What is basal temperature
Measurements of the usual temperature indicator, which are made, for example, for a cold (under the armpit), are too approximate, they are rough. To record the subtle changes occurring inside, you will need direct access to the internal tissues. Here we need to clarify what basal temperature is. It is an indicator measured in accessible cavities. There is access to the mouth, vagina and rectum. It has been established that the measurement is least distorted when determining the temperature in the anus. That's why they use exactly this measurement. The change in indications is associated with the production of the hormones progesterone and estrogen in the body. When a corpus luteum forms in place of a mature egg, progesterone is produced in much larger quantities. After the passage of critical days, progesterone in the blood decreases, as large quantities leave the body with menstrual blood.
But at this moment the follicle begins to mature, and the level of estrogen in the blood increases. An increase in progesterone generally causes an increase in temperature, and a decrease in progesterone and an increase in estrogen contribute to a decrease in BT. Thus, basal thermometry is a reflection of fluctuations in hormone levels.
Standard options
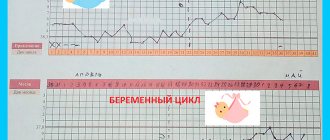
It’s not worth talking about certain diseases based solely on temperature levels. But this information is needed in order to suspect some problems and undergo the necessary studies to confirm or refute the diagnosis. At the same time, it is impossible to judge by just one cycle; measurements must be taken over at least three months. If the picture repeats every month, then together with the gynecologist you can draw any conclusions by analyzing how the basal temperature changes before menstruation. The norm for it cannot be established in absolute values. It depends on both the values in the second and first phases. If a woman’s readings before ovulation are around 36.4 degrees, then after it they may not exceed 36.9. At the same time, an increase in temperature to 37 on the day of menstruation will not indicate the approaching critical days, but the onset of pregnancy.
What is the normal basal temperature before menstruation?
One of the most important evidence of the healthy state of the female body is the basal temperature before critical days. It may change, but within certain limits. Of particular importance is preparing the body for pregnancy. If conception, unfortunately or fortunately, does not occur, preparations for menstruation will begin.
This period of the menstrual cycle is considered its second phase. At the same time, not only should progesterone levels increase, but estrogen levels should also decrease slightly. As a result, the blood should become hotter, as evidenced by the basal temperature. The norm is determined by the individual characteristics of a woman, her lifestyle, and metabolism. On average, this value is above 37 degrees. First it should be a little higher than this indicator, and then a little lower.
So, for example, a week or 8-9 days before menstruation, the first day of which is the beginning of the cycle, the level of thermometry readings should be from 37.1 to 37.2. After several days, a gradual decrease in the data obtained must begin. The basal temperature before the start of a new menstrual cycle, namely 2-3 days before it, should begin to fall, decreasing smoothly, gradually. Its values can be about 37 degrees and slightly lower. When the temperature does not drop, this is a signal to check with a gynecologist, as inflammation of the appendages is possible.
If before menstruation the thermometry curve, 4-5 days before it, went slightly down from the level of 37.1-37.2, and then rose again to these values and continues to remain within the same limits, without rising higher, such a BT chart may signal that it’s time to think about the high probability of pregnancy. The process and health status must be kept under control, since in this situation there is a risk of miscarriage.
The beginning of a new menstrual cycle should never be marked by a strong upward movement of the thermometer. The values may fluctuate slightly on the first day, and also on the second. But the readings normally do not increase more than 37.3. When growth increases more than expected, for example, to levels of 37.5 and above, we can with a high degree of probability talk about the presence of an inflammatory pathology.
- At values of about 37.5 and slightly higher, we are talking about adnexitis or inflammation of the appendages.
- When the elevated temperature reaches 37.9 and above, endometritis can almost certainly be suspected.
On the third day of the menstrual cycle, or a little earlier, a decrease in readings should occur. At this point, progesterone production is reduced and continues to decline. This is followed by basal thermometry. The fall lasts as long as menstruation occurs. By the end of the bleeding, the BT should be approximately 36.5 degrees. At the same time, depending on individual characteristics, the indicators, of course, change. But the temperature should clearly be lower than during the period before the critical days.
Why does BT increase?
With diseases such as endometritis or endomyometritis, the basal temperature during menstruation begins to increase from the first days and can reach 37.5 degrees, but the woman’s overall body temperature is normal.
The second reason for the increase in BT is pregnancy, which was interrupted during the menstrual period. If the BT from the moment of ovulation until the end of the discharge reached a temperature of over 37 degrees, and in the last days or after the end of menstruation it very sharply decreased, then there is a huge probability that the pregnancy has failed.
Another reason for the increase in BT is the process of inflammation of all appendages. If the basal temperature during menstruation, from the very beginning to the end of the discharge, is above 37, then this may indicate the process of inflammation of the appendages.
An equally significant reason for the increase in BT is the process of inflammation of the tubes, as well as the cervix. If BT during menstruation, or more precisely, in the last 1-2 days, increases sharply, then this indicates inflammation in the cervix and tubes (provided that the discharge lasts from 4 to 5 days).
However, if BT increased for only 1 day, then this does not mean at all that the woman has any disease or that an inflammatory process is occurring.
Basal temperature after menstruation is normal
The cessation of menstruation indicates the beginning of preparation for ovulation. During this period, estrogen levels begin to rise, while the basal temperature in women gradually decreases. Its value varies from 36.3 to 36.7. Higher values will not allow the follicle to develop and form a healthy egg. When taking measurements, you can notice that, as a rule, small fluctuations in the graph appear. The spread of values within 0.5 degrees lasts about a week. There is a special point that you should pay attention to. During the study period, there is a sequence of days when the obtained data remains almost unchanged. At this point, the basal temperature after menstruation is constant. Its norm is not precisely defined. But after 5-6 days of this period of stability, three days are revealed, marked by an increase in the indicator by 0.1-0.2 degrees. A temperature increase of 0.2 degrees occurs only on one day. Then the curve returns to its previous level. It is precisely this fluctuation in thermometry values that indicates the imminent onset of ovulation.
In this case, if you want to get pregnant, you need to make an effort. If pregnancy is not planned, sex should be protected.
Measurement methods
Remember that there are rules for measuring BBT, and you need to measure it correctly at all times:
- the time of its measurement must be strictly observed; it can be measured a little earlier, but not later than always;
- basal temperature after critical days, during or before their onset should be measured with one thermometer;
- it should be measured through the oral cavity, vaginally or through the rectum; You should choose only 1 measurement method and use it constantly;
- It is necessary to measure BT immediately after waking up and without making any sudden movements. This factor can lead to changes in readings;
- every hour, immediately after the woman wakes up, BT will increase, which is why it needs to be measured instantly;
- adhere to the measurement time, if BT is measured vaginally or through the rectum, then the procedure should take at least 5 minutes, but if the measurement occurs through the oral cavity - 3 minutes;
- You should only use a mercury thermometer, as it shows more correct results;
- it does not matter whether BT is measured before or after menstruation - it must be measured in a supine position.
It is important to record the temperature immediately after measurement in a special chart so that you do not forget the result later.
BT before the onset of the menstrual period constantly decreases, this process is unchanged.
In order to obtain more accurate and correct BT indicators, it is necessary to measure it between 6 and 8 o’clock in the morning. It is very important that before the measurement the person has a quiet, healthy sleep of at least 3-6 hours.
Just a few days after the end of menstruation, BT remains at around 36.5 to 36.9, after which it gradually decreases. And after ovulation, BT increases sharply.
Temperature standards at different stages
Deviations of values from the average norm should not be scary. The reliability of data in most cases can be reduced for many reasons. As a result, basal temperature is subject to variation. Therefore, in order to rely with a high degree of reliability on the resulting graph, observations must be carried out over not just a couple of months, but even years. Then it will be possible to compare the results obtained with established average standards. When assessing the data, as well as based on the existing cyclical changes that are characteristic of the female reproductive system, you can notice several clearly distinguishable stages:
- the first days of bleeding;
- end days of menstruation;
- interval from critical days to the monthly onset of ovulation;
- the actual period of ovulation;
- the interval from ovulation to the approach of critical days;
- the very eve of menstruation.
The indicators for these phases are approximately as follows:
- Period. At the beginning, thermometry readings are kept within the range of 36.9-37.3. By the end, these data are at the level of 36.3-36.8.
- Ovulation. There is a dip in the data graph to the lowest value, and then an increase in indicators to the area of 37 degrees.
- Before ovulation. The thermometer shows a value much lower than before the period, about 36.4.
- After ovulation. The thermometer shows a characteristic temperature of about 37.1. Deviations of 0.1 degrees are permissible in both directions.
- Before menstruation. There is a gradual and steady shift in readings downward. Then a slight, short-term rise is possible, but not higher than 37.3, which ends with a further decrease in temperature.
When the indicators do not meet the norms, suspicions arise about the presence of pathology. Its main symptom is the absence of a clear, smooth pattern of data changes on the graph. This can occur in almost every woman, although not constantly in each cycle. If such a lack of movement in the graph is observed for more than one cycle, when 3-5 months are monitored, this indicates an anovulatory pathological process. When the reduced difference between different phases of the current cycle becomes apparent only once, it may then not be too dangerous. The ovaries just rest during the cycle.
When, following ovulation, the temperature does not rise to the recommended values, but only rises by 0.3 degrees, this indicates insufficient ovarian function. In this case, the body lacks both estrogen and progesterone.
If thermometry showed an increase in the received data to a level of 37 degrees, but this value fell almost immediately and did not rise 3-7 days after the time of ovulation, then this indicates a low level of progesterone.
What does BT show before and during menstruation?
The situation is considered normal when a couple of days before the start of menstruation, the BT curve on the graph begins to fall. And on the first day of critical days it reaches 37.0 - 37.1 °C. Further, despite the amount of menstrual flow, BT must decrease during normal menstruation.
If there is an inflammatory disease in the reproductive system (for example, endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa - or endomyometritis - inflammation of the uterus itself), the basal temperature during menstruation will become higher (37 - 37.6 ° C), although the temperature in the armpit will remain unchanged normal.
If BT was high before the onset of critical days and does not fall before them, remains at 37 ° C during the entire menstruation, but decreases after it, this indicates pregnancy.
When BT in the second phase is low (36.9 - 37 °C), and by the time of menstruation it increases and becomes more than 37 °C on critical days, then inflammation of the appendages may develop.
A rise in BT at the end of menstruation and provided that its duration does not exceed 5 days can be a consequence of inflammation in the tubes or, in rare cases, of the cervix.
A sharp jump in BT during menstruation for one day does not mean anything: it is unusual for inflammation to begin and end so abruptly.
If you have scanty periods or other characteristics, high BT values may mean a pregnancy that is at risk of miscarriage.
How to measure
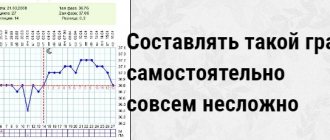
In order for the readings noted on the graph to objectively reflect the changes occurring in the body, you need to follow some important rules and avoid possible violations. First you need to prepare your writing materials - a notebook and pen. You can later transfer the thermometer readings to a computer, because there are many programs that allow you to easily and quickly visualize the resulting set, presenting it in the form of a curve - a broken or smooth line. But at the initial stage, it is enough to only be able to record the readings. In addition to the data determined on the thermometer, you need to record the date, as well as all special situations that occurred on the eve of the measurement.
While the process may seem simple, it's a good idea to check out some tips on how to properly measure your morning basal rates. Measurement is assumed to be performed through the rectum.
- Thermometry is carried out using the same device. The mercury thermometer is placed so that it penetrates the cavity at a distance of 2-3 cm. BT is measured within 6 to 7 minutes. When using an electronic device, the time is reduced to 1-2 minutes.
- Before you measure, you need to get a good night's sleep. It is advisable that no alarms be observed for at least 6-8 hours. When this is not possible, the readings may not be informative. If there was less than 4-5 hours of restful sleep before the measurement process, these readings will be distorted due to the awakening of the adrenal glands and their effect on hormonal levels.
- When you wake up, before you start measuring your basal temperature, you can’t even spin around. In addition, of course, it is prohibited to stand up, walk, sit down, drink or eat, or shake off the thermometer.
- You need to have next to you in the evening: a pre-tested thermometer, pieces of paper and a recording medium. Everything should be in close proximity, for example, on the bedside table.
- The sampling time should be the same every day. It is optimal if it falls between 5 and 7 am. Then, if necessary, you can continue to stay in bed and fall asleep again. It is allowed to change the exact time of measurement, but no more than 20-30 minutes.
- It must be borne in mind that the results obtained will most likely be distorted if there was a violation of the rules on the days of measurement:
- do not take psychotropic, sedative, stimulant drugs, alcohol;
- don't have sex;
- do not be nervous;
- do not be exposed to heavy physical activity;
- do not overeat and do not starve.
Other factors also influence the information content of the readings. It is reduced:
- diseases of the intestines and respiratory tract, as well as colds, poisoning, including exacerbations and chronic pathologies;
- receiving hormone therapy;
- moving, hiking, life changes;
- manifestations of herpes.
An acute condition that arises, for example, a rise in temperature, the appearance of fever, negatively affects the quality of readings over the next 2 weeks.
What happens during menstruation
Typically, basal temperature measurements begin at the beginning of the monthly cycle, that is, on the first day of menstruation.
The initial phase of the cycle is characterized by the removal of accumulated toxins from the body. Therefore, before menstruation, women feel a certain physical discomfort:
- Nagging pain in the lower back or lower abdomen;
- Soreness and slight tightness in the chest;
- Dizziness;
- Frequent headaches.
In addition to physical changes, women experience severe mood swings, unreasonable anger or depression.
This condition is associated with sudden changes in hormonal levels. At the end of the luteal period, the maximum amount of progesterone produced by the body is observed. The hormone is very active in this phase. If conception does not occur, then its concentration decreases. It is replaced by estrogen, which replaces progesterone during the menstrual period.
During menstruation, the endometrium begins to reject its functional particles, which manifests itself in the appearance of bleeding. After a few days, the endometrial cavity is restored, and menstrual flow ends.
On average, a woman’s body loses from 20 to 60 g of blood every day, which differs significantly from normal blood loss: it does not clot and has a specific smell.
Sudden hormonal changes lead to psychological and physical imbalances. Although some women have never experienced symptoms of premenstrual syndrome and tolerate natural functional changes quite well.
These hormonal surges also change BT readings in different phases of the cycle. Their values determine not only “important” days for conception, but also various deviations in women’s health.
A number of doctors believe that measurements can not be taken during critical days, since during this period the numbers are not as important as, for example, in the middle of the cycle. And they certainly do not recommend using the vaginal method of measurements - during the period of bleeding it is unhygienic and even harmful.
Let's consider what basal temperature should be during menstruation and why its indicators may differ from the norm.
Basal temperature 37.2 – what does this mean?
During the second half of the menstrual cycle, when the oocyte matures, there is a high probability of the formation of an embryo and its implantation into the uterine mucosa. Of course, this situation is assumed in the case of sexual contact. But, nevertheless, this does not always happen.
When critical days approach, thermometric indicators measured every morning are on the rise. In this case, it may be noted that the basal temperature is constantly maintained at 37.2. Not many people know what this means. But doctors suspect pregnancy in such a situation. Indeed, in this case, a high level of progesterone is maintained. It is produced so that the inner layer in the uterus can grow sufficiently. The embryo will subsequently be implanted into it. It is progesterone that helps thicken the inner layer and maintain a high temperature after preliminary growth.
If conception did not take place for various reasons or it is objectively excluded, such a temperature of 37.2 can remain for a long time due to an excess of progesterone or an incorrectly performed measurement process. If there are no sharp jumps noted on the resulting temperature graph, the readings do not deviate by large amounts, it is recommended to wait for your period and monitor the subsequent change on the graph. When there is no movement on it, or it occurs spasmodically, this may be the consequences of illness, stress and other reasons. It would be a good idea to see a gynecologist.
It is especially dangerous if the observed temperature level of about 37.2 degrees is not confirmed by a proven rapid pregnancy test. In conditions of probable conception, when sexual intercourse has taken place, this situation is very similar to the condition of an ectopic pregnancy. It is clear that this puts lives at risk. Surgery will be required.
Indicators during ovulation
An unusual basal temperature before or during your period may indicate a number of problems. But measurements on other days are no less indicative. Normally, the next morning after the release of the egg, a woman observes an increase in temperature. It can be either sudden or gradual. For some, on the very first day it increases by 0.4 degrees, for others this difference increases in 2-3 days. Both of these situations are completely acceptable. In the case when the rise in values takes more than 3 days, one can suspect the inferiority of the egg released from the ovary or a lack of estrogen. As a rule, it is almost impossible to get pregnant in such a cycle.
What should be the basal temperature during ovulation?
To be sure that the body is working correctly, you need to make sure that the existing basal temperature after ovulation is 37 degrees. A deviation of 0.1 degree higher is possible. This helps ensure that there are no disruptions in the production of the necessary hormones, sufficient progesterone is produced, and the overall balance is not disturbed. The fact that there is healthy estrogen production can also be indicated by basal temperature before ovulation. What thermometry turns out to be depends on the functioning of the ovaries. The egg matures in them, and this should take place at a temperature no higher than 36.6. Otherwise, the formation of the oocyte will not be able to occur correctly.
So what basal temperature, measured before ovulation, can shed light on many secrets of the female body. For example, a rise in the temperature graph that occurs before ovulation suggests suspicion of inflammation. You need to think about whether the appendages might have caught a cold. Infections and decreased immunity sometimes also contribute to inflammation. You need to monitor your diet, undergo examinations, and take tests.
If the graph of the measured morning temperature before ovulation, during ovulation itself, and also after it is an inexpressive cluster of points located chaotically, without a clearly defined picture of two levels, this makes it difficult to determine the date of such an important event. After all, if you know when ovulation took place, you can predict the onset of pregnancy, as well as calculate the start time of your critical days, which occur in 2 weeks. But the absence of a clear signal on the temperature graph can cause doubts and concerns. The reason for the absence of a clear picture indicating the presence of ovulation may be either a violation of the measurement rules or the absence of ovulation itself. And this is already an undesirable pathology.
By taking constant measurements and drawing up a schedule over several cycles, you can find out what the basal temperature should be at ovulation in the next menstrual cyclic period. And this will help solve many problems, perhaps even fulfill dreams and hopes. And the most important thing is to ensure your good health.
What is the BT in phase No. 2?
The norm in phase 2 is considered to be BT that has risen to 37.2 - 37.3 °C. The difference in average temperatures is taken into account.
Evidence of low temperature in phase 2 (in accordance with phase 1) may be weak functionality of the corpus luteum (progesterone). To support phase 2 and pregnancy, a supplementary course of progesterone (usually Duphaston, Utrozhestan) is indicated.
If the temperature values of phase 2 do not increase by the required 0.4 divisions, should this be regarded as a failure of the second period? Not necessarily, but it can't be ruled out. The BBT cannot be used to judge the full functioning of the corpus luteum, the duration of the phase (a high temperature can be recorded several days after ovulation), or the concentration of progesterone, a derivative of the corpus luteum. The values on the thermometer are not indicative of determining progesterone levels; to do this, you need to wait a week from the moment of ovulation and donate blood for analysis.
What values indicate the completion of ovulation? Before ovulation the values are lower, after it they are higher. An increase in BT will indicate that ovulation has occurred.
What should be the temperature between the first and second phases, how much is the difference?
The difference between the average BT levels of phases 2 and 1 should be equal to 0.4-0.5 °C. Cases of a slight deviation in temperature, which is an individual feature of the female body and does not indicate a violation, are not taken into account.
This can be easily checked using additional methods - ultrasound, hormonal blood tests, etc.
When, throughout the entire cycle, the marks on the graph have approximately the same level or the curve resembles a “fence” shape (alternating low and high values), then it is judged that there is no ovulation in a given monthly cycle - anovulation.
To make sure of this, ultrasound monitoring is carried out over several cycles to determine the absence or presence of ovulation. For healthy women, it is considered normal to have several anovulatory periods every year. However, if such a picture is present during each cycle, the gynecologist should be notified. The complete absence of the ovulatory process does not allow full menstruation; the presence of so-called menstrual-like bleeding is noted. Their regularity may also vary.
How many days can the graph grow? Normal recovery is no more than 3 days. A large flatness in the graph indicates estrogen deficiency and a weak, defective egg. Greater difficulties with fertilization arise when BT has high rates in phase 1 and growth lasts more than 3 days.
Atypical is the lengthening of phase 1, although this does not affect the normal cycle. That is, a cycle with a longer 1st phase is the norm.
When phase 2 lasts less than 12 days, this means phase insufficiency, low concentration of progesterone.
What should the temperature be at the beginning of pregnancy? In the absence of bleeding and the establishment of BT in phase 2 for more than 18 days, the development of pregnancy cannot be excluded.
Regular recording of basal temperature helps determine pregnancy in the early stages - almost in the first couple of days after conception. The fact that the meeting of sperm and egg has nevertheless taken place is signaled by an increased basal temperature. In addition, monitoring such data often helps to notice in time any problems in the development of the fetus, for example, to prevent miscarriage, etc. What does the expectant mother’s basal temperature of 36.9C indicate? Should we panic in this case?
What is basal temperature?
This is the name given to the temperature inside the body measured at complete rest. Based on its indicators, it is customary to determine the period of ovulation, therefore such measurements are especially popular at the stage of pregnancy planning. The standard basal temperature is 37C. But as the ovulation process begins, the data increases by about 0.4C. This allows us to draw a conclusion about the maturation and release of the egg. When conception does not occur, closer to menstruation the temperature drops again to 37C. If the data remains at an elevated level, there is a high probability of pregnancy.
Why are measurements needed?
As mentioned above, it is customary to measure basal temperature data when planning pregnancy. This allows you to calculate the days most favorable for conception.
Also, such measurements are carried out with the opposite purpose, to determine when it is better to refuse sex or use additional contraceptives.
A graph of basal temperature data is used to determine the general condition of the endocrine system and clarify the date of the next menstruation.
In addition, doctors may advise regularly measuring readings while expecting a baby in order to notice in a timely manner if something goes wrong. Such measurements are usually carried out in cases where there is a possibility of miscarriage and other similar problems.
It must be borne in mind that the temperature in our tissues is in constant fluctuation and depends on a variety of factors: stress, overheating and hypothermia, food intake, etc. That is why measurements should be carried out when the body is in a state of maximum rest and is not yet exposed to influence of external factors. Basal temperature measurements are carried out in the morning, just after waking up.
Basal temperature readings
The standard thermometer reading at the initial stage of the cycle is 36.6-36.7C, but shortly before ovulation they decrease slightly. Directly on the day of ovulation, basal temperature rises to 37C and above. The data remains elevated after the egg is fertilized for about four more months. The temperature changes due to intense production of progesterone. This substance is necessary for full conception, as well as for the preservation and development of the fetus.
When recording basal temperature, a pregnant woman may encounter numbers of 36.9C or even lower. This situation is possible and does not always indicate a threat of interruption. When the basal temperature exceeds the data of the first phase of the cycle by at least 0.4 C, you don’t have to worry.
In addition, gynecologists claim that these values are especially informative only in the first four weeks of pregnancy; only a percentage of doctors believe that they need to be known until the end of the first trimester.
However, if your basal temperature drops during pregnancy, it is better to see a doctor. Sometimes this condition is explained by decreased synthesis of progesterone and, accordingly, the threat of miscarriage. Thanks to timely diagnosis, doctors have time to take the necessary measures and save the situation. Sometimes low basal temperature indicators indicate fetal freezing.
It should be borne in mind that the thermometer readings may differ if you take measurements incorrectly.
You should not measure your temperature every hour or two, because the results of such measurements will be very different. For example, in the morning the thermometer may show 37.2C, and in the afternoon 36.9. Such fluctuations are absolutely within normal limits.
Basal temperature is recorded in the morning, only at the same time. In the evening, prepare a thermometer by placing it near your bed so that you can easily reach it without getting up. In the morning, apply cream to the tip of the thermometer and insert it into the rectum about two to three centimeters. The duration of measurements is five to seven minutes. If you get out of bed before taking measurements, the data may be skewed, usually downward.
Basal temperature sometimes drops even as a result of minimal physical activity. Experts do not even advise turning over while lying in bed, let alone getting out of it. The value may also change if the sleep preceding the measurement was shorter than four hours.
Basal temperature readings are disrupted due to sexual contact, as well as due to taking certain medications. In addition, you need to take into account that electron thermometers tend to give an error of plus or minus a couple of degrees.
If, while waiting, you find out that your basal temperature is 36.9C, do not panic, this can be explained by completely normal reasons. An additional visit to the doctor will certainly dispel your worries and worries.
Comments (0)
Doctors' opinion
Most of the processes that take place in the female body do not pass without leaving a trace. According to doctors, knowing a number of indicators, including temperature, will help determine them. Basal thermometry is designed to reveal many intimate secrets and features of the reproductive system. This method is able to tell about pregnancy long before it is determined by the results of ultrasound or hCG tests. If you do the measurement procedure correctly and regularly, you can prevent the development of unwanted changes in the body. A well-made graph can confirm good health or suggest that a woman should see a doctor.
Basal temperature before menstruation
Basal temperature values before menstruation
Basal temperature before menstruation: should it fade?
To begin with, let’s take a look at the defined term. We all know that the normal temperature in the groin area should be 36.6 °C. If your body temperature is lower or higher than normal, we immediately feel bad and want to take medicine. And the basal temperature axis does not affect us like that. We cannot detect a sharp temperature drop of five degrees. Well, basal temperature is, roughly speaking, the temperature of our mucous membranes, which characterizes the processes that take place in our body. It’s really important to be careful when you’re a doctor, but not everyone is a doctor. Nowadays, such information may be needed by ordinary people, more precisely, women, since the main information about BT changes is important to them? On the other hand, basal temperature changes during the period of ovulation, which means nutrition and family planning, so mastering this method is important for a woman who wants to become pregnant.
BT is changing and the schedule will be
It’s easy to measure your basal temperature: this is how you use a basic thermometer. It is necessary to moderate the temperature not in the groin recess, but in the rectum, in the groin or in the mouth. By checking the temperature before menstruation, you can determine whether menstruation will begin soon. And, before speaking, if ovulation has begun, during the period before menstruation it can be noted.
And what is the basal temperature (BT) before menstruation when there is gestation and positive ovulation? What do the numbers on a thermometer characterize? Let's take a look at various situations and possible reasons for defying illegal norms.
Basal temperature before menstruation 36.9°C
And there are no reductions in the other half of the menstrual cycle. We are talking about the number of days of mature eggs. The Danish cycle is highly anovulatory. Ale does not allow women to be diagnosed with infertility. So, as it happens in 20-25 year old women with a good ovulatory reserve, such cycles can occur 2-3 times a day.
The basal temperature before menstruation is 37.0, 37.1, 37.2
degrees, then you can also tell about vaginess. And, having said everything, that’s how it became. And if BT arrives before the start of your period, it is possible that they will no longer be available for the next nine months.
Basal temperature before menstruation 37.3°W
a little more than what was put in. Possible activity outside the norm is associated with nervous strain and inflammatory processes in the body. In this situation, it is important to consult your doctor.
Basal temperature before menstruation 37.4°C
often associated with a lack of estrogen. It is unlikely that you will get sick during a period of elevated basal temperature. It’s not a good idea to go to the doctor. A gynecologist can refer you to an endocrinologist for an appointment. It is possible that due to the plans of pregnancy you will have to check. It is important to identify the reason for such a high basal temperature.
If you decided to use this method during planned pregnancy to identify possible reasons for the absence of conception or to determine the day of ovulation. Remember that a stable (over at least 3 menstrual cycles) increase in basal temperature before menstruation, such as a decrease below 36.5 ° C, are criteria that you should not lose without respect. If you are about to get sick, then any changes on the temperature chart should be explained by your gynecologist.
Important nuances
If on any of the days before the measurements the normal daily routine was disrupted, then the temperature will not be indicative. If you drank alcohol in the evening, got up a couple of hours before the measurement to go to the toilet, or were close in the morning, then the values obtained may differ significantly. Even a simple stomach upset or stress the day before can cause fluctuations in the temperature curve. This, by the way, is one of the reasons why it is impossible to judge a woman’s health status on the basis of just one graph. But it should also be noted that even an ideal graph, in which two clear phases emerge with a good difference in indicators, and the basal temperature before menstruation is 36.9 degrees, does not yet mean that the woman is in excellent health. For example, measurements will not provide any information about the size of the endometrium in the uterus or adhesions in the tubes. Therefore, even with normal indicators, you should not neglect visits to the gynecologist.
Basal temperature before menstruation: why measure it? First, let's look at the definition of the term. We all know well that the normal temperature in the armpit should be 36.6 °C
If our body temperature is lower or higher than normal, we immediately feel unwell and want to take sick leave. But basal temperature does not affect us that way
We will not be able to feel even a sharp temperature drop of half a degree.
So, basal temperature is, roughly speaking, the temperature of our mucous membranes, which characterizes some of the processes occurring inside our body. It’s very interesting to observe this as a doctor, but not all of us are doctors.
Why might such information be needed by an ordinary person, or more precisely, a woman, since mostly data on changes in BT is important to her? The fact is that basal temperature changes during the period of ovulation, therefore, if there is a question about family planning, then mastering this method is important for a woman who wants to get pregnant
We measure BT and build a graph
Measuring basal temperature is quite simple: this method uses a regular thermometer. Just measure the temperature not in the armpit, but in the rectum, vagina or mouth. By measuring your temperature before your period, you can find out how soon your next period will come. And, by the way, if ovulation has occurred, this can be determined during the period before menstruation.
But I wonder what the basal temperature (BT) before menstruation will be in the absence of pregnancy, with positive ovulation? What do the numbers on the thermometer characterize? Let's look at various situations and possible reasons for deviations from generally accepted norms.
Basal temperature before menstruation 36.9°C
and there are no jumps in values on the graph in the second half of the menstrual cycle. This indicates the absence of a mature egg. This cycle was probably anovulatory. But this does not give grounds to diagnose a woman with infertility. Since even 20-25 year old women with a good ovulatory reserve can experience such cycles 2-3 times a year.
If the basal temperature before menstruation is 37.0, 37.1, 37.2
degrees, then this may indicate pregnancy. And, most likely, this is what happened. And if the rise in BT was before the expected menstruation, perhaps they will no longer be, at least in the next nine months.
Basal temperature before menstruation 37.3°C
a little higher than expected. Perhaps a deviation from the norm is associated with nervous overstrain, inflammatory processes in the body. In this situation, it is advisable to consult your doctor.
A basal temperature before menstruation of 37.4°C is often associated with estrogen deficiency. It is unlikely that you will be able to get pregnant during a period of elevated basal temperature. But you shouldn’t put off going to the doctor. The gynecologist can refer you to an endocrinologist for an appointment. You may have to wait a little while planning your pregnancy.
It is important to identify the cause of such a high basal temperature
If you decide to use this method when planning a pregnancy to determine possible reasons for the lack of conception or to determine the day of ovulation, remember that a stable (for at least 3 menstrual cycles) increase in basal temperature before menstruation, as well as its decrease below 36.5 ° C - criteria that should not be ignored. If you are trying to get pregnant, then any changes in the temperature chart that you do not understand should be explained by your gynecologist.
Construction of a graph and reasons for deviations from the norm
At least once, almost every woman in the world has noticed that her temperature is elevated. And at the same time, the general condition of the body is quite normal. And if 36.6 degrees is considered normal, then on some days in women this figure can reach 37.3 and higher.
This happens because a woman’s body produces hormones unevenly in different cases. Therefore, temperature indicators are constantly changing.
The normal basal temperature will be as follows:
- 36.7, if there are 2-3 days left before menstruation;
- 37 – 37.3, if it is the third week of the cycle (14-20 days) and the progesterone phase.
If a woman becomes pregnant, her BT will also be increased. Moreover, there should be no discharge on menstrual days. If they do exist, then you need to be wary of a miscarriage.
There are many sites on the Internet that offer to create a BT schedule. Moreover, the programs that calculate it take into account all factors. But you can do this yourself if you carefully record all the indicators.
There are several good reasons for creating a BT schedule:
- no matter how much she wants, a girl cannot get pregnant for a year;
- the level of hormones in the body may be disrupted;
- it is possible to determine infertility;
- if a couple has a desire to have a child of a certain gender.
Creating a graph like this helps you figure out the following:
- on what days does the egg mature and does it happen at all?
- was there ovulation or not?
- check the correct functioning of the endocrine system;
- are there any disorders in the reproductive system;
- what violations can be identified;
- whether the ovaries produce the required amount of hormones;
- you can determine what day your next period will be;
- Did you manage to get pregnant?
If the schedule is drawn up correctly, then the woman has the opportunity to identify the problem before it worsens. But it never hurts to get additionally examined by a doctor.
The BT schedule should include the following items:
- exact number;
- cycle day;
- number of BT;
- Notes should indicate those factors that influence the result.
If a woman notices any problems, she should definitely contact a gynecologist. You can calculate the changes yourself, but this result will not be one hundred percent accurate.
Non-standard temperature readings
Some deviations from accepted norms (for example, 38°C) are individual and may mean the development of various gynecological diseases
In any case, if they are detected, you need to pay attention to your health and seek advice from a specialist, like this: with a lack of progesterone, menstruation appears prematurely, rectal temperature tends to constantly fall;
with a lack of progesterone, menstruation appears prematurely, rectal temperature tends to constantly fall;
with endometritis – a noticeable increase in temperature;
with inflammation of the appendages, an increase occurs, etc.