Definition of the concept
In obstetrics and reproductive medicine there is the concept of “biochemical pregnancy” (BCP). This condition is not considered a pathology. This is the name given to a pregnancy that is terminated at an extremely short period of time, shortly after the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Spontaneous abortion occurs in the first 4 weeks after conception.
According to medical statistics, BCB is observed in 50% of women. However, the vast majority of patients do not even suspect that they were pregnant. After all, at such short periods there are no clinical signs of gestation. Pregnancy cannot yet be detected during a gynecological examination or ultrasound. You can find out that the process of fertilization of the egg and implantation of the embryo has taken place only with the help of an analysis for human chorionic gonadotropin or a highly sensitive pharmacy pregnancy test.
Rejection of the fetus at such an early stage looks like regular periods, which come on time or with a very slight delay (no more than a few days). Therefore, during natural conception, HDB most often goes unnoticed.
Definition of the term
Biochemical pregnancy is a conception that has occurred, but for unknown reasons has not gone further. The name “biochemical” comes from the term “biochemistry,” which means the science of the composition of living cells. We can say that such a pregnancy occurs at the cellular level, and the problem, most likely, also lies at the cellular level.
This conception begins like all pregnancies. An egg fertilized by a sperm moves through the fallopian tubes to the uterus and even manages to attach to its walls. But, something goes wrong and the onset of menstruation terminates the pregnancy. For women who are not expecting a pregnancy, everything happens as it should. The only thing that may confuse them at that time is a delay in the menstrual cycle. But then your periods come, maybe a little heavier and more painful, but they are there - that means everything is fine.
Blood sampling to determine pregnancy
For women who expect pregnancy as a miracle, a delay in the menstrual cycle is a great joy. They are already running to the pharmacy to get a pregnancy text, then to a gynecologist for an examination, and from there to an ultrasound. Although none of the authorities she has passed tells her about the onset of pregnancy, she is already happy and preparing to be a mother. The next day, most likely, the woman will take blood tests, which will confirm the pregnancy in less than a week.
But after a day or two, menstruation begins, which, along with blood, removes the embryo from the uterine cavity. This will be called a biochemical pregnancy.
FOOTNOTE
75% of pregnancies end in spontaneous miscarriages. Most often, a woman is not even aware of her interesting situation. She does not develop any symptoms and her health does not change.
Reproductive techniques and BCB
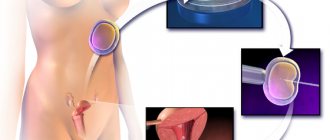
Obstetricians and gynecologists began to widely talk about BCB after the introduction of in vitro fertilization and other assisted reproductive techniques into medical practice. These technologies have helped many patients conceive a child even with complex forms of infertility.
However, cases of biochemical pregnancy after IVF are quite common. What does this mean? Such statistics do not mean that reproductive techniques have a negative impact on pregnancy. With natural conception, such a pregnancy occurs no less often, but in most cases it is not detected.
After IVF, the patient must have a blood test for hCG. This test is done no later than 2 weeks after the procedure. This allows you to determine the presence of pregnancy at a very early stage. Therefore, it is possible to track its interruption in the first weeks. BCB after in vitro fertilization is much more often detected due to early diagnosis.
Next, we will consider in detail the causes and treatment of biochemical pregnancy after IVF. The prognosis for the success of a repeat procedure is not as unfavorable as many patients mistakenly assume.
Treatment
Experts do not consider it necessary to treat biochemical pregnancy after IVF. This decision is due to the fact that this is not a disease. After spontaneous rejection of the fetus occurs in the early stages of development, there is no need to carry out special treatment with medications or clean the uterine cavity, since during menstruation the endometrium with the embryo comes out completely. Reproductologists, together with the woman, begin to look for the cause of the pathological process in order to direct all actions towards eliminating it. This is the only way to avoid a repetition of the scenario. At the same time, even a single case of pregnancy of a biochemical type is fully analyzed.
After a biochemical pregnancy has been diagnosed before a new IVF protocol, reproductive specialists advise using the following recommendations:
- go for a consultation with a hematologist to check hemostasis indicators;
- consult an immunologist;
- get tested for APS;
- additional therapy for the partner when the cause of infertility is the male factor;
- donate progesterone, estradiol and D-dimers on the day of puncture, then on the day of replantation, and then at 4-5 dpp, at 7-8 dpp;
- genetic diagnosis of both partners.
If a biochemical pregnancy was diagnosed after IVF, then a further protocol is prescribed no earlier than 2-3 months later. Moreover, this period is not specific, since everything here is determined by the woman’s health status, the reasons why the fetus failed, and her individual tolerance to manipulation.
Be that as it may, the woman has undergone implantation, which means that after the cause is stopped, the long-awaited conception will occur.
Etiology
It is very difficult to determine the exact causes of fetal rejection soon after implantation. After all, cases of BCB are also observed in absolutely healthy women during natural fertilization. This phenomenon is currently insufficiently studied due to difficulties in diagnosis.
Doctors suggest that the following circumstances may be the causes of biochemical pregnancy after IVF:
- hormonal imbalances;
- genetic disorders in the fetus;
- the use of drugs to stimulate ovulation;
- autoimmune reactions;
- blood diseases in women;
- influence of external unfavorable factors.
Next, we will look at the above causes of BCB in more detail.
Hormonal disorders
The hormone progesterone is responsible for pregnancy, especially at the initial stage. If a woman’s body develops a deficiency of this substance, this can cause the embryo to be rejected soon after its implantation. Doctors prescribe progesterone-based drugs to many patients after IVF, but such therapy does not always help to successfully carry the fetus to term.
The cause of early termination of pregnancy can also be an excess of androgens in a woman’s body. Male hormones suppress the production of progesterone.
Childbirth after IVF
Childbirth after IVF can be natural or surgical (by caesarean section). Conception using ART is not a clear indication for surgical delivery. The question of the advisability of independent childbirth after IVF is decided on an individual basis, usually on a commission basis. In this case, the condition of the woman and the fetus is dynamically assessed, the course of pregnancy and the presence of other potentially aggravating factors are taken into account. And in many cases, a decision is made about a planned caesarean section, especially in cases of multiple pregnancy.
But natural childbirth is also possible after IVF. At the same time, the fact of conception using ART is the basis for increased attention to the woman in labor. The development of any abnormalities and signs of fetal hypoxia requires an early resolution of the issue of the need for emergency surgical delivery.
Chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo
Reproduction doctors believe that genetic disorders in the fetus are the main cause of spontaneous termination of gestation in the early stages. This can occur against the background of the patient’s complete health. The body recognizes and rejects an embryo with defective chromosomes.
Currently, doctors use preimplantation genetic diagnosis. This study allows us to detect the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus. However, this test is very expensive, and patients often refuse it.
Ovulation stimulation
Quite often, when using a long protocol, cases of biochemical pregnancy after IVF are observed. What it is? A protocol refers to a regimen of drug therapy to induce ovulation. After all, for successful IVF it is necessary to obtain several mature eggs.
With a long protocol, the patient is prescribed high doses of drugs with follicle-stimulating hormone. Therapy lasts about 3-5 weeks. This can affect the natural hormonal balance in the body and trigger BCB. Therefore, doctors currently use a long protocol only for strict indications. In most cases, short stimulation with hormonal drugs is used, which lasts 12-15 days.
Other reasons
The immune system in the female body can malfunction. She may perceive the embryo as a foreign object and begin to produce antibodies against its cells. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected soon after implantation. This reaction more often occurs in chronic autoimmune pathologies in women, but can also be triggered by random failures.
Biochemical pregnancy after IVF is often observed in patients with blood diseases. For example, increased thrombus formation (thrombophilia) can cause gestation interruption. With this pathology, the vessels feeding the embryo become clogged with blood clots. This causes rejection of the fertilized egg in the first weeks.
Influence of external factors
Biochemical pregnancy after IVF can also be provoked by unfavorable external influences. The following factors can lead to interruption of gestation at an early stage;
- stress;
- malnutrition;
- unhealthy lifestyle of the patient;
- general weakened state of the woman’s body;
- work in hazardous conditions.
Therefore, doctors strongly recommend preparing for pregnancy in advance. Before the IVF procedure, it is necessary to cure chronic diseases, eat well and give up bad habits in advance.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms of biochemical pregnancy after IVF? This condition is almost impossible to notice by external manifestations; it is determined only through laboratory diagnostics. After all, the fetus is rejected at such an early stage, when there is no delay in menstruation and other classic manifestations of pregnancy (breast engorgement, morning sickness, etc.).
Miscarriage with BCB occurs during menstruation. The fertilized egg is released along with the blood. The discharge may be more abundant than usual and contain dark red clots. Sometimes there is slight pain in the lower abdomen. However, in many patients, embryo rejection proceeds without any peculiarities, and they mistake early miscarriage for normal menstruation.
Biochemical pregnancy
home
Pregnancy management
Biochemical pregnancy after IVF
Biochemical pregnancy is a child of the progress of medical science. Its diagnosis has become possible relatively recently, since testing for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) became widely available and “home” diagnostic pregnancy tests - test strips - became widespread.
That is, biochemical pregnancy occurred in women of fertile age even before the advent of these tests, but its diagnosis was extremely difficult.
So what is a “biochemical pregnancy”?
Biochemical pregnancy is a pregnancy that ends in very early fetal death. Most often it is asymptomatic. Only a delay of menstruation from one day to two weeks is possible. Then a spontaneous miscarriage occurs in the form of another menstrual bleeding. As a rule, bleeding is a little heavier and longer than usual, and may be accompanied by cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Subjective signs of pregnancy, called questionable in the medical literature (changes in appetite, taste preferences, nausea, vomiting, changes in sense of smell, etc.) are usually absent and do not have time to develop.
What can cause biochemical pregnancy?
The first place among the causes is occupied by chromosomal disorders that occur when there is an error in the divergence of chromosomes during the division of embryonic cells, or when an egg is fertilized simultaneously by two or more sperm. This anomaly is almost always detrimental to the embryo.
Many researchers believe that spontaneous miscarriages are an element of natural selection aimed at eliminating carriers of chromosomal mutations, since when studying abortus (material extracted from the uterine cavity after a spontaneous abortion), 60 to 80% of embryos with chromosomal abnormalities are found.
The second most important are inflammatory changes in the uterine mucosa (for example, endometritis), they prevent the implantation of even a healthy fertilized egg and its further development.
Among other reasons, there are anatomical, immunological, endocrine factors, but in fact, they are more likely to cause habitual miscarriages, and biochemical pregnancy develops much less often as a result of these problems.
Causes and main risk factors for this phenomenon:
- A woman's age is one of the main risk factors. The older she is, the higher the likelihood of early miscarriage: up to approximately 80% in women over 45 years of age.
- A history of spontaneous abortion also plays a role: with three cases, the risk is more than 40%.
- Bad habits - smoking more than 10 cigarettes a day, drinking 4-5 cups of coffee a day.
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs immediately before conception - they interfere with implantation, increasing the risk of miscarriage by 25%.
- Further, fever, injuries, lack of folic acid, harmful production factors, heavy physical labor, stressful situations, unsettled family life, etc.
Biochemical pregnancy after IVF
One of the problems that women who decide to use assisted reproductive technologies may encounter is biochemical pregnancy after IVF. What is it, how to prevent its interruption at such an early stage - these are the typical questions that patients ask their doctors.
Biochemical pregnancy with IVF is practically no different from the same with natural conception. The only difference is that the risk of early miscarriage in patients of reproductive clinics is higher than in ordinary women. This is because they already have some reproductive dysfunctions, which may serve as risk factors.
In order to increase the chance of normal conception with subsequent normal development of the fetus, it is necessary to first establish the cause of problems with its implantation. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the influence of risk factors. To do this, a number of additional studies are being carried out.
Often, to increase the chance of successful fertilization, ICSI or PICSI is additionally performed as part of the IVF procedure to select more suitable sperm, which should provide a better final result. After all, the main cause of biochemical pregnancy is mutations, and they can be a consequence of the low quality of the genetic material of sperm.
Our specialists
doctor
Khabarov Sergey Vyacheslavovich Chief physician of the clinic, obstetrician-gynecologist, MD.
Sign up Schedule
Kuznetsova Irina Andreevna Gynecologist-reproductologist, Ph.D.
Sign up Schedule
Diagnostics
The hCG blood test is the only method for diagnosing biochemical pregnancy after IVF. What it is? Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone that begins to be produced in the body a week after conception. If its readings are more than 5 units, then this indicates pregnancy.
If the embryo has taken root and is developing, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin constantly increases. In the first weeks of gestation, the concentration of hCG increases daily by 2 times. This is considered the norm.
After in vitro fertilization, an hCG test is taken several times. This is necessary to monitor the implantation of the embryo and its further development. If the hormone level was initially high and then fell, then this is a sign of biochemical pregnancy after IVF. Usually, soon after the hCG concentration decreases, the patient experiences menstrual bleeding and the rejected embryo comes out.
During an IVF procedure, the patient is usually given two fertilized eggs. In this case, jumps in hCG levels may occur. Hormone levels may fall and then rise again. This suggests that one of the embryos died, and the second took root. If the patient successfully develops both fertilized eggs, then the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin constantly increases.
You can also find out about pregnancy in the early stages using pharmacy tests that respond to an increase in the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin. However, this does not replace the hCG test. After all, tests do not show the exact level of the hormone. Therefore, they cannot be used to diagnose BCB.
Basal temperature from A to Z
[email protected] , I read you, and remembered myself... perhaps someone will consider what I write to be nonsense, but at the beginning of planning everything was the same for me! Not every month, but quite often. About 5 days after O these symptoms began. A swollen belly, some strange stretching in the abdomen, either on the right or on the left, waking up at night (I woke up in the middle of the night and could no longer sleep), sometimes I even felt nauseous... and of course, tests with a barely noticeable second line. Every time I was sure that I got pregnant during this cycle, I was also sure that it was implantation... I’ll call it this way - “my heart told me.” But about 2 days before M, all symptoms disappeared! And M came. Sometimes the symptoms continued, and M came a few days later. But this really happened, and it’s not my fantasy...that’s why I believe you. I still remember several such cases when I was 100% sure that it worked! I showed photos of the tests to others, and they also saw // and these symptoms, you can’t confuse them with anything... and they didn’t happen every month, so it’s not my imagination... Then there were several unsuccessful pregnancies, and only after the 3rd they checked hemostasis, genetics, and immunogram. The reason for the failure turned out to be precisely the immune system. She destroyed all pregnancies like a foreign body. In a “normal” woman, the immune system also attacks the fetus, this is normal, but “normal” women immediately begin to produce antibodies that protect the baby from the mother’s immune attack, and the pregnancy continues to develop. I did not produce these antibodies at all. In a nutshell, “a strong immune system.” I’ve never been sick either, once every 2 years I had a mild cold, the kind that goes away in 2 days... and that’s it! Because my immune system easily coped not only with pregnancies, but also with all sorts of viruses and bacteria... this, by the way, is inherited. I got it from my dad. He has never been sick in his 60 years! He doesn't know what the flu is! Several times in my life I had a cold, just snot, that’s all. And after I found out all this, everything fell into place... I believe and know that what I felt was implantation. Later I did LIT. After it, by the way, I was sick very often, especially in the first months - cold after cold... but that’s not what I’m talking about. What you described is possible. I’ve encountered this myself, but to find out for sure, you need, of course, to have a full examination. Once upon a time, the girls on this site also told me what kind of examinations I needed to undergo, and I am very grateful to them for that! Perhaps, if I myself had not insisted on these particular examinations, I would also still be waiting for a miracle from heaven... my doctor did not want to do an immunogram for me until the end, she was sure that this was not the reason. I insisted! Before that, I didn’t even know that such an analysis existed. Therefore, listen to the advice of others, check everything! And a spermogram is also a must! After all, my husband is 11 years older, that is, he is already 57. At this age, I think it’s rare for anyone to boast of a good spermogram. And the fact that he already has children doesn’t mean anything either. Sperm changes, and very quickly , and not always in a good way.
edited after 4 minutes
Is therapy needed?
Patients often ask about the prevention and treatment of biochemical pregnancy after IVF. Its causes are often associated with random failures that may not recur in subsequent conceptions. BCB itself does not require special therapy. After its spontaneous interruption, there is no need to scrape the endometrium or take any medications. The embryo at this stage is very small in size and completely exits the uterus.
If gestation was interrupted at a very early stage, then it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. This will help to identify the etiology of biochemical pregnancy after IVF. Treatment is necessary if, during the diagnosis, pathologies are identified in the patient that prevent the successful gestation of the embryo.
Forecast
Biochemical pregnancy is not always a sign of habitual miscarriage. This also does not indicate that the woman will have problems conceiving in the future and will become infertile. In many patients, after spontaneous termination of BCB, a normal pregnancy occurred already in the next menstrual cycle, which was safely carried to term.
If BCB occurs after IVF, then doctors recommend repeat artificial insemination after 3 months. This interval is necessary to restore the reproductive system. If the interruption of gestation occurred under the influence of random factors, then the chances of successfully carrying subsequent pregnancies are quite high.
If a biochemical pregnancy occurs after the transfer of cryopreserved (frozen) embryos, then a repeat IVF protocol is carried out in the next menstrual cycle. In this case, a three-month break is not required.
If BCB occurs again, IVF attempts are temporarily stopped. The patient must be thoroughly examined, the cause of miscarriage must be determined and a course of treatment must be taken. Only after this can you begin a new in vitro fertilization procedure.
In medical practice, there are often cases where natural conception occurred during the three-month interval between BCB and the new IVF protocol. This was observed in approximately 25% of women. Most likely, this is due to the fact that in the process of preparation for artificial insemination, strong stimulation of the ovaries is carried out. In some cases, this triggers the process of spontaneous ovulation. The cause of long-term infertility is eliminated, and the woman becomes pregnant naturally.
Natural pregnancy after unsuccessful IVF attempts
Girls, I want to share a story; I used to look through the entire Internet in search of such stories. So, I did insemination, it was unsuccessful, then we went for IVF (paid) there were 5 cryoembryos, cryo-, because I ended up in intensive care, with hyperstimulation!!! then there were transfers, on the second transfer the hCG rose to 69, but on day X it was less than 1.2! In general, it's all over. After terrible depression, quarrels and a desire to get a divorce. I started collecting and submitting documents for the QUOTA. Well, at the same time, the idea of doing laparoscopy came into my mind (I want to say that during all this time, none of the doctors even suggested or told me about this procedure, laparoscopy).
In general, I came to OMM, to O.V. Patsyuk, head. department, he said let’s try, he sent me for an ultrasound and tests. A week later I was lying on the operating table. Everything went well, I had laproscopy and hysteroscopy (although I had already had hysteroscopy before the second IVF attempt). They said that I had some kind of shell polykestosis (I don’t remember the word), in short, the ovaries were in shells, they did a resection (trimmed the shells), well, the endometrium was not much inflamed, they scraped it. The doctors, of course, were shocked that by the age of 25 I had already undergone IVF, with such a common disease. Well, a month after the operation they called me and invited me to come to a meeting with my IVF doctor in a month. Two weeks later I called them back and refused the place. Because I didn’t need it anymore. HCG was three digits. I didn’t believe it for a long time and retook it twice))))) now everything is fine with us, we are still growing in the tummy, but we will soon appear))) I want to say that the clinic where I did IVF was paid and diagnosed me with multifollicular ovaries , lack of ovulation, polycystic disease. (but for some reason they didn’t send me for laparoscopy, apparently I was a money bag for them). My husband supposedly had teretozoospremia! Girls, believe in miracles, pray every day and God will send you your miracle. Go to church for confession and communion and God will send you the right people and help you. Just believe! and be careful with paid clinics!!!! sorry for the many letters
Preparing for a repeat procedure
In order for a subsequent IVF attempt to be successful, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes the following examinations:
- consultation with an immunologist and hematologist;
- analysis for various types of antibodies;
- determination of the chromosome set (for both spouses);
- coagulogram.
If any pathologies were identified during the diagnosis, they must be eliminated before embryo transfer. In some cases, a course of therapy is required not only by the woman, but also by her husband.
When carrying out the following protocol, careful monitoring of the patient’s hormonal levels is carried out. Before embryo transfer, a detailed blood test is performed to determine the level of progesterone and estrogen. After IVF, the hCG test is taken much more often than in the previous protocol. Doctors also strongly recommend preimplantation genetic diagnosis. These measures help prevent re-interruption of gestation in the early stages.
Why are the risks increasing?
Couples who consult a doctor for IVF are, on average, older, have concomitant diseases and aggravated factors in the form of the very fact of infertility.
It is very difficult to unravel the tangle of cause-and-effect relationships and separate one from the other. To compare any factor and its role, it is necessary to have two absolutely identical groups that differ only in one factor. In the case of pregnancy after IVF or spontaneous pregnancy, the groups will always differ in the presence or absence of infertility. Therefore, conclusions must be drawn very carefully.
A study was published in 2012. The course of pregnancy and childbirth was assessed depending on the duration of previous infertility. It turned out that what was most significant was the duration of infertility, not the manner in which it was achieved. Those. The longer the infertility lasted, the more difficult the pregnancy was. Another 2001 study assessed couples with unexplained infertility, some of whom became pregnant. The results were similar. The duration of infertility played a role, but the method of achieving pregnancy played a role.
Does IVF technology itself play a role in the risk of pregnancy complications?
Ovarian stimulation.
During ovarian stimulation, follicle-stimulating hormone is prescribed. It helps to ripen all the follicles that began to develop in this menstrual cycle. Without this help, only one follicle will mature, the rest will disappear. In addition to the egg, estrogens are produced in the follicle. Estrogens are the main female hormones; they affect a huge number of cells in the body. But we are primarily interested in their effect on the endometrium. In normal concentrations this effect is positive, but in excess it is rather negative. When several follicles grow during stimulation, they all secrete estrogens, a lot of estrogens, more than needed. In addition, an early increase in progesterone is often observed during stimulation. These hormonal changes lead to a decrease in the embryo's chances of implantation, and when pregnancy occurs, to an increase in the risk of obstetric complications. The way out of this situation is cryopreservation of all embryos and embryo transfer in a natural cycle. In this case, the risks of complications are significantly reduced.
Transfer of a thawed embryo in a natural cycle.
The negative effect of stimulation on the endometrium can be eliminated if the embryo is transferred in a natural cycle. In this case, stimulation is not required, but only observation of physiological changes in the ovaries and endometrium. On the desired day, the embryo is placed in the uterine cavity. For the body, such a pregnancy will be completely normal, because no one interfered with its work. Therefore, the risks will be the same as with an independent pregnancy (or lower, but more on that later).
Insufficiency of the corpus luteum.
Progesterone is required to maintain pregnancy. Progesterone acts primarily on the endometrium, changing it to suit the needs of the embryo. Progesterone is formed in the ovary, in the corpus luteum, at the site of the ovulated follicle.
During ovarian stimulation, medications are prescribed to prevent early ovulation. These medications not only interfere with early ovulation, but also interfere with the formation of a full-fledged corpus luteum. Because of this, it is necessary to administer external progesterone for the first few weeks until the placenta completely begins to secrete progesterone in sufficient quantities.
Transfer of several embryos into the uterine cavity
Multiple pregnancy after IVF is almost always a preventable complication. It is called iatrogenic, i.e. called by a doctor. If there is effective cryopreservation, there is no need to transfer two or more embryos. Therefore, the risk of this complication after IVF can be brought to the level of risk during independent pregnancy.
How can IVF technology reduce the risks of pregnancy complications compared to the risks of spontaneous pregnancy?
Exclusion of chromosomal and monogenic diseases.
When IVF technology can help achieve better results compared to spontaneous pregnancy. So far this concerns reducing the risk of miscarriages and preventing the conception of children with chromosomal abnormalities and monogenic diseases.
Miscarriages before 12 weeks of pregnancy in 50-70% of cases are associated with chromosomal abnormalities of the embryo. Parents usually have a normal set of chromosomes (karyotype). The risk of these abnormalities increases with age. With severe anomalies, pregnancy stops developing; with relatively mild ones, it can end in the birth of a sick child, for example, with Down syndrome.
Carrying out IVF with preimplantation genetic screening significantly reduces the risk of miscarriages and eliminates the birth of children with chromosomal abnormalities. The positive effect is especially pronounced in women over 35 years of age.
Opinions of patients and doctors
Quite a large number of women have had cases of biochemical pregnancy after IVF. In the reviews, some patients report that the subsequent attempt at artificial insemination was successful and they were able to safely carry the fetus to term.
However, the situation often repeated itself, and BCB constantly occurred during several attempts at artificial insemination. In these cases, the patients were prescribed an examination and a course of treatment. Many women note that a successful attempt at IVF took place after treatment with special drugs that improve the quality of eggs.
Reviews also report cases of natural conception after BCB. Many women have successfully carried their pregnancies to term. However, some patients experienced cessation of fetal development and miscarriages in the first trimester. This suggests that after BCB it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and identify the causes of miscarriage.
Reproduction doctors consider the very fact of successful embryo implantation to be a positive prognostic sign, even if the gestation was subsequently interrupted at the initial stage. If the attachment of the fetus has taken place, this indicates the good condition of the patient’s endometrium. This means that the chances of a successful pregnancy are quite high and there is no reason to refuse subsequent IVF attempts.
How to prepare for a new pregnancy?
If BxB did happen, this is not a reason to give up. If we are talking about artificial conception, then the probability that the embryo will take root the first time is no more than 40%, depending on the situation. To increase the chances of fertilization, additional research is necessary:
- karyotype of the implanted embryo;
- checking the pair's set of chromosomes for compatibility;
- MAP test for men;
- Coagulogram, if there is a suspicion that the female body is prone to thrombosis.
The chance of getting pregnant is not one hundred percent. Out of 100 women, only 40 will get the long-awaited pregnancy.
The process of artificial insemination is not new. Biochemical pregnancy with IVF occurs quite often. The couple is informed about this by the specialists who carry out the procedure. It is worth considering IVF as a way to get pregnant, but it is not recommended to resort to it if attempts have not been successful within 2 years. Also, during the first biochemical pregnancy, reproductive specialists can advise ICSI, which excludes the fertilization of a genetically “wrong” egg or sperm.