The period after childbirth when a woman breastfeeds her baby is called lactational amenorrhea. This is a natural physiological method of contraception, therefore it is considered the safest.
However, it is effective only if the woman exclusively breastfeeds the baby and the baby asks her at least 5-6 times a day.
As soon as the child turns 6 months old, this method becomes ineffective and requires additional means of protection against unwanted pregnancy.
Contraception after childbirth is necessary, because the female body needs at least a year to recover and achieve a new pregnancy.
When can you start having sex?
Immediately after giving birth, a woman begins to bleed, which can last for about a month. During this period, sexual relations should be completely excluded.
- Firstly , any movement in the vagina may be painful for a woman; during childbirth, her perineum often ruptures, and the vagina stretches to such a size that the penis is simply lost in it.
- Secondly , the hormonal background, in particular the hormone prolactin, is focused on milk production, and this reduces the level of lubrication, for the production of which estrogen is responsible. It also affects female libido, which fluctuates at zero level during the postpartum period.
I don’t want sex, friction instead of pleasure brings pure pain, as if the penis is covered with sandpaper.
- And thirdly , bleeding increases the risk of infection entering the body. The inner surface of the uterus after the placenta is separated is covered with numerous injuries, and it takes 4-6 weeks for them to heal.
Don't forget about psychological problems.
During pregnancy, a woman can gain 20-30 extra pounds, and during lactation it is almost impossible to get rid of them.
In addition, the young mother has absolutely no time for herself, she feels unattractive, fat, and this does not help increase her libido. A man, after a long period of abstinence, may insist on intimacy without understanding his wife’s excuses. This behavior can provoke postpartum depression in a woman, which occurs against the background of hormonal changes and is aggravated by psychological problems.
Conclusion : ideally, you can begin sexual activity no earlier than a month after giving birth, and preferably after a month and a half.
COOK
The abbreviation COC stands for combined oral contraceptives, which are familiar and familiar to many women.
Of course, their effectiveness when used correctly reaches one hundred percent, but there are several “buts”.
Firstly, when breastfeeding, you can use combined oral contraceptives no earlier than six months after the birth of the child. But if we are not talking about breastfeeding, then this method of protection against unplanned pregnancy can be used as early as a month after birth.
Secondly, COCs do not have the best effect on lactation: the quantity and quality of milk changes, and it is better to stop breastfeeding. In addition, consultation with the attending gynecologist is necessary.
Thirdly, skipping a dose significantly reduces the contraceptive effect, so self-discipline is mandatory here.
To the unconditional “pluses”
COCs can be safely attributed not only to an excellent contraceptive effect (if used in accordance with the instructions), but also to the prevention of inflammatory processes in the pelvis, and the prevention of certain gynecological diseases and the mammary gland, and hair and skin become noticeably better, which is good news .
When can I get pregnant again?
There is an opinion that from the moment postpartum bleeding stops until the onset of the first menstruation, conception should not occur in a nursing mother due to lactational amenorrhea. And, thanks to breastfeeding, you can extend this period by almost several years. Actually this is not true.
Pregnancy can occur just two weeks before the onset of the first postpartum menstruation, and a woman can only find out about the possibility of conception by measuring her basal temperature in the morning. Its increase indicates ovulation.
However, irregular hours, fatigue and constant care for the baby prevent a woman from monitoring changes in her body. Therefore, if a woman does not plan to give birth to a second child after the first, if she had a caesarean section, if she is weakened and does not feel well, she should take care of additional contraception, and not rely on the methods of our grandmothers and great-grandmothers, who lived in other environmental conditions and didn’t experience as much stress.
In principle, a healthy woman can become pregnant a month after giving birth, if everything went well, she feeds her newborn not only with breast milk, and her postpartum bleeding has stopped.
In general, doctors advise you to wait at least six months.
During this period, all internal microtraumas will heal, the woman will get stronger and recover for a new pregnancy, and the older baby will not have a great need for breast milk. However, any hormonal imbalance can prevent pregnancy. And, even if a woman wants to achieve a new conception, disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamus will not allow her to achieve her plans.
Lactational amenorrhea
The lactational amenorrhea method is a natural method of contraception based on the suppression of ovulation by the hormone prolactin, which stimulates lactation. This method is effective if lactation is accompanied by amenorrhea, and is also complete without the use of supplementary feeding, and is performed “on demand” of the child with optimal breaks between feedings of no more than 4 hours during the day and 6 hours at night. The method is effective in the first 6 months. after childbirth [9]. If at least one of these conditions is not met, it is necessary to use other methods of contraception [10].
The lactational amenorrhea method has the following important advantages: easy to use; does not have a negative impact on the health of mother and child; serves as a prevention of postpartum complications; has no contraindications; not associated with sexual intercourse. The disadvantages of this method include: limited effectiveness (only with strict adherence to the rules of breastfeeding); lack of protection against sexually transmitted diseases; the need to combine this method with other methods of contraception when reducing the amount of milk and introducing supplementary feeding [11].
Is it possible to get pregnant while breastfeeding?
From time immemorial, mandatory breastfeeding of a newborn was considered the most effective way to protect against pregnancy. This condition of the female body is called lactational amenorrhea.
Lactational amenorrhea is that prolactin, released during active breastfeeding, blocks the production of the hormone estrogen, which stimulates ovulation and, accordingly, in this case, conception cannot occur.
The slightest decrease in the frequency of feeding leads to a decrease in prolactin levels, and, therefore, increases the possibility of a new pregnancy.
One should also take into account the fact that for the first six weeks after giving birth, a woman should completely exclude sexual relations.
It turns out that you can use a natural method of contraception in the postpartum period for no more than 5 months, until menstruation returns.
In any case, the time will come when you will again need to think about additional methods of contraception.
Adviсe
- Try to abstain from sexual intercourse for at least six weeks after your baby is born. This is the recommended period to give your body time to recover. If this happens, use a condom during this period. It will also help protect you from infections while your body returns to normal.
- You can use an emergency form of contraception if necessary. The main drug that can be used after unprotected sexual intercourse during lactation remains levonorgestrel (Postinor, Escapelle, etc.). This substance is an artificial analogue of progesterone. There is a recommendation, which is also sometimes noted in the instructions for the medicine, to abstain from breastfeeding for 24 hours after taking it. But studies, including the most recent ones, have not confirmed the need for this.
- If you have any questions about which method to use to prevent pregnancy while breastfeeding, ask your doctor for advice.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
What contraceptive methods are right for me if I'm breastfeeding?
Hormonal fluctuations in a woman’s body significantly reduce the effectiveness of other natural methods of protection against unwanted pregnancy. Hence, the method of measuring basal temperature, the calendar method, and changes in the composition of cervical mucus can be considered ineffective.
Barrier methods of contraception are the safest and most effective for nursing mothers.
However, a cap, condom or diaphragm can only be used after the end of the postpartum period, which lasts approximately 1.5 months after birth. Only then the uterus and vagina regain their previous size.
The advantage of barrier methods of contraception is that they can be used as needed. The inconvenience is that you will have to prepare for the sexual act itself almost half a day in advance. There can be no talk of spontaneity and playfulness. But the effectiveness of the barrier method is quite high. The use of spermicides (creams, gels, sponges, suppositories that kill sperm) additionally protects against sexually transmitted infections.
The condom (male and female) is almost 100% effective, however, women during lactation experience vaginal dryness, as well as allergic reactions to latex, so it can only be used in tandem with lubricants and lubricants.
The intrauterine device is the most reliable method of contraception for both breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding women. Its effectiveness reaches 99%.
There are hormone-containing intrauterine devices, for example Mirena, which release the hormone levonorgestrel in small doses.
The IUD can be inserted no earlier than 1.5 months after normal childbirth and no earlier than 6 months after cesarean section.
Postpartum contraception - how to protect yourself after childbirth
The need for contraception after childbirth
A miracle happened.
The baby you've been waiting for for nine long months has finally arrived. Now you, parents, are completely immersed in caring for him. At first, both of you are terribly tired, night feedings are exhausting, and you can’t even think about resuming sexual relations. Yes, and extra pounds have appeared, the figure is not the same as before pregnancy. No, you need to wait a little, especially since the doctor recommends not having sex for the first 4-6 weeks... But nature takes its toll, and your sexual relationship will soon resume. Contraception is probably the last thing on your mind right now. Is it worth taking care of her at all, isn’t breastfeeding enough? It’s worth it if you want to avoid an unplanned pregnancy in the first months after giving birth, because, contrary to popular belief, this is not so uncommon. Studies have shown that in women who breastfeed, menstruation resumes on average after 2-6 months, depending on the intensity of feeding, and in non-breastfeeding women - 4-6 weeks after birth. If you do not have lactation or breastfeed irregularly, then ovulation, and therefore the ability to conceive, can resume as early as 25, and on average 45 days after birth. And since ovulation occurs 14 days before your period, you may already be fertile without knowing it.
Consequently, pregnancy can occur even before the first menstruation appears, so in order to start using contraception, you should not wait for the restoration of the menstrual cycle, the start of complementary feeding and a reduction in the frequency of breastfeeding.
According to surveys, two-thirds of Russian women resume sexual relations within a month after giving birth, and within 4-6 months - almost all (98%). At the same time, doctors are greatly alarmed by the fact that after giving birth, 20-40% of sexually active Russian women do not use any methods of contraception. Meanwhile, the probability of pregnancy in the absence of reliable contraception in nursing mothers 6-8 months after birth reaches 10%, and in non-breastfeeding mothers - 50-60%. Thus, women who have recently given birth in Russia should be considered a high-risk group for unplanned pregnancy.
And pregnancy during this period is generally extremely undesirable. Doctors believe that the minimum interval between births should be about 3 years. Why? Despite the fact that the involution of the organs of the reproductive system (their return to their previous state) ends 4-6 weeks after birth, complete restoration of the body takes at least 1.5-2 years. Breastfeeding also places a significant burden on a woman’s body. But after this, a woman still needs to replenish her supply of important microelements, such as iron, calcium, etc. As studies have shown, when pregnancy occurs earlier than 2 years after birth, the risk of developing pregnancy complications doubles (preeclampsia, anemia, intrauterine growth retardation), childbirth and the postpartum period.
Thus, we inevitably come to the conclusion that in the postpartum period and for 2 years after childbirth, a woman needs effective, reliable and safe contraception.
Choosing a contraceptive method after childbirth
Ideally, you should get advice and choose a suitable method of contraception after childbirth during pregnancy. If you don’t have time before giving birth, consult a doctor at the maternity hospital. If you still cannot decide on a contraceptive method or you have doubts and questions, then before resuming sexual relations (even while breastfeeding), you should definitely seek advice from a gynecologist, for example, an antenatal clinic or a family planning and reproduction center. The purpose of this article is to give a general idea of contraceptive methods during the postpartum period and how these methods are combined and how compatible they are with breastfeeding, but you should only determine which of these methods is right for you in consultation with your doctor.
A non-breastfeeding woman should start using contraceptives from the moment she resumes sexual relations. Moreover, if there are no special contraindications, she can choose any of the modern arsenal of contraceptives.
The method of contraception for a nursing woman depends on the feeding regimen and the time elapsed after childbirth. In addition, the contraceptive should not adversely affect the child’s health or milk secretion. If you are exclusively breastfeeding, the start of contraception can be delayed by 6 months. If feeding is infrequent or early initiation of complementary feeding (all this is typical for residents of developed countries), a contraceptive method should be selected during a mandatory postpartum visit to the doctor no later than 6 weeks after birth.
And one more important note: the various methods of contraception, which will be discussed below, have different effectiveness, some of them involve serious limitations in use, and not all can be used in the first weeks after childbirth. Be prepared in advance for the fact that during this important and responsible period of your life, when it is better to postpone the next pregnancy in any case, different methods of contraception will often have to be combined, either by increasing the effectiveness of a method that is ideal for you, but not reliable enough, or by “ensuring yourself” in those circumstances when the effectiveness of a reliable method is reduced for some reason. And in determining the need and principles of combining various methods, as well as in selecting the most suitable remedy for your couple, again, only a doctor will help.
Methods of contraception after childbirth
Abstinence
Abstinence (sexual abstinence) has 100% contraceptive effectiveness, but most couples are not satisfied with this method even for a short time.
Lactational amenorrhea method (LAM)
Mechanism of action and characteristics. After childbirth, a woman’s body produces the hormone prolactin, which stimulates milk production by the mammary glands and at the same time suppresses ovulation, resulting in lactational amenorrhea (absence of menstruation during breastfeeding). This effect of prolactin on a woman’s body determines the contraceptive effect of breastfeeding. Each act of breastfeeding stimulates the secretion of prolactin, but if the break between feedings is too long (more than 3-4 hours), the level of prolactin gradually drops. Breastfeeding, started immediately after birth, is an effective method of natural contraception and at the same time provides the child with the most complete nutrition. In addition, sucking stimulates the production of oxytocin, a hormone that promotes not only the contraction of the muscles of the areola of the mammary gland (due to which milk is released from the nipples), but also the contraction of the uterus, which leads to a rapid restoration of its size and shape after childbirth.
MLA involves exclusive or near-exclusive breastfeeding, both during the day and at night. The effectiveness of MLA is maximum if feeding does not occur according to a schedule, but at the child’s first request (even at night), sometimes several times an hour, on average from 12 to 20 times a day, of which 2-4 times at night. The break between feedings should not exceed 4 hours during the day and 6 at night. In this case, each time it is necessary to give the baby the breast, and not express milk. The contraceptive effectiveness of MLA remains at an acceptable level if the share of complementary feeding is no more than 15%.
Terms of application. The first 6 months after birth with proper breastfeeding.
Efficiency. 98%.
Advantages
- Easy to use.
- Gives a contraceptive effect immediately from the start of use.
- Does not affect sexual intercourse.
- Promotes uterine contraction, reducing the risk of postpartum complications (bleeding) and leading to a speedy recovery of the body.
- Does not require medical supervision.
- Beneficial for the child (breastfeeding provides him with the most adequate nutrition, promotes the development of immunity, and reduces the risk of infection).
Flaws
- Requires strict adherence to the above breastfeeding rules.
- Not suitable for working women.
- Short-term use (6 months).
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
Hormonal methods
ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES (OK)
OCs containing only progestins (“mini-pills”)
The tablets contain progestins - synthetic hormones, the contraceptive effect of which is to reduce the amount and increase the viscosity of cervical mucus (which prevents the passage of sperm into the uterus), change the structure of the mucous membrane of the uterine body (this prevents embryo implantation) and suppress ovulation.
Start of use. Breastfeeding women can start taking pills 5-6 weeks after birth, non-breastfeeding women - from the 4th week after birth or with the onset of menstruation.
Efficiency. 98% when taking pills correctly and regularly in combination with breastfeeding.
Advantages. They do not have a negative effect on the quantity, quality of milk and duration of lactation.
Flaws. In the first 2-3 cycles of use, intermenstrual bleeding is often observed, which is a consequence of the body’s adaptation to the drug. Some women may experience menstrual irregularities, including amenorrhea.
Features of application. OK prescribed by the doctor. They must be taken daily, without breaks, strictly at the same time. Violation of the time of taking or skipping pills, as well as the simultaneous use of certain antibiotics, anticonvulsants and sleeping pills, vomiting or diarrhea reduce the contraceptive effect. The ability to conceive is usually restored immediately after stopping the drug. After stopping feeding, you should switch to combined OCs, which are more effective.
Combined OK
They contain the hormones gestagen and estrogens, which suppress the growth and maturation of follicles and ovulation, as well as preventing implantation.
Start of use. After stopping breastfeeding, combined OCs are started to be taken with the resumption of menstruation. If you have not breastfed at all, you can use this type of contraception from the 4th week after birth.
Efficiency. When taken correctly and regularly, the effectiveness approaches 100%.
Advantages. After stopping taking the pills, the ability to conceive is quickly restored.
Flaws. It is not advisable to use during breastfeeding (estrogens reduce milk secretion and the duration of lactation).
Features of application. Similar to the use of OCs containing only progestins.
PROGESTAGENS, LONG-ACTING
Highly effective long-acting products. These include, for example, the injectable drug “Depo-Provera” and the subcutaneous implant “Norplant”.
Start of use. The first administration of the drug to nursing women is no earlier than 6 weeks after birth, to non-breastfeeding women - from the 4th week after birth.
Efficiency. 99%.
Advantages. They do not affect the quantity and quality of milk, the duration of lactation, and do not have a harmful effect on the child. One injection of Depo-Provera provides contraception for 12 weeks. "Norplant" provides protection against unwanted pregnancy for a period of 5 years. Removal of the implant is possible at any time.
Flaws. The disadvantages of OCs containing only progestins are similar (frequent intermenstrual bleeding and the onset of amenorrhea).
Features of application. Prescribed and administered by a doctor. In the first 2 weeks after administration, additional contraceptives should be used. It is necessary to strictly observe the intervals between administration of the drug. “Norplant” must be removed after 5 years, since after this period the effectiveness of the method sharply decreases. After discontinuation of the drug, restoration of a regular menstrual cycle and the ability to conceive usually occurs within 4-6 months.
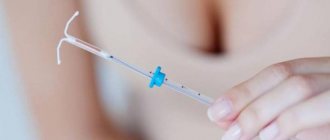
Intrauterine contraceptives (spirals)
Start of use. In case of uncomplicated labor and no contraindications, an intrauterine device (IUD) can be inserted immediately after birth. This does not significantly increase the risk of infectious complications, bleeding or uterine perforation. The optimal time for insertion is 6 weeks after birth, which reduces the incidence of IUD loss.
Efficiency. 98%.
Advantages. Compatible with breastfeeding. Provides protection from pregnancy for up to 5 years. Gives a contraceptive effect immediately after administration. The IUD can be removed at any time. Restoring the ability to conceive after removal of the IUD occurs very quickly.
Flaws. Sometimes it causes discomfort in the lower abdomen resulting from contractions of the uterus during breastfeeding. For some women, in the first months after insertion of an IUD, menstruation may be heavier and more painful than usual. Sometimes the IUD comes out.
Features of application. The IUD is inserted by a doctor. It is not recommended for women who have suffered from inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, both before pregnancy and in the postpartum period; as well as women who have multiple sexual partners, since in this case the risk of inflammatory diseases increases.
Barrier methods of contraception
CONDOM
Start of use. When resuming sexual activity after childbirth.
Efficiency. On average 86%, but with proper use and good quality it reaches 97%.
Advantages. The method is easily accessible and easy to use, and does not affect lactation or the health of the child. Greatly protects against sexually transmitted infections.
Flaws. If used incorrectly, the condom may slip or break. Use is associated with sexual intercourse.
Features of application. You should not combine the use of a condom with the use of fatty lubricants, which can cause the condom to rupture. Use a neutral lubricant with spermicide.
DIAPHRAGM (CAP)
Start of use. Not earlier than 4-5 weeks after birth - until the cervix and vagina shrink to normal sizes.
Efficiency . Depends on correct application. During breastfeeding, it increases to 85-97% due to a decrease in the ability to conceive at this time.
Advantages. Does not affect lactation and baby's health. Provides partial protection against some sexually transmitted infections.
Flaws. Use is associated with sexual intercourse.
Features of application. A medical professional should select a diaphragm for a woman and teach her how to use this method of contraception. After giving birth, you need to clarify the size of the cap; it may have changed. Used together with spermicides. The diaphragm should be removed no earlier than 6 hours after sexual intercourse and no later than 24 hours after its insertion.
SPERMICIDES
This method of chemical contraception is the local use of creams, tablets, suppositories, gels containing spermicides - substances that destroy the cell membrane of sperm and lead to their death or impaired motility.
Start of use. When resuming sexual activity after childbirth. While breastfeeding, they can be used independently; in the absence of lactation, they should be combined with other means of contraception, in particular with a condom.
Efficiency. When used correctly, 75-94%. The contraceptive effect occurs a few minutes after administration and lasts from 1 to 6 hours depending on the type of drug.
Advantages. In addition to those described for the condom, it provides additional lubrication.
Sterilization
Sterilization is a method of irreversible contraception in which ligation or clamping of the fallopian tubes (in women) or ligation of the vas deferens (in men) is performed surgically.
FEMALE STERILIZATION
Start of use. It is performed immediately after an uncomplicated birth under local anesthesia using laparoscopic access or by minilaparotomy, as well as during a cesarean section.
Efficiency. 100%
Advantages. The effect occurs immediately after the operation.
Flaws. Irreversibility. Low likelihood of postoperative complications.
Features of application. The method is acceptable only for those who are absolutely sure that they do not want to have more children. The decision to use the method should not be made under pressure from circumstances or emotional stress.
MALE STERILIZATION (VASECTOMY)
Under local anesthesia, a small incision is made in the scrotum and the vas deferens (similar to the fallopian tubes) is ligated. Sexual desire, erection, and ejaculation are not disturbed in any way, only the ejaculate does not contain sperm.
Efficiency. 100% if you follow the rule: you should use a condom for the first 3 months after surgery. The effectiveness of vasectomy can be confirmed by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate, detected using a spermogram.
Disadvantages and application features. Similar to female sterilization.
Natural Family Planning Methods
Based on abstinence from sexual intercourse on days favorable for conception.
Start of use. Only after establishing a regular menstrual cycle.
Efficiency. No more than 50% if all rules are followed.
Advantages. No side effects. Spouses bear joint responsibility.
Flaws. Determining favorable and unfavorable days requires special training of the couple by medical staff, careful record keeping, self-control and self-discipline. It is not recommended immediately after childbirth, as it is difficult to determine the timing of ovulation and first menstruation.
Can hormonal methods be used?
As for hormonal drugs, breastfeeding women should immediately abandon combined drugs, and it is better to prefer contraceptives containing the hormones gestagen and progestin.
They do not affect the composition and quality of mother’s milk in any way, and hormones will not affect the mother’s health either. The contraceptive properties of hormonal drugs reach 99% , but there are significant drawbacks.
The pills must be taken at the same time every day, and any deviation from the schedule can negate the entire contraceptive effect.
And due to caring for the baby, the new mother does not even have time to eat normally. Therefore, when taking hormonal contraceptives, you need to set an alarm on your phone to remind you to take your pills at the same time every day.
Another disadvantage is the incompatibility of hormonal contraceptives with antibiotics, as well as the side effect of vaginal discharge and menstrual cycle disruption. In general, hormonal contraception should only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Intrauterine contraception
Intrauterine contraception is an effective method of contraception. Intrauterine devices do not affect milk production.
An intrauterine device can be placed immediately after childbirth or caesarean section (within 48 hours). If this has not been done, then you can start using intrauterine contraception 6-8 weeks after birth (after the cessation of postpartum discharge). During the first week after administration, sexual activity and intense physical activity are not recommended.
The advantages of the method are its cost-effectiveness and convenience.
If menstruation has resumed, then the device is installed on the 2-3 day of menstruation, if not, then on any day. After this, there may be moderate bleeding for several days.
Intrauterine devices are contraindicated for inflammatory processes in the genital organs, since the spiral can contribute to the rise of infection and penetration into the abdominal cavity. For women who experience symptoms of pelvic inflammation while using intrauterine contraception, the device is removed. Also, the IUD cannot be installed in case of pathological changes in the uterus (developmental anomalies, uterine fibroids, deforming the uterine cavity, cervical stenosis).
Multiloud Cu-375
Currently, the most common copper-containing IUDs are, for example, Multiloud Cu-375 (price about 1,800 rubles). These spirals should be used for no more than 5 years.
Juno Bio – E380 super
The copper and silver-containing spiral Juno Bio - E380 super can be used for up to 8 years. This is a domestically produced spiral, the price is about 150 rubles. The silver or gold core contains spirals from Eurogine (use period 5 years). Gold and silver ions protect the pelvic organs from the development of inflammatory reactions.
The mechanism of action of intrauterine contraception is to suppress the functional activity of the endometrium, its thinning is observed, as well as an increase in the contractile activity of the uterine muscles. Therefore, implantation of a fertilized egg becomes impossible. However, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases.
The frequency of expulsion (“fallout” of the coil) is 6-16%. Expulsion most often occurs in the first months of using the IUD, more often on the days of menstruation. In this case, a woman may feel nagging pain in the lower abdomen, the presence of a foreign body in the vagina, and the “antennae” of the spiral becomes longer.
Fertility (the ability to fertilize) usually returns within the first year after the IUD is removed.
Mirena
In addition, you can use the Mirena . Mirena is a combination of intrauterine and hormonal contraception. It is a T-shaped system that daily releases a certain dose of the hormone (20 mcg of levonorgestrel). In this case, the dose of the hormone in the blood is lower than when using a mini-pill; it practically does not penetrate into milk. The effect on body weight is extremely small, practically non-existent. Due to the combination of two mechanisms of action (intrauterine and hormonal contraception), efficiency increases (99.9%).
The IUD is installed for a period of 5 years, but at the request of the woman it can be removed earlier, at any time. Ovulation is maintained in 85% of cases. Fertility is restored immediately after the IUD is removed.
The Mirena IUD, unlike other coils, does not contribute to the penetration of infection from the vagina into the uterus, as it causes thickening of the cervical mucus.
The use of the method is limited by its relatively high cost - about 7,000 rubles. Although if you calculate the monthly costs, then when using Mirena for 5 years you spend about 120 rubles per month. Contraindications are the same as for other means of intrauterine contraception.
Expulsions occur with a frequency of 3-6%. The risk of ectopic pregnancy is much lower than with other intrauterine contraceptives.
In the first 3-5 months of use, intermenstrual spotting may occur, but the total blood loss is lower than during normal menstruation. Amenorrhea (lack of menstruation) may occur. For women with heavy, long periods, the use of Mirena can have a positive effect on their health, as menstrual blood loss decreases and, as a result, the level of hemoglobin in the blood increases.
After the IUD is removed, the cycle is restored. 2% of women may experience acne when using Mirena. The same side effects as the mini-pill may occur, but are even less common.
After starting to use any intrauterine contraception, it is necessary to conduct a follow-up examination with a gynecologist after a month, then after three months, then, if there are no complaints, one visit per year is sufficient.
Contraception you can forget about
The safest and most effective method of protection against unwanted pregnancy is the installation of an intrauterine device. Moreover, it is suitable for both non-lactating and nursing mothers. In the latter case, a woman may experience some discomfort in the lower abdomen, since the uterus contracts slightly during breastfeeding. Some IUDs, such as the Mirena, contain the hormone progestin, which is slowly released over the course of a year and blocks the attachment of a fertilized egg to the walls of the uterus.
In general, the IUD is practically safe, and it is installed a month and a half after birth.
Condom, aka condom
A long-known remedy that has many advantages, including a high degree of reliability: if both partners use a condom correctly, then its effectiveness as a contraceptive can be close to one hundred percent, and this is important. But if the manufacturer's instructions for use and storage of this product are not followed, then the effectiveness is noticeably reduced.
An undoubted advantage
A condom can be considered to mean that you can use this method of contraception immediately, as soon as after childbirth the female body has recovered sufficiently and it is possible to begin sexual activity. It is important that a condom is easy to purchase, it is easy to use, and the use of a condom does not affect lactation and feeding in any way (that is, the baby will not be harmed under any circumstances). In addition, a condom protects not only from unwanted pregnancy, but also from STDs and HIV infection, and no other method of contraception is capable of this.
But there are also some “buts”, that is, shortcomings.
Firstly, a condom is needed for every sexual intercourse, and you need to make sure that there are always condoms in the house. Secondly, with intense sexual activity, some couples consider this method to be quite expensive. Thirdly, some men do not like to use condoms because they believe that using a condom changes sensations for the worse. And, above all, it is very important to follow all the manufacturer’s instructions and advice, and this, unfortunately, is not always done.