Causes of papillomas in pregnant women
Breast lesions are considered intraductal because they usually occur in the nipple area.
It is important to seek help in time. If the growths are ignored, bloody fluid may begin to be released. Often these are symptoms of malignant transition. Nipple formations are a serious reason to see a doctor. They can be located both on the epidermis layer and inside the mammary gland. The pathological area is determined by palpation, usually a dull pain is felt. Often papilloma appears in the area of the halo or covers the center of the nipple.
The development of papillomas on the nipples during pregnancy is directly related to hormones and their changes. During pregnancy, the immune system weakens, causing the occurrence of unwanted pathologies. Papillomatosis does not have the ability to adversely affect the fetus and its development, but it is advisable for the expectant mother to start taking care of her health in advance.
Consulting a doctor is important, especially considering that papilloma can get into the baby’s mouth during breastfeeding. A microcrack may form on the growth, through which the infection can pass on to the child. In practice, warts are removed during the gestational period or a decision is made to “wait”, since papilloma on the nipple area during pregnancy tends to go away after childbirth.
Formations on the halo or in the middle of the nipple cause great concern. Such localization is often injured by friction from underwear. The cracks that appear allow infection to pass through. Papillomas also interfere with the ability to fully feed the child, and in addition, there is a risk of infection of the baby.
The formations inside the ducts should be studied thoroughly so as not to miss a cancer cell. If the center of the nipple or the nipple itself is retracted, this is a dangerous signal. The tumor is stable in this area. It does not spread metastases, but gives distension and pain. Any injury can cause severe bleeding. In addition, an irritated tumor can spread to nearby tissues.
The disease can appear on any part of the mammary gland. On the surface, it is easy to find and neutralize papilloma, but it is worth checking the internal ducts in order to exclude the presence of cancer cells.
Doctors believe that the main reason for the development of HPV during pregnancy is hormonal imbalance.
Factors in which infection enters the body:
- sexual contact (the sexual partner was infected);
- tight, small underwear (friction occurs);
- swimming pools, saunas, baths (public places where a woman can have her genitals in contact with surfaces);
- bad habits, chronic diseases (decreased immune system).
During pregnancy, especially at 29 weeks, you should avoid such situations, as the risk of infection is greatest.
The disease can remain in the body for a long time, and only manifest itself at the moment of conception. The main location of the growths is on the halo of the papilla or directly on the nipple itself, but there are cases when the tumor also appears on the mammary glands.
There are both external and internal formations. The latter are small bumps that are the same color as the surrounding skin.
It must be remembered that papilloma found on the nipple during pregnancy is a virus that has the potential to degenerate into cancer.
Discomfortable sensations due to illness:
- the presence of discharge (the main thing is not to confuse it with milk, which is released when the pregnancy is quite long);
- burning sensation in the nipple area;
- painful sensations on palpation.
There is no clear answer to the question why papillomas appeared during pregnancy. There is still no scientific evidence that would indicate the exact cause of their occurrence. Most doctors agree that human papilloma in pregnant women appears due to factors such as:
- Hormonal changes in the body, during which the active production of hormones occurs that enhance the growth of epithelial cells.
- Skin damage due to friction with tight clothing. The expectant mother experiences rapid weight gain, and, consequently, her usual clothes become tight. In those places where clothing rubs against the skin (sleeve armholes in the armpit area, chest area, groin), small tumors appear, which subsequently grow and create discomfort for the pregnant woman. Typically, expectant mothers gain excess weight in the 2nd and 3rd trimester, which is when papillomas appear on the body. After the baby is born, papillomas resolve on their own, without surgical intervention.
- Weakening of the immune system and exacerbation of chronic diseases, including activation of the papilloma virus, which did not make itself felt before pregnancy.
The changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman aggravate the “dormant virus” and single or group neoplasms appear on her body, which do not pose a threat to the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus. The exception is papillomas located on the genital mucosa and are large in size.
To avoid all possible dangers of developing the disease, a woman should be tested for HPV before conceiving a child. If the analysis is confirmed, the woman is prescribed a course of treatment with strong antiviral drugs.
New growths on the skin are always a cause of concern if they occur during pregnancy. The human papillomavirus, which causes the appearance of condylomas and warts, is an infectious disease with a high degree of contagiousness.
There are three ways of transmitting the virus from a carrier to a healthy person:
- contact and household;
- vertical - from mother to child during birth;
- sexual - through sexual contact.
Pregnancy is accompanied by external and internal changes throughout the body. The location of the internal organs changes, and a complete restructuring of the hormonal levels occurs.
During pregnancy, as a result of hormonal changes, immune decline occurs.
This process is necessary to prevent the body from rejecting the fetus. This phenomenon allows the infection to activate in the body and cause the appearance of external symptoms of the disease.
Condylomas are a particular danger for a pregnant woman - genital papillomas that affect the intimate area and can spread inside. Large-scale papillomatosis can disrupt the course of pregnancy and, in the early stages, lead to its spontaneous completion. There is a risk of growth of formations along the birth canal, which can lead to difficult childbirth and threaten the life of the newborn.
An unfavorable consequence of an abundant growth of condylomas is a high probability of transmitting HPV to a child. While passing through the birth canal, the newborn comes into close contact with the growths, and as a result becomes infected. Children born in this way develop similar formations in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. To prevent risks, it is advisable to perform a caesarean section.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what to wear when you have fungus.
The most dangerous phenomenon that can be caused by papillomavirus is the development of cancer. Some strains of HPV are highly carcinogenic, provoke cellular degeneration, and cause erosion, dysplasia, and cervical cancer. During pregnancy it can lead to miscarriage.
Causes
Papilloma infection can remain latent for a long time without manifesting itself in any way.
About 90% of people are carriers of HPV, but the manifestation of the disease is preceded by the following reasons:
- Decreased immunity during the gestational period;
- Chronic immune diseases;
- Acute forms of chronic diseases;
- Hormonal changes that cause changes in the structure of skin tissue;
- Endocrine pathologies, including hereditary ones, for example, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus;
- Damage to the formation sites of warts, moles, birthmarks;
- Extreme weight gain, also overweight.
All causes of the development of the disease are directly or indirectly related to a decrease in the protective function of the body.
Where do papillomas appear during pregnancy?
Removal of papillomas is a relatively simple, quick operation that does not require special training or a difficult rehabilitation period. Many therapies require the use of anesthesia. The administration of anesthetics is unacceptable during pregnancy; the components can negatively affect the development of the child in the womb.
Carrying out invasive procedures without painkillers is dangerous; there is a risk of spontaneous abortion.
Treatment methods should be selected taking into account the woman's situation. The doctor needs to assess the ratio of benefit to the mother and risk to the fetus. If possible, it is advisable to postpone the operation until the postpartum period. If the doctor has identified the need for urgent intervention, gentle methods of treating tumors are selected.
The main methods of treatment during pregnancy are:
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave excision.
Cryodestruction is a procedure of removal with liquid nitrogen. Modern methods of using ultra-low temperatures make it possible to remove growths from any area of the skin. Treatment is carried out using a special device that supplies the required doses of gas. The doctor directs the tip to the problem area and applies nitrogen directly to the formation. Under the influence of low temperature, the cellular connections of the viral growth are destroyed.
Within 14 days, the destruction and death of the neoplasm occurs. The procedure itself is unpleasant, but painless and does not require anesthesia. Some people are sensitive or intolerant to such discomfort. In this case, another removal technique is selected. The downside of the event is the high likelihood of subsequent appearance of scars, cicatrices, and prolonged healing. This type of treatment is not recommended if the growths are located on the face or are large in size.
Electrocoagulation is the effect of electric current. The procedure is carried out using a special device that generates a direct electric current. During the operation, the specialist directs a pen with a thin tip to the formation and removes it. If there are hanging warts or genital warts, they can be removed by pulling them by the stem. Electric current promotes cell evaporation.
The advantage of this method is the absence of blood during surgery. Due to its coagulative property, blood vessels are welded together.
Radio wave excision. This procedure is known as radioknife, or Surgitron. The treatment method is gentle and suitable for treating pregnant women. The essence of the technique is the effect of high-frequency electrical waves on the body of the growth. During an operation with a radioknife, there is no direct contact between the device and the formation; coagulation of small blood vessels occurs. The procedure is painless, does not require special preparation, and is suitable for removing growths of any size and location.
It is not recommended to remove papillomas with a laser during pregnancy or resort to surgery. The laser and scalpel require the use of anesthesia, which is extremely undesirable for the unborn child.
At home, papillomas can be removed using safe means that will not cause harm to the body of the mother and child in the womb. Celandine juice is considered a popular and effective folk remedy. It is obtained from the root, stem or leaves of the plant. Apply the juice generously to the growth several times a day. The course of treatment lasts until the formations disappear. You can remove papillomas using baking soda, garlic, and baked onions.
The papilloma virus can appear on any part of a woman’s body, but its “favorite” places are: neck, face, groin area, armpits. These are the places on the body where mechanical effects on the skin occur. For example, papillomas on the neck are subject to daily friction from the collar of clothing, the chest and armpits are rubbed by a tight bra, and the groin area is rubbed by underwear.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IcvntFvEV0c
Particular attention should be paid to tumors that appear on the chest of a pregnant woman, especially on the nipples. Most often, papillomas are localized in the area of the areola, large duct or nipple. If you notice a wart in the armpits or on the skin of the chest and it does not cause discomfort, there is no need to worry.
Papilloma does not pose any danger; in most cases, it resolves on its own after childbirth or, if desired, can be removed. But, if papilloma is found on the nipples, you need to consult a specialist. It is worth remembering that soon a woman will have to breastfeed a child, and the presence of papillomas on the nipples is extremely undesirable, since the baby, when swallowing the areola, will injure it.
If papillomas appear in the genital area during pregnancy, the expectant mother has many concerns about whether they are dangerous for the fetus. We can say with complete confidence that while the fetus is in the womb, neoplasms on the genitals of a pregnant woman are not dangerous for it. But, during birth, the baby may be infected with a virus, so the pregnant woman is prescribed either drug treatment, or removal of the papilloma is recommended, especially if it is large.
The decision on treatment or surgery is made by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. In some cases, during the period of exacerbation of HPV in intimate places before childbirth, the gynecologist may resort to cesarean section to eliminate the possibility of infection of the child. And after his birth, the papillomas can be removed.
Many expectant mothers ask whether papillomas are removed during pregnancy and what surgical methods are used to remove them. Modern medicine offers several ways to get rid of papillomas:
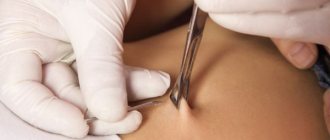
- Excision by classical surgery. This method allows you to study the material and conduct a histological examination of the tissue. However, there is a possibility of bleeding after surgery, and unaesthetic scars may remain after surgery.
- Removal using a radio knife. This is a high-tech, painless method of getting rid of a tumor on the body using energy waves. The tissue excised with a radioknife is sent for histological examination. The positive aspects of the method are the absence of relapses at the site of papilloma removal.
- Laser removal. One of the most progressive methods of getting rid of papilloma, which uses a laser beam. This method allows you to remove group multiple neoplasms, including on the mucous membranes and on the cervix. Laser removal does not cause complications, relapses or scars. The method completely eliminates bleeding after papilloma removal, since the blood is baked.
- Cryodestruction - freezing papilloma using liquid nitrogen. As a result of manipulation, the tumor tissue dies.
We suggest you read what you should not eat during thrush
It is recommended to remove papilloma in the 1st trimester, while it is small in size. But, having removed the tumor, the pregnant woman should pay attention to her immunity in order to protect herself from the possible recurrence of papilloma.
Under no circumstances should you try to remove papilloma using traditional methods. Incompetent treatment or disposal of papilloma can cause skin infection or burns. The danger of independent intervention in neoplasms is that the papilloma can subsequently degenerate and become a malignant tumor.
Now there are many methods for getting rid of HPV. Removal of warts during pregnancy is carried out exclusively on an individual basis. In this case, the consent of not only the woman, but also the gynecologist is required.
It is advisable to remove papillomas in the first months, at which time the growth is small. There are several operational methods, namely:
- Excision. Bleeding may occur during the event. The procedure leaves scars. There is no guarantee that the wart will not return;
- Radio knife. The process is painless and takes little time. No relapses are observed;
- Application of laser. Removes groups of growths and single elements. Used in the presence of papillomas on the cervix. There are no scars left and adjacent tissues are not affected. Bleeding was excluded due to sealing of the vessels.
Removing the growth alone is not enough. Immunity must be normal, otherwise the weak body will again be attacked by the disease. It would be more correct to start taking immunomodulators, but only on the recommendation of a doctor. And then, they should be taken before conception. These medications may be harmful during pregnancy. During the gestational period, you need to adjust your diet, follow a routine, and walk more.
It is worth noting that in the absence of medical indications, it is not recommended to remove papillomas. Expecting a baby is a wonderful period, but breast papillomas can disrupt this euphoria. At the slightest formation on the chest, you need to show it to the gynecologist. The specialist will make a decision and answer all questions.
The appearance of warts on the neck and genitals
Why can papillomas appear on the neck during pregnancy? It is impossible to single out a specific cause for the appearance of papilloma on the neck. They can appear on any part of the skin. Specialists can conduct research and identify what type of virus caused the appearance of tumors on the neck.
When papillomas appear on the patient’s neck, the first problem that appears is a deterioration in appearance. And they can also be in places that are exposed to clothing. In this case, the person will experience:
- pain;
- itching;
- the tumor may bleed.
For example, if the collar of a shirt or outerwear constantly clings to the papilloma, this can provoke a violation of its integrity and subsequently an increase in size.
What affects the appearance of warts on the neck:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- exposure to the environment and low temperatures;
- mechanical impact.
What do papillomas on the neck look like during pregnancy? They will hang down on a stalk, and some patients tie them with a string to get rid of the wart. The danger is that this may trigger the activation of the appearance of new tumors in even greater numbers.
One of the features of the appearance of warts on the neck may be failure to comply with normal hygiene or the presence of bad habits. But this does not exclude the virus from entering the body. Therefore, all women upon reaching thirty years of age are recommended to undergo preventive testing for HPV.
Features of the manifestation of papillomas during breastfeeding
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
If, if you are a carrier of HPV, papillomas do not arise during pregnancy, it is likely that foci of infection will be detected during breastfeeding. To produce milk, the female body needs a lot of vitamins and microelements. If they are not supplied in the required quantity from food, the body begins to use its own reserves. Women during breastfeeding are characterized by vitamin deficiency. Leads to a decline in the activity of immune defense.
Growths can occur on any part of the body. The appearance of formations in the mammary glands, nipples and halos is unpleasant for a nursing woman. Due to constant contact with the baby's oral cavity, the skin of the breast may be injured, and the newborn may become infected.
In cases where condylomas grow into the milk ducts, lactation is disrupted, pain and inflammation appear. The condition impairs the proper functioning of the glands and the feeding process.
Removal of papillomas is quite acceptable during breastfeeding. Some painkillers and post-treatment medications do not pass into breast milk. Makes it possible to use laser and surgical interventions.
When to tell your doctor about papilloma
The disease develops as a result of the awakening of the HPV virus. Everyone has it, but usually in sleep mode. At the time of remission, there are no questionable marks on the skin.
The disease manifests itself over time. Infection occurs quickly. It is important to know that during pregnancy, papilloma causes discomfort in terms of wearing a bra and feeding.
The doctor should be notified if the papilloma:
- Growing;
- There is itching in the nipple area;
- There was discharge from the chest.
If treatment is delayed, the formation may develop into a malignant form. Then you will need to go to an appointment not with a gynecologist, but with an oncologist.
Which papillomas do not need to be removed?
Removal of tumors during pregnancy is not always a necessary measure. In most cases, the doctor will recommend that you avoid the excision procedure until after delivery. It is not necessary to output:
- flat warts on the hands and feet;
- papillomas in the face, neck, décolleté;
- in the armpit;
- formations on the stomach and back;
- spines on the soles and palms.
If the growths are not located in the place of probable damage, there is no friction with clothing or shoes, treatment can be started after the birth of the baby. When the growth is small in size, does not bleed, there is no pain or discomfort, there is no cause for concern.
What is the danger
Many women are interested in eliminating benign papillomas during pregnancy. They believe that these rashes are dangerous not only for them, but also for the fetus. Whether pregnant women should worry about this or not, their attending physician will be able to answer.
For woman
The appearance of a benign papilloma for a pregnant woman cannot be called a serious threat. Most types of such growths are not prone to degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Expectant mothers should be wary of flat rashes that form in the cervical area. They can lead to changes in epithelial cells and cause dysplasia. Another complication of the disease is cancer of the affected organ.
For children
The papilloma virus can be transmitted from a mother to her child. But babies' immune systems usually manage to fight off the infection. If a primary infection occurs during pregnancy, the woman risks losing the fetus.
Doctors cannot yet say exactly how the infection affects the development and condition of the child in the womb and how dangerous HPV is for him.
Possible complications and precautions
Papillomavirus can lead to complications if the growths are widespread or in the presence of oncogenic strains. Often papillomas disappear on their own after the birth of the child. The possibility of dangerous consequences cannot be excluded. Excessive growths on the genitals can lead to infection of the internal organs of the small pelvis, the development of inflammatory processes and other unpleasant pathologies.
It is almost impossible to protect yourself from HPV infection. One of the most common and contagious diseases. A woman can get vaccinated against dangerous malignant strains of the papilloma virus and prevent the development of cervical cancer. In other cases, it is necessary to maintain the full functioning of the immune system. Whether growths appear on the body depends only on the state of the immune system.
The appearance of papillomas during pregnancy is a fairly common problem. To avoid the development of dangerous pathologies, in order to maintain pregnancy, it is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to remove papillomas: PROVEN METHODS
The article has been reviewed
by the site editors
How to get rid of it and what preventive actions need to be taken
Preventive measures mainly focus on a few important aspects.
Firstly, a woman at a young age can get vaccinated, which will protect against infection. Among the preventive medications, there are two drugs: Cervaris and Gardasil. Each of them acts on a specific group of strains. It is important to vaccinate prematurely, as this is prohibited during pregnancy and lactation.
Secondly, maintaining the immune system is extremely necessary. Proper nutrition, eating healthy foods with sufficient vitamins and microelements will help the immune system to be normal.
Whether or not to treat a skin lesion is a decision for a pregnant woman to make on her own. But in any case, you need to inform your gynecologist about the presence of the virus, because this is important for the fetus.
We recommend reading:
- Human papillomavirus in women
- Is it possible to have sex if you have HPV?
- Papilloma on the chest
Papilloma virus during pregnancy
Papillomas are benign neoplasms on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The neoplasm looks like a small growth, usually flesh-colored, brownish, and sometimes burgundy. Externally, papilloma resembles a mole or wart.
Neoplasms can be either solitary or located in small groups. Most often, papillomas appear on the body of a pregnant woman in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Their locations in pregnant women are the neck, face, arms, mammary glands, armpits, and genitals. If a woman has previously had papillomas on her body, then after hormonal changes in the body, the neoplasms can increase in size and spread to new areas of the body.
The papilloma virus is quite common; about 100 strains of HPV are known to medicine. Almost a quarter of the entire population of the Earth are carriers of this virus. There is a high probability of becoming infected with the virus, both from a patient with HPV and from its carrier. Infection with the genital form of the disease occurs through sexual contact, during unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as through household contact, through contact with the mucous membrane of its carrier. In addition, a pregnant woman who carries the virus is more likely to pass it on to her baby during childbirth.
Effect on the pregnant woman and fetus
Since papillomas are a viral disease, many women are concerned about their possible impact on the intrauterine development of the fetus and the course of pregnancy in general. If the tumors are not located on the genitals, then they do not pose any danger.
When papillomas are located on the genitals, the growth of rashes accelerates, and the risk of damage and bleeding increases. Vaginal discharge also appears - a moist environment, ideal for the proliferation of HPV and other infectious agents. Against this background, hormonal imbalances and decreased immunity may occur. Read more about how to strengthen your immune system during pregnancy →
Diagnosis and timely treatment
A visit to a doctor is necessary, because with a thorough examination, a specialist will identify subtle deviations from the norm.
External signs are visible growths in the nipple area. If during the examination the doctor reveals lumps in the nipple area, further examination becomes necessary. X-ray examination will not bring a positive result, therefore galactography is used. A special substance is injected into the ducts through the nipple, after which the patient is sent for an X-ray. This procedure makes it possible to fully identify the pathology.
If it is impossible to postpone the removal of papilloma on the chest while a woman is carrying a child, the following procedures are used:
- removal of papillomas with liquid nitrogen;
- by surgical intervention;
- laser therapy is used.
If the infection does not develop rapidly, the doctor will suggest postponing the procedure until the postpartum period.
For many women, papillomas on the nipples during pregnancy disappear on their own over time. This is explained by the fact that after childbirth the level of HPV in the body decreases. But this does not mean that the infection has left the body, and it is worth focusing on improving the health of the body. It is necessary to take a course of rehabilitation.
A pathology such as HPV in pregnant women is treated by oncologists and dermatologists. All doctors should be careful when examining a woman. The formation is visible upon visual examination, but to understand the severity of the papilloma, you need to take a biopsy.
If the doctor suspects a pathological process inside the breast, an ultrasound is recommended to view the thickness of the glandular tissue. If there is a dense formation on the halo, it is recommended to undergo an x-ray. In this case, contrast is used, only with it can the growth be seen. This is only done if nipple discharge is present.
Both during and without pregnancy, it is important to maintain normal health. Any deviation of immunity in the low direction can lead to dire consequences. Papilloma on the nipple during any pregnancy (complex, mild) requires close attention from doctors, since in some cases it may be cancer.
Diagnosis and timely treatment
Papillomas on the body of a pregnant woman, if they do not cause physical and psychological discomfort to the woman, are harmless and do not pose a danger to the course of pregnancy. Therefore, HPV treatment is not prescribed for pregnant women, only in individual cases. It is worth remembering that it is impossible to cure the papilloma virus and get rid of it forever. After a course of treatment with medications, you can only stop the spread of papilloma on the body and “silence” the infection.
- Any drug treatment is stressful for the expectant mother, which affects the baby.
- After childbirth, most tumors that appear on a pregnant woman’s body disappear on their own, without treatment or removal.
- Removal of papillomas is carried out under local anesthesia, which is extremely undesirable for the baby.
HPV can be detected during a routine gynecological examination; to confirm the diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the surface of the cervix and cervical canal) or a colposcopy is performed. Also, upon registration, all women are given a blood test for the human virus to identify the HPV strain.
Safe Treatment Methods
The growths do not interfere with the course of pregnancy and often disappear after childbirth. Removal using various methods will not affect the situation; the papilloma may pop up in another area of the skin.
It is advisable to undergo HPV treatment when planning a pregnancy. It will relieve you from unnecessary worries while carrying a child. You can get vaccinated against human papillomavirus before you become sexually active.
Only topical medications are prescribed.
Pharmacy drugs
Drug treatment during pregnancy involves the use of ointments, gels, solutions that remove growths, and drugs that stimulate the immune system. These include:
| Name | Action | Mode of application |
| Kipferon | Suppositories for rectal and vaginal administration. Helps cope with condylomas in the vagina. The action is aimed at increasing immunity, eliminating papillomavirus. The drug has anti-inflammatory properties. | Suppositories are inserted into the vagina, 1-2 pieces (depending on symptoms), 2 times a day. Therapy lasts about 10 days. |
| Galavit | Suppositories designed to combat the HPV virus. The drug has an anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating effect that changes virus cells. | Take one suppository once a day for 10 days, then one suppository every other day. A full course of therapy requires 25 suppositories. |
| Viferon | Available in the form of suppositories and ointments. Helps cope with growths in the vagina, stimulates the immune system, controls formations, thanks to its antiviral properties. | One suppository is administered rectally. The course is about 10 days. |
Prevention of HPV during pregnancy
If a woman is not a carrier of the HPV virus and this has been confirmed by tests and examinations, she should protect herself from possible infection with the genital form of the virus and use barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse if she has a non-regular partner. If a virus is detected, it is advisable to undergo drug treatment before conception.
To avoid the appearance of tumors in places such as the armpits, groin, and neck, it is not recommended to wear tight underwear or tight-fitting clothes that rub the skin and provoke the appearance of papillomas. The factor of heredity cannot be ruled out either. In most cases, if the mother had papillomas during pregnancy, her daughter will have them when she is pregnant.
Waiting for the birth of a baby is a happy period in a woman’s life and papillomas are a nuisance that should not overshadow pregnancy. If you notice small pointed warts or growths on your body that were not there before, this is a reason to seek advice from a gynecologist.
Diagnosis of HPV
Often, papillomas are discovered during a gynecological examination during the initial consultation with a doctor about pregnancy. Some mothers have complaints about the appearance of genital warts in the area of the external genitalia. Such patients are prescribed special diagnostic tests:
- cytological analysis of a fragment of the cervical canal mucosa;
- colposcopy;
- antibody titer study;
- Digene test (amplification);
- PCR diagnostics.
Analysis of sequential chain reactions makes it possible to most accurately determine DNA, HPV strains, the degree of their oncogenicity, and how long ago a person was infected. The material for the study is blood, urine, and amniotic fluid. Based on the results obtained, the doctor selects a treatment regimen.