Who is the surrogate mother?
Surrogacy is a new technique in the field of reproductive medicine. The embryo is created outside the body of the genetic mother, then it is placed in the uterus of the surrogate mother, where she carries it for the next 9 months. In the process of surrogacy (in the standard course of the process), three persons are involved:
- First person: genetic father.
- Second person: genetic mother.
- Third party: surrogate mother.
Requirements for a surrogate mother
- Good health, mandatory absence of chronic diseases.
- Reproductive age: 20-35 years.
- A woman must have more than one child.
- A woman should not suffer from syphilis, HIV and hepatitis.
- The female incubator has no bad habits.
Before the procedure, the woman undergoes testing by a psychologist and legal advice.
If the surrogate mother is legally married, then she will need to provide her husband’s consent to the procedure, as well as undergo a whole range of tests:
- Blood for hepatitis and syphilis.
- A smear to determine the cleanliness of the cervical canal and vagina.
- Checking the microflora of the urethra.
- Cardiogram.
- Blood per group.
- Blood for Rh factor.
- Fluorography.
- Urinalysis (general).
- Cervical smear for oncocytological analysis.
- Examination for the following viruses: ureaplasmosis, herpes, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus.
In addition, the woman must undergo examination by a therapist, gynecologist and psychiatrist.
How to become a surrogate mother
To become a gestational courier, a woman must meet a certain list of requirements:
- age within 20-35 years;
- she must already have established herself as a mother and have at least one child conceived without the use of ART;
- if the woman is married, then the consent of the spouse, certified by a notary;
- a state of health that allows you to bear and give birth to a healthy child;
- certificate of good conduct;
- It is preferable to have a positive Rh factor.
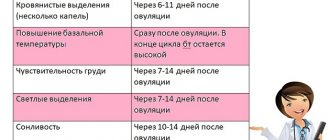
Read also: What drugs are used to stimulate ovulation?
If a woman wants to become a surrogate mother, she submits her documents to an organization that acts as an intermediary. After which her candidacy is considered and offered to future parents.
Reasons for surrogacy
If we consider the side of genetic parents, then surrogate mothers resort to the services of:
- Couples who cannot have a child naturally.
- Couples for whom the IVF procedure did not bring results.
- Women whose uterus is missing (has been surgically removed).
- Gay couples.
- Women in whom pregnancy is associated with a threat to life.
- Women with serious pathologies in the female sphere, with uterine deformities.
On the part of a surrogate mother, a woman chooses to carry someone else’s child for the following reasons:
- A good monetary reward that will allow her and her family to live in material prosperity.
- Material stability at the gestation stage (the woman is fully provided with: food, accommodation, medicines).
- The surrogate mother is entitled to official paid maternity leave.
- You can earn money and take care of your children at the same time.
Cost of surrogacy in Russia
In Russia, the first official surrogacy procedure was carried out in St. Petersburg in 1995.
All expenses for medical support of the surrogate mother, the cost of mediation services (lawyer), and payment of remuneration are borne by the biological parents.
The surrogate mother is paid after transferring her parental rights to the child to the genetic parents.
There are no uniform prices for surrogacy services. The cost of the service is determined by the economic development of the region.
The price for services is formed as follows:
- Costs for medical examination, observation, and medications largely depend on the status and location of the clinic (more expensive in capitals and large cities) and average 650,000 rubles.
- The funds allocated for food for the surrogate mother are 20-30 thousand rubles monthly.
- The cost of one IVF procedure is about 180 thousand rubles. Often pregnancy does not occur on the first try, so you have to do several replantations, which is an additional expense.
- The fee of a lawyer whose competence includes legal support of the contract starts at 50,000 rubles.
- The birth of a child, especially with complications, can cost up to 600 thousand rubles.
- The amount of monetary remuneration for a surrogate mother ranges from 800 thousand to 2 million rubles.
The minimum amount that a surrogacy program will cost biological parents will be an average of 1.9 million rubles, and the maximum reaches 4 million rubles.
Fertilization technologies
Modern medicine practices several methods of surrogacy.
Genetic mother's egg
The first method: the egg of the genetic mother is taken as biological material.
This is the standard option. First, both mothers (genetic and surrogate) go through a preparatory stage, which includes taking tests and synchronizing the women’s cycles. The last procedure is necessary to obtain the maturity of the inner layer of the uterus, into which the embryo will subsequently be implanted. The surrogate mother is given special hormonal drugs that increase the maturity of the endometrium. At this time, a woman should not take hormonal contraceptives. In the clinic where the woman is observed, hormones are monitored and an ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is performed. The fertilization procedure itself is identical to the IVF procedure. The genetic mother of the child also undergoes hormonal therapy. It allows the follicles to mature. When these elements reach the desired size, the follicular fluid is removed. For this purpose a puncture is used. Eggs are obtained from the liquid and fertilized with the sperm of the genetic father. After fertilization, 3-5 days should pass. On the specified number of days, the embryos must be implanted into the surrogate mother’s uterus. They will find out about pregnancy after 12-14 days. For these purposes, a woman does an hCG test. Three weeks later, the surrogate mother must undergo an ultrasound procedure.
Donor sperm
The second method: donor sperm is taken as biological material.
This method is used when a man has problems in a couple. Then the sperm of a donor who must be under 40 years old is taken as a donor. The donor must sign a waiver of parental rights. Donor sperm is frozen for six months before fertilization. The rest of the procedure proceeds as during standard insemination. Material from the biological mother and donor is used to fertilize the surrogate mother's egg.
Donor egg
The third method: a donor egg is taken as biological material.
The third method is used when it is not possible to take an egg from the biological mother. The reasons for this: menopause of the genetic mother, disruption of the ovaries, hereditary diseases and more. You cannot use a surrogate mother's egg here. There must be eggs from different people. Acquaintances, relatives or anonymous people can act as donors. If the donor has no contraindications, then synchronization and egg retrieval are performed. She is then fertilized with her father's sperm. The prepared material is transferred into the uterine cavity.
Surrogacy how fertilization occurs
Fertilization in this case involves the procedure of transplanting a ready-made fertilized egg, previously taken from a married woman, and the sperm of her husband. In conditions specially created for favorable growth and development of the embryo in the first weeks of life, the number of fertilized eggs is monitored, which increases the chances of the surrogate mother getting pregnant soon.
This technology is comparable to a minor surgical intervention, since the preparation of the surrogate mother meets all the criteria for preoperative preparation. Along with this, the woman is prescribed in advance a course of special medications that stimulate the immune system, as well as hormone therapy, which a candidate for surrogate mother must know, because taking such medications entails some changes in the body.
How does surrogate insemination occur?
The day on which the embryo transfer will be performed is determined based on data about the surrogate mother’s menstrual cycle. The most favorable period for pregnancy is selected and the procedure is carried out. A woman, in a hospital setting, is invited to lie down on a gynecological chair, having previously been given anesthesia, and with the help of endoscopic instruments, one or two embryos are introduced into the uterine cavity. If fertilized eggs remain in large quantities, they can be used in the future, in case of unsuccessful attempts to transfer embryos, resorting to cryopreservation.
After a successful procedure, pregnancy usually occurs after 10-14 days. During this time, the hormonal course of progesterone and hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) for the woman continues continuously. Perhaps this is the most exciting stage of the procedure, since the onset of a successful pregnancy can only be determined with the help of a clinical blood test, in which the level of hCG will increase every day.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
For many people, surrogacy is their last and only chance to have a long-awaited child. Modern medicine has provided people with this opportunity. During preparation for surrogacy, you can find out not only the gender of the child, but also health deviations.
However, against the backdrop of great advantages, this procedure has its own special disadvantages.
Due to the high cost of surrogacy, the procedure cannot be afforded by a poor family.
There is a possibility that the mother who carried a “strange” child will not be able to part with him. That is, she will keep it for herself. In this case, biological parents suffer from awakened maternal instinct.
Very often, fraudsters act under the guise of a surrogate mother or intermediaries.
The entire procedure takes place in an atmosphere of psychological instability. There is a possibility that the terms of the contract will not be observed on both sides. After the surrogate mother gives birth to the child, the relationship between the parties is terminated. However, there are times when mothers begin to become friends. Common concerns and problems bring them together.
"Surrogacy" and "Civil Marriage"
According to Part 4 of Art. 51 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, persons who are married to each other and have given their consent in writing to the implantation of an embryo into another woman for the purpose of bearing it, can be registered as the parents of a child only with the consent of the woman who gave birth to the child (surrogate mother).”
Civil registry office employees interpret this article as follows: a man and a woman must be in a registered marriage until the embryo is transferred to a surrogate mother.
Is this circumstance a basis for refusing to provide services to a single woman and (or) persons in a “civil marriage”?
Let's start with the fact that, according to the content of Art. 2 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation - Family legislation sets the conditions and procedure for marriage, termination of marriage and invalidation, regulates personal non-property and property relations between family members, and also determines the forms and procedure for placing children without parental care into the family.
Art. itself 51 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation is called “Record of the child’s parents in the birth register.”
Consequently, the norms of the Family Code do not apply to medical institutions, but Art. 51 defines the grounds for issuing a birth certificate, and does not contain any prohibitions on the provision of medical services depending on the patient’s marital status.
However, it is too early to consider the problem solved, because the absence of grounds for refusal to provide medical services does not imply the possibility of the registry office to apply the norm of Part 4 of Art. 51 of the Family Code and issue a birth certificate.
On the other hand, according to Part 9 of Art. 55 Federal Law “On the Fundamentals of Protecting the Health of Citizens in the Russian Federation”, Surrogacy is the bearing and birth of a child (including premature birth) under an agreement concluded between a surrogate mother (a woman carrying a fetus after the transfer of a donor embryo) and potential parents, whose germ cells were used for fertilization, or by a single woman for whom bearing and giving birth to a child is impossible for medical reasons.
However, if the content of the Family Code of the Russian Federation regulates the procedure for registering the birth of a child and does not apply to the rights of citizens in the provision of medical services, then the norms of the law “On the Fundamentals of Health Protection” are accordingly not guiding for the civil registry office.
In other words, unmarried persons or a single woman have the right to infertility treatment with the participation of a surrogate mother, but the law does not directly provide for a mechanism allowing birth registration in such situations.
It should be noted that this situation is not hopeless.
According to Art. 5 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation - if relations between family members are not regulated by family law, the norms of family law governing similar relations (analogy of law) are applied to such relations.
The legislator, understanding that the Family Code, for completely objective reasons, cannot contain “answers” to all questions in the field of family law, allowed us to apply the principle of analogy of law (similar legal relations).
Of course, it is far from a fact that registry office employees will find the strength to independently make a decision and register a birth, guided by the general norms of family law, but in this case, in the 4th part of Article 16 of the Federal Law “On Acts of Civil Status” and in Art. 11 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, provides for the possibility of appealing the refusal of the Civil Registry Office in court.
At the moment, there is a practice of positively resolving this issue in court, as well as the practice of resolving the issue at the level of the registry office.
Price issue
Of course, many are interested in: how much does surrogacy cost? The whole procedure consists of several articles:
- The fertilization procedure and necessary medications - 600,000 rubles.
- Food for a surrogate mother is about 20,000 rubles per month.
- Payment for surrogate mother services – at least 500,000 rubles
The amount of payments may be higher. The collected egg may not take root the first time. As a result, customers (biological parents) will incur additional costs.
Preparing for the genetic parents procedure
In the surrogacy program, an obligatory stage is the IVF procedure, during which the biological parents provide their genetic material.
The list of mandatory tests is supplemented if, during the examination, previously hidden pathologies are discovered that can negatively affect the quality of germ cells.
List of tests for IVF in a man:
- Spermogram indicators: volume, viscosity, ejaculate color, sperm activity and morphology.
- Blood testing for HIV infection, hepatitis B, C; syphilis, for IgG, M to cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus types I and II.
- Smear on flora from the urethra.
- Smears from the genital tract for infection: chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, herpes.
Tests for women:
- Determination of group affiliation and Rh factor of blood.
- Clinical and biochemical blood test.
- Establishment of hormonal status: FSH, LH, prolactin, estradiol, thyroid hormones.
- Microscopy of smears from the vagina, urethra, cervix.
- Blood tests for HIV infection, syphilis, hepatitis B, C, for antibodies to cytomegalovirus, to herpes simplex virus.
Some myths
Over the entire existence of surrogacy, many interesting facts, thoughts and myths have gathered around it. We will try to explain the most discussed of them.
Legislation and who can become a surrogate mother
- Only a woman who has at least two children of her own can become a surrogate mother. Official Russian healthcare documents say that in order to carry someone else’s child, a woman only needs to have at least one child.
- Only persons who are legally married can resort to surrogacy. Official marriage is one of the conditions of the procedure. But it is not mandatory. Otherwise (unregistered relationships), when registering a child, the name of the surrogate mother may be written in the mother column. Therefore, lawyers advise legitimizing your relationship even before the procedure. If single women resort to the procedure, then their name will appear in the mother column. Only this will require the consent of the surrogate mother.
- Surrogacy is illegal. In our country, a law was passed in 2011 according to which surrogacy is completely legal.
- It is better to adopt than to resort to surrogacy services. A surrogate mother will give you a baby of your own blood and genes, who will be completely similar to your family members. As a result of adoption, the child will be completely different, alien.
- An older woman (genetic mother) cannot resort to surrogacy. You can have your own child even at 50 years old. The most important thing is that a woman has at least one egg mature. You can also freeze the egg and use it in the future. But there is a danger: the biological mother is going through menopause. There is a risk of getting a child with abnormal development.
- Surrogacy is used by women who do not want to spoil their figure. Even this happens, but it is extremely rare. Basically, women resort to surrogate mothers after experiencing great grief: the absence of a very desired child for many years.
Give it up - won't give it up
- The surrogate mother gives her child into other hands , because she carried him. A woman is carrying a child that is not her own. It is a kind of incubator for the fetus. He doesn't physically belong to her. The surrogate mother writes consent to record the names of the genetic parents in the birth book. The document is drawn up in writing and confirmed by stamps. The described point must be specified in the contract.
- In most cases, the woman does not give the child away, but keeps it for herself. The procedure is based on a legally formalized contract with clearly defined responsibilities and rights of each party. Therefore, even if the surrogate mother does not give up the child (and she has the right to do so), her actions can always be challenged in court. You need to understand that it is extremely difficult, painful and emotionally difficult for a surrogate mother to part with the child she carried for 9 months. Psychologists prepare them for the fact of separation in medical centers. And in almost 100% of cases the work is carried out successfully.
- A woman can keep the “custom-made” baby for herself within three days after giving birth. The time for the mother to make a decision is not specified by law. She must give or refuse consent to the child before being discharged from the hospital, which is three days. However, the law has a general period for registering a child (one month).
Who does he look like?
- The child will have her blood. It is not true. The circulatory systems of the fetus and the pregnant mother are in no way connected. There is no blood connection between the child and the surrogate mother.
- The child will be similar in appearance to a surrogate mother. Not true. It carries the genetic information of its biological parents .
- Surrogate children are different from natural children. Not true. In many cases, these children are in excellent health because they are constantly monitored by doctors. Gestation and the birth itself are under the strict supervision of specialists.
- You can use biological material from a surrogate mother. In the described case, the child will carry the genes of the surrogate mother. That is, he will not completely (genetically) belong to his biological parents.
Requirements for biological parents
In order to use the services of a surrogate mother, the biological parents must have indications for this. For example, several miscarriages, several unsuccessful attempts to transfer an embryo during IVF, or serious health problems: kidney failure, heart disease, etc. Indications for surrogacy for a biological mother can be found in Order of the Ministry of Health No. 107n in paragraph 79.
Direct indications for surrogacy are:
- Absence of the uterus: as a result of surgery or acquired.
- Deformation of the cervix or uterine cavity.
- Pathological condition of the endometrium.
- Three or more unsuccessful IVF attempts while repeatedly obtaining high-quality embryos.
- Recurrent miscarriage: a history of three or more spontaneous miscarriages.
The procedure is also available to a single woman, but she will need an anonymous donor of biomaterial, but otherwise the procedure will be similar.
The procedure for applying for surrogacy for a single man is not regulated by law.
In order to reduce risks when registering a child, the parents must be officially married. The fact is that according to the law, when registering a child, the surrogate mother must issue permission to register the child as genetic parents. Since there is no mention of single mothers or fathers, children are registered with them, but difficulties may arise.
Often parents have to go to court. If single biological mothers usually easily win in court, then for parents who are not officially married or for single fathers, situations with court decisions may be different. The latter will have additional problems during registration: if the surrogate mother refuses to indicate information about her in the “mother” column, then formally the child will have neither a mother nor a father. But there are opposite decisions, according to which the regional branch of the Pension Fund obliged to issue a certificate for maternal capital to a single father.
Religious question
The Church does not approve of surrogacy. Her attitude is only negative. Priests and church ministers believe that if God does not send a child to a family, then this is for a reason. This is a challenge. It needs to be overcome. Perhaps the childless couple bears their punishment in life for what they have done.
The Church believes that childless couples can fulfill another mission on Earth: to take an orphan or orphans into their home.
The church also condemns the surrogate mother herself. She has no right to give away the child she gave birth to. By doing this, she absolves herself of responsibility. It causes irreparable harm to the child’s soul, since the spiritual connection between them is lost.
Supporters of giving birth to a child with the help of another woman believe that surrogacy also does not occur without the will of God.
Despite all the subtleties, ambiguities, doubts, high cost and disadvantages, surrogacy is a very popular procedure. Anyone can use it (from different angles). Information about clinics and customers can be found on the Internet.
Similar articles
No similar articles
Cases from practice
Love triangle and surrogate mother
As a result of infertility treatment under the Surrogate Motherhood program, the surrogate mother experienced a multiple pregnancy.
3 years after the birth of the children, it turned out that the genetic parents were not married, while the genetic father had a legal spouse all this time, who, having learned about what had happened, decided not only to dissolve the marriage, but also to “punish” everyone involved in the breakup of her families.
As a result, this angry woman managed to find a surrogate mother, who gave her a power of attorney to represent her interests in court.
Using the power of attorney received, the woman, on behalf of the surrogate mother, filed a claim in court to challenge maternity.
The claim was that, according to the Plaintiff, the surrogate mother believed that she was also the biological mother.
Satisfying the claims implied making significant changes to the issue of division of property jointly acquired during the marriage between the genetic father and the “lawyer” of the surrogate mother.
Additionally, the genetic father could have significant difficulties
The plaintiff initially claimed that she did not give written consent to register her genetic parents in the registry office, but under the pressure of the evidence presented, this argument was abandoned, replacing it with the argument that consent was given to her in a state of deep misconception into which her genetic parents had led her.
The surrogate mother was unable to explain what exactly the “misconception” was.
The issue of the marital status of the genetic parents was also raised by the Plaintiff.
The plaintiff argued that the medical institution was obliged to verify the marital status of patients, believing that treatment under the program
“Surrogacy” for unmarried persons is prohibited by law.
The absurdity of the stated claims was beyond doubt, but it had to be proven within 2 years.
During the consideration of the case, the court interviewed witnesses, examined the evidence presented, and also ordered a genetic examination.
The surrogate mother refused to undergo the examination, although it was she who initially instructed it to be carried out.
The court made the right decision and rejected the claims.
Registration of birth in the registry office
After giving birth and signing all the necessary documents, the surrogate mother prepared for discharge, and the genetic parents went to the registry office.
Employees of the district registry office informed about the need to provide a copy of the license of the clinic where IVF was done, as well as a special certificate.
Genetic parents were forced to look for an option to quickly obtain a certified copy of the clinic’s license and resolve the issue of processing other documents.
The difficulty was that the IVF procedure was carried out in St. Petersburg, and the registry office in which registration actions were supposed to be carried out in Moscow.
Preparation of documents in the maternity hospital
There was no lawyer in the maternity hospital who could provide qualified assistance in preparing the necessary documents.
As a result, the chief doctor, fearing the possibility of being involved in a lawsuit, initially refused to certify the surrogate mother’s signature, and then demanded the provision of an agreement between the genetic parents and the surrogate mother, as well as other documents, some of which, in the opinion of the chief doctor, should have been required notarized.
The demands of the chief physician were outside the legal framework and were justified solely by his inner convictions.
With the help of a lawyer, the genetic parents urgently filed a complaint with a higher control and supervisory authority, whose employees promptly responded to the request and explained in an accessible form to the chief physician the specifics of his performance of his official duties.
Brother and sister were born 24 days apart
After repeated unsuccessful attempts to treat infertility, it was decided to increase the likelihood of pregnancy by transferring (implantation) embryos to 2 surrogate mothers.
As a result, both surrogate mothers became pregnant, and one of them had a multiple pregnancy, which was the cause of premature birth.
Doctors refused to induce premature birth or perform a caesarean section on the second surrogate mother to synchronize the birth date of the children, because there was no medical indication for this.
As a result, the difference in date of birth between the two siblings was 24 days.
The registry office employees explained that they would be happy to help, but the Family Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of changing the date of birth in order to maintain family and medical confidentiality for children born by a surrogate mother, in contrast to similar cases when adopting children from an orphanage. Understanding that every time parents present their children’s birth certificates at work, in kindergarten, school or when traveling abroad, they will be forced to answer questions that are not pleasant for them, and also fearing for possible psychological trauma to their children, it was decided to contact one from the district courts of Moscow.
The court satisfied the parents’ demands and ordered the registry office to “synchronize” the children’s birth dates.
The surrogate mother tried to sell HER child
Crime reports are replete with reports of parents trying to sell their children, but this story has a fundamental difference from the others - the decision to “sell” the child was made before pregnancy!
Having accessed the global Internet, the woman found an advertisement for a married couple looking for a surrogate mother.
The day before the embryo transfer procedure, the doctor saw in the ultrasound image that the surrogate mother was already pregnant!
The surrogate mother did not invent tales and immediately told the truth - she was haunted by the thought that as a result of embryo transfer, pregnancy might not occur and then she would not be able to earn money, but the idea came immediately - guaranteed to get pregnant naturally, and a partner was found fast…
Confirming full awareness of the actions taken, the “surrogate” mother said: “I understand that in reality I would give birth to my own child, and they (the couple) would think that genetically this is their child... and I would still give it to them.” .
When asked that, in essence, she wanted to sell her own child, the former surrogate mother responded with silence.
An attempt by a surrogate mother to “return” the children 2 years after birth
2 years after the birth of twins, the surrogate mother was very “upset” when she learned that the genetic parents were not married.
The surrogate mother formalized her “disorder” in the form of a statement of claim challenging maternity.
The court hearing the case rejected the surrogate mother's claims and retained parental rights for the genetic parents.
Genetic mother
Based on the experience of the center, Katarina Kartamysheva sketches another social portrait of a woman who turned to the services of the institution:
— A successful businesswoman, 38-40 years old, who has spent years of her life on career growth. As a rule, he has a prosperous family, into which the children had difficulty fitting in. At first - for reasons of “I don’t want, I don’t need it, I don’t have time”, then - “I’ll have time, I’ll have time”, and when I decided that it was time, it turned out that “I can’t”...
Olga seemed to match the portrait sketch made by Katarina. The young woman is successful in her career and happy in her marriage. But she had to cooperate with the surrogate mother for a completely different reason - at that moment she already had three beautiful daughters, but she and her husband really wanted a boy.
“I couldn’t give birth on my own—I had several caesarean sections.” We resorted to the help of a surrogate mother, but our fourth girl was born. And we also love her madly.
— What were you most worried about when you were expecting your baby?
“I don’t know what word to define the feeling that I experienced in the first moment when they gave me the girl in my arms. I immediately realized that it was mine. Although I often thought about how I would get through this again - after all, I don’t remember how to treat children, my eldest daughter is already 23. But no, everything just came to mind. And it doesn’t matter how my daughter was born...
Anna, 42 years old, cannot have children:
- There is no need to spoil our people! Already, thank you, they ruined it with the sexual revolution. And surrogacy, in my opinion, is a continuation of destructive actions, a continuation of the degeneration of our society. I see surrogacy as a consequence of the corruption of morals. They couldn’t kill us with real weapons, so they began to harass us from the inside. The children we give birth to need to be raised and raised with dignity. It’s worth thinking about why there is poverty around, why there are so many dysfunctional families, why alcoholism and smoking flourish. Let the state solve these problems, then they will give birth more boldly. And there will be no fear for the future of the children.
Igor, 20 years old, student:
— Surrogacy is the only salvation for Russia. If we don’t have our own children, the Chinese will replace us.
Natalya, 31 years old, mother of two children:
“People need to mature to such things.” All the same, I think that a woman who “ordered” a child for herself will constantly remember that it was not she who carried it, that she could not give birth herself. And then, if difficulties arise with upbringing, who can guarantee that she will not blame her problems on the surrogate mother?
Daria, 22 years old, student:
— It turns out very strange and sad: if a woman gives birth to a child, then it is very difficult for her to support him, she has to survive from penny to penny. And if she is engaged in a career and achieves success, then there is no time left for children...
Dmitry, 35 years old, lawyer:
- Surrogacy? Why not! For a woman, the main thing is children. And if, due to certain circumstances, she cannot give birth herself, but she is given the opportunity to have her own child, albeit in such an unusual way, then she should definitely take advantage!
Help from AP Surrogacy is a technology of human reproduction in which a woman voluntarily agrees to become pregnant in order to bear and give birth to a biologically alien child, who will then be given to be raised by other persons - genetic parents. They will be legally considered the parents of this child, despite the fact that he was carried and given birth by a surrogate mother. Pregnancy in a surrogate mother occurs after the transfer of an embryo obtained by artificial insemination of the genetic mother's egg with the father's sperm. In 1985, despite opposition from the British Medical Association, IVF pioneers Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards pioneered the use of surrogacy to treat infertility. They conducted a surrogacy program for a couple from the UK. The embryos of the genetic parents were transferred to the sister of an infertile woman, and in 1989 the first child born by a stepmother was born. In Barnaul, surrogacy has been practiced since 2004. However, in the Russian Federation there is no legislative framework for auxiliary measures of this kind. Currently, this problem is not in the medical, but in the legal sphere.