puncturing the abdominal wall with a puncture adapter.
Ultrasound is used as a primary study. If the test reveals a large accumulation of suspended matter in the amniotic sac, additional tests are prescribed. They must confirm the presence of infections in the mother. And if doctors suspect serious fetal pathologies, they prescribe amniocentesis.
Amniscopy can be used only in later stages, when it is necessary to identify complications of pregnancy and possible post-term pregnancy. They are fraught with placental insufficiency. It is necessary to take all measures for a quick delivery. The presence of suspensions in the fluid, which confirm the detachment of the membranes, are the first signals for doctors to take emergency measures.
Treatment
The presence of suspension in amniotic fluid is not a pathology. Therefore, it is not classified as a separate disease. Their presence may indicate serious illnesses or be an individual feature of the development of a short life. Doctors, as a rule, offer treatment with phobenzine, actovegin or hofitol.
If suspensions are found in the amniotic fluid at week 20, pregnant women wonder what to do. Go to the doctor, undergo additional examination for infections and take medications for possible hypoxia of the baby.
When diagnosing the latter, do not despair. You should undergo treatment prescribed by your doctor. It should contain drugs that activate cellular metabolism and improve their oxygen supply. While taking blood thinning medications.
Suspension in amniotic fluid
Pregnancy is one of the most beautiful periods in a woman’s life, which opens up new facets of her personality, inspires and fills her soul with pleasant warmth... The expectant mother every time looks forward to meeting her baby with impatience and excitement in her chest, and let it only pass through the screen for now monitor in the ultrasound room. Carefully delving into every word from the doctor’s mouth about the condition of the fetus, you can hear: “There is a suspension in the amniotic fluid!” Well, having received such information, we do not panic, but try to understand the current situation.
What kind of “beast” is the suspension in the waters?
Suspensions are the waste products of the fetus (extraneous impurities) found in the amniotic fluid. This can be desquamated epithelium, vellus hair, elements of cheese-like lubricant (hyperechoic suspension), which belong to a fine suspension.
Such impurities, in most cases, appear at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy, are common, have virtually no effect on the development of the fetus and indicate the normal course of the gestation process.
The presence of suspension at the end of pregnancy is a sign of post-term pregnancy.
Suspension in waters at earlier times, along with other individual signs, may be associated with the presence of infection. So, for example, the cause of this may be ureaplasmosis.
Even though ureaplasma is unable to cross the placenta, the passage of a newborn through the birth canal of a mother with such a disease can be fraught with disease of the girl’s genital organs, kidneys, skin and eyes of the child.
Therefore, in the second and third trimesters it is necessary to undergo special treatment.
Weakened immunity during pregnancy and its inability to resist infections, including viral ones, can also with a high degree of probability lead to the appearance of suspensions in the amniotic fluid. Taking herbal immunomodulating homeopathic medicines prescribed by the doctor will support the immune system, and perhaps at the next examination there will be no impurities in the waters.
Sometimes an increased concentration of protein in the amniotic fluid may act as a suspension, which is a normal phenomenon, the so-called individual “constitution”.
As for meconium - original feces, which, due to intrauterine discharge, can also be classified as suspension (found in 10% of all births and up to 40% in cases of post-term pregnancy), here opinions are divided regarding its effect on the fetus.
Some representatives of medicine believe that meconium in the amniotic fluid is a sign of intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus, while others argue that there is no connection between these phenomena, and the staining of water with meconium is only a factor for identifying pregnant women at risk for preventing meconium aspiration of the newborn.
Suspension in amniotic fluid - treatment
As a rule, if only “suspension in the amniotic fluid” is diagnosed, drug treatment is not prescribed. To prevent fetal hypoxia, as a risk factor, it is recommended to take Actovegin, Hofitol, and Fobenzym.
Since the suspension determined by ultrasound at any stage of pregnancy is not a marker of its abnormal course, the following procedures can be prescribed as an additional examination and clarification of the result if chromosomal pathologies are suspected, if hypoxia is suspected (checking the meconium color of the water):
Thus, having received a diagnosis of the presence of suspended matter in the waters during pregnancy, first of all, you need to understand that while additional examinations and consultations with experienced doctors on this issue are carried out, the only real cure for your baby will be your peace of mind.
| What a woman sometimes has to listen to during pregnancy. Unclear diagnoses are scary. And sometimes it’s completely in vain. Likewise, the diagnosis of “calcifications in the placenta” sounds scary, but does not pose a serious threat. Especially if you know what mommy should do in such cases. This is what we will talk about next. | Antenatal fetal death Antenatal fetal death cannot pass without leaving a trace on a woman’s psyche. But life goes on - the body is restored after the removal of the dead fetus, the bitterness of the loss is smoothed out, the woman can try to become a mother again. And there is a very high probability that the attempt will be successful. It is only important to follow some recommendations. |
| Intrauterine growth retardation We all want to give birth to healthy children. But sometimes the mother’s illness or genetic reasons interfere with this, leading to retardation of intrauterine development of the fetus. Why this happens, what different degrees of delay mean, read our article. | Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy Retrochorial hematoma during pregnancy is not the most difficult and dangerous complication. However, it requires a special lifestyle for a pregnant woman. Why a retrochorial hematoma occurs, how to treat it, and how to properly save a child with such a diagnosis are in our article. |
Source: https://womanadvice.ru/vzves-v-okoloplodnyh-vodah
Possible consequences
Amniotic fluid with hyperechoic inclusions can have consequences only if the pregnancy is complicated. According to medical statistics, in 40% of premature births, suspensions were found in the amniotic fluid. In 17% of newborns with hypoxia, the mother also had the presence of suspensions.
The presence of infection in the mother's body is extremely undesirable. This requires treatment with antibiotics, and this is not a clear-cut issue during pregnancy. Save a child’s life, or cause irreparable damage to his health. Side effects from antibiotics can affect the development of vital organs and systems in a child.
Conception should be planned carefully. Get tested for infections in the body. If present, undergo treatment. Take a course of therapy to strengthen the immune system. And only then is the expectant mother’s body ready for fertilization and bearing a healthy baby.
Suspension in waters during pregnancy
During the long months of waiting, expectant mothers experience worries about the health of their unborn child and worry every time before the next ultrasound. It is this procedure during pregnancy that is considered the most informative and allows you to make sure that everything is fine with the child.
Some mothers, during their next study, are faced with the concept of suspensions in amniotic fluid. Of course, a lot of questions arise as to why they appear in the amniotic fluid and whether their presence is dangerous for the developing fetus.
What is amniotic fluid
Experts define amniotic fluid with the term “amniotic fluid” and it is a liquid medium that surrounds the developing fetus. Amniotic fluid plays an important role in the formation and development of the unborn baby:
- is a kind of protective barrier that prevents the penetration of infections to the developing fetus;
- maintains a sterile environment for the baby;
- protects the fetus from the effects of various negative environmental factors.
Amniotic fluid is completely colorless and transparent, but at certain stages of pregnancy it may turn yellowish.
One of the dangerous and alarming conditions is the coloration of the amniotic fluid in a pink or bloody color, as this may indicate placental abruption.
When diagnosing such a pathology, it is necessary to place the pregnant woman in a medical institution, where, during an ultrasound examination, the degree of placental abruption will be determined.
What are suspended matter in waters?
The impact of unfavorable factors on a woman’s body during pregnancy leads to clouding of the amniotic fluid and the appearance of various impurities. Suspensions that appear in amniotic fluid are dissolved waste products of the fetus.
In the case of echo determination of suspensions, which may include vellus hair, particles of cheese-like lubricant and desquamated epithelium, they are called finely dispersed. They usually appear in the third trimester of pregnancy and do not have any negative effect on the developing fetus.
If fine suspensions in amniotic fluid are detected in an earlier period of pregnancy, this may be a sign of progression of intrauterine infection or indicate infection of the expectant mother’s body.
This can lead to the development of various complications after the birth of the baby and he may be diagnosed with the following unpleasant pathologies:
- pneumonia;
- conjunctivitis;
- rashes on the skin of various types.
Sometimes the presence of suspensions in the amniotic fluid can be a sign of a high concentration of protein and this phenomenon should not cause concern to a woman during pregnancy, as it is considered normal. Amniotic fluid may contain particles of meconium, the baby's original feces.
Diagnosis of pathology
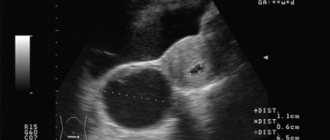
To determine suspended matter in amniotic fluid, various diagnostic methods are used:
- The safest and most informative way to detect pathology is ultrasound.
- Amnioscopy is a special method during which a device is inserted into the cervix to assess the state of amniotic fluid. Most often, this research method is used when there is a risk of developing oxygen deficiency during post-term pregnancy.
- Amniocentesis involves puncturing the bladder through the abdominal wall of the uterus. This method is used to diagnose pathology in the second trimester of pregnancy and, in addition to identifying suspended matter in the amniotic fluid, allows one to determine the chromosome set of the developing baby.
Experts pay attention specifically to the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid, as this allows them to determine the severity of the fetal condition.
Features of pathology treatment
If the results of the studies show the presence of hyperechoic suspensions in the amniotic fluid, then no treatment is carried out in this case. As a preventative measure, in some cases the following medications may be prescribed:
- Chophytol;
- Actovegin;
- phobenzyme
Diagnosis of the onset of fetal hypoxia requires the prescription of drugs whose main effect is aimed at:
- blood thinning;
- increased oxygen metabolism;
- normalization of blood flow in the uterus-placenta system.
During pregnancy, the condition of the fetus is constantly monitored and the main attention is paid to the following parameters:
- baby weight gain;
- heartbeat;
- number of movements;
- Doppler results.
If there are signs of infection of the fetus or expectant mother, then antibiotic therapy and sanitation of the woman’s genital tract are prescribed. If the child's condition worsens, a decision is made to perform an early delivery. If the pregnancy is post-term, then green waters are the reason for emergency delivery.
For a normal pregnancy, the detection of minor impurities in the amniotic fluid is considered common.
The appearance of original feces in the amniotic fluid is considered a dangerous condition, as this is a sign that the child is not feeling well.
The result of such a pathological process can be the birth of a premature baby, the development of intrauterine infection and even the death of the baby.
Source: https://beremennostnedeli.ru/zdorove/zhaloby-i-problemy/vzves-v-vodax-pri-beremennosti.html
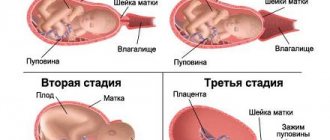
Throughout the entire period of intrauterine life, the baby is in the amniotic sac filled with fluid. As pregnancy progresses, the amount of amniotic fluid increases, and closer to the time of birth, on the contrary, there is less fluid. The baby not only floats freely inside the amniotic sac, but also swallows water, training the reflexes that he will need after birth.
The nature of amniotic fluid plays an important role in the diagnosis of complications during pregnancy. Often, during an ultrasound examination, an expectant mother learns about the presence of suspended matter in the waters during pregnancy, which undoubtedly frightens and alarms not only the woman herself, but also the doctor. What to do in such a situation, and how serious is the appearance of an impurity in the amniotic fluid?
Suspension in water during pregnancy: is this normal or not?
If everything was fine with the mother and child during the gestational period, then when released during childbirth, the amniotic fluid will be colorless, transparent or slightly cloudy due to the content of epidermal scales, vellus hairs and fetal lubrication - free floating particles or suspension.
Suspension in the waters during pregnancy may indicate oxygen starvation of the child, in which particles of meconium appear in the liquid, as well as a sign of intrauterine infection, which also leads to turbidity.
IMPORTANT! Suspension in amniotic fluid in the absence of other clinical symptoms is normal and does not require treatment.
What to fear if suspension appears in the waters during pregnancy?
Turbidity of amniotic fluid is observed in the following conditions:
Urogenital infection, chronic infectious diseases. Suspension in the waters during pregnancy in this case often appears in the first trimester, after which the doctor refers the woman for additional examination to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe antibacterial therapy.
Colds. After suffering from ARVI and influenza, amniotic waters are cloudy during ultrasound diagnostics, and a fine hyperechoic suspension can be detected.
Post-term pregnancy. In post-term pregnancy, when the gestational age exceeds 41.5 weeks, the placenta is not able to fully function; calcifications form in its tissues, which disrupt blood flow. In this case, the fetus may experience hypoxia, as a result of which an admixture of meconium is detected in the waters - a coarse suspension.
Violation of fetal-placental blood flow.
The most common cause of the appearance of pathological suspensions in waters during pregnancy is chronic fetoplacental insufficiency, which is characterized by impaired blood flow in the mother-placenta-fetus system, as a result of which the supply of nutrients through the blood is disrupted and the child experiences oxygen starvation. In this case, the amniotic fluid contains original feces - meconium, which colors the water greenish.
Bleeding. Suspension in waters during pregnancy is red in color - a sign of premature detachment of placental tissue. This condition is life-threatening and therefore requires immediate surgical delivery.