Incomplete spontaneous abortion
Spontaneous results in miscarriage or premature birth of a non-viable fetus. The question of how long the fetus can remain viable is quite controversial. Today, abortion is considered to be the termination of pregnancy before the 20th week or the birth of a fetus weighing less than 500 grams.
Incomplete spontaneous abortion means that placental abruption occurs, resulting in severe bleeding with particles of the fertilized egg. The situation is complicated by the fact that all signs of pregnancy disappear, but at this time serious violations occur. In some cases, a woman may experience attacks of nausea and pain in the pelvic area.
When is cleaning necessary for an early miscarriage?
Someone, having learned about a spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages, will breathe a sigh of relief due to the fact that an unwanted pregnancy was terminated, while others will be upset that the expected motherhood will not happen. But most women, wanting to avoid unpleasant complications, will turn to gynecologists with the question of whether cleaning is necessary after a miscarriage or not.
The answer depends on what caused the miscarriage and what the ultrasound results showed. If the study determines the remains of the fertilized egg, cleaning will be needed to prevent complications.
Incomplete vacuum interruption
Incomplete abortion with vacuum is quite rare. This is a very serious consequence, characterized by the fact that the fertilized egg remains partially or completely in the uterine cavity. In addition, membranes may remain in the uterine cavity. Such a violation can occur as a result of an incorrectly performed procedure, a violation of the structure of the uterus, or previous infectious diseases.
To prevent the risk of incomplete abortion, you need to carefully conduct a comprehensive examination. This will allow you to determine the location of the fertilized egg before the procedure.
Contraindications
Surgical cleansing of the uterus is not performed in the presence of the following pathological conditions:
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes occurring in acute form;
- rupture of the walls of the organ;
- cuts to the body of the uterus;
- malignant neoplasms.
Best time for this procedure
The manipulation is carried out before the start of the menstrual cycle. In emergency cases, surgery is performed during menstruation or uterine bleeding.
Causes of incomplete abortion
Dangerous complications after abortion can lead to the development of sepsis. There are certain reasons for incomplete abortion, among which the following should be highlighted:
- medical error;
- hormonal disorders;
- carrying out late-term abortion;
- heredity;
- food poisoning;
- inflammatory processes.
All these factors can lead to the fact that the expulsion of the fetus from the uterine cavity may be incomplete. As a result, infection may occur and additional curettage may be required. All these complications can lead to infertility.
Instrumental methods of abortion (artificial abortion)
Instrumental removal
fetus is used in 97% of cases. For gestational ages less than 12 weeks, curettage is used almost exclusively.
Vacuum aspiration method
at a period of 4-6 weeks, it requires less expansion of the cervical canal or does not require it at all. The curette is a small flexible cannula (4, 5 or 6 mm in diameter), although a rigid plastic curette (6 mm) or a metal curette designed for endometrial aspiration biopsy can also be used. The cannula is connected to a vacuum generator (usually a mechanical or manual vacuum pump, sometimes a vacuum aspirator), and then inserted into the uterus through the cervical canal and the contents of the uterine cavity are carefully but thoroughly removed. In the first weeks, failure to terminate a pregnancy using this method is more common than in later periods.
After the 7th week, abortion usually requires dilation of the cervical canal (use a larger diameter suction curette as the fetus enlarges). Gentle dilatation is achieved using tapered dilators of increasing size until the opening is large enough to accommodate a cannula of the desired diameter. Disposable cannulas are usually sized according to the stage of pregnancy. So, at the 8th week a cannula with a diameter of 8 mm is used, and at the 12th week a cannula with a maximum diameter of 10 mm is used. To reduce the risk of damage to the neck during mechanical expansion, dried seaweed (kelp) or other expansion agents that swell by osmosis are often used. They are inserted through the internal opening of the cervical canal and left there for 4-5 hours, usually overnight. The swelling of plant material and/or the resulting stimulation of prostaglandin release leads to dilation of the cervical canal.
Main symptoms
The first signs of incomplete abortion are observed literally 1-2 weeks after the operation. The main symptoms are considered:
- nagging and sharp pain in the pelvic area;
- temperature increase;
- pain on palpation of the abdomen;
- heavy bleeding;
- symptoms of intoxication.
When the first signs appear, you should definitely consult a doctor for diagnosis and subsequent treatment. Such a violation can have a detrimental effect on a woman’s health, as well as her reproductive system. In particularly severe cases, this can lead to death.
Spontaneous cleaning of the uterus during a frozen pregnancy
Domestic doctors are increasingly resorting to wait-and-see tactics, which are widespread abroad. It consists in the fact that if the patient is feeling well, cleaning can be postponed for up to a month. But it is important to undergo an ultrasound regularly, about once a week.
After 2 weeks of waiting, the uterus cleanses itself in:
- one in three out of four women who have had an incomplete miscarriage;
- half of the patients with anembryonia;
- thirds of women whose pregnancy regressed.
You should immediately seek medical help in cases where:
- bleeding began;
- body temperature increased;
- pain appeared in the lower abdominal segment.
Carrying out treatment
If an incomplete abortion occurs, emergency care should be provided immediately after the first signs of a disorder occur. In case of severe bleeding, a large-diameter venous catheter is installed and an Oxytocin solution is injected. In addition, it is imperative to remove any remaining fruit. If curettage occurred without complications, then observation is indicated for several days, and then the patient is discharged.
If there is significant blood loss, administration of ferrous sulfate is indicated. To eliminate pain, Ibuprofen is prescribed. When the temperature rises, the use of antipyretic drugs is indicated.
Features of pregnancy and childbirth after cleansing
Women who have previously undergone uterine cleansing need to be especially careful during pregnancy.
If a woman did not wait long and became pregnant immediately after curettage, she risks losing the baby or getting placenta previa. This is due to the fact that the endometrium did not have time to recover after surgery. Such women are usually under the supervision of a doctor all the time and can be hospitalized for a long time. The doctor must prescribe maintenance medications.
If the girl did not give birth and had a cleaning done, the uterine cervix could be injured. In this regard, she will not be able to hold the growing fetus, which will lead to a miscarriage. In such cases, the cervix is sutured before delivery.
Some ladies cannot psychologically come to terms with the loss of the previous heir (if the reason for the purge was a miscarriage or missed pregnancy). Constant worries keep the uterus in good shape, which can also lead to the loss of the child. Here you will need the help of a psychologist and the support of loved ones.
To make pregnancy and childbirth as successful as possible, you need to:
- eat a balanced diet;
- walk more in the fresh air;
- do not rush to get pregnant after curettage;
- do not lift heavy things;
- be less nervous;
- take vitamins;
- Take any medications in consultation with your gynecologist;
- at the first deviation, go to the hospital.
Possible complications
The consequences and complications can be very serious, ranging from prolonged bleeding to inflammatory processes and even sepsis. Complications are divided into early and late. Early ones are observed immediately after an abortion or miscarriage, and include:
- discharge;
- penetration of infection;
- chronic inflammation of the uterine cavity.
Late complications can occur several months or even years after the abortion. These may be adhesive processes, hormonal disorders, as well as deterioration in the functioning of the reproductive sphere.
Possible consequences after a miscarriage
Of course, some complications may arise after cleaning, because this is a standard surgical operation.
The first complication that is possible is bleeding, which can occur immediately after curettage. These discharges are identical to those that a woman observes during her menstruation. The only thing is that in most cases bleeding is characterized by a blood clotting disorder. In this case, the woman must inform the doctor about this and he will prescribe oxytocin injections.
The second consequence that a woman can expect after curettage is the phenomenon of hematometer, that is, blood clots begin to accumulate in the uterus and all this leads to the formation of an inflammatory process. The reason for this phenomenon is a spasm of the cervix, which occurs literally a few hours after the end of the curettage procedure.
To prevent the occurrence of cervical spasms, it is necessary to take antispasmodics, for example No-Shpu, after curettage. This medication ensures that the cervix will be in a fairly relaxed physiological state for a short time.
Prevention of complications
Following certain simple rules will help to significantly reduce the risk of complications. It is imperative to avoid sexual relations in the first 3 weeks after an abortion or miscarriage. Control of discharge is required, it is important to avoid physical activity for 2 weeks, and follow basic hygiene rules. During the first month it is forbidden to swim in the bathroom, the sea, or use tampons. In addition, it is important to regularly visit a gynecologist for examination. After a medical abortion or spontaneous miscarriage, you need to visit a doctor a week later and make sure that all the remains of the fetus are expelled.
It is more often diagnosed after taking drugs for artificial termination of pregnancy (mifepristone, mifegin, etc.). The pathological condition develops due to incomplete rejection of the fertilized egg. This complication occurs in women who decide to undergo the procedure in late pregnancy (7-8 weeks). The presence of remnants of embryonic tissue may be indicated by painful sensations in the lower abdomen. They are cramping, acute, occur suddenly, and taking painkillers gives only a temporary effect. Sharp pains can be replaced by dull, pulling pains that radiate to the lower back, sacrum, and perineum. They intensify during sexual intercourse and gynecological examination. Characteristic signs of incomplete abortion include bleeding from the cervical canal. The discharge can be either spotty, barely noticeable, or copious and long-lasting. Prolonged bleeding sometimes leads to dizziness, increased heart rate, and increased sweating. Ignoring this symptom can have serious consequences. Remains of embryonic and placental tissue often provoke disruption of the microbial flora and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. If inflammation develops, the pain syndrome becomes more pronounced. It is accompanied by symptoms of an acute inflammatory process:
- serous discharge from the genital tract,
- discomfort in the perineal area,
- burning, itching of the genitals.
The patient often develops a fever, fatigue, joint weakness, nervousness, and irritability.
When contacting a gynecologist, in addition to the signs of incomplete abortion, the doctor should rely on instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods. To clarify the pathology, an ultrasound examination is performed; individual components of the embryo or blood clots are visualized in the image. The development of the inflammatory process is indicated by an increased level of leukocytes when taking a smear or blood test. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is necessary to remove fetal remains and develop antibacterial therapy. To solve the first problem, surgical curettage of the uterine cavity is performed under general anesthesia. The inflammatory process is eliminated through antibiotics. In addition, hormonal therapy is possible; some patients need to stop bleeding after an abortion with medications. Women who discover signs of incomplete abortion should immediately contact a specialist to identify the pathology. Untimely treatment can further affect reproductive function, cause infertility, cause menstrual irregularities, serious hormonal imbalances and the development of gynecological diseases (endometriosis, endometritis, uterine fibroids, etc.). A.
Diagnosis
1.
Clinical picture.
The expulsion of parts of the fertilized egg is accompanied by bleeding and cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Both patients and doctors may mistake blood clots for parts of the fertilized egg. When examined in mirrors, smoothing of the cervix is determined, and during bimanual examination, the opening of the internal pharynx, part of the fertilized egg in the vagina or in the cervical canal is determined. To assess blood loss, find out whether the patient had dizziness or fainting when standing up, and evaluate postural changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
2.
Laboratory research
a.
General blood test (in case of acute blood loss does not always reflect its degree).
b.
Determination of Rh factor.
V.
In case of severe bleeding, orthostatic hypotension and tachycardia, the blood type and Rh factor are determined.
G.
In case of repeated abortion, a cytogenetic study of the remains of the fetal egg is carried out.
B.
Treatment
1.
First measures.
For severe bleeding, install a large-bore venous catheter (at least 16 G) and inject 30 units of oxytocin in 1000 ml of lactated Ringer's solution or saline at a rate of 200 ml/hour or higher (in early pregnancy the uterus is less sensitive to oxytocin than in late). Because oxytocin has an antidiuretic effect, urine output may decrease during infusion. In this regard, the infusion is stopped immediately after the bleeding stops. An abortion is used to quickly remove the accessible parts of the fertilized egg from the cervical canal and its cavity, after which the bleeding, as a rule, stops. After the patient’s condition has stabilized, they begin to remove the remaining fetal egg.
2.
Removing the remains of the fertilized egg
a.
Technique of operation.
The patient is placed on a gynecological chair, covered with sterile sheets (as in childbirth) and sedatives are administered. If general anesthesia is not possible, pethidine is administered, 35-50 mg IV over 3-5 minutes. During the infusion, the respiratory rate is monitored; if it is depressed, naloxone is administered, 0.4 mg intravenously.
The cervix is exposed with speculum. The vagina and cervix are treated with a povidone-iodine solution. A paracervical blockade is performed with a 1% solution of chloroprocaine. Using a 20 G needle (lumbar puncture needle), the anesthetic is injected under the mucous membrane of the lateral vaginal vaults at 2, 4, 8 and 10 hours (3 ml at each point, 12 ml in total). To avoid the anesthetic getting into a large vessel after puncturing the mucous membrane, the syringe plunger is slightly pulled in the opposite direction. If administered quickly, the patient may experience tinnitus or a metallic taste in the mouth. Bimanual examination determines the size and position of the uterus. The cervix is grabbed by two pairs of bullet forceps by the front lip and brought down to the entrance to the vagina. The direction of the cervical canal is determined with a uterine probe. If necessary, the cervical canal is dilated using Hegar or Pratt dilators to the dilator number (in millimeters) corresponding to the gestational age (in weeks). For example, at 9 weeks of pregnancy, Hegar dilators up to No. 9 are used. Removal of the remnants of the fertilized egg begins with vacuum aspiration, as it reduces blood loss and is less traumatic. The diameter of the vacuum device nozzle should be 1 mm less than the expander number. To avoid perforation, the nozzle is inserted only to the middle of the uterine cavity. After vacuum aspiration, the uterine cavity is scraped with a sharp curette.
b.
Uterine perforation
usually occurs after 12–14 weeks of pregnancy. Treatment of perforation depends on its location, the presence or absence of internal bleeding, as well as on what was used to perform the perforation and whether the remains of the fertilized egg have been removed. Perforation by the nozzle of a vacuum apparatus is often accompanied by damage to internal organs. With median perforation using a dilator, uterine probe or curette, injury to large vessels rarely occurs. To exclude bleeding and peritonitis, observation for 24-48 hours is indicated. Lateral perforation may be accompanied by damage to the uterine artery or its branches. Laparoscopy is indicated. If the remnants of the fertilized egg are not removed, the intervention of an experienced doctor is required. Curettage is completed under laparoscopy or ultrasound control. Before repeated curettage, oxytocin or methylergometrine is administered.
V.
During curettage, attention is paid to malformations and diseases of the uterus, which can cause spontaneous abortion.
d.
After curettage,
if it passed without complications, observation for several hours is indicated. In case of large blood loss, a general blood test is repeated. If the condition remains satisfactory, the patient is discharged. To prevent infectious complications, it is recommended to abstain from sexual activity, douching, and not use vaginal tampons for two weeks. For large blood loss, iron (II) sulfate is prescribed orally. Ibuprofen is usually prescribed for pain relief. Women with Rh-negative blood are administered anti-Rh 0 (D)-immunoglobulin intramuscularly. If moderate bleeding persists, methylergometrine is prescribed, 0.2 mg orally 6 times a day for 6 days. In the absence of complications, examination is carried out 2 weeks after curettage. If bleeding increases, pain appears in the lower abdomen, or the temperature rises above 38°C, the patient should immediately consult a doctor. If there is a suspicion of retention of parts of the ovum, an ultrasound scan and repeated curettage of the uterine cavity are performed. After this, to exclude ectopic pregnancy, the level of the beta subunit of hCG in the serum is examined.
d.
Psychological support
. After a spontaneous abortion, a woman often develops feelings of guilt and depression. It is important to give her the opportunity to express her feelings. It is better not to rush into talking about a future pregnancy. In case of severe psychological trauma, a woman is advised to contact a psychological support group.
Incomplete abortion
- this is a pathological condition during a woman’s pregnancy, during which the fertilized egg is completely detached from the uterine cavity, the child died, but it is retained in the female body. This diagnosis can be made before pregnancy.
important
In later gestation, termination of pregnancy is called antenatal fetal death and cannot be classified as an abortion or miscarriage. This pathology can occur in 2-3% of all cases of miscarriages or incorrectly performed medical abortions (especially).
Why is curettage performed, and how long does recovery take?
Endometriosis is a disease that causes the endometrial glandular tissue to grow outside the uterus. As a rule, endometriosis occurs in the fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, bladder, abdominal cavity, rectum and other internal organs.
Most often, women who belong to the childbearing age category of 25-40 years can hear such a diagnosis. Less often, but such cases are possible, endometriosis is detected in a teenager during the formation of a regular menstrual cycle.
Sometimes in advanced situations, pathology can provoke the active development of cysts and subsequently infertility. In most cases, endometriosis does not harm the normal development of the fetus, but if pathology is present, the chances are significantly reduced. Therefore, treatment is necessary.
Curettage is prescribed in cases where drug treatment has not been successful. Surgery may also be prescribed if complications have developed that cannot be eliminated in any other way.
Curettage is prescribed if it is established: endometrial hyperplasia, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, spontaneous miscarriage, frozen pregnancy, uterine bleeding of unknown etiology, a combination of pathologies, endometriosis, infertility.
Gynecological cleansing of the uterine cavity involves removing the functional mucous layer of the uterus. Further restoration of the endometrial membrane occurs due to the germ layer itself. This is a fairly common procedure; a gynecologist prescribes it for almost every third woman. Surgical intervention to eliminate tissue endometriosis is best performed 3 days before the upcoming menstruation.
Indeed, sometimes curettage of the uterine cavity is carried out for diagnostic purposes, in order to determine the nature of the informative tissue sample or to find out whether degeneration into cancer has begun.
What the consequences will be directly depends on the experience of the operating surgeon who directly performed the curettage of the cavity. If all the rules of the surgical technique are strictly followed and the woman’s medical history does not indicate the presence of concomitant pathologies that may affect the restoration of the cavity, then complications should not arise. It is imperative that if endometriosis overlaps with concomitant diseases, the reproductive organs doctor must calculate all the risks.
It is considered normal when a woman feels mild, tolerable pain, as during menstruation after surgery. Such painful sensations are more reminiscent of a spasm, as the uterus contracts and returns to its previous size.
If there are no problems, then restoration of the uterine cavity occurs quite quickly; as a rule, complete tissue regeneration occurs in one menstrual cycle.
It is during the postoperative period that a woman should pay attention to the nature of the discharge and its intensity; alarming signals can be recognized from them.
The question of how long it will take to restore the uterine cavity after curettage cannot be answered accurately; it all depends on the general condition of the female body, its reserves and related factors.
As a rule, this period varies between 14-15 days.
Many people are interested in what needs to be done after cleaning to shorten the recovery period:
- you cannot have sexual intercourse;
- do not douche, do not use various gels, ointments, vaginal suppositories;
- take antibiotics;
- use only a pad, not a tampon;
- You can’t play sports or lift weights;
- strictly observe genital hygiene;
- avoid hypothermia;
- You cannot visit saunas, steam baths, solariums, etc. for a month;
- You cannot take a bath, only shower, do not swim in the lake, sea or other bodies of water.
If you follow general recommendations, you can reduce the recovery of the uterine cavity and avoid consequences. Also, you should not be afraid of such a procedure as curettage. Today, thanks to new and technologically advanced equipment, any complications are reduced to a minimum. Cleaning the cavity helps eliminate various gynecological problems that interfere with conception and bearing a child. That is why this procedure helps many people experience the joy of motherhood.
Causes
The reason for the incomplete expulsion of the fertilized egg from the woman’s uterine cavity may be certain conditions and their combinations
:
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- exposure to radioactive radiation;
- severe infections and inflammatory diseases of the mother, including food poisoning;
- history of abortion;
- medical termination of pregnancy more than 45 days from the beginning of the last one;
- hereditary predisposition;
- alcohol and drug abuse during pregnancy;
- hormonal disorders.
When is surgery needed?
Before determining whether curettage is necessary after a miscarriage, it is worth considering what happens in the female body when the fetus is rejected and spontaneous abortion occurs at a short period of time (up to 20 weeks).
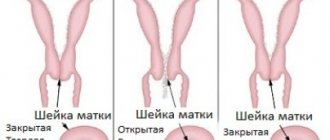
First, nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen, sometimes cramping and unbearable, and brownish-colored bloody discharge from the vagina may appear (many women, unaware of their pregnancy, mistake it for menstruation, which is painful due to delay). At this stage, it is still possible to save the fetus, because the cervix is still completely closed. But, unfortunately, at this moment, few women seek medical help.
Further inside the uterus, the chorion (from this organ the placenta, or baby's place, subsequently develops), through which the embryo was connected to the maternal body, gradually exfoliates. The fetus begins to experience oxygen starvation. At this stage, spontaneous abortion can no longer be prevented. As a rule, if the pain is not very severe, then the woman notices increased bleeding, which she considers to be menstrual.
The dead embryo is finally detached from the uterine wall, but still remains inside the reproductive organ.
The uterus begins to contract vigorously, trying to expel the foreign body. In this case, the bleeding may remain the same or increase slightly.
Finally, the dead fertilized egg is expelled, when vaginal discharge becomes profuse, with many bloody clots. This usually happens on the 2-3rd day after the start of bleeding. Sometimes women notice that a large gelatinous clot has fallen out, which frightens them, and sometimes it goes unnoticed.
Removal of the fertilized egg from the uterus can be:
- complete (doctors leave such a miscarriage without cleaning);
- incomplete (additional curettage is needed to remove the remains of the embryo or placenta).
If you neglect the curettage procedure during an incomplete abortion, there will be a risk of developing inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries.
Signs of incomplete abortion
Symptoms and signs of incomplete abortion are as follows.
- . They occur periodically, with spasms and pulling sensations, radiating to the lower back and perineum. The intensity can vary from mild discomfort that practically does not bother the pregnant woman to severe and unbearable pain that impairs the woman’s ability to work.
- from the genital tract of varying intensity (usually red, but can also be brown).
- Enlarged uterus
, soft and painful on palpation. - Increased
body temperature of a woman. - An instrumental examination (ultrasound)
reveals a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity without heartbeat or fetal movement.
Treatment methods
First of all, it is necessary to remove the dead fetus and complete the abortion process. Inducing contractions with medication and waiting for the fetus and its membranes to come out on its own is ineffective, and this causes severe cramping pain in the woman.
information
In almost all cases they use (classical abortion). The effectiveness of the procedure and complete cleaning can be judged by the results of hysteroscopy (examination of the uterus using an optical instrument).
After removal of the fertilized egg, antibiotic therapy
. Most often, Ceftriaxone is used 1 g into the gluteal muscle for 7-10 days.
oral combined contraceptives for 4-6 months.
. They are prescribed by a gynecologist individually, depending on the woman’s hormonal background. They will normalize the functioning of the reproductive system and prevent future miscarriages.
Unfortunately, even with a variety of contraceptives that can prevent unwanted pregnancy by 99%, two scarlet lines on the test sometimes cause problems. The only way out in this case is to terminate the pregnancy - abortion. No matter what type of surgery a woman chooses with her gynecologist, there is almost always a risk that the pregnancy will continue. This happens infrequently - in about 1% of cases, but this condition is extremely dangerous for a woman’s health. Pregnancy can continue for several reasons:
- Insufficient qualifications of the doctor.
- Incomplete examination of the patient before surgery.
- Ectopic pregnancy (in this case, a regular abortion will be ineffective, since an ectopic pregnancy is a separate complex case in gynecology).
The fact is that the correct location of the fertilized egg can only be determined using an ultrasound using a vaginal sensor. If this research is not carried out, the risk that the abortion will be incomplete increases.
How is curettage performed?
The main purpose of curettage is to remove the top layer of the uterine lining, which is shed during menstruation.
Curettage is performed in the operating room, on a gynecological chair.
Cervical dilatation and curettage can be very painful and unpleasant, so this procedure is almost always performed under anesthesia, but in some cases (for example, immediately after childbirth, when the cervix is dilated), curettage can be performed without anesthesia. In most cases, intravenous injection of special drugs is used as anesthesia for curettage, which within a few seconds puts the woman into a state of shallow sleep and completely eliminates painful sensations and memories of what happened during curettage.
Before curettage, the doctor inserts a dilator into the vagina, which allows you to straighten the walls of the vagina and makes the cervix visible.
Next, the doctor dilates the cervix - to do this, he holds the cervix with a special instrument and inserts a probe with a rounded end into the cervical canal. In order to achieve sufficient dilatation of the cervix, the doctor may remove the first probe and replace it with another one with a slightly larger diameter.
After sufficient dilatation of the cervix, the doctor can perform hysteroscopy (examination of the inner surface of the uterus using a special video camera) or proceed directly to curettage.
To carry out curettage, a special instrument (curette) is used, which resembles a small spoon with a long handle. With careful movements of the curette, the doctor scrapes the top layer of the uterine lining and collects the resulting tissue in a test tube, which will then be sent to the laboratory for histological analysis.
In general, the procedure for cervical dilatation and curettage can take up to 30-40 minutes.
In most cases, not only the uterine cavity, but also the cervical canal is subjected to curettage. This procedure is called separate diagnostic curettage (RDC). First, the cervical canal is scraped (cervical canal scraping), and then the uterine cavity is scraped. Materials obtained from curettage of the cervix and uterine cavity are collected separately and then subjected to histological examination as separate samples.
What to do if the pregnancy continues after an abortion?
If the abortion is performed unprofessionally, fragments of the fetus or the entire fetus may remain in the uterine cavity. What to do if the termination of pregnancy was unsuccessful?
Firstly
, you need to know what signs indicate that you are still pregnant: 1. Bleeding that started a few hours after surgery.
If there is something left on the walls of the uterus, it is not able to contract, which is why bleeding occurs. 2. Cramping pain in the lumbar region. 3. Body temperature may often increase, which is a sign of an additional infection. Secondly
, you need to understand what this condition means for the female body: 1. As a result of bleeding, the body loses a lot of blood, so anemia may develop.
2. An infection may occur, which will delay the recovery period for an indefinite period. 3. And most importantly, an incomplete abortion can cause disruption of a woman’s reproductive functions, and sometimes leads to infertility. Thirdly
, you need to urgently consult a doctor (preferably the one who performed the abortion): 1. The doctor will refer you for an ultrasound using a vaginal sensor. 2. If the study shows that there is still something left in the uterus, the doctor will suggest repeating the abortion procedure in a way convenient for you. 3. It happens that in such cases women decide to keep the child and give birth. There are many risks to consider here:
- Abortion is a serious intervention in the body. You need to understand that a child carried after an incomplete abortion may be born with serious abnormalities and pathologies.
- After such manipulations, the body experiences enormous stress, so there is a possibility of miscarriage at a later date.
- The psychological aspect plays a huge role - after an abortion (even an incomplete one), the spiritual connection between mother and child is broken. Therefore, this can cause psychological problems in a woman.
4. Even if the re-operation was successful, it is imperative to perform a second ultrasound. 5. After repeated cleaning, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy. 6. If you are unsettled by this situation, it is best to contact a women's psychologist. It will help you cope with all your fears.
Today it is not uncommon for a woman to decide to terminate a pregnancy for one reason or another. It often happens that she chooses a medicinal method, which can be done in the early stages of pregnancy. But this method carries many dangers, one of which is incomplete abortion.
Incomplete abortion is one of the most dangerous post-abortion complications, which can cause the development of sepsis. Among the reasons that may contribute to the development of this complication are:
There are many factors that can cause this complication to occur. But, according to statistics, incomplete abortion is very rare, approximately 1-4 percent. But still, such cases do happen. Therefore, knowing everything why an incomplete abortion can occur, a woman should take this much more seriously.
No discharge after surgery
There are very often discussions on the forum about why there is no discharge after curettage or it stops the next day, but cramping pain remains, sometimes accompanied by fever. In this case, we can talk about a hematometer - an accumulation of blood clots in the uterus, the cervical canal of which is already closed, and their expulsion is impossible. These clots literally burst the reproductive organ, causing sharp spasms. They can provoke sepsis of adjacent tissues.
Therefore, if after curettage or cleaning of a frozen pregnancy there is no discharge, immediately consult a doctor for a re-examination and evacuation of bloody concentrations. The lack of medical intervention in this situation leads to serious consequences. It’s worth thinking about if the blood loss was minor and lasted only one day, but the pain continues to cause discomfort.
Signs of incomplete abortion
Most women do not even know what signs can be used to determine that an incomplete abortion has occurred. And because of this, it happens that they go to the hospital even when only direct surgical intervention can help, and quite serious, since every day the infection, caused by an incompletely released fertilized egg, spreads very quickly. So, the main signs of incomplete abortion include:
- An increase in temperature that occurs due to the spread of infection
- The soft consistency of the uterus, unfortunately, only a gynecologist can determine this
- Bleeding that continues for a fairly long period of time after an abortion (more than two weeks).
Having noticed at least one of these symptoms, a woman should immediately contact a specialist, especially if it was a medical abortion. This should be done quickly because an incomplete abortion can lead to the development of other complications that may even threaten the patient’s life, and will also affect the future ability to conceive and bear children.
Progress of the procedure
Many women, who have already experienced the stress of losing a child early and learning that pieces of the fertilized egg remain in the uterine cavity, are very afraid of the procedure ahead of them. But fears are in vain - cleaning after a miscarriage occurs in exactly the same way as during an abortion. It is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Depending on the results of ultrasound diagnostics, the method is selected:
- Vacuum (if the remains of the embryo are small).
- Curettage (this is done if, during a spontaneous abortion in the early stages, the fetus died and did not come out of the uterus completely, but it is very difficult to determine the location of the remains of the fertilized egg on the endometrium).
The operation proceeds as follows:
- The woman is given anesthesia (general or local - the doctor decides).
- The uterine cervix is opened using special instruments and the upper layer of the endometrium is removed (the mini-operation takes 15-20 minutes).
After this, as with a regular abortion, which is done for a short period of time, the patient spends a couple of hours under medical supervision and goes home.
The normal consequences of such a gynecological mini-operation will be:
- Moderate pain in the lower abdomen, similar to menstrual pain (lasts from several hours to several days and does not require drug treatment).
- Profuse bleeding, which should continue for at least 10 days (earlier cessation may be a sign of cervical spasm and the fact that blood is accumulating inside it).
Women after a miscarriage often worry about the upcoming curettage, but it is worth understanding that this is a routine and fairly simple procedure for specialists, which most often goes well. Doctors choose one of the cleaning methods:
- Vacuum aspiration. It is used if a miscarriage occurs at 6-12 weeks of pregnancy and the fetal remains are small. This method is not used for acute infectious diseases of the genital organs, ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage that occurred less than six months after the previous birth.
- Curettage (scraping with a special instrument - a curette). The method is used for numerous remnants of the fertilized egg, the location of which is difficult to determine.
Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a general blood test and coagulogram, and stops eating 8-10 hours before. On the day of cleaning, the woman is given an enema, and the doctor conducts an examination to determine the shape and size of the uterus. The operation is carried out in several stages:
- the patient is placed in a gynecological chair;
- she is given anesthesia (local or general anesthesia is used);
- the vagina is treated with an antiseptic to prevent infection;
- the cervix dilates;
- Using a vacuum device or curette, the specialist cleans off the top layer of the endometrium along with the remains of the fetus;
- if you have a hysteroscope (miniature video camera), the doctor examines the uterine cavity to make sure that the operation was successful;
- the resulting biomaterial can be sent for genetic analysis to determine the causes of spontaneous abortion;
- An ice pack is placed on the patient's stomach.
Treatment and consequences
Once an accurate diagnosis has been made and it is confirmed that this is an incomplete abortion, treatment must begin immediately.
There are several methods of treatment:
- Medication. Here drugs are prescribed that promote further expulsion of fetal remains. This is mainly done with medications that promote increased contraction of the uterus. In this case, the pain, in particular nagging pain, will intensify.
- Surgical. In this case, either curettage is performed, which is carried out under local or general anesthesia. This usually takes about half an hour. After this procedure, the woman is sent for a hormonal study and is also prescribed antibacterial drugs. In addition, the woman will be closely monitored by the attending physician for some time.
Like any other procedure, there are a number of complications that may arise after the procedure:
- Damage to the walls of the uterus. This may impair the ability to further conceive a child.
- Infections
- Bleeding
Incomplete abortion is a very unpleasant and dangerous complication after an attempt to terminate a pregnancy, which can lead to very serious consequences.
In order to avoid serious problems, it is worth knowing what signs an incomplete abortion may have, so that you can consult a doctor as quickly as possible to correct the situation. In any case, before deciding to terminate a pregnancy, you need to consult with a specialist who will recommend a safer method and will also monitor this process in order to avoid possible complications! Learn more about incomplete abortion from this video:
Incomplete abortion, what is it and is it dangerous to health? Let's consider different situations, since termination of pregnancy can be spontaneous or caused by medical intervention. This determines what to do if there is still a pregnancy after an abortion, that is, treatment tactics.
Medical termination of pregnancy
The so-called abortion pill has become a very popular alternative to surgery. But there is one problem - this is when the fertilized egg and its membranes do not completely leave the uterus. That is, when incomplete occurs. According to statistics, this happens in 2-5% of cases.
What to do? It is better to discuss this issue with your doctor in advance. According to standard recommendations, an ultrasound examination after an abortion is performed on days 10-14, but if this is done after 5-7 days, then it is possible to notice signs of incomplete abortion in time and prescribe medications. This is usually Oxytocin. Then there is a high probability that everything will be fine. An uneven endometrium is not a reason for surgical uterine curettage. But if on an ultrasound on days 10-14 they see precisely the remains of embryonic tissue, it is usually recommended to carry out vacuum aspiration to prevent the inflammatory process.
If an incomplete miscarriage occurs, or even the fertilized egg remains in the uterus and continues to develop, you still need to terminate the pregnancy. The fact is that the drug taken will almost certainly seriously affect the child’s health; he may have developmental defects.
Vacuum aspiration
Sometimes an incomplete mini-abortion occurs when using this method of abortion. More often this happens when the uterus has an irregular shape, for example, bicornuate, when the fertilized egg develops in the “horn”.
If after this procedure the embryo continues to develop, you want to continue the pregnancy, and doctors do not consider this dangerous to health, then it is quite possible to keep the child.
If not, then hysteroscopy with curettage of the uterus may be suggested. This is when the uterus is cleaned using a special optical device. This makes incomplete abortion almost impossible.
Abortive cleansing
Abortive curettage in case of artificial termination of pregnancy is used at 10–12 weeks and is considered the least safe method. It is carried out in two stages. The first, dilatation, involves widening the cervical canal with surgical instruments or special drugs (which is less effective). The second stage, curettage - cleaning the cavity and walls of the womb using a curette - a medical surgical spoon. The process is painful, therefore it is performed under general anesthesia in the absence of contraindications.
Cleaning a frozen pregnancy is carried out in the same way if the fetus froze and remained in the womb, as well as if the miscarriage took place partially. Oh, read the article at the link.
It happens that pharmabortion or vacuum aspiration did not provide a complete termination of pregnancy. The remaining embryo particles must be removed to avoid sepsis of adjacent tissues. This process is carried out through cleaning.