Chest pain is a sign of several pathological conditions, some of which pose a direct threat to life. Diseases that are not vitally dangerous also lead to the occurrence of symptoms. An important skill for people far from medicine is the ability to distinguish between vital and relatively harmless pain, provide first aid, and stop a heart attack.
What can hurt in the middle of the sternum?
There are 6 main causes of discomfort in the chest area.
Angina, heart attack
It develops suddenly, more often after physical exertion, due to spasm of the coronary arteries and oxygen starvation of the myocardium. The sensations arise directly in the center of the sternum or radiate to any point of the body on the left side. There are cases when heart pain was accompanied by tingling in the heel, dental phenomena, numbness and pain in the hand or stomach area. The nature of the pain is squeezing, pressing, often pulsating.
Neuralgia, osteochondrosis
The result of inflammation of large nerve trunks (and intercostal ones too). Unpleasant sensations arise against the background of hypothermia, intensify gradually, reaching a maximum on the 2-3rd day of illness. In some cases, the onset is abrupt and the pain is stabbing in nature. The lumbago debuts at the moment of physical activity, when bending the body. It can occur in the sternum on the right and left.
Respiratory tract diseases, colds, bronchitis, tracheitis
The sensations are weak or moderate, intensified by coughing. Physical activity does not affect the severity of the symptom. There are other signs of infection of the upper respiratory tract: shortness of breath, increased body temperature, general toxic syndrome, sputum production.
Injuries of the sternum, esophagus, respiratory tract
The patient has a history of damaging effects: blows, foreign body getting stuck, falls from a height onto the chest, medical procedures (bronchoscopy). The pain is moderate, often dull in nature. There are accompanying signs: hemoptysis, vomiting “coffee grounds”, uncontrollable cough, acrocyanosis in case of damage to the upper respiratory tract.
Hypertension
The development of an attack is caused by stress, refusal to take medications prescribed by a doctor, and physical activity. Chest pain is localized behind the sternum, to the left and right of it. The nature of the sensations is similar to a heart attack, the pain can be partially relieved with nitrates. The patient may experience nausea. The pathology is accompanied by a nagging headache in the back of the head. Sometimes a rush or a feeling of heat develops.
Heartburn
Reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus, irritation of the mucous membranes. Accompanied by belching, burning behind the sternum, difficulty swallowing. The attack occurs after eating or when the patient is lying down.
It is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis without appropriate examinations. In some cases, the symptoms are vague or resemble another disease. If a person experiences pressing pain in the middle of the sternum, changes in the cardiovascular system should first be suspected.
A differential test to rule out a heart attack is a drug test. A Nitroglycerin tablet is placed under the patient’s tongue or Nitrospray (Isoket) is sprayed. If within 1–2 minutes the patient’s condition has noticeably improved, then there is a coronary pathology. The lack of effect indicates another origin of the pain.
Note: there is no reaction to nitrates in acute myocardial infarction. There are a number of other signs that may suggest this disease. Diagnostic difficulties arise with an erased and asymptomatic course.
Another sign to suspect a coronary attack is the persistence of pain at rest. With neuralgia and injuries, the symptom intensifies during movement, however, it partially subsides when the patient is in a supine position. In infectious diseases, pain occurs mainly during coughing.
A characteristic sign of neuralgia is increased discomfort when tapping your fingers on the edge of the costal arch. In addition, the intensity of the pain increases when trying to stand up or sit down. Sometimes there is irradiation to the area of the shoulder blades. Neuralgia does not spread to other parts of the body.
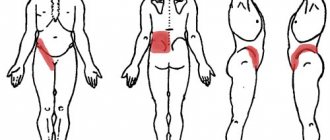
Chest pain due to osteochondrosis
Pain with thoracic osteochondrosis can be of different types. The term dorsago is what experts call “sternal lumbago.” The attack begins suddenly and is accompanied by very severe pain, a feeling of chest tightness and lack of air. Sometimes accompanying symptoms occur: stiffness, retardation of movements, tension in individual muscles.
Often the pain is felt when standing up suddenly after a long period of sitting. This pain impulse does not last long and subsides quickly.
The situation is different with dorsalgia. Her symptoms are completely opposite. Severe pain does not appear immediately. At first, the patient experiences mild discomfort, and then prolonged dull, aching pain appears.
When to Call Emergency Help
Emergency measures are required for patients with an intractable heart attack and suspected myocardial infarction. If there is a history of coronary artery disease and the pain is of a compressive nature, it is necessary to call an ambulance team, regardless of the severity of the accompanying symptoms. Classic signs of AMI include:
- A sharp decrease in blood pressure to shock levels (70/40).
- A squeezing or stabbing pain behind the sternum.
- Pallor.
- Impairment of consciousness up to its loss.
- Cold sweat.
- No effect from taking nitroglycerin.
- Swelling of the jugular veins.
- Tachycardia more than 100 beats per minute.
25% of AMI are asymptomatic or with an unclear clinical picture. There are gastralgic (stomach pain), asthmatic (shortness of breath), anginal (resembling an infection of the upper respiratory tract) variant of the course.
EMS assistance is required for patients with injuries to the esophagus and respiratory tract. A sign of severe damage is:
- Black or brown vomit.
- Cough producing large quantities of scarlet blood.
- Intense pain in the esophagus.
- Decrease in blood pressure by 10–20 mm Hg. Art. relative to the usual indicators.
- Open wounds in the sternum area.
- Crepitation of bone fragments.
- Strong impacts to the problem area in the recent past.
- Shortness of breath, increased breathing by 20% of normal or higher.
- Blue tint of earlobes, lips.
In the absence of the described signs, emergency medical attention is not required. The patient is recommended to visit the clinic with a local doctor as soon as possible.
Aching
Myocarditis
If aching, squeezing pain is felt in the left side of the chest, inflammation of the myocardial muscle can be suspected. This disease is accompanied by disturbances in the rhythm of its contraction, as a result of which the person experiences general weakness and difficulty breathing. In this case, you should not delay a visit to the doctor, since this condition may be a harbinger of cardiomyopathy - pathological changes in the heart muscle that are life-threatening.
With chronic inflammation of the pancreas and gallbladder, there is often aching in the left half of the sternum. During acute attacks of these diseases, the intensity of pain increases sharply, and it begins to radiate to the area under the ribs.
Myocarditis
Diseases according to accompanying symptoms
In the absence of characteristic signs, diagnosis is carried out based on the phenomena that are observed in the patient.
It's hard to breathe when inhaling
Occurs due to a mechanical obstruction in the respiratory tract. If a symptom is detected against the background of complete health, the presence of a foreign body is first suspected. The gradual development of the “clinic” gives grounds for oncological alertness. In some cases, the phenomenon occurs against the background of paralysis of the diaphragm, however, there is no pain in the sternum.
Lump in throat
An extremely nonspecific symptom is observed in patients with angina pectoris, inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, hysterics, and dry cough (as well as in people suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia). In combination with squeezing pain, it is an indirect sign of a heart attack; if a cough is present, it is an indirect sign of infectious processes.
It hits the back between the shoulder blades
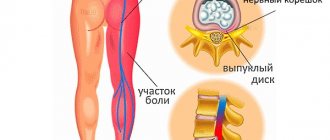
Occurs mainly in neuralgia and osteochondrosis. Shooting indicates compression of the nerve trunks by an intervertebral hernia or spasmodic muscle layers.
Dry cough
In 90% of cases, it is evidence of infectious diseases, including acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, and whooping cough. Occurs when the airways are incompletely blocked by a foreign body or tumor. Occurs in 0.5–1% of people who have a heart attack.
Pain in the middle of the sternum when moving
It is a sign of stable angina (attacks only during physical activity) or neuralgia. The symptom should be assessed as part of the overall clinical picture. If sensations occur during physical activity, there is a history of ischemic heart disease, and the phenomenon is relieved by nitrates, then a conclusion is drawn about its cardiac origin. Lack of effect from nitroglycerin, irradiation to the shoulder blades, connection with physical activity, recent hypothermia is evidence of inflammation of the nerve trunks.
Diagnostic methods based on external signs do not accurately determine the disease. The patient needs an objective examination, including an electrocardiogram at rest and under stress, sputum analysis, and chest x-ray.
Diagnostics
To cope with chest pain and forget about it for a long time, you should undergo a comprehensive examination.
Minimum diagnostics for patients with chest pain include:
- consultation with a doctor and collection of anamnesis (the specialist asks the patient about diseases of the heart, stomach, lungs, symptoms of pathology, medications taken, etc.);
- ECG (if necessary, an additional stress test is performed);
- radiography;
- gastroscopy (comprehensive examination of the stomach);
- angiography of the coronary vessels (a series of images of the vessels of the heart muscle).
Additionally, auxiliary research methods may be prescribed - a blood test for markers of myocardial damage, CT, MRI, ultrasound of the abdominal organs and blood vessels.
The first stage of diagnostic procedures is making an appointment with a qualified medical specialist. Depending on the nature of the pathological process, the attending physician may be:
- Gastroenterologist.
- Vascular surgeon.
- Cardiologist.
- Neuropathologist.
If you are not completely sure of the cause of the pain syndrome, then you should seek advice from your local physician. Based on the results of the preliminary conversation, the patient may be prescribed the following diagnostic measures:
- X-ray examination of the chest.
- Gastroendoscopy.
- Chromoendoscopy of the esophagus.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart and abdominal cavity.
- Holter monitoring.
Depending on the nature of the pain and the additional symptoms accompanying it, additional diagnostic methods may be applied to the patient.
First aid what to do
The measures are fundamentally different for each of the conditions considered. If it is not possible to accurately determine the disease, it is recommended to provide the patient with rest and a flow of fresh air. If blood pressure is low, place the person so that the legs are higher than the head. If breathing problems are present, the front end of the bed should be elevated. A semi-sitting position is recommended. After this, you need to call doctors.
Heart attack
The basis of emergency measures is the use of fast-acting nitrates. If paroxysm develops during physical activity, it is stopped. The patient is placed in bed, the body position is free. A fast-acting way to introduce nitrates is to spray Isoket spray. One press releases 1.25 mg of Isosorbide Dinitrate. It is better to apply the solution to the sublingual space (from 1 to 3 doses of the drug).
It is acceptable to use tablet forms of drugs, nitroglycerin. Prescribed 0.5–1 mg sublingually. Before the doctor arrives, you should not exceed the minimum dosage. If there is no improvement 5 minutes after administration, the administration is repeated. The lack of effect from 3 doses of Nitroglycerin indicates the development of AMI.
If there is a significant decrease in blood pressure, Nitroglycerin should not be used. The drug sharply dilates blood vessels, leading to increased hypotension and the development of steal syndrome. In 1/3 of patients with preserved consciousness, severe short-term headache occurs.
Acute myocardial infarction
In case of AMI, help consists of prompt hospitalization in the ICU. At the prehospital stage, the patient should be given to chew ½ tablet (150–200 mg) of acetylsalicylic acid. If the SBP remains above 90 mm Hg. Art., and the pulse is more than 50 beats per minute, it is permissible to give 1 tablet of Nitroglycerin under the tongue (ACC/AHA recommendations from 2002). For tachycardia, Propranolol is indicated at a dose of 0.5–1 mg/kg body weight. Everything except ASA should be used only if it is impossible to immediately hospitalize a person for one reason or another.
Neuralgia, osteochondrosis
In case of severe pain, the patient should take any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol). Therapy can be supplemented with muscle relaxants (Mydocalm, Tolperisone). Rest, dry heat on the affected area, and temporary limitation of physical activity are recommended. If there is an intervertebral hernia, the patient should consult a neurologist to assess the possibility of surgical treatment of the disease.
Foreign bodies of the upper respiratory tract and esophagus
Removing a foreign object should be done as quickly as possible. It is not advisable to wait for doctors to arrive in this situation. To remove a foreign object from the respiratory tract, the patient should be positioned so that the head and chest are below the level of the pelvis, then pat the back with force in the shoulder blade area. If consciousness is preserved, assistance is provided with the patient standing. The victim should be clasped with his arms from behind so that the palms are closed in the epigastric region. When a person tries to cough, it is necessary to increase the exhalation pressure with a sharp upward push. Often this method allows you to remove an item in 1-2 attempts.
If there are foreign bodies in the esophagus, emergency measures to remove them are not taken. There is no threat to life. You should wait for the ambulance and transport the person to a health care facility, where the object will be removed using special endoscopic equipment.
Injuries of the respiratory tract, esophagus, accompanied by bleeding
Before the doctors arrive, the victim should be placed in a semi-sitting position. Ice wrapped in soft cloth is placed on the area of the sternum projection. The use of tablet hemostatic agents is acceptable, but in case of massive bleeding it is not advisable. Moderate hemorrhages are an indication for taking Etamzilate at a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight. It is necessary to ensure patency of the airways and prevent their obstruction by blood clots. To do this, the patient's mouth is periodically cleaned by twisting a bandage (without unrolling) or a gauze swab wrapped around the index and middle finger.
In case of sternum injuries, the patient should be given a supine position without a pillow and ensure rest. For severe pain, analgesics are prescribed. If open wounds are present, gauze should be applied to stop bleeding and prevent infection. Treatment with antiseptic compounds is carried out only along the edges of the damage. Pouring solutions into a wound is strictly prohibited.
ARI, ARVI, bronchitis
The patient should be kept at rest. If the body temperature exceeds 38 °C, an antipyretic is given (Paracetamol, Aspirin). The patient should not be covered with a warm blanket even if he complains of chills. Allow only a light blanket. To ease breathing and reduce pain, inhalations with anti-inflammatory drugs are performed. For bronchospasm, hormonal drugs (Pulmicort) are used. General toxic syndrome is relieved with the help of complex formulations (Coldrex, Rinza, Theraflu).
Hypertension
Increases in blood pressure by 20 units or higher require drug correction. The first aid drug is Captopril. Take the drug 25 mg, under the tongue. The medicine begins to act within 20–25 minutes. You should not try to reduce your blood pressure quickly. Normalization of indicators should occur over several hours. Otherwise, there is a risk of vascular collapse. In the absence of Captopril, it is allowed to use Dibazol (0.02 mg) in combination with Papaverine (40 mg). Hospitalization is required when blood pressure rises by more than 30–40 units from normal, and the presence of a clinical hypertensive crisis (sharp deterioration in health, severe headache, blurred vision, coordination, neurological disruptions).
Heartburn
For one-time elimination of unpleasant symptoms, you can use enveloping agents (Maalox, 1-2 sachets per appointment). In addition, systemic antacids (Famotidine tablets 20–40 mg) are effective. It is not recommended to use baking soda to reduce acidity, since the neutralization reaction occurring in the stomach leads to the release of gases and overstretching of the walls of the organ. This method can be used once, if there are no other means of combating heartburn.