Painful sensations on the eve and during menstruation bother most women and girls. This is considered a variant of the norm and depends on the individual characteristics of the body. But this situation, when after ovulation the lower abdomen feels tight, is much less common. And therefore, many girls are concerned about the reasons for this condition. After all, this can be a normal phenomenon, and sometimes it can be a signal of serious diseases and pathologies.
Causes
To understand the reasons why the lower abdomen feels tight after ovulation, you need to fully understand the physiology of this period. Once the egg has matured, it leaves the follicle, causing injury within the body. Naturally, this may be the cause of pain in the first place. They are especially noticeable in women with increased sensitivity to pain. For others, these processes may go completely unnoticed.
In any case, this is all individual, and depends on the level of the girl’s pain threshold and the physiology of her body. Such causes of pain in the lower abdomen after ovulation are natural and should not cause much concern.
In the next phase, painful sensations can have different types of manifestation, depending on the individual characteristics of the female body:
- stupid;
- cramping;
- spasmodic;
- weak or muffled;
- short-term or long-term;
- piercing and others.
If after ovulation you feel pain in the lower abdomen and lower back for quite a long time, and you notice spotting, you should consult a doctor to determine the exact cause of this pain. Perhaps discomfort may be an indicator that embryo implantation has occurred and you are pregnant.
Also, if there is pain, this may indicate more serious complications, for example, miscarriage or increased uterine tone, and it is better to find out about this as early as possible in order to have time to take the necessary measures for a successful outcome of events.
Another cause of discomfort may be problems with the woman’s health. In this case, you should also not delay going to the clinic.
The discomfort itself can be felt not only in the lower cavity, but also radiate to the left or right side, as well as to the lower back. This is the norm and indicates which ovary the mature egg comes from.
Basically, the ovaries work in turns and alternate every month, but there are exceptions when one of them “misses” its duties, but this also should not cause you much concern. It’s just that another ovary will take over its function this month.
Postovulatory syndrome and methods for its elimination
After the ovulation period, the ruptured follicle, which released a mature egg, closes and fats and a certain luteal pigment begin to form in it. In this way, the uterine cavity prepares to receive the embryo.
The period of formation of the “corpus luteum” begins - a unique temporary organ that ensures the production of necessary hormones, in particular progesterone, which contributes to a successful pregnancy.
If you exclude the possibility of conception, pain may be associated with postovulatory syndrome. According to statistics, every fifth or sixth woman after ovulation has a tummy tug, as before menstruation, and this amounts to about 15-20% of the entire female population of the planet who are ready to bear children.
During this period, a woman may experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower part of the body, pulling or sharp, tingling;
- weakness, which may result in a slight decrease in performance;
- sudden mood swings and emotional instability;
- possible increase in sexual libido;
- uncharacteristic vaginal discharge.
Symptom relief
- To make the postovulatory period as pleasant as possible, you can use some recommendations. For example, a warm bath can help relieve unpleasant symptoms. At the same time, the muscles of the torso and the whole body will relax, thereby reducing pain.
- You can add a few drops of essential oils to lift your mood or, conversely, calm you down.
- A warm heating pad or water bottle can also help relieve soreness if you place it on your stomach and lie there for a while.
- If this option is not very suitable, you can take painkillers. But you should be careful when taking them, since painful sensations can be “signs of pregnancy in the early stages.”
Ovulatory syndrome
The most common cause of pain after ovulation is ovulatory syndrome. A mature follicle ruptures, from which an egg emerges onto the surface of the ovary.
During this period, progesterone begins to be actively produced, vascular fragility increases, basal temperature rises, and white discharge may be observed. Women also note bloating. Such symptoms may subside on the third day after ovulation. Their appearance is due to:
- rupture of a large, tense follicle;
- contraction of the fallopian tubes necessary for the capture and advancement of the reproductive cell;
- accumulation of large amounts of cervical mucus in the cervical area;
- presence of constipation before menstruation.
Tingling in the lower abdomen begins 11–14 days before the expected start of menstruation. Unpleasant sensations may appear on the right or left side of the abdomen, depending on which follicle ovulation occurred in.
According to statistics, after ovulation, nagging pain appears in 20% of women. Most often they have a weak, short-term character, but sometimes they can acquire pronounced features.
Before the germ cell leaves the follicle, it stretches its membrane, causing pain receptors to be irritated. Then the egg is released, which is accompanied by a small volume of serous fluid and blood entering the abdominal area. These components begin to affect the peritoneum and provoke the appearance of pain in the middle stages of the menstrual cycle. This phenomenon is called postovulatory syndrome. Sometimes the unpleasant sensations can be intense, which is why women confuse them with the symptoms of appendicitis or adnexitis.
Ovulatory syndrome does not have any specific symptoms for diagnosis, so such a diagnosis is made by doctors only after rejecting other possible conditions of the body.
To eliminate the discomfort that has arisen, it is necessary to use drugs aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, recommended by specialists, but most often, even intense symptoms disappear on the 5th day after the release of a mature egg.
When pain after ovulation is normal
You have no reason to worry, and this is not considered a deviation from the norm if, after a couple of days after the ovulatory phase, you feel:
- pain in the appendage area, pulling, aching;
- mild pain radiating to the lumbar region;
- pain with a bias towards the right or left side.
It is important to note that normally such symptoms should not appear very strongly and should not exceed a period of 48 hours. Therefore, monitor your well-being during this time, and if there is no improvement in your condition, do not postpone your visit to the doctor.
What to do to relieve pain
If a woman regularly experiences heaviness in the lower abdomen or intense pain during and after ovulation, you can relieve the symptom by doing the following:
- Reduce physical activity for a while, and reduce the intensity when playing sports.
- Drink more fluids before the ovulatory process.
- Spend more time on rest, try to improve the quality of your sleep.
- Avoid stressful situations. You can engage in meditative practices and listen to calm, relaxing music.
- Pay special attention to your diet. Proper nutrition improves physical and mental well-being during ovulation. It is recommended to exclude legumes, caffeine-containing drinks and chocolate, as well as fatty, fried and very salty foods during this period.
- Applying a warm heating pad to the ovarian area helps reduce pain. But you need to know for sure that ovulation occurs at this time, otherwise you can, on the contrary, do harm.
- For severe painful spasms, you can use painkillers - No-shpa, Ketarol, etc.
p, blockquote 33,0,0,0,0 —>
Attention! If you had unprotected intercourse before ovulation and the pregnancy is planned, you should abstain from any painkillers.
If a woman constantly has too much stomach pain during ovulation, her doctor may recommend taking birth control. They help reduce symptoms, however, their long-term use is unsafe due to the constant suppression of hormonal activity.
When to sound the alarm
If the pain does not stop after two days or even intensifies, this should alert you, since this may be a sign of not only gynecological, but also general diseases of the body. Here are some reasons why your lower abdomen hurts after ovulation:
- cystitis;
- inflammation, for example, of the ovaries, appendix, etc.;
- abnormal implantation of the fertilized egg;
- tumor formation;
- disruption of the body's reproductive system;
- hormonal balance is disrupted;
- burst cyst on the gonads;
- overwork.
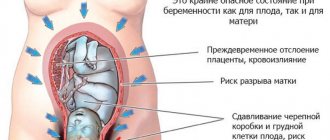
If you feel a sharp piercing pain in the lower abdominal cavity, call an ambulance immediately. This may be a symptom of a dangerous pathology - ovarian apoplexy. There is a rupture of the soft tissues and mucous membranes of the ovary, which provokes internal bleeding. Thus, urgent surgical intervention is required, in this case it is not only about the health, but also about the life of the patient.
Apoplexy often occurs during ovulation on its own, or the cause may be intense sexual intercourse, severe physical activity, or lifting weights.
be careful
It would be a good idea to consult a doctor if you experience the following symptoms:
- the lower abdomen hurts after taking painkillers, the nature of the pain is sharp, piercing;
- you notice bleeding;
- dizzy and loss of appetite;
- feel nauseous and weak;
- observe a temperature above 38°C;
- it hurts to go to the toilet;
- broken stool;
- shortness of breath;
- feel the tone of the abdominal muscles.
Such symptoms may indicate that a woman’s life may be at risk, or pathologies may develop and lead to infertility.
Also, various pathologies contribute to the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen, which often lead to serious complications from the gynecological system.
The following pathological diseases can cause the described symptoms in the lower body:
- infection of tissues by bacteria;
- fungal infections;
- inflammatory processes;
- oncology.
The microflora of the female genital organs is positive and is responsible for the acid-base balance of the environment. But in any organism there are also opportunistic bacteria, which, under the influence of various negative factors, are activated and affect the microflora of internal organs, thereby provoking tissue necrosis and triggering inflammatory processes. And this, in turn, can cause pain symptoms after ovulation.
The same situation is observed with fungal infections. As soon as the immune system weakens under the influence of negative changes, the Candida fungus found in the human body attacks the vaginal microflora. Injuries to the uterus, hypothermia of internal organs, viral infections, and stress contribute to the active functioning of the fungus.
Inflammation is another cause of pain in the lower abdomen. It can occur for a number of reasons due to the adverse effects of the external environment or any accompanying processes in the body. Inflammation of internal organs often occurs from hypothermia, so girls are not recommended to sit on a cold surface.
Oncological damage to organs can also cause nagging pain. Although this disease has not yet been thoroughly studied, it is known that this disease affects the inside of the cell nucleus and affects its DNA. The affected cells actively multiply and, thus, a tumor develops. This can cause unpleasant symptoms.
Characteristic discharge
A woman can determine ovulation by how she feels, as well as the presence of some symptoms. Among them, one of the most common is discharge from the genital tract.
They are characterized by several features:
- First of all, a few days before the possible onset of ovulation, there is an increase in discharge that occurs normally. However, they will not be accompanied by pathological symptoms.
- In some situations, particularly attentive women note the appearance of mucous, slightly sticky discharge. This will indicate that the body is preparing for fertilization against the background of ovulation.
- Normally, the cervical canal contains mucous discharge that has a thick consistency. Due to such characteristics, they perform many important functions. But when ovulation occurs, the mucus thins and becomes more easily stretchable, released from the cervical canal. This can be characterized as the release of a mucus plug from the cervix.
If the discharge is pathological in nature and manifests itself as unfavorable symptoms, then it should be concluded that there is an infection or a microflora disorder in the body. During the period of ovulation, the manifestations will also be the most dangerous, as they can lead to the development of generalized inflammation.
Video
In this video you can clearly see the real process of ovulation and the release of an egg from the ovary, and what damage occurs during this process.
Despite all the naturalness and naturalness of the unpleasant sensations caused by ovulation, the causes of pain can be all kinds, and often pose a threat not only to a woman’s health, but also to her life. And provided that this sign may indicate internal bleeding, you should act immediately. Therefore, pay attention to how you feel and do not ignore unpleasant signs.
Tell us, who felt pain after ovulation, what conclusion did your attending physician make? What exactly was causing these symptoms? Share your story in the comments.