- June 25, 2018
- Pediatrics
- Marinichenko Sergey
The birth of a child is always a joyful and happy moment for a family. Despite modern medicine and its significant progress, disruptions occur in natural physiological processes. For example, childbirth has remained a rather complex event from a medical point of view. Their course cannot be 100% predicted by the most experienced gynecologist. Therefore, newborns sometimes receive various types of injuries during childbirth.
How to treat hematomas in children?
You should not expect a magical effect from ointments; they only promote rapid resorption of the hematoma, pain relief and tissue restoration.
Each drug must be selected correctly, taking into account the age of the child and the characteristics of his body.
The following rules will help you choose suitable ointments for children:
- Each drug has indications and age restrictions. If a child is just starting to walk and gets injured, then the ointment should be for children from one year of age. For older children, it is worth purchasing another drug.
- Before using the ointment for its intended purpose, it is important to test for allergies. To do this, a small amount is applied to the back of the hand and the reaction is assessed after 20 minutes. If your hand itches and turns red, the ointment is not suitable.
Before using the drug, you need to cool the damaged part of the body. With this you can eliminate swelling and reduce the size of the hematoma. A cold compress should be applied for 15-20 minutes.
What happens next to the hematoma?
As soon as the hematoma has formed and increased in size, its growth stops .
It can greatly disturb the child, be accompanied by discomfort, pain and lead to severe nausea and even vomiting.
The condition of the hematoma does not change within one to two weeks. After this time, the hematoma begins to decrease in size and self-resorb .
At the same time, the patient's condition begins to improve noticeably. The child is less capricious, begins to eat better and falls asleep. Within 3-5 days, the hematoma resolves and completely disappears.
However, there are cases when the hematoma does not disappear . It retains its size. In this case, the help of a doctor is necessary. The hospital performs aspiration of the hematoma. The blood is carefully drained using two needles. This is a short procedure that immediately leads to the baby’s recovery.
How is brachydactyly inherited? Read about it here.
Pharmacy remedies for bruises for children
When choosing a suitable product, the age of the child must be taken into account. It is also worth checking the individual tolerance of the active ingredients of the ointment and making sure there is no allergy to them.
In order not to make a mistake when purchasing an ointment, you should determine the nature of the damage in advance. For example, to relieve swelling, you need to choose a warming agent, and to neutralize inflammation, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Troxevasin ointment
The active substance of the drug is troxerutin.
Advantageous characteristics include:
- strengthening blood vessels;
- restoration of capillaries;
- removal of decay products from the injured area.
In addition, the ointment is considered a good antioxidant. It can be used from six months of age.
Bruise-Off
The drug is based on medicinal leech, ethoxydiglycol and pentoxifylline.
The ointment acts on the damaged area in the following way:
- quickly relieves signs of hematoma;
- restores tissue;
- improves blood circulation;
- relieves swelling;
- moisturizes the skin.
The drug is allowed to be used by children over 6 months of age.
In addition to the indications, there are also contraindications:
- ointment is not used if the blood does not clot well;
- in case of an allergic reaction to one of the active ingredients.
Ointment Rescuer
The product contains natural substances, such as sea buckthorn and olive oil, ghee, calendula extract, beeswax, vitamins for skin restoration, essential oils of tea tree and lavender, and rose oil.
The ointment can be used for various skin injuries, be it an insect bite, burn or bruise.
The drug can be used at any age, provided there are no allergic reactions to individual substances included in the composition.
Heparin ointment
Under the influence of this drug, bruises and other skin damage heal faster.
The active ingredients of the ointment are benzocaine and nicotinic acid. They eliminate pain and dilate blood vessels.
The ointment can be used for therapeutic purposes from the age of 5.
Drug Dolobene
The product is also recommended for use by children over 5 years of age.
Due to the influence of active substances:
- swelling and inflammation are eliminated;
- decay products come out of damaged tissue;
- the injured area stops hurting.
Doctors do not recommend using the ointment if you have the following diagnoses:
- impaired renal and liver function;
- heart disease;
- asthma.
In addition, the product should not be used by pregnant and lactating women, or if there is damage to the integrity of the skin.
The drug can be prescribed to persons over 5 years of age.
Ointment Finalgon
The drug is allowed to be used to treat bruises in children over 12 years of age. Due to the active substances, an analgesic and relaxing effect is noted.
Finalgon helps well with arthritis, injuries, bruises, radiculitis, and ligament damage.
Why does a bruise take a long time to go away and how to speed up this process
Every person would like to know why a bruise does not go away for a long time? By bruise we usually mean a hematoma, that is, a spill of blood from damaged blood vessels into the surrounding tissue. If the hematoma is located close to the surface, in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, it is called a bruise. Damage to small blood vessels occurs as a result of impact, pressure, and compression of the skin. Depending on the individual location of the blood vessels, different people require different amounts of force to bruise.
How long does it take for a bruise to go away?
The protein hemoglobin, which is part of human blood, contains iron, and iron tends to oxidize and be reduced. This is what causes the difference in color between venous and arterial blood. The arterial one is brighter, scarlet, and the venous one is darker, burgundy. When a vessel is damaged, the bruise has a dark red, burgundy color, and after the restoration of oxyhemoglobin to hemoglobin it becomes violet-red. With normal tissue restoration, after five days hemoglobin breaks down into two components, methemoglobin and verdochromogen, which have a green tint. Verdocromogen breaks down into bilirubin and biliverdin, which gives the bruise a yellow color after about seven to ten days. It is because of these chemical reactions that bruises fade and change color depending on how old they are. Since the substances break down unevenly, the bruise may be multi-colored. The decay time of substances depends on many factors:
Normally, shallow damage to blood vessels should completely resolve within fifteen to twenty days, regardless of location. In most cases, bruises disappear within one to two weeks. An alarming sign is if the child has bruises
Source
Useful tips
Parents of traumatized children should consider the following recommendations:
- For children under one year old, the bruised area should be anointed with calendula or arnica oil. These agents prevent the process of swelling. They are quite affordable and can be bought at any pharmacy.
- If the bruise or sprain is serious, you should not try to treat the child with traditional medicine.
- It is worth using more effective synthetic or plant-based medications that provide excellent pain relief.
- If you are injured, more than just local treatment may be required. Sometimes you need to go to the hospital to prescribe anti-inflammatory and pain medications by mouth.
In any case, it is not recommended to select potent ointments and tablets on your own. Only a doctor can assess the situation and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Bruises (hematomas) are accumulations of blood located under the skin; they can appear with open or closed injuries and are accompanied by rupture of blood vessels. Organs and tissues bleed when damaged, and cavities with liquid or coagulated blood remain at the site of bruises. There is an extensive classification of bruises (hematomas) depending on their location, the condition of the blood vessels and blood. When a bruise (hematoma) occurs, pain is felt in the damaged area, the skin color changes and can turn from purple-red to greenish, swelling and an increase in temperature may appear at the site of the bruise. Internal hematomas can only be identified by a feeling of pain or tightness and with the help of diagnostic tools, such as tomography.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of hemorrhages manifest themselves to the greatest extent approximately on the third day after birth. By this time, the birth tumors usually subside, leaving a small lump.
Other symptoms of hematoma:
- Swelling. By pressing on this loose formation, you can feel the presence of liquid.
- Head asymmetry. The swelling acquires clear boundaries.
- Minor hemorrhages. They are small red dots located in the area of the pathological process.
- Blueness of the skin, which gives the child an unhealthy appearance.
- Pronounced pain when pressed.
General symptoms:
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- enlarged pupils;
- lethargy;
- poor appetite;
- Frequent regurgitation in newborns.
There are also more severe symptoms characteristic of intracranial hematomas:
- coma;
- convulsions;
- Sopor.
Only a doctor can diagnose hemorrhages. To make an accurate diagnosis you will need:
- Visual inspection. The doctor determines the clinical picture of the formation.
- Blood analysis. Shows platelet count and degree of clotting.
- Ultrasound. Necessary to determine the size, depth and location of the hematoma. A cerebral hernia can be detected.
- MRI or CT. This is an additional diagnostic method, which is prescribed depending on the location of the hematoma.
- X-ray examination. Allows you to determine the presence of bone damage.
- Electroencephalography.
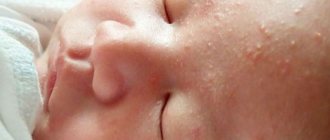
The main symptom is a visible lump on the skin that is red-blue in color. If the hematoma is located on the arms, legs or buttocks, no associated symptoms are observed. If a child’s hematoma forms on the head, then the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sleep disturbance.
- Frequent colic.
- Lack or decreased appetite.
- In some cases, strabismus may develop.
- The head size exceeds the norm.
- Cramps.
- Profuse regurgitation.
If we are talking about a hematoma on the body, it is noticeable visually, in which case no diagnostics are required. If the doctor suspects an intracranial hematoma, the child is prescribed an ultrasound examination, and in some cases magnetic resonance imaging may be needed. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor determines whether treatment is necessary.
The head of a child with a formed hematoma looks asymmetrical, and the boundaries of the formation itself are always clearly defined. The lump is soft to the touch, easily dented, and an accumulation of liquid is clearly felt inside. There are small red pinpoint hemorrhages on the surface of the skin in the area of the hematoma. Gradually the skin color becomes bluish.
At this time, the child looks lethargic and sick, and often cries. Pressing on a hematoma in a newborn clearly causes him pain. These babies have increased sleepiness. The decision about the need for an examination is made by the doctor; it is carried out in a hospital setting.
We invite you to read: Vision of a newborn up to 1 year: norm and pathology - Articles
The doctor conducts an external examination, prescribes a blood test, ultrasound examination and x-rays. These methods make it possible to determine the exact size and depth of the hematoma that has arisen, and the presence of possible damage to the bones of the skull.
Diseases by symptoms
Any symptom is a signal from the body that any organ, department or entire system is damaged. To find out why bruises occur in a newborn, you need to rule out certain diseases. Make sure that your baby undergoes timely diagnosis, find out why the bruises appeared, and how to quickly and effectively improve the condition.
List of diseases that cause bruises:
- Bruises, blows;
- Blood diseases;
- Platelet dysfunction;
- Bacterial infection;
- Allergy;
- Anemia;
- Hemophilia;
- Infectious diseases;
- Diathesis;
- Lack of vitamins.
At birth, small hematomas resulting from childbirth may remain on the baby’s face and body. They usually do not require treatment and go away on their own within one year. If your baby's bruises appear for no apparent reason or are located in unusual places, and you notice drops of blood in the diaper, contact your pediatrician immediately. If at the same time the infant’s temperature rises, he is restless or, on the contrary, very lethargic and sleeps a lot, then call an ambulance.
Types of formations
There are 2 types of hematomas that can form after childbirth in a newborn:
- Cephalohematoma is a blood clot between the cranial bone and the periosteum, a thin plate covering the bone.
- Brain hematoma in newborns is a rarer and more severe complication of childbirth: an intracerebral hematoma can be extensive or localized to a small focus in any part of the brain;
- epidural hematoma is diagnosed when hemorrhage occurs in the cavity between the bones of the skull and the lining of the brain due to injury;
- subdural hematoma occurs due to damage to the vessels between the dura cerebral and arachnoid membranes.
- Cephalohematoma is a blood clot between the cranial bone and the periosteum, a thin plate covering the bone.
- Brain hematoma in newborns is a rarer and more severe complication of childbirth: an intracerebral hematoma can be extensive or localized to a small focus in any part of the brain;
- epidural hematoma is diagnosed when hemorrhage occurs in the cavity between the bones of the skull and the lining of the brain due to injury;
- subdural hematoma occurs due to damage to the vessels between the dura cerebral and arachnoid membranes.
Treatment and specialists
Only a qualified specialist should treat bruises in a newborn. Only a doctor can tell you how to treat bruises, how to get rid of complications from bruises and prevent their occurrence. The following doctors can answer the question of what to do if your baby has bruises.
Specialists to contact if bruises occur:
First of all, if bruises of unknown origin occur on the baby’s body, you should contact a pediatrician. In order to determine the cause of the disease, you will first need a blood test, which will show whether blood clotting (platelet function) is impaired. Since the baby's skin is very thin, and the capillaries are located very close to the surface, bruises can remain on it even after slight pressure, but they also pass quickly and without leaving a trace.
The appearance of a child's skin is one of the indicators of his health. Most newborn babies have pimples on their skin, and some have bruises. The reasons for their occurrence lie in the changes that occur with skin pigments immediately after birth. They will disappear within a few weeks.
Bruises on a child's legs
Bruises in children are common. Childhood is impossible without bruises and falls. But sometimes hematomas appear spontaneously and are not at all associated with external damage. Problems with platelets, and, consequently, with blood clotting, can be determined even on the basis of a detailed clinical blood test. As in an adult, another cause of bruises can be a lack of vitamins. Therefore, you need to adjust the baby’s nutrition. If, along with them, the child’s general condition worsens, you should immediately go to the doctor.
How does a bruise form?
Why does a bruise (hematoma) form? The process of its formation starts at the moment of rupture of the walls of the subcutaneous capillaries. The blood from them enters the surrounding tissues, and the affected area becomes purplish-red.
Over time, many leukocytes arrive at the site of damage. Their task is to destroy red blood cells trapped in tissues. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, the breakdown of which produces two pigments - green (biliverdin) and yellow (bilirubin). Mixing the colors of all these substances provokes a gradual change in the shade of the bruise: from red to purple, then to blue, then to yellow-green and yellow. In the end, all pigments are absorbed by the liver and excreted from the body, and the hematoma disappears.
The period during which the bruise goes away depends on the extent of the damage to the capillaries and the area: tissue on the head is restored in about 7 days, and on the legs this process can take about a month.
The main reasons why hematomas appear on the head and body in children are injuries and bruises.
What does it look like and where is it located?
Externally, the injury does not look like a bruise , the color of the skin on the affected area does not change.
Only upon closer examination are pinpoint hemorrhages noticeable.
In appearance it is a small ball that rolls slightly when pressed. This occurs due to fluid accumulated inside.
Fluid does not accumulate inside immediately, but gradually, as the child has a blood clotting deficiency. Over the course of two to three days, the hematoma increases in size. Its decline is observed on the 7-10th day of the baby’s life .
The hematoma completely resolves by 3-8 weeks of life.
The hematoma is located on only one cranial bone. It can be localized on the crown, back of the head, front and side of the head. Usually it is noticeable on the top of the head , or a little lower, at the back of the head.
Soft tissue injuries
Increased motor activity and imperfect coordination lead to children often falling and hitting surrounding objects. This problem is especially relevant for babies who are just learning to walk. They do not yet understand that at the moment of falling they need to put their hands up, and in most cases the bruises occur on the head. As a result, painful bruises, bumps, swelling and bruises form on the forehead.
To prevent the appearance of a hematoma on the head or body, a cold compress must be immediately applied to the injured area. The best option is ice wrapped in several layers of fabric. Thanks to this, the vessels will narrow and blood will not be released from them. If a bruise has already formed, it is recommended to use a special ointment.
Causes
In late pregnancy, the fetus assumes a cephalic presentation. In the second stage of labor, it moves head first along the birth canal. The skull is subjected to severe compression, but under normal conditions it does not deform. The following reasons contribute to the appearance of hematomas in infants:
- severe compression of the fetal skull by the mother’s pelvic bones (complications during and after childbirth often occur in women with a narrow pelvis);
- surgical delivery (at birth by cesarean section, the child’s body suffers from the consequences of a sharp change in external pressure);
- prematurity (the blood vessels of a child born prematurely are characterized by increased fragility);
- large fetal body weight;
- abnormal course of labor (hematoma can occur with premature rupture of amniotic fluid and absence of contractions);
- protracted or rapid labor (can contribute to injury to the blood vessels of the baby’s head during its passage through the birth canal).
Important information: Instructions for use of ointment (cream) Express Bruise
Remedies for bruises
There are many drugs that help resolve bruises. The most popular of them:
- Gel "Troxevasin". The active ingredient is troxerutin, which strengthens the walls of blood vessels. It should not be applied to open wounds. The ointment should be rubbed into the affected areas twice a day.
- Gel “Bruise-OFF”. Active ingredients: leech extract and pentoxifylline. They accelerate the dissolution of blood clots and prevent their formation. Apply the product to the bruise about 5 times a day.
- Ointment-balm “Rescuer”. Ingredients: essential oils, sea buckthorn oil, vitamins, beeswax. The drug helps in resolving bruises and healing abrasions. Requires application several times a day as it absorbs. It is better to cover the ointment with a bandage on top.
Theoretically, ointments for bruises can be used from any age, but before treating bruises on the body of newborn babies, you must always consult a doctor.
The average period of use of gels is 5-7 days. During this period, the hematoma should either disappear or become inconspicuous.
Dangerous symptoms
With a strong blow, a bruise in a baby is an external manifestation of serious internal injuries. Dangerous places for bruising are the back of the head and temples, as well as the stomach. For newborns, trauma of any location can lead to health problems, especially if they fall from a height.
For bruises and bumps on the head, forehead (possibility of concussion):
- nausea, vomiting
- headache
- pale skin
- breathing problems
- squint and so on
With a hematoma on the bridge of the nose (risk of nasal fracture):
- darkening of the skin under the eyes
- changing the shape of the nose
In case of abdominal injury (risk of damage to internal organs):
- strong pain
- pale skin
- dry mouth and thirst
- lowering blood pressure
If the limbs are damaged (risk of fracture), pain when moving.
Regardless of the location of the injury (risk of infection):
- increase in body temperature some time after the injury
- severe swelling and hyperthermia of the skin in the affected area
In these situations, you should not use ointment or other remedies for bruises; it is important to get the baby to the hospital as soon as possible.
How is it different from a birth tumor?
Hematoma is very often confused with a birth tumor. In fact, these two phenomena differ in certain ways. The main differences are :
- The hematoma is located on one cranial bone, and the tumor is localized on several at once.
- The tumor can simultaneously be localized not only on the head, but also on the thigh and buttock. A hematoma occurs in only one place.
- The tumor formation is very dense, the liquid does not flow when pressed, which is typical of a hematoma.
- The tumor is not accompanied by hemorrhage, so it resolves much faster. The hematoma lasts longer.
Bruises under the eyes
Bruises under the eyes of infants can appear as a result of a blow to the bridge of the nose. Why do blue shadows sometimes “decorate” a baby’s face without previous bruises? Main physiological reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. The characteristics of the skin under the eyes are inherited - a thin epidermis and a large number of capillaries. If one of the parents has the same problem, then it will not be possible to remove the bruises. It is strictly forbidden to apply regular ointment against hematomas to the area under the eyes.
- Overwork and lack of sleep. Teething, increased nervous excitability, improper daily routine - all these factors lead to the baby being too tired and not getting enough sleep, as a result the skin under his eyes becomes darker. The weakening of the body after illness can aggravate the situation. E.O. Komarovsky advises solving this problem by normalizing the schedule and taking long walks in the fresh air.
Pathological causes of blue under the eyes in children under one year of age:
- Poor nutrition. Insufficient caloric content of the diet, the presence of foods with chemical components and a lack of basic vitamins cause disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. It is important to monitor the baby’s nutrition: up to 6 months, he should receive the required amount of breast milk or formula, then cereals, vegetables, fruits, meat and other products should be gradually introduced into the menu.
- Anemia is a decrease in hemoglobin levels as a result of iron deficiency. Another sign of pathology is pale skin. Diagnosed based on a blood test. Anemia in newborns and infants must be treated by normalizing the diet and/or iron supplements.
- Worms. Due to the fact that there are parasites in the intestines, the process of absorption of nutrients by its mucous membrane is disrupted. Other symptoms are decreased immunity, rash on the body, itching near the anus. Worms are detected using stool analysis. Therapy is carried out with antiparasitic drugs.
- Foci of chronic infection in the body (tonsillitis, carious teeth). These reasons are relevant for children over one year old. Bacterial waste products enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body. Since the skin under the eyes is very thin, changes in the capillaries become noticeable very quickly. These diseases must be treated under the supervision of a doctor.
Birth injuries: hematoma in a newborn
One of the most common birth injuries is hematoma in newborns. Experts usually associate the appearance of a hematoma with the difficulty of the child passing through the birth canal and the associated overloads.
The birth of a baby is a whole event in any happy family. First of all, a young mother experiences a special range of different experiences and emotions. Perhaps everything related to pregnancy and childbirth are the most striking events in her life.
However, although at the moment when the first cry of her baby is heard, she is overwhelmed by a powerful wave of enormous love for this new person who was born thanks to her, she also remembers the difficulties that she had to go through for this. Many hours of childbirth, contractions, pushing - all this is very energy-consuming for the female body. However, as soon as she sees her little blood, these impressions will dull, and her fatigue, thanks to the surging hormones, will pass almost instantly. However, her memory will not completely erase those experiences.
It is worth noting that a lot is always said about women’s impressions of childbirth: what pain it is and what effort it costs. In addition, a woman in labor usually has someone to support her: there are doctors and midwives around her, and sometimes even loved ones (for example, her loved one, the father of her baby).
At the same time, almost no one thinks about something else: what the second main character of the events, the baby, is experiencing at this time. Passing through the birth canal is a road designed by nature itself. Moreover, such experiences are necessary for a child like air: they have a certain impact on the formation of him as a personality, including such a quality as the ability to overcome difficulties even in the most difficult and almost hopeless situations. Perinatal psychologists have written entire volumes of scientific essays on this topic.
On the other hand, everything that happens during childbirth is perhaps the first real stress in the baby’s life. The womb, in which he was warm and comfortable for nine whole months and where everything was given to him even before he had time to feel the need for it, suddenly begins to stubbornly “drive” him out. However, he does not move towards the exit very quickly: he has to wait until the cervical tissues become more pliable and part, letting him through and bringing closer the moment of his meeting with the closest people in the world.
It should be said that the road was not easy for the baby. It is extremely narrow - there is only room in it for him to barely squeeze through. To successfully complete this task, the baby has some protective mechanisms. One of them is elastic seams and fontanels of the skull, allowing the widest part of his body - the head - to fold at the right moment to quickly overcome the birth canal in its most difficult part - the pelvic bones.
Sometimes, when something in the birth process deviates from the “standard” scenario, the protection may not work as expected. Because of this, birth trauma occurs - not uncommon even with the modern level of development of medicine. Quite often there is such a variant as a hematoma in a newborn.
When a woman, immediately after giving birth, is given her son or daughter in her arms for the first time with the words: “Well, who was born to you there? “- she is usually in a euphoric state, and therefore her baby seems to her simply an ideal of beauty and perfection. This is the origin of the so-called unconditional love, which, according to experts on human souls, can only be experienced by a mother for her child, adoring him simply because he exists in the world and paints her existence in the brightest colors.
Meanwhile, when the woman in labor still manages to examine her little native “lump,” she notices all the “mistakes” that look very frightening. However, even in the absence of treatment, within literally a day or two, the swelling in this area subsides, and the body tissues acquire a more or less normal appearance.
Experts attribute the appearance of a hematoma precisely to the overloads that the baby has to endure as it passes through the birth canal. Because of this, in that part of the body (in most cases, the head) with which it “paved the way” to the outside world, stagnation of fluids occurs: blood and lymph, followed by swelling. Another cause of hematoma is the difference between the air pressure inside the mother’s organs and outside. The result is a violation of the integrity of the walls of small vessels (which simply burst) and hemorrhage. In addition, similar birth injuries also occur in children born before their due date.
Although already within the first week, a maximum of ten days, there is usually no trace left of the hematoma, there are also more complex cases. Fortunately, this happens quite rarely and is primarily due to not very good heredity.
So, some children are extremely prone to bleeding. In addition to genetic factors, this also happens for other reasons: due to a serious lack of a number of vitamins and other nutrients necessary for normal blood clotting.
In this situation, the hematoma located under the skin will not disappear, but on the contrary, it will only grow in volume. In this case, correctly prescribed treatment is the only salvation. Typically, a child with a similar problem is given injections with substances that have the property of stopping bleeding, for example, calcium chloride. If you neglect the doctor’s prescriptions, then you can wait for suppuration to begin at the site of the hematoma, and this is already fraught with a fair number of complications.
One of the most effective medicines in this case is breast milk. For example, the immunoglobulins included in its composition will help not only the speedy healing of wounds, but will also help ensure that birth injuries do not have consequences for the health of the baby.
The doctor will definitely pay attention to which tissues are involved in the hematoma. In a standard situation, several cranial bones are located in this area of the head, and the sutures between them become slightly invisible due to the tumor.
However, in about one or two out of a hundred newly born children, another injury is hidden under such swelling - a cephalohematoma. This type of generic tumor appears in only one bone - and blood accumulates under its periosteum. If you press your finger on this place, you will feel as if waves are scattering across the water surface.
It happens that, hidden behind another, more extensive tumor, cephalohematomas become visible only a couple of days after the birth of the baby. If very little blood has accumulated in them, then within seven to ten days it will be noticeable how the swelling gradually subsides. By the age of one month, the baby will not have a trace of such a hematoma.
Medical intervention is required only in those situations when there is a fair amount of blood in such a tumor. Here there is a danger that this fluid will be absorbed into neighboring tissues and supply the body with additional bilirubin, which is why the newborn will develop “long-lasting” jaundice. In addition, cephalohematoma can degenerate into hardening, as a result of which the bone grows and cranial deformation occurs.
To prevent such consequences, tumor puncture is usually performed.
In short, if you follow all the recommendations of an experienced doctor, there will be no threat to the life and full development of the child. When all such worries are over, the new family member will again begin to bring only joy.