Good day, dear friends!
You won’t believe this: today I finally decided to start a conversation with you about antibiotics. You have received such a request more than once. But I didn't want to touch on this topic.
And there are 2 reasons for this:
Reason number one.
I really don't want to give you a tool to recommend antibiotics for yourself because I am completely against it!!!
After reading this article, you will understand why.
I know, I know, for some of you this issue is not even discussed. These are prescription drugs, and no amount of persuasion from customers will force you to take on the role of the attending physician.
But this does not always happen...
Reason number two. As I already told you, talking about medications to specialists, many of whom are much better versed in this topic than I am, to put it mildly, is incorrect.
But you still ask to talk about it.
Therefore, today we will begin to discuss basic issues that, in my opinion, you need to know about antibiotics.
We'll look at:
- What are antibiotics?
- Why are not all antimicrobial agents classified as antibiotics?
- How are they divided?
- How do antibiotics work?
- Why do they sometimes not work?
- How to prevent microbial resistance to antibiotics?
- What are the principles of rational antibiotic therapy?
- Why shouldn't you recommend antibiotics yourself?
The saddest thing is that the topic of antibiotics worries not only you, pharmaceutical business specialists.
Every month, in Yandex alone, about a MILLION people search for information about antibiotics.
Look what they ask:
- Antibiotics for the respiratory tract and bladder.
- Antibiotics for children and pregnant women. (Nightmare!).
- Antibiotics for gastritis, wounds, chlamydia.
- The antibiotic is “good”, “powerful”, “mild”, “best”.
- External and internal antibiotic. “Staphylococcal” and even “hormonal” antibiotic. Wow!
And everything in the same spirit...
It’s scary to imagine what they’ll read there, how they’ll understand it, and what actions they’ll take.
I really want that, thanks to you, the population’s literacy in this matter increases, and that the phrase “give me some antibiotic” is never heard in your pharmacy again.
Well, let's get started.
Negative effects on the digestive system
Once in the stomach, antibiotics increase the acidity inside it, causing increased secretion of gastric juice. Frequent use of antibacterial drugs leads to the development of gastritis and the formation of stomach ulcers.
The main signs of digestive disorders are abdominal pain, bloating, and flatulence. Symptoms appear immediately after taking the drug and stop after the drug is absorbed into the intestines.
To avoid complications, doctors often recommend injection treatment with antibiotics. It is recommended to take tablets immediately after meals, since food creates a kind of protective barrier for the gastric mucosa.
Self-medication
Self-medication is the main and most common mistake. can be very effective and save the health and even life of a child. Before prescribing an antibiotic, the doctor must examine the sick baby and, if necessary, perform a series of tests that will help make the correct diagnosis. Depending on the severity of the disease, the age of the baby, and the type of bacterial infection, the doctor selects the optimal antibiotic for treatment, its dosage and duration of treatment.
You cannot prescribe an antibacterial drug to your child yourself, even if it helped another child recover.
Intestinal dysbiosis develops in 90% of cases
When using antimicrobial drugs, not only pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed in a short time, but also the beneficial intestinal microflora, which is responsible for the health of the entire body, is inhibited. The main signs of dysbiosis are bloating, changes in stool (constipation, diarrhea). This disease can manifest itself both during treatment and after completion of the treatment course.
To prevent the occurrence of dysbiosis, as well as for its direct treatment, it is necessary to use preparations containing beneficial bacteria (probiotics), which completely restore the intestinal microflora.
general characteristics
Today, there are already a large number of drugs belonging to the vast world of antibiotics - substances of natural or semi-synthetic origin that have the ability to destroy certain groups of pathogenic microorganisms or prevent their growth or reproduction. The mechanisms and spectrums of action of antibiotics may be different. Over time, new types and modifications of antibiotics appear. Such diversity requires systematization. Nowadays, antibiotics are classified according to their mechanism and spectrum of action, as well as their chemical structure. According to their mechanism of action they are divided into:
- bacteriostatic, inhibiting the growth or reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms;
- bactericidal, which help destroy bacteria.
The main mechanisms of action of antibiotics:
- disruption of the bacterial cell wall;
- suppression of protein synthesis in the microbial cell;
- disruption of the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane;
- inhibition of RNA synthesis.
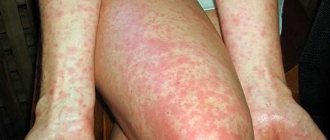
Serious allergic reactions
With frequent use of antibiotics, allergization of the body will increase. An allergy to antimicrobial drugs can cause significant harm to the body; if allergic symptoms are ignored for a long time, bronchial asthma can develop. Therefore, when taking antimicrobial drugs, you need to carefully monitor any reactions that occur.
The main symptoms of allergies are skin rashes, itching, swelling, urticaria, and very rarely - anaphylactic shock. If these signs are present, you should immediately stop taking the drug and visit a doctor. After diagnosis, the doctor will select another drug that is safe for health.
Oral and vaginal candidiasis
Candidiasis is an infectious disease with pronounced symptoms. When taking antimicrobial drugs, not only pathogenic bacteria are killed, but also beneficial microorganisms that inhibit the proliferation of Candida fungus. The main signs of candidiasis (thrush) are itching of the skin, a white dense coating on the oral mucosa and a cheesy discharge from the vagina.
Symptoms of candidiasis may appear approximately 14 days after treatment ends. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is advisable to use special antifungal drugs and local antiseptics during antibacterial therapy.
Macrolides
This is the second group. Macrolides are natural antibiotics with a complex cyclic structure. They are a multi-membered lactone ring with attached carbohydrate residues. The properties of the drug depend on the number of carbon atoms in the ring. There are 14-, 15- and 16-membered compounds. Their spectrum of action on microbes is quite wide. The mechanism of action of antibiotics on a microbial cell is their interaction with ribosomes and thereby disrupting the synthesis of proteins in the microbial cell by suppressing the reactions of addition of new monomers to the peptide chain. Accumulating in the cells of the immune system, macrolides also carry out intracellular destruction of microbes.
Macrolides are the safest and least toxic among known antibiotics and are effective against not only gram-positive, but also gram-negative bacteria. When using them, no unwanted side reactions are observed. These antibiotics are characterized by a bacteriostatic effect, but at high concentrations they can have a bactericidal effect on pneumococci and some other microorganisms. According to the method of production, macrolides are divided into natural and semi-synthetic.
The first drug from the class of natural macrolides was erythromycin, obtained in the middle of the last century and successfully used against gram-positive bacteria resistant to penicillins. A new generation of drugs in this group appeared in the 70s of the 20th century and are still actively used today.
Macrolides also include semisynthetic antibiotics - azolides and ketolides. In the azolide molecule, a nitrogen atom is included in the lactone ring between the ninth and tenth carbon atoms. A representative of azolides is azithromycin, which has a broad spectrum of action and activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, some anaerobes. It is much more stable in an acidic environment, compared to erythromycin, and can accumulate in it. Azithromycin is used for a variety of diseases of the respiratory tract, genitourinary system, intestines, skin and others.
Ketolides are prepared by adding a keto group to the third atom of the lactone ring. They are distinguished by less addictive bacteria when compared with macrolides.
Nephrotoxic consequences
Against the background of the toxic effects of antibacterial drugs, kidney problems may appear. With urine, these organs remove toxic substances and filter the blood. Violation of these processes leads to the development of severe intoxication, which will lead to kidney failure.
The main symptoms are severe thirst, an increase or, conversely, a decrease in the volume of daily urine excreted. After taking antimicrobial drugs, an increase in urea levels in the blood is possible. The risk group includes patients with kidney pathologies, young children, elderly people, and pregnant women.
Why should you not stop using it?
People are wondering whether it is possible to interrupt the course of taking antibacterial medications. The doctor warns about why antibiotics need to be taken in a course. If no side effects occur, then the course of treatment cannot be interrupted. This causes bacteria to become resistant to drugs. Untreated microbes will become resistant to drugs in the future. It will be more difficult to cure the disease, since the effectiveness will be much lower. Often an untreated disease becomes chronic. People who do not take the drug prescribed by the doctor are at great risk. The interrupt results in:
- to loss of effect from treatment;
- to the development of resistance in bacteria;
- to an exacerbation or to the transition of the disease to a chronic state.
Interrupting the course of antibiotics is allowed only in one case - if serious side effects occur. If you feel unwell, you will need to act in accordance with your doctor’s recommendations. Side effects are treated symptomatically. They also require dosage reduction or complete interruption of medication.
It is worth noting that taking antibiotics cannot be long-term. Typically the course consists of 1-8 weeks. If complete cure cannot be achieved, a break is taken. Complex and chronic diseases are treated comprehensively. When taking a break from medications, other methods of therapy are used. People are often interested in how many days they take antibacterial medications. The minimum period of admission is 7 days. The maximum period depends on the type of drug and the individual characteristics of the person. The question of how much medicine you can take almost always arises. It is worth understanding that all this depends on many factors. If the effect of treatment is greater than the possible harm, the duration of treatment can be increased to 2 months. However, in this case it is preferable to use injections. Due to under-drinking of the drug, difficult-to-treat diseases are created.
Hepatotoxic consequences
The liver is an organ that filters and cleanses our body of harmful substances. Therefore, it is the liver that takes the main toxic blow. Damage to the liver tissue is manifested by increased temperature, dark urine, and signs of jaundice. As a result, the immune system suffers, glycogen accumulation is disrupted, physical inactivity, lethargy, weakness, and increased appetite appear.
What happens if you take antibiotics often? Liver dysfunction leads to problems throughout the body. If the patient has chronic liver diseases, but it is impossible to replace antibiotics with other drugs, then hepatoprotectors should be taken at the same time and adhere to a gentle diet.
How to avoid consequences when treated with antibiotics
Numerous studies confirm that antibiotics are completely useless in the treatment of viral and fungal diseases. Their use gives positive results exclusively in the fight against bacterial infections.
During treatment, it is advisable to drink plenty of fluids, preferably clean water. To prevent digestive problems, it is recommended to follow a diet and eat only easily digestible foods.
Fatty, smoked, fried, salty foods should be completely excluded from the patient’s menu.
Low-fat fermented milk products should be included in your diet. To support immunity, you can take various vitamin complexes.
Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines belong to the class of polyketides. These are broad-spectrum antibiotics with a bacteriostatic effect. Their first representative, chlortetracycline, was isolated in the middle of the last century from one of the cultures of actinomycetes, they are also called radiant fungi. A few years later, oxytetracycline was obtained from a colony of the same fungi. The third representative of this group is tetracycline, which was first created by chemical modification of its chlorine derivative, and a year later also isolated from actinomycetes. All other drugs of the tetracycline group are semi-synthetic derivatives of these compounds.
All these substances are similar in chemical structure and properties, in activity against many forms of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, some viruses and protozoa. They are also resistant to the habituation of microorganisms. The mechanism of action of antibiotics on a bacterial cell is to suppress the processes of protein biosynthesis in it. When drug molecules act on gram-negative bacteria, they pass into the cell by simple diffusion. The mechanism of penetration of antibiotic particles into gram-positive bacteria has not yet been sufficiently studied, however, there is an assumption that tetracycline molecules interact with ions of certain metals that are found in bacterial cells to form complex compounds. In this case, the chain is broken during the formation of the protein necessary for the bacterial cell. Experiments have proven that bacteriostatic concentrations of chlortetracycline are sufficient to suppress protein synthesis, but large concentrations of the drug are required to inhibit the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Tetracyclines are used in the fight against kidney disease, various infections of the skin, respiratory tract and many other diseases. If necessary, they replace penicillin, but in recent years the use of tetracyclines has decreased markedly, which is associated with the emergence of resistance of microorganisms to this group of antibiotics. The use of this antibiotic as an additive to animal feed also played a negative role, which led to a decrease in the medicinal properties of the drug due to the emergence of resistance to it. To overcome it, combinations with different drugs that have a different mechanism of antimicrobial action of antibiotics are prescribed. For example, the therapeutic effect is enhanced by the simultaneous use of tetracycline and streptomycin.
How to recover after taking antibiotics
Taking antibiotics contributes to the development of dysbiosis. To restore the intestinal microflora, it is advisable to take medications containing lactobacilli (probiotics) - Acipol, Linex or Hilak-Forte - for a month. For complex disorders, prebiotics are prescribed, for example, Duphalac. Before choosing the right drug, you should consult your doctor.
After antibiotic therapy, fungal infections of the mucous membranes often occur. Mostly candidiasis (thrush) develops. In this case, Fluconazole or Nystatin are used for treatment. They can be found in every pharmacy in the form of ointments, suppositories or tablets. But the treatment must be supervised by a doctor.
When taking antibiotics, the liver cells are the first to be affected. Despite the fact that this organ is capable of recovering on its own, you can speed up the cleansing process and help the liver return to normal faster. To do this, it is advisable to take any hepaprotectors; the drug Essentiale-Forte is considered the most effective; in a budget option, you can use Karsil.
To restore immunity, a course of immunomodulators is recommended; the most famous are Anaferon and Immunal. For general strengthening of the body, it is useful to drink various vitamin complexes, such as Revit, Complivit, etc.
To quickly restore the body after antibiotics, you need to consume fresh vegetables and fruits as much as possible. It is useful to drink freshly squeezed juices; they speed up the process of removing toxins from the body, have a stimulating effect on the immune system, and saturate the intestines with healthy fiber. It is necessary to include in the diet fermented milk products rich in live lactobacilli - kefir, yogurt and others. Lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
New generation antibiotics for adults and children, pregnant and lactating women
Many still remember the times when such drugs were not used in any form in the treatment of pregnant women. And if the patient was breastfeeding, she had to choose between illness and cessation of lactation. But medicine has stepped forward and today there are options for more or less safe treatment of infections in expectant and existing mothers, as well as very young children.
Modern drugs are developed taking into account the protective mechanisms that bacteria produce in response to the use of antibiotics. In addition, scientists strive to minimize the harm of the drug by inventing ways for its precise delivery to the site of infection (for example, special capsules that dissolve only in a certain part of the digestive system). More advanced methods of purifying components are used, which often reduces toxicity.
The most popular and relatively safe antibiotics at the moment are: - a combination of amoxicillin with clavulanic acid -
Angina
Flux
If the inflammatory process is localized in the gum tissue, you need to take antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading. But you should also be sure to rinse your mouth as often as possible. It is good to do this with a solution of furatsilin (crush the tablets and dissolve in boiled water). If there are no preparations for rinsing, brew herbs, make a solution of baking soda.
An urgent visit to the doctor is required.
Cystitis
As a rule, people encounter this disease more than once. And they already know what treatment to take to relieve an acute attack of cystitis. The most effective antibiotic in this case is Monural. For adult patients, a single dose of 3 g of medication is prescribed. You can take the same dose a day after the first. Children over 5 years old can drink 2 g of Monural - once.
To alleviate the condition, warm baths with herbs (chamomile) are used. You can take antispasmodics (No-spa), hold a warm heating pad between your legs. You should drink more.