A polyp on the cervix is often diagnosed in women of childbearing age. Features of changes in mucous tissue are caused by multiple endogenous and exogenous factors. Pathological growths can occur both before pregnancy and after conception. In the second case, the disease is left under the control of specialists until delivery. The risk group includes young women with previous abortions, disordered sex lives, long-term drug treatment and hormonal disorders. Treatment during pregnancy comes down to observation.
What is a decidual polyp
Decidual polyp - what is it? This is a neoplasm with bulging into the lumen of the cervix.
Focal proliferation is the result of disruption of the normal proliferation of endocervical tissue.
According to statistics, it is diagnosed in every 5th woman in the form of small growths that begin to develop from the functional layer of the endometrium with the onset of pregnancy.
Decidual tissue is equipped with blood vessels, delicate and easily vulnerable.
In case of tissue injury, women may experience bleeding, cramps in the lower abdomen, and fever.
If an infection occurs when it gets into small cracks, the development of an inflammatory process will begin. And this entails a danger to the natural process of bearing a child.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine polyps?
Will it be possible to get pregnant with an endometrial polyp? A question that often worries nulliparous women does not have a clear answer. According to statistics, there are many cases of successful conception in the presence of a polyp in the uterus. If the endometrium grows unnaturally, pregnancy is possible; the polyp does not interfere with conception. If the pregnancy is planned in advance, you will first need to undergo an ultrasound, visit a gynecologist, and undergo tests. If a polyp is detected, you need to undergo a course of treatment, and, if necessary, remove the polyp. If conception occurred in the presence of minor foreign bodies in the uterus, then regular visits to the doctor will not hurt you. The problem must be kept under control, since the growth can lead to placental abruption, which can lead to a decrease in the flow of blood into it. It’s hard to imagine, but development may stop, nutrition and oxygen supply to the embryo may be disrupted, hypoxia will appear and there will be a threat of miscarriage.
Causes
The formation of a polyp in the cervical canal is the result of a violation of the structure of the endometrium with rapid growth with an unstable hormonal background. The body begins to react inadequately to the new condition.
Other provoking causes of decidual polyp during pregnancy with a settlement on the cervix:
- a sharp increase in estrogen levels;
- suppression of the immune system;
- chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- addition of urogenital infection;
- old cervical injury.
The bulging of decidual tissue into the cervical canal can be provoked by the incorrect position of the fetus in the uterus.
Reference! Pathology may exist even before pregnancy. The polyp begins to grow rapidly, blocks the entrance to the uterus and conception becomes impossible. Women are diagnosed with infertility.
A polyp can only be detected during diagnostics.
It happens that a small growth is localized before pregnancy and is detected during pregnancy.
The polyp requires removal, but in the postpartum period, if it does not have a detrimental effect on the course of the interesting situation of expectant mothers.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of polyps are not fully understood. But some circumstances have been identified under which their origin and growth occur. These include:
- hormonal imbalance;
- vascular pathology;
- frequent diagnostic scrapings;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system;
- traumatic injuries;
- unsuccessful births and abortions.
They are provoked by:
- endocrinology diseases;
- bad heredity;
- high sugar;
- high blood pressure;
- excessive production of estrogen with excess weight;
- with inactivity, stagnation forms in the pelvic area;
- frequent use of pharmaceuticals;
- failures in exchange processes;
- presence of infection in the body;
- incomplete detachment of the placenta during labor;
- venereology diseases;
- abortion caused by pharmacological drugs;
- incorrect use of the spiral.
Types of decidual polyps
Gynecologists distinguish several types of benign formations in order to subsequently recognize their structure and nature during histology analysis.
Worth knowing! Polyps can be true or false. Pseudopolyps are not dangerous and often disappear without a trace in women giving birth after the birth of a child. True polyps are a reason for a biopsy with the removal of a piece of tissue from the cervical canal and subsequent study in order to timely detect cancer.
Based on their structure, polyps are divided into 3 types:
- glandular – safe with a loose structure, formed as a result of hormonal imbalance;
- fibrous (dense neoplasms) prone to malignancy, more often observed in women during menopause or serious hormonal abnormalities;
- glandular-fibrous, consisting of glandular cells and connective tissue, requiring excision;
- adenomatous - the most dangerous (precancerous) requiring immediate removal and observation by an oncologist.
Can a polyp be confused with pregnancy?
In unclear situations, a knowledgeable and experienced doctor will be able to distinguish a polyp from pregnancy. To do this, it is enough to have basic knowledge and have the results of tests and diagnostics. Establishing the correct diagnosis is not difficult, since endometrial growths differ from the fetus in shape and shade. The fertilized egg is round and dark in color, while the polyp is lighter. Misdiagnosis in such cases is extremely rare. But, if you still want to be sure, then contact another specialist to re-confirm.
Symptoms
A single small growth formed in the cervical canal does not hurt and bothers women. It is detected in the gynecologist's office during examination on the chair.
Symptoms of a decidual polyp are mild or absent.
Periodically, whitish mucus may come out of the vagina.
If the polyp is the result of a disease, it may be accompanied by bleeding during periods of exertion: weight lifting, sexual intercourse, intense training in the gym.
Polypous tissue is penetrated by many blood vessels. Even minor damage or rupture leads to:
- bruising;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- leakage of copious mucus and blood from the vagina.
Reference! Polyps often do not bother women even during pregnancy.
If a polyp is accidentally injured, then there is immediately a danger of infection (STDs, trichomoniasis, genital herpes, candidiasis, chlamydia).
In this case, the decidual tissue begins to grow rapidly and pathologically, provoking miscarriage, premature birth, and all sorts of complications in women - colpitis, fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometrial polyposis.
Surgical treatment of polyps in the uterus during pregnancy.
The most common ways to combat pathology are:
- Hysteroscopy (laser polyp removal) is a modern and safe method that involves minimal medical intervention. It is carried out using a device that is a tube with an instrument and a video camera - a hysteroscope, which is inserted into the uterine cavity through the genital tract, and then the polyp is eliminated. In this case, the doctor sees the area of manipulation, which makes it possible to exclude incomplete removal of the tumor.
- Curettage is an outdated method that is undesirable to use. Elimination of the polyp is carried out blindly, as a result of which there is a possibility of relapse of the pathology. In addition, the operation is very traumatic, quite painful, and can lead to bleeding from the genital tract and perforation of the uterine wall. Curettage is carried out under general anesthesia with the obligatory subsequent placement of the patient in a hospital.
- Hormonal therapy. The effectiveness of this method is only 30%. After using medications, there is a small risk of the polyp degenerating into a malignant neoplasm. In some cases, the pathology may recur.
Curettage and hormonal therapy during pregnancy are not allowed if a woman wants to keep the child. Treatment of the disease is best postponed until the postpartum period. In case of severe pain that cannot be treated with analgesics, heavy bleeding, purulent complications, or cancerous degeneration of uterine polyps, the patient may be offered emergency surgery, as well as medical or surgical abortion.
Why are they dangerous?
A polyp of the cervical canal is dangerous because it is easily wounded.
If it becomes damaged under significant loads and begins to bleed, it causes the development of an inflammatory process.
The situation becomes threatening for pregnant women and begins to pose a threat to the fetus.
If a single polyp does not affect the course of pregnancy on its own, then if localized in the uterine cavity, under the influence of a number of provoking factors, sudden increased growth may begin.
It is worth mentioning: what are the dangers of placental polyps during pregnancy. The danger lies in complications when the growth requires urgent excision or scraping with electric current.
Also, a polypous growth can cause premature delivery, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, inflammation of the endometrium, malignancy with degeneration into a malignant tumor and serious consequences.
Polyps remain dangerous even after excision, because they can leave scars on the cervix and lead to obstruction of the cervical canal.
This happens in cases of incorrect, incomplete cauterization of the polyp stalk by inexperienced doctors.
The pathology begins to cause complications. A threat is created for women when questions arise about whether it is possible to become pregnant with a polyp of the cervical canal in the future.
Possible complications
The appearance of formations during pregnancy can be characterized by serious complications and consequences. Among them:
- dysfunction of the ovaries;
- inflammation of the endometrium;
- the appearance of cancer cells;
- pathologies of fetal development;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- placental abruption;
- inflammation;
- uterine rupture;
- heavy bleeding;
- sepsis;
- problems during childbirth caused by weak uterine contractions;
- freezing of the child.
If the endometrial polyp is small in size and there is no growth or transformation during pregnancy, then it is not dangerous for the unborn baby. Exceptions occur only in situations where:
- malignant growths. Their mandatory removal is necessary;
- the polyp becomes inflamed and becomes a source of infection. Measures are taken to eliminate inflammation;
- leads to dilatation of the cervix, causing early labor and miscarriage. A pessary is used (a ring to hold the body of the uterus or suturing is performed, the sutures from which are removed before childbirth).
Diagnosis and treatment
It is not difficult for gynecologists to identify a polyp using mirrors. The best diagnostic option is colposcopy, which can detect even small single growths.
The gynecologist takes a piece of tissue and sends it to the laboratory for cytology testing.
Biopsy is a diagnostic method for suspected cancer, when doctors need to find out the nature of the tumors and find the differences between the decidual polyp and other growths of cervical tissue.
It happens that:
- transvaginal examination in case of formation of polyps from endometrial tissue;
- hysteroscopy in case of localization of the polypous leg near the uterine cavity;
- PCR for suspected STDs using a vaginal smear and redirection for bacterial culture as a biomaterial to detect infection.
If during gestation a pseudopolyp measuring no more than 10-11 mm is detected in women, removal or treatment is not carried out if there are no signs of isthmic-cervical pathology.
Doctors choose a wait-and-see approach, monitoring polyps throughout a woman’s pregnancy and only making a decision about removal after birth.
The main thing is for women to remain completely at rest in the position, not to strain or lift heavy objects, so as not to provoke injury to the growth or bleeding.
Reference! Doctors make a decision on urgent excision of a polyp only if it grows rapidly and reaches an impressive size, and if there is bleeding from the uterine cavity during pregnancy in order to prevent complications.
If there is a suspicion of degeneration into an oncological tumor, or if there is a risk of termination of pregnancy, they resort to urgent removal of the tumor.
Diagnostic measures
An integrated approach is required to diagnose and detect tumors in the uterus. It is formed from the data collected by the doctor during the examination of patients and the results of examinations. For this:
- examination is performed using gynecological speculum. The procedure identifies tumors in the cervix or uterine prolapse;
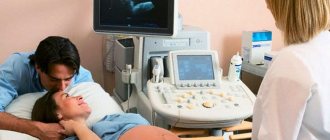
- To identify polyps in the body of the uterus, an ultrasound is necessary. Inspection and palpation are not able to determine the appearance of neoplasms. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the parameters of the uterus, expansion, thickness of the endometrial layer, which necessarily increases when a polyp forms;
- hysteroscopy is performed. The technique is considered the most informative and is performed by introducing a microscopic device with a video camera into the cavity. The procedure allows you to accurately recognize the location, quantity, configuration and color of growths;
- lab tests. When performing hysteroscopy, the body of the polyp is pinched off and a histological examination of its cells is performed;
- diagnostic curettage is performed for subsequent laboratory analysis of cells;
- metrography. Necessary x-ray examination of the cavity and body of the uterus. Contrast is used to help detect uneven endometrial layer and small foreign growths.
All diagnostic techniques require modern equipment and appropriate knowledge of doctors. Modern clinics have the ability and the necessary resources to guarantee an accurate and timely diagnosis of a polyp at an early stage, referring to the detected slight thickenings and formations in the endometrium.
When is surgery necessary?
The operation is not performed if the course of pregnancy with a polyp is calm and does not bother the expectant mother in any way.
Surgery to remove a decidual polyp is performed in the following cases:
- infection, accession of infection;
- the appearance of ulcers on the surface of the polyp;
- heavy bleeding;
- hypertonicity of the uterus;
- spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased uterine tone as a sign of miscarriage;
- reaching polyps over 2 cm in size.
Danger
Polyps discovered during pregnancy do not pose a particular threat, since they tend to spontaneously resolve at certain times, or come out during natural childbirth. If the pregnancy ends with a cesarean section, the doctor usually suggests removing the polyps surgically some time after the operation.
Most often, a polyp of the cervical canal poses a serious problem for non-pregnant women, as it blocks access to the seminal fluid into the uterus, as a result of which the woman cannot become pregnant.
One of the most unpleasant complications that can arise from a polyp during pregnancy is its infection. In this case, doctors usually prescribe antibiotic therapy to the expectant mother.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency provoked by a polyp can also become a serious problem, as a result of which, under the pressure of the growing fetus and the polyp located in the cervical canal, the cervix opens prematurely. This situation can provoke premature birth, as a result of which a child is born with low weight and undeveloped organs and systems, which most often leads to fetal death.
Sometimes doctors suggest removing a polyp during pregnancy, but the feasibility of this surgical intervention is significantly lower than the risk it poses for a developing pregnancy . Therefore, usually the polyp is simply observed until natural birth occurs.
If the presence of neoplasms is suspected and their condition is assessed, the gynecologist usually performs a smear from the cervical canal. Next, the results of the smear are deciphered according to the following indicators - for the presence of infections and using the Papanicolaou method, which reveals pathologies of the cervix, including precancerous conditions.
The procedure for taking a smear is very simple and painless, it is carried out within 1-2 minutes. Using a special spatula, the doctor carefully takes a scraping from the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, which is then transferred to a clean glass. Next, the smear is sent for analysis to the laboratory, where it is examined under a microscope or a LHC culture is performed.
Normally, in a non-pregnant woman, the length of the cervical canal is from 30 to 40 mm. During pregnancy, its length changes depending on the period. Throughout pregnancy, the canal lengthens, shortening shortly before birth.
Below are the averages for each trimester of pregnancy:
| I trimester of pregnancy | The length of the cervix is up to 35 mm, the cervix is dense, bluish in color. |
| II trimester of pregnancy | Cervical length 35-45 mm |
| III trimester of pregnancy | The length of the cervix is 10-15 mm, it shortens before the approaching birth |
Just before birth, the length of the cervical canal should not exceed the norm of 10 mm.
If during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy there is an insufficient length of the cervical canal, this may indicate isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which is a threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
How does a polyp get eliminated?
Most often, polyps do not interfere with childbirth; they come out on their own during delivery, together with lochia and the inner lining of the uterus.
Surgical removal of a polyp of the cervical canal during pregnancy is a radical option in cases of severe inflammation, necrosis of the polyp, and heavy bleeding.
Women during pregnancy are prescribed gentle techniques:
- laser polypectomy with the introduction of an endoscope to monitor the process of cauterization of damaged vessels;
- thermocoagulation;
- targeted hysteroscopy – a painless, low-traumatic option for polyp removal during gestation;
- cryodestruction with burning of the polyp with liquid nitrogen;
- constriction in the case of localization of the tumor near the external pharynx by throwing a cord over the leg of the polyp and twisting it for subsequent tissue necrosis.
Curettage of the cervical canal in women during pregnancy is not performed.
If a polyp bleeds during pregnancy, what should you do? Doctors prescribe gentle removal methods at any trimester: cauterization with electric current, laser, radio loop.
After removal, the doctor redirects the tissue sample for histology to exclude or confirm the malignancy of the formation, and redirect the woman for consultation with an oncologist.
Is it possible to conceive after removal of endometrial polyps?
You can conceive a child after removing growths from the cervix within 4-6 months. Doctors do not recommend postponing pregnancy for a long time, as there is a risk of relapse. Even after cleaning, part of the neoplasm’s stalk remains on the mucous membrane, which can grow again without appropriate therapy.
To speed up the onset of conception, after surgery it is necessary to undergo a course of hormonal therapy.
The myth that infertility occurs after the removal of polyps has long been refuted by doctors. This is confirmed by both scientific research and real-life cases.
Prevention of formations on the cervix
It is important for pregnant women to monitor their well-being daily and prevent complications from developing.
Prevention measures:
- be seen by a doctor in a timely manner;
- register early;
- prepare the body for conception;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- adequately choose contraceptives;
- do not ignore the spontaneous appearance of uterine bleeding, strange, foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
A decidual polyp does not affect the course of the birth process and will probably disappear on its own after the hormonal levels are restored and the child is born.
The main thing is that it does not begin to pathologically modify its shape or grow rapidly. These are signs of degeneration of decidual tissue in the cervical canal into pathological tissue. The risk of cancer increases. And here it is necessary to immediately excise the tumors in order to avoid the development of oncology, cervical cancer in women.
Drug therapy for polyps during pregnancy.
To eliminate the symptoms of pathology during pregnancy, the use of medications is indicated. Of course, this approach does not allow removal of a cervical polyp during pregnancy, but it completely eliminates the possibility of interruption of gestation and infection of the mother due to surgical intervention. After childbirth, a woman can eliminate the tumor in the most optimal way.
Drug therapy for polyps during pregnancy involves:
- Reducing pain that can negatively affect fetal development through the use of analgesics. These medications are prescribed only by a doctor, guided by the possible consequences of their use for the unborn child and the condition of the pregnant woman.
- Maintenance therapy. For minor bleeding caused by polyps, taking iron, folic acid and vitamin B12 supplements is indicated. This is necessary in order to prevent the development of anemia. To strengthen the immune system during pregnancy, vitamin and mineral complexes are recommended.
- Hormonal medications are prescribed in exceptional cases. The course of treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting under the close supervision of medical personnel. Before prescribing medications, a qualitative assessment of the patient’s condition is necessary.
- Treatment with antibacterial drugs is indicated if the pathology has led to infectious complications. In this case, the main task of doctors is to prevent intrauterine infection of the fetus. The course of drugs is selected individually, based on the severity of the disease and the likely complications for the child.
Not a single woman is immune from the appearance of polyps in the uterine cavity. Even thorough preparation for conception does not guarantee that neoplasms will not occur during pregnancy. Fortunately, in most cases, the pathology does not pose a serious danger to the mother and fetus, so its treatment is postponed until the postpartum period.
Polyp and pregnancy: reviews
If you go to any forum for pregnant women where this topic is discussed, you will probably find scary reviews. But in reality, polyp and pregnancy in most cases are absolutely normal. Apart from the fact that pathology actually occurs as a side effect from taking Utrozhestan, as evidenced by many mothers (according to the results of medical reports).
Pregnant women also confirm that if the doctor convinces them to forget about the polyp until the end of pregnancy, then this is justified: they safely gave birth to healthy children, and in many of them the polyp disappeared without a trace.
But in those women who had polyps removed during pregnancy, the formations often grew back, and even larger than before. Therefore, for your own peace of mind, it is better to listen to the opinions of several doctors. Still, now is not the best time for any invasion of the genital organs, especially if the uterus is already in good shape.
Especially for - Larisa Nezabudkina
Cervical polyp during pregnancy: in what cases should it be removed?
A cervical polyp is diagnosed during pregnancy in 25% of women and, in fact, is a normal variant. However, at the same time, the expectant mother immediately has a question: how does the presence of this education affect the unborn child?
Let's consider why growths can form on the cervix, and what danger they can pose during the period of bearing a child.
What is a polyp?
A polyp is a growth of the endocervix, that is, the epithelial tissue lining the lumen of the cervical canal. It can be asymptomatic, but more often its characteristic sign is the presence of pathological discharge in a woman. Upon examination, both single and multiple growths can be diagnosed.
Externally, the polyp in the cervical canal resembles a mushroom in its structure. Its stem is penetrated by many capillaries. The color of the formation can range from pale pink to purple-red. The length of the growth usually does not exceed 2 cm. As the polyp grows, it can be born into the vaginal cavity and become injured, causing bleeding.
Ferrous.
The result of the proliferation of endocervix glands.
Fibrous.
They come from connective tissue and have a tendency to malignancy.
Glandular-fibrous.
Mixed option.
However, most often women develop decidual polyps during pregnancy. This is a special group of formations of this type that arise as a result of hormonal changes in the female body.
Reasons for appearance
In 90% of cases, a cervical polyp discovered during pregnancy is of a hormonal nature. In this case, we are talking about decidual formations and the process is called deciduosis.
This condition occurs due to an increase in the concentration of the hormone progesterone in the blood. It, in turn, causes an increase in the thickness and blood supply of the mucous membrane of the uterus and cervical canal. Because of this, the endocervix can grow in size and protrude into the vaginal cavity.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of this pathology may be:
- Trauma to the cervix in previous births;
- Damage due to surgical interventions (abortions, diagnostic curettages);
- Chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system (including sexually transmitted diseases);
- Hormonal instability of the body, leading to menstrual irregularities.
On many forums you can find women’s assumptions about the medicinal nature of the development of cervical polyposis. That is, some pregnant women note that their polyps formed while taking hormonal drugs to maintain pregnancy (Duphaston or Utrozhestan).
However, there is no reliable data about this cause of the pathology, and you should not independently cancel the medications prescribed by your doctor because of the risk of developing this type of pathology.
Neoplasms that do not tend to grow and degenerate, as a rule, do not bring any harm to a pregnant woman. The main concern for her is the appearance of minor changes in the nature of the discharge.
However, a cervical polyp that increases in size during pregnancy can cause the following complications:
- Threat of early pregnancy termination;
- Inflammation of the cervical canal and vagina;
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which can lead to premature birth;
- Malignization of the process;
- Severe bleeding from the cervical canal.
To prevent the occurrence of these pathological conditions when a polyp is detected during pregnancy, a woman must strictly follow all doctor’s recommendations related to the diagnosis and treatment of this process.
If a doctor discovers a polyp of the cervical canal in a girl during pregnancy, then his main task is to find out the nature of its occurrence. When deciduosis is confirmed, in most cases no action is taken, and the main action in relation to it is observation.
First.
Periodic contact bleeding.
Second.
Ulcerations on the surface of the formation.
Third.
Suspicion of malignancy of the process.
Fourth.
As the polyp grows, there is a threat of miscarriage (spasms and pain in the lower abdomen, dilatation of the cervical canal).
Removal of cervical canal polyps is painless and completely safe for a pregnant woman. The growth is removed from the cervical canal by unscrewing.
It is very important to completely remove the polyp tissue, otherwise it may grow back. For this purpose, shallow curettage of the cervical canal is performed.
Further tactics depend on the location of the polyp bed: if it grew near the internal os, then sutures may be required on the cervix to prevent miscarriage. The removed lesion is necessarily sent for histological examination.
If there are appropriate indications, surgical intervention is usually performed between 16 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. This period is considered the safest in terms of threat to pregnancy. If the case is urgent (severe bleeding or detection of cancer cells), then surgery can be performed at any stage of gestation.
Impact of the disease on pregnancy
It is best if the expectant mother takes care of her health in advance, so that treatment during pregnancy does not harm the fetus.
Any polyp must be removed before conception because doctors will have to use anesthesia to do this. Very often, the disease prevents pregnancy from occurring (prevents the passage of a fertilized egg), but it happens that it is conception that provokes its appearance. Typically, a polyp during pregnancy does not harm either the mother or the child. If the baby was able to attach to the wall of the uterus, then the polyp is not touched until the baby is born. In some difficult cases, emergency removal of the tumor will be required. Such measures are resorted to only if it threatens the life of the embryo. If the pathology was discovered and removed before pregnancy, then it is necessary to be examined again, because it is possible that it will reappear.
The course of the disease may be complicated by bleeding (this is usually characteristic of formation in the cervical canal). What should a woman do if a polyp bleeds during pregnancy? Blood is released during sexual intercourse or examination by a gynecologist. In the absence of mechanical influences, it can be released only in the presence of large formations.
A large cervical polyp can cause spotting and bloody discharge with an unpleasant odor. They can disappear and reappear, strengthen and weaken. If a woman experiences similar symptoms, then she needs to: consult a specialist, reduce physical activity, stop being sexually active, and carry out hygiene procedures more often. Even with a bleeding tumor, a healthy and strong baby can be born.
How to treat during pregnancy?
In this case, a woman needs to regularly visit a gynecologist to monitor her condition. Sometimes the expectant mother is prescribed medications, such as Duphaston, to restore progesterone levels. Doctors recommend abstaining from sexual activity and reducing physical activity.
Uterine polyp
Detected uterine polyps require constant monitoring during pregnancy. Therapy is not required if the growth does not increase in size and there is no inflammatory process. Otherwise, the specialist selects individual treatment, which may consist of:
- antibacterial therapy;
- use of antiseptics and antifungal drugs;
- taking hormonal drugs.
A polyp formed in the cervical canal can constantly bleed and ulcerate, which threatens the normal course of pregnancy. In this case, you will need to use radical methods. Typically, the polyp is removed using a laser, endoscopy, or polypectomy.
Cervical polyp
Polyps on the cervix occur in 25% of pregnant women and in most cases are decidual. Such growths can resolve on their own at different stages of gestation or immediately after childbirth. Indications for polyp removal may include:
- frequent bleeding;
- growth size more than 12 mm;
- malignancy (fibrous formation);
- inflammation of the cervix;
- threat of fetal infection.
Diagnostic methods
A polyp in the uterus during pregnancy is detected during a complete examination of the woman. The following should be considered sufficient diagnostic measures:
- transvaginal ultrasound performed using a special sensor;
- survey hysteroscopy, in which an optical device (hysteroscope) inserted into the uterine cavity determines the size and shape of the formation, its location;
- histological laboratory examination of the growth.
The main way to treat endometriotic growths is to remove them surgically. But for pregnant women, the doctor does not always choose a radical treatment route due to the risk of harm to the fetus. Drug treatment and traditional medicine methods help slow down the development of education, but do not get rid of it.
Indications for surgical removal of a polyp in the uterus during pregnancy should be considered:
- the size of the formation is more than 1 cm;
- progressive growth;
- continuous bleeding;
- inflammatory process;
- formation of necrosis;
- threat to the normal development of the fetus.
Surgical intervention to remove a polyp in the cervical canal during pregnancy can be carried out using a laser, radio wave, or electrocoagulation. The most common radical way to combat endometrial polyps is hysteroscopy.
To do this, under local anesthesia with the help of surgical instruments, the cervical canal is expanded, where the formation is excised with a special device - a hysteroscope.
Then selective destruction of the endometrium is carried out. All material obtained during the operation is transferred to the laboratory for research.
If an inflammatory process in the uterine mucosa is detected against the background of an endometrial polyp, the doctor prescribes gentle anti-inflammatory treatment.
In other cases, removal of the growth is carried out after childbirth and the end of the woman’s lactation period.
A highly qualified doctor should be involved in diagnosis and treatment, since during pregnancy it is very important to eliminate all risks. Therefore, the specialist must select a therapeutic method based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the nature of the pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a polyp on the cervix, then the period of bearing the baby is carried out according to special tactics. The main task of the expectant mother is not to ignore warning signs and to control from the first days of conception:
- — vaginal discharge: color, composition, structure, smell;
- - the presence of pain during an examination by a gynecologist or after sexual intercourse.
During pregnancy, the female body experiences changes in hormonal balance. That is why the interesting position of a woman and an endometrial polyp are completely compatible phenomena. However, the appearance of formation is accompanied by complications, the most dangerous of which is inflammation. To eliminate it, anti-inflammatory therapy is required. If a growth on the cervix contributes to the spread of infection, then treatment includes antimicrobial drugs.
Pregnant women should not worry about this. Yes, the appearance of polyps is an unpleasant phenomenon, but not fatal. Basically, even when polyps occur, pregnancy proceeds without complications. The main thing is to keep the disease under control.
In most cases, the disease manifests itself in the form of aching pain and slight vaginal discharge, which during pregnancy is quite difficult to identify, since such symptoms are inherent in every woman who is in an interesting position.
Removal during pregnancy cannot be performed. The surgical procedure is performed after childbirth. However, there is a special type of growth - placental, which occurs against the background of the remains of a child's place and is accompanied by severe bleeding. This usually happens a few weeks after the baby is born. In this case, the uterus is cleaned, and the removed material is sent for histological examination.
Transvaginal ultrasound is one of the main methods for detecting a polyp in the uterine cavity. The doctor uses a special sensor to determine the location of the polyp and its size. The procedure is absolutely painless for the patient. To obtain a reliable result, it is better to undergo an ultrasound scan 5-7 days after the start of menstruation.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is considered a more reliable and accurate study. This is a method of minimally invasive examination of the cavity of a muscular organ, which makes it possible to identify intrauterine pathologies. A special device is inserted into the patient’s uterine cavity, which allows one to evaluate the structure of the polyp and its size.
Sometimes a polyp can be detected during an examination on a chair or during colposcopy (if the polyp is located in the cervical canal). In this case, the doctor must additionally prescribe an ultrasound scan to the patient.
It is impossible to diagnose a polyp during pregnancy on your own. Diagnostics is carried out by a specialist using various methods:
- Examination on a gynecological chair. A gynecologist examines the cervix and vagina using medical mirrors. This method allows you to detect only large growths in the cervical canal or vaginal tissue. Polyps growing inside the uterine cavity cannot be diagnosed by visual examination.
- Ultrasonography. This method is used if a woman has uncharacteristic discharge streaked with blood. An ultrasound is necessary to determine the cause of the blood. In some cases, this is contact discharge associated with injury to the growth, but there may also be a threat of spontaneous abortion.
- Colposcopy is performed using a special device (colposcope) to examine the cervix. Colposcopy is performed at any stage of gestation, since the procedure does not pose a danger to the baby or the expectant mother. An examination of the cervix is carried out using a microscope, and the doctor takes a section of altered tissue for cytological examination. Diagnostic results make it possible to determine the type of formation and its effect on the course of pregnancy.
- Histological examination. As a rule, histology is performed after surgical removal of the polyp. As a result of such a study, you can find out the type of polyp.
Treatment
To treat a polyp of the cervical canal, exclusively surgical methods are used. That is why the following reasons may be indications for surgery:
- The size of the polyp exceeds 12-15 mm;
- It grows quickly;
- Symptoms of polyp necrosis;
- There are symptoms of dyskaryosis (changes in the cell nucleus).
There are gentle methods for removing polyps, such as laser, electro- and radio surgery. But the main method of removing polyps is still the method of scraping the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
In some cases, after removal of a polyp, hormonal therapy is indicated, which is another contraindication for this operation during pregnancy.
Decidual polyp
A characteristic feature of decidual polyps is their occurrence exclusively during pregnancy. It is believed that their appearance is provoked by changes in hormonal levels in the female body.
A distinctive feature of this type of polyp is the large number of blood vessels, which is why it can provoke fairly frequent bleeding.
Types of decidual polyps
This polyp is called decidual (chorionic) due to the tissue from which it consists. Decidual tissue is the transformed endometrium lining the uterine cavity. Its excessive growth under the influence of hormonal changes provokes the formation of growths (polyps) on the mucous membrane of the uterus or cervical canal.
There are two types of decidual polyps:
- Decidual polyp (false);
- Tumor-like diciduosis (dangerous form).
Symptoms of decidual polyp
The main symptoms by which one can judge the presence of a polyp are:
- Regular bleeding - from moderate to intense;
- Drawing and aching pain in the uterine area;
- The appearance of bloody discharge after examination or sexual intercourse;
- Spotting (beige, brown, brown, pink shades).
Diagnosis and treatment of decidual polyps
The presence of decidual polyps is usually diagnosed during a routine examination of the cervix. To accurately determine the type of neoplasm, the doctor usually prescribes a colcoscopy, a smear on the flora and an ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
This type of polyp cannot be surgically removed during pregnancy, as this leads to the threat of abortion . Usually doctors prescribe local antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs to avoid the development of infection, and sexual rest. Regular monitoring of the condition of the polyp throughout pregnancy is also mandatory.
Most often, after childbirth, the polyp disappears on its own as soon as the woman’s hormonal levels return to normal. If this does not happen, the formation is removed surgically (curettage), or using a laser.
Polyp: what is it, what types are there?
An endometrial polyp is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of focal hyperplasia (proliferation) of the endometrium of the uterus (the internal mucous membrane lining the cavity of the smooth muscle organ). Most often, the formation has the shape of a mushroom on a stalk. Sizes vary from a few millimeters to 2 or more centimeters.
Endometrial polyps are divided into 3 groups:
- fibrous - not treated with hormonal drugs, are a common cause of infertility, located on the bottom of the uterus;
- glandular - the cause of their occurrence is hormonal imbalance, often disappear on their own after the menstrual cycle is renewed;
- adenomatous - represent a high danger, are a precancerous condition, require urgent surgical intervention.
Sometimes polyps can be located in the cervical canal (between the uterus and vagina). Such formations do not pose a threat to the mother and child, but if they are large, they interfere with conception by blocking sperm from entering the uterine cavity.
An imbalance of hormones in a woman’s body, in particular progesterone and estrogen, can provoke the occurrence of hyperplasia. The proliferation of endometrial cells forms polyps - growths that resemble mushrooms in shape. The neoplasm has a thin base (pedicle) and a wide cap. Polyps can be solitary or appear in groups. Pregnant women are often diagnosed with decidual polyps of the cervical canal.
The size of the growth varies from 1 mm to 2 cm, but in some cases it can be larger. By structure, polyps can be:
- glandular;
- fibrous;
- mixed.
Uterine polyps
A formation such as a uterine polyp during pregnancy is considered benign, that is, it does not provoke cancer. However, its growth causes serious consequences, such as infertility. The embryo will not be able to enter the uterus and attach to its wall, because the quality of the endometrium suffers from the neoplasm. If pregnancy does occur, then most likely it will end in a miscarriage.
Uterine polyps are usually small in size, ranging from a few millimeters to centimeters. Therefore, they do not often threaten a woman's reproductive ability. Large formations are considered dangerous.