Flu shot when planning pregnancy
Medical portal
- Allergy
- Infertility
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Blood diseases
- Diseases of the esophagus
- Kidney diseases
- Back diseases
- Thyroid diseases
- Bronchitis
- Vaccines
- Haemorrhoids
- Gynecological
- Hypertension
- Fungus
- Hernias
- Children's
- Diabetes
- beauty
- Migraine
- Operations
- Edema
- Poisoning
- Pancreatitis
- Parasites
- Weight loss
- Respiratory
- Injuries
- Urological
- Herpes
Photo
Video
If a woman is preparing for pregnancy during an impending flu epidemic, it is advisable to get vaccinated in advance to avoid possible health risks. When planning, vaccination is completely safe, so doctors recommend expectant mothers to resort to this preventive measure. Even if conception has taken place, it is better to get vaccinated than to risk suffering from possible complications of the flu (premature birth, miscarriage, developmental defects in the child, exacerbations of chronic diseases in the mother, etc.), although administering the vaccine is also not entirely safe for the fetus and may contraindicated for individual reasons.
That is why vaccination before pregnancy should be included in the list of health measures along with taking vitamins, a balanced diet, giving up bad habits and treating chronic infections and inflammation.
Why get vaccinated before pregnancy?
Getting a flu shot before pregnancy has several benefits:
- the woman’s immunity is normal (during pregnancy it is necessarily reduced so that the body does not reject the embryo with half-alien genetic information), so the vaccination will be easier to tolerate and antibodies will appear faster;
- vaccination is recommended a month before pregnancy, so that antibodies to the virus are guaranteed to be developed in the blood (usually this process is carried out 2 weeks before);
- Naturally, vaccination is relevant before the outbreak of an epidemic, and not at its height;
- if you give an injection of serum after conception, when the protective properties are weakened and the infection is raging, the risk that antibodies will not have time to form and the woman will still become infected is very high;
- the flu vaccine is not given in the first trimester - only in the 2nd or 3rd, so the expectant mother runs the risk of becoming infected precisely in the early stages, when it is most dangerous for the fetus;
- Not any vaccine is suitable for pregnant women, but only inactivated ones;
- During pregnancy, the mortality rate from influenza is high - up to 30%.
Immunization is the most effective way to protect yourself from viruses, but not 100%, so the decision is up to you.
Which vaccines are best to get vaccinated?
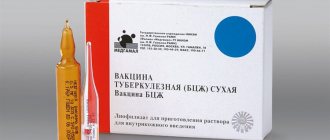
There are only two drug options: live vaccines (with weakened pathogens) and inactivated drugs. The virus is killed in them. The last option is the most preferable when planning pregnancy. All modern anti-influenza drugs contain dead microbes.
Such vaccines contain surface antigens of various viral strains. Moreover, every year the composition of the drugs changes (that is, a new vaccine is created). It all depends on which strain is expected to circulate this season.
The reason for the constant updating of anti-influenza drugs is that the influenza virus is constantly changing. Therefore, doctors have not yet been able to develop a “preemptive” vaccine.
Today, the flu vaccine market is represented by the following drugs:
- Influvac and Grippol;
- Fluarix and Agrippal.
And also Vaxigrip and Begrivak. After vaccination, the body begins to induce specific immunity to those influenza viruses whose strains are included in the composition of this drug. After 8-12 days, immunoprotection is completely formed and lasts up to 12 months.
Influenza vaccine Influvac
Many vaccines also contain immunomodulatory components that strengthen immunity to infection. Influenza vaccination at the PB stage is given once. At the time of the procedure, the woman must be healthy.
If there are signs of ARI (even cough and runny nose), as well as with exacerbation of chronic diseases, vaccination is postponed. The woman should make a full recovery. The injection is given intramuscularly with a dose of 0.5 ml (in the shoulder). After which you should remain under medical supervision for another 30 minutes.
It is important to understand that any flu vaccine does not guarantee 100% protection against infection. But even if you get sick, the infection will be easy, with “erased” symptoms.
How to get vaccinated?
Expert opinion
Lobzeva Diana Andreevna Obstetrician-gynecologist-reproductologist. Member of the Russian Association of Human Reproduction (RAHR).
The best time to get a flu shot is one month before conception. Please note that vaccines must be adapted to the current strain of the virus. Updated antigen composition is usually available in September–November
Before getting vaccinated before pregnancy, find out whether this procedure will harm you, get tested to rule out contraindications. It is necessary to determine whether there are immunoglobulins G and M in the blood - proteins that store data on contact with specific strains.
Information about the influenza virus is valid only for 12 months from the date of illness or vaccination. Then the immune system needs to be “reminded” of the need to produce antibodies. Because the flu virus is constantly evolving, last year's vaccinations will likely not be effective in the new season.
If there are class G immunoglobulins in the blood, then there is no need to get vaccinated - the body “remembers” about the infection. If immunoglobulins M are detected, vaccination is contraindicated for another reason - the person is already infected and the process is in an acute stage. If there are no antibodies in the blood, vaccination before conception will help avoid infection.
Should I get a measles vaccination or not when planning a pregnancy?
The need for specific vaccine prophylaxis at the stage of pregnancy planning is due to the peculiarity of the state of the woman’s immune system after conception.
To prevent the fetus from being recognized as a foreign agent that should be rejected and expelled from the body, the immune system has to significantly limit its activity. Against the backdrop of a decrease in general protective forces, a woman is especially susceptible to attacks from infections; diseases of a pregnant woman ricochet to the fetus.
If a woman has previously had measles or has completed a full course of measles vaccination in childhood, her body has specific immunity against this disease. To decide whether a measles vaccination is needed in preparation for conception, it is recommended to take a blood test for serological tests.
In a laboratory study, a quantitative indicator of specific proteins - class G immunoglobulins is determined. These antibodies are formed in the bloodstream during illness or vaccination and remain for life after recovery or a course of immunization.
Physiological indicators G have reference values that the doctor is guided by when interpreting the results:
- the presence of class G antibodies in the blood in sufficient quantities indicates that the woman has already had measles or was vaccinated in childhood and is protected by high specific immunity to this disease. In this case, measles vaccination is not necessary;
- the level of immunoglobulin G below acceptable values indicates low activity of measles immunity. A woman at the stage of pregnancy planning may require a single booster vaccination to stimulate it;
- the absence of G antibodies indicates that specific immunity to measles has not been formed in the body. In this case, during the period of preparation for pregnancy, it is considered advisable to carry out a two-stage vaccination against measles with a month interval between vaccinations.
Maternal immunoglobulins G penetrate intraplacentally into the blood of the fetus and remain in its vascular bed after birth. These antibodies create passive measles immunity, which protects the baby during the first year of life and then fades away.
Types of vaccines
There are 4 main influenza vaccines in the Russian Federation:
- "Influvir"
- "Pandeflu"
- "Monogrippol"
- "Monogrippol neo" (consists of fragments of the killed virus).
“Influvir” is a live vaccine, administered intranasally, “Monogrippol neo” is an inactivated serum for intramuscular injections. It is suitable for patients with allergies to chicken eggs.
If you haven’t had time to get the seasonal vaccination, your doctor may recommend Grippol a month before conception. During pregnancy, children's "Grippol plus" or "Monogrippol neo" is recommended.
There are other types of vaccines. Thus, doctors recommend high-quality, expensive vaccinations, for example, Ultrix.
The vaccine is contraindicated for some women. In this case, persuade relatives living nearby to get vaccinated before planning a child.
In addition to the seasonal flu vaccine, it is advisable to get vaccinated against swine flu with an interval of 3 to 4 weeks.
Application diagram
The flu vaccine at the stage of pregnancy planning is given once in the autumn-winter period. At the time of vaccination, the woman must be absolutely healthy. If signs of acute infection or exacerbation of chronic diseases appear, vaccination should be postponed until complete recovery.
The drug is administered intramuscularly in a dose of 0.5 ml into the upper third of the shoulder. After vaccination, the woman should be under the supervision of a nurse for 30 minutes.
During vaccination, the following adverse reactions may occur:
- pain and swelling at the injection site;
- slight increase in body temperature, weakness;
- mild runny nose and headache;
- muscle pain;
- allergic reaction.
If any side effects occur, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Contraindications to vaccination:
- signs of acute infection at the time of vaccination;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- allergic reaction to the previous administration of the drug;
- allergy to chicken protein.
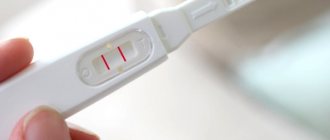
If you suspect pregnancy, you must donate blood for hCG before vaccination. If the test result is positive, vaccination should be postponed. You should consult your doctor about the possibility of vaccination during pregnancy.
How to vaccinate during pregnancy
Flu in the first 24 weeks of pregnancy often leads to miscarriage, but vaccination can only be done at a later date. Domestic medicine is against vaccination before the 12th week, since the vaccines available in the Russian Federation in the early stages have a detrimental effect on the development of the fetal nervous system and can cause enormous harm at this time. Vaccination is practiced abroad in any trimester, since special safe anti-influenza serums have been developed there.
Do not be afraid to get vaccinated in the 2nd and 3rd trimester - the vaccine will benefit both mother and child. The killed virus contained in it is not capable of causing harm to the body. On the contrary, after vaccination during the gestation period, both mother and baby will develop immunity for as long as 12 months, which is very important at first, when the newborn cannot be vaccinated.
Early pregnancy after measles vaccination: possible risks to the fetus
There have been no special studies of early (relative to measles vaccination) pregnancy. However, theoretically, the possibility of intraplacental infection of the fetus with the measles virus cannot be excluded, as a result of which abnormalities in its development or spontaneous termination of pregnancy may occur.
Assumptions, conclusions and recommendations were developed based on clinical observations of women who had measles during pregnancy.
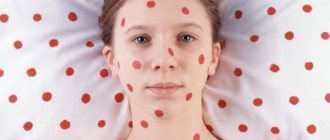
An encounter with the measles virus in the early stages of pregnancy leads to congenital pathologies of the fetus and spontaneous abortion in twenty percent of cases. The most common complication - dementia (mental retardation) - is not diagnosed by ultrasound, so it is not possible to determine during the gestational period whether a pregnant woman falls into this 20% group.
The measles virus infects cells of the nervous tissue, and fetal developmental abnormalities primarily affect the functioning of the nervous system and brain. The most dangerous complication is viral meningoencephalitis, the mortality rate of which, according to WHO estimates, reaches forty percent.
The causative agent of measles, which affects a pregnant woman in the early stages, can provoke the development of other complications in the child:
- pneumonia;
- hydrocephalus;
- stomatitis;
- anomalies of the upper or lower extremities;
- deafness;
- blindness;
- cardiac failure.
In Russia, like most developed countries, there are no official recommendations on abortion due to vaccinations.
However, some doctors, in order to prevent complications from the measles vaccination when an early (before three months after vaccination) pregnancy occurs, recommend terminating it.
Women who wish to keep the child are prescribed additional examination:
- blood test for serological test (presence of antibodies to the causative agent of measles);
- screening - ultrasound diagnostics and biochemical blood testing, which is repeated three times during the gestation period.
The results of observations of women who became pregnant before the expiration of the three-month period after measles vaccination, described in medical publications, are encouraging: most of them gave birth to healthy babies on time.
Consequences of influenza infection during pregnancy
Flu during pregnancy is very dangerous for both the expectant mother and her child, especially in the 1st trimester. Influenza is characterized by intoxication of the entire body, and through the blood, toxins penetrate the placenta and affect the fetus. In the first 12 weeks, organs are formed and the nervous system is formed. High temperature at this time is fraught with the appearance of seizures, encephalopathy, cerebral palsy, and damage to the placenta in the embryo. Developmental delay, premature birth and even fetal death are possible. If the prognosis is unfavorable, doctors recommend an abortion.
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, the risks are much lower, but they still exist.
There also remains a danger to the health and life of the expectant mother, whose immune system is weakened. She is more likely than other patients to suffer from post-influenza complications such as inflammation of the lungs, middle ear, and brain. The likelihood of death increases if not treated correctly. In addition, it is more difficult for pregnant women to select safe and effective drugs against the virus, because strong drugs can harm the baby. In view of all these nuances, it is better to get vaccinated before pregnancy.
How soon can you get pregnant after vaccination?
Before planning a pregnancy, a woman should do a blood test to detect antibodies to the disease.
In their absence, vaccination is mandatory. Since the body develops immunity within three months, it is recommended to plan to become pregnant after vaccination no earlier than 120 days later.
After the last vaccination, experts recommend using contraception for 3 months to prevent abortion.
In an unplanned pregnancy, if infection occurs in the first two trimesters, the child may be born with abnormalities . To prevent complications, termination of pregnancy is recommended in most cases. However, compared to other infectious diseases, measles is not a categorical indication for abortion.
Such a measure is resorted to only after a thorough examination of the patient has been carried out and all possible risks have been weighed.
When the expectant mother falls ill at 16 weeks, the prognosis is less frightening. After all, it is by this period that the placenta is fully formed, thereby protecting the fetus from the negative effects of the measles virus.
In the last stages of pregnancy, the risk of complications increases again, which does not exclude premature birth or infection of the baby during passage through the birth canal.
In addition, encephalitis or pneumonia may begin to develop. In this case, the mother and child are isolated in a separate room. The baby is exclusively breastfed, which allows him to receive the necessary amount of antibodies from his mother.
Reviews
On forums dedicated to motherhood, you can find positive reviews about influenza vaccination, advice from women who have successfully given birth, who were vaccinated during pregnancy, and those who managed to get vaccinated before conception. There are many reviews from those who are categorically against vaccination, considering it useless against constantly mutating strains of the virus. There are also reviews from women who have experienced side effects from vaccines and therefore do not advise other expectant mothers to get vaccinated.
Comparing the information, you can come to the conclusion that it is better to get vaccinated and not go through the entire pregnancy than to constantly live in anxiety for fear of contracting the flu. Of course, there are reviews online of mothers who have had the flu while pregnant without any consequences, but you shouldn’t risk repeating their experience.
On forums, patients share not only their experiences, but also specific information about new types of vaccines that gynecologists advise them at appointments, their pros and cons, as well as possible side effects. Based on what you have read, you can prepare to discuss this issue with your gynecologist and decide for yourself whether or not to vaccinate.
Contraindications and adverse reactions to vaccination
Most often, the flu vaccine does not cause negative side effects, but sometimes they can occur.
The following adverse reactions are generally possible after vaccination: What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- headache;
- swelling and redness may form at the injection site;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- in rare cases, a fever may occur.
Also, the flu vaccine has several contraindications, and not every woman will be able to get vaccinated when preparing for pregnancy. This category includes people:
- with allergies to chicken eggs and antibiotics;
- with fever;
- with an infection in the body.
In the midst of an epidemic, you cannot get vaccinated.
To avoid the negative consequences that the influenza vaccine can cause, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Only a healthy person can be vaccinated after suffering a virus or infection - no earlier than two weeks later.
- If you feel unwell on the day of vaccination, you should reschedule the procedure.
- A couple of days before vaccination, you should not try new foods or cosmetics to avoid allergies.
- If a woman has vaccine anxiety, she can find out if she needs the vaccine. To do this, you need to take a blood test for immunoglobulins G and M. If the test reveals the presence of class G, then there is no need to be vaccinated, because the body is ready to fight the disease on its own. The presence of class M means that vaccination is contraindicated because the person is already infected and is in the acute stage of the process.
- If no antibodies are detected, you can and should get vaccinated.
Do not be afraid of the consequences of vaccination if it is indicated for you, because complications from an illness during pregnancy can have a much stronger impact on the health of the unborn child, as well as negatively affect the mother’s body.