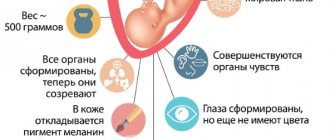
Hello, expectant mothers. You are all looking forward to the first movements of the baby during pregnancy, because from this moment the woman begins to feel her baby in the literal sense. And now you will have to control the number of movements, because they indicate the normal or pathological development of the baby.
In today’s article I will tell you at what time the first movements begin, why sometimes they weaken or, on the contrary, become more frequent, and when you need to worry. Interesting? Then let's go!
In general, the beginning of movement in the mother’s tummy occurs at 7-8 weeks
, but so far the baby is so small that the woman simply cannot feel these movements. Starting from the 10th week, the baby moves more consciously.
By 17 weeks
The baby begins to react to light, bright flashes, sharp sounds and other external stimuli.
This reaction is expressed in the form of movements. Clenching/unclenching fingers, fingering the umbilical cord, touching the face, begin at 18-19 weeks
. But when do you start to feel these moments?
Doctors have identified the average period during the first pregnancy, from which a woman begins to feel her baby - from the 20th week
.
During the second or subsequent pregnancy - at 18 weeks
. With my first daughter, I felt the first movements at 22 weeks, and with my second daughter, at 20 weeks. It seems to me that during the third pregnancy everything would be felt earlier.
So, all these data are average, because every woman’s body is individual
. For example, slender ladies begin to feel the baby earlier than women “in the body”. It has also been proven that if your placenta is located in front of the uterus (on the front wall), then you will feel movements a little later.
How to understand movements?
Imagine the feeling of being pushed from within or some kind of vibration occurring (again, from within). Some people confuse the baby's movements with churning in the stomach. The longer the period, the more distinct the pushing becomes.
You can feel the first movements from 16-24 weeks of pregnancy. You must remember this moment (how can you not remember it) and tell your gynecologist about it. The doctor will record this information on your exchange card.
More experienced mothers can already determine by the kicks how the baby is positioned. If the tremors are felt in the lower abdomen, then the baby is head up, and if you feel movements in the diaphragm, then the baby is head down.
Normal movements during pregnancy
The baby in the womb is constantly in motion until he sleeps. It has been proven that at 20-21 weeks the baby makes up to 200 movements within one day
. In the period from 26 to 32 weeks, the total number of movements increases to 600, and after that the activity decreases, since the baby is already too big and it is difficult for him to toss and turn and move in his mother’s tummy.
Many factors directly influence motor activity. Now I will list them:
- Mommy's nutrition
. If she is hungry, the baby will move more actively. That's right, he also wants to eat! If you eat, you will also feel that the baby has become more active. This especially happens after eating your favorite sweets, thanks to which the baby receives a portion of energy and thus gets rid of it. - Times of Day
. At night and in the evening, the baby moves more actively. Therefore, many mothers cannot sleep for a long time, especially in later stages... Believe me, I sometimes thought that they were playing football in my stomach. - Physical exercise
. Usually, when doing household chores or any physical activity, the baby moves little. But as soon as the mother sits down to rest, the movements become stronger and more frequent. Well, that means when your baby is born, he will become just as active. - Emotional state of a woman
. If the mother begins to worry, to be afraid of something, then the baby will either calm down or begin to move very actively. I remember, as soon as I started to get nervous, my stomach was shaking. This was a hint to me - stop worrying. - Mother's pose
. If the mother is in an uncomfortable position for a long time, the baby will react to this with painful and strong movements. This can happen when lying on your back for a long time, which causes the uterine vessels to be compressed and less blood flows to the baby. - Ambient sounds
. Often, in response to sharp loud sounds, the baby calms down, or, on the contrary, begins to move actively.
Many mothers are very worried if the child stops moving for 3-4 hours. Well, understand, he also wants to sleep and at this time this is exactly what he does. During wakefulness, about 15 thrusts occur per hour.
Method of counting fetal movements
The baby's movements indicate his successful development. If they are too strong, painful, or, on the contrary, weak, then this is not a good sign. This may be caused by chronic or acute hypoxia
.
Also, if movements become painful or strong, then you may have oligohydramnios.
, while
polyhydramnios
is accompanied by weak motor activity.
There are several methods by which you can determine the baby’s motor activity:
- Sadowski method;
- Pearson method;
- Cardiff method.
Now I will describe them in more detail.
Sadowski method
You need to count the baby's movements in the evening from 19 to 23 hours. This period is due to the fact that you have dinner, after which you rest, and it is precisely as a result of this that the activity of the baby increases.
Write down the time when you started counting, lie down on your left side and start counting. feel 10 or more movements within an hour
, then you can stop counting. If the number of movements is less than 10, then continue your observations.
A slowdown in movements for two hours (if there are less than ten of them in 2 hours) is not a good diagnostic sign. In this case, it is worth undergoing additional ultrasound diagnostics, CTG or Doppler testing.
Pearson method
This method involves counting hair movements from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. You will have to spend all this time in a calm mode, since excessive body movements will reduce the activity of the fetus.
Record the start of the count and watch every movement
. Once you count 10 movements, look at your chart. If less than an hour passed between the first and tenth movement, then everything is fine with you. If more than an hour has passed and there are still no ten movements, then provoke your child to make them.
Lie on your back, eat something sweet, go up the stairs and continue counting. If the baby behaves actively, then everything is fine. But when rare movements continue throughout the day, you need to tell the doctor about it.
Cardiff method
Here, too, 12 hours is taken as a basis, only the expectant mother can choose the time herself. As a result, 10 movements should occur during this time. If you count less in 12 hours, consult a doctor.
If you notice that for 6 hours you have no movements at all, or the activity is too small, then this is already a formidable indicator
. Maybe the baby is suffering from a lack of oxygen. In this case, call your doctor immediately.
To determine if everything is okay with the baby, the doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat using a stethoscope. Normally, the heart beats 120-160 beats per minute (stronger in girls, weaker in boys). Even if everything is normal, it is better to insist on a CTG - a procedure that will show whether the child is suffering from a lack of oxygen.
For every expectant mother, the movements of her baby are touching and exciting moments.
. I really missed them after the birth of my children. It's nice to lie down in the evening with your husband and watch your tummy move. In the later stages, it was even possible to determine what exactly he was pushing with a hand or a leg. It's so cool!
For every expectant mother, the Pregnant Woman's Handbook
. From it you will learn everything and even a little more about your situation, what tests to take, their interpretation and much more.
I advise you to watch the useful video “Fetal movements. When should you worry?
:
Monitor your baby’s activity, remember all the baby’s movements during pregnancy, and at the slightest suspicion of decreased activity, consult a doctor.
Every woman who is going to become a mother remembers for the rest of her life the moment when she felt the first movements of her child.
If until this time pregnancy was perceived more as a source of various restrictions and a growing belly, now it becomes clear that a new life is growing inside. Any movements are perceived as the main evidence of the child’s normal functioning.
How often should a baby move?
A little man in his cozy world can be very active. 10 pushes within an hour are considered normal. At this time, the child changes position, turns, moves his arms or legs. Sometimes mothers feel rhythmic frequent tremors. These are not active movements, but ordinary hiccups. At week 25, the baby may hiccup quite often.
Doctors recommend that women, especially during their first pregnancy, keep a special calendar. This could be a notebook or notepad with notes regarding the mother’s feelings and the child’s reactions. Starting from the 21st week, it is worth writing down even what seems small and insignificant in this calendar.
For example, how a child reacts to music, to his grandmother’s voice (he has recognized his mother’s voice for a long time). This helps not only to preserve memories, but also to understand the reason for the baby’s activity or dissatisfaction.
Women should not panic if the child has not completed the required 10 movements within an hour. Even in the womb, babies need sleep. But the calm period should not last more than three hours. Pregnant women often complain that their babies are active at night. The fact is that the periods of sleep and wakefulness for mother and baby may well not coincide. The baby's body knows when to sleep and when to dance.
The expectant mother does not feel all the movements of her child. At 32 weeks, for example, the baby can perform more than 500 actions per day. Some of them are extinguished by amniotic fluid, some occur in the thick abdominal wall or placenta.
From the 32nd week, movement activity gradually decreases. Now, based on the baby’s movements, the doctor can determine its position in the uterus. With a cephalic presentation, the mother feels the main shocks above the navel, and with a breech presentation - in the lower abdomen.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, movements become stronger, but less frequent. The baby no longer has room for active action. However, movements should not disappear completely. If the mother has not felt a single movement within 12 hours, then she needs to contact a doctor.
First fetal movement
Women do not recognize the first movements as manifestations of the child’s activity; they may think that it is just a grumbling intestine or an itchy stomach. The child begins to move as early as the seventh week of intrauterine development, but at this time he is so small that it is impossible to feel his movements. Most often, the first movements can be noticed at about 20 weeks of pregnancy.
If it is a woman’s first pregnancy, then this sometimes happens at 22-24 weeks, and if it is the second or any subsequent one, then movements are felt already from 17-18 weeks. Perhaps this is also due to the fact that experienced mothers listen to themselves more clearly and already know what signs to pay attention to. This phenomenon is also explained by the fact that the uterus of a multiparous woman is itself more sensitive.
Also, the timing of the first noticeable movement of the baby also depends on the build of the expectant mother, since obese women, due to the shortcomings of their figure, can only detect fairly noticeable movements of the baby, and this is typical already at 22-25 weeks of pregnancy.
If a woman is expecting her first child, then she may simply not know what sensations to expect and what indicates the normal development of pregnancy or some abnormalities. At first, the baby’s movements bear little resemblance to kicks or blows, which are usually talked about, since there is still enough space for him and a lot of space where he can move freely. That is why if a woman thinks that something is wrong with her, it is better for her to see a doctor, but her stomach continues to grow, but there is no reason to worry.
Sometimes it happens that a delay in “moving” may be due to incorrect movements. In this case, you can consult several specialists and go through. If the mother leads an active lifestyle, then she may also not notice the movements of the fetus, since she simply does not have time to pay attention to the “light stroking” from the inside.
)
What determines the mobility of a child in the womb?
Many people believe that a baby’s character is formed in the tummy. Here's your answer: a toddler who is too active will make itself known right away. Although this is not always the case. Often, a baby’s movements are evidence not of his temperament, but of his well-being, development and health. Therefore, the task for a pregnant woman is very important: to analyze every step of her little one, learn to understand and feel it. Any deviations from your normal life together should be recorded.
Normal movements during pregnancy
There are no clear “normal” indicators. Although it is generally accepted that, starting from the 25th week of pregnancy, the baby should move at least 10 times per hour.
Fetal movement activity
The baby's peak activity in intrauterine development will occur around the beginning of the third trimester. At this time, the child has already grown enough for the mother to feel him well, but he does not yet experience any special tightness inside the abdomen.
Experts have even developed a special calendar in which expectant mothers should mark periods of activity and rest for their child. These data make it possible to assess the condition of the baby in intrauterine life and sometimes even prevent the development of certain pathologies.
Indicators of fetal motor activity - norm and deviations
During the day, the fetus inside the mother has periods of wakefulness followed by periods of sleep - motor activity varies accordingly, which is why gynecologists who monitor the development of pregnancy recommend taking into account the baby’s motor activity over a sufficiently long period of time.
The number of movements also directly depends on the duration of pregnancy - at the end of the first half, at 18-20 weeks of gestation, the first movements felt by the expectant mother are limited to 200 movements in 24 hours, while by the beginning of maternity leave (30-32 weeks) the number of movements increases up to 600.
There are factors whose influence can enhance fetal movements. These include:
- time of day - the baby is more active in the evening and at night, which in some cases prevents the expectant mother from resting normally;
- the woman’s condition – severe stress (psychological) stimulates motor activity, while the woman’s physical activity has a calming effect on the child (the baby is more active when the mother is resting);
- food intake - with a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the serum (slight hunger in matter), movements intensify. A rapid increase in glucose concentration after eating sweets has the same effect;
- – they can enhance or slow down motor activity;
- prolonged stay of the mother in an uncomfortable position.
In an hour, a woman usually feels 10-15 pushes while the baby is awake; doctors consider the absence of fetal movements for 3-4 hours in a row (during sleep) to be normal indicators.
)
When assessing the motor activity of the fetus, both the child’s excessively violent tremors and weak, rare movements are taken into account - both of these symptoms may indicate the development of acute and chronic oxygen starvation. These conditions require the mandatory attention of a doctor, and the successful outcome of pregnancy may depend on the timeliness of treatment.
In addition, slower movements may indicate, and the feeling of pain accompanying the child's kicks becomes the first manifestation.
Today in medical practice the following methods are used to assess the activity of fetal movements:
- Pearson method - a pregnant woman should count the kicks and movements of the baby for 12 hours in a row at rest. Initially, the scale marks the start time of observation (the first movement of the fetus), and then the expectant mother must count the number of movements and mark the time of the 10th movement on the graph. A normal indicator is considered to be a result when less than 60 minutes pass between the first and tenth fetal movement. If the time interval is longer, then doctors advise the woman to use any method that helps stimulate the motor activity of the fetus. In the event that none of these methods gives the expected result, an in-depth examination of the pregnant woman is necessary.
- The Cardiff method evaluates fetal movements for 12 hours in a row
, but the woman can choose the time of the study herself. The graph (table) shows the start time of counting, as well as the time of every 10th fetal movement. If a woman marks more than 10 movements on the graph during the entire observation period (12 hours), then the motor activity of the fetus is considered normal. If the expectant mother does not register 10 fetal movements during observation, an immediate consultation with a gynecologist and an in-depth examination are necessary. - The Sadowski method evaluates the movements of the fetus after the expectant mother has eaten dinner
- at rest and with an increase in glucose concentration, motor activity normally increases. It is usually advised to choose a time from 19 to 23 hours for observation. If during any hour of this time period the fetus makes 10 movements, then further observation is stopped. In the case when a woman registers less than 10 fetal movements in two hours in a row, immediate additional instrumental studies (tocography, ultrasound, Doppler) are necessary.
Before using any of the methods for assessing the motor activity of the fetus, the gynecologist prescribing such a test must tell the woman what signs she should pay attention to and if any symptoms occur, she should immediately seek help from the medical staff of the clinic (call an ambulance) ). These signs include:
- obvious change in the mode of fetal movement;
- complete absence of fetal movements felt by the woman for 6 hours in a row.
These signs indicate the development and progression of fetal hypoxia - only timely medical intervention can correct the situation and save the child. During the examination, the doctor will auscultate the fetal heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope (normal heart rate is 130-160 beats per minute).
In addition, a cardiotocographic study will be carried out in a hospital setting - simultaneous recording of fetal heart rate, motor activity and uterine tone remains one of the most reliable methods for detecting hypoxia.
Many mothers are frightened by situations when the baby is very active at first, and then remains silent for a long time. In this case, doctors advise stimulating the baby to calm your own nerves. To ensure the desired effect, you can drink a glass of milk or eat something, and then lie down to rest. Usually, the entry of new food into the mother’s body causes the baby to move actively, especially if the mother has eaten too much and the food is now putting pressure on the baby.
However, you should not rely only on your own strength. If periods of calm are repeated quite often or, conversely, the child is too active, then you need to inform your doctor about this, as this may indicate a risk of developing hypoxia and strangulation by his own umbilical cord. Gynecologists consider a normal phenomenon to be a decrease in the child’s activity before birth, as he is preparing for birth.
)
The baby begins to actively move literally in the second month of its intrauterine existence. But expectant mothers are always concerned about when they will feel the first movements, and how often the baby should make itself known throughout pregnancy.
When does fetal movement begin during pregnancy?
First you need to understand how a child’s motor activity develops in utero.
The first organ that begins to actively contract in the fetal body is its heart. It begins to form and beat already from 20-22 days from the moment of conception. The first muscle fibers are gradually formed, which initially contract independently of the nervous system, chaotically and separately. These contractions are necessary for the full formation of all muscle groups in the future.
As the nervous system begins to form and form and the fetal stage of development begins, this is the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, the nervous system already takes control of motor activity. At this point, the nervous tissue gradually takes over control of the muscle tissue and their contractions due to incoming impulses.
The first motor reflexes in the fetus are observed already at 10-12 weeks, and the fetus begins to actively move in the uterine cavity.
What can a fetus do in terms of movements at different times:
- at 9 weeks can swallow
- at 10 weeks, changes the trajectory of movement, pushing away from the walls of the uterus
- at 16 weeks, responds to sounds and voices with movement
- at 17 weeks he squints and blinks
- at 18-20 weeks, he unclenches his fingers, clenches his fists, touches the umbilical cord, touches his face, and can cover it with his hands.
Gradually, the movements of the fetus become more coordinated and clear, due to motor activity the development of the fetus occurs, both physical and neuropsychic. His movements are closely connected with the senses and perception of the surrounding world.
Why are fetal movements needed in the womb?
From the very first months of intrauterine life, a child develops ideas about ideal conditions. They can help the baby navigate the signals and stimuli coming to him. Conventionally, the fetus realizes that through movements it can change the intensity of influences on it, shield itself from loud sounds, eliminate discomfort, and receive nutrition and oxygen.
During this period, the unborn child needs a lot of nutrition and oxygen; if they are not enough, the fetus moves more actively, as if stimulating the placenta to release additional portions of blood saturated with oxygen and nutrition.
If the mother takes an uncomfortable position, squeezing large vessels along the spine, the fetus reacts to this with movements, forcing the mother to take a more comfortable position on her side. If he accidentally presses the umbilical cord loops, this also forces him to move, changing his body position to a more advantageous one.
The same can be said about the mother’s nutrition, which definitely goes to your baby. Therefore, in Mom’s Store, pay attention to proper balanced nutrition for pregnant and lactating women. These will help you eat quality food and nourish the baby in your tummy.
Note. Return of food and cosmetic products at our expense is possible only if the packaging is undamaged.
At what stage can you feel fetal movements?
A woman can feel the first real movements of the baby starting from the 16th week. It is difficult to describe the sensations precisely - they are similar to water pouring, gurgling, stroking, fish swimming, slight twitching or fluttering in the stomach, as if butterflies are fluttering inside. Gradually, the movements become more and more distinct, and after a few weeks they can be felt by others by placing their hand on the pregnant woman’s stomach.
The initial movements of the fetus will be barely noticeable, without clear localization. As pregnancy progresses, they become more clear and coordinated.
It is advisable to remember the date of the first movements so that you can tell your doctor. This date plays a role.
It must be said right away that not all expectant mothers hear their baby at this stage.
- More often, at 16-19 weeks, the first movements of women who are going to become mothers again are recorded.
- But those who carry a new life within themselves first notice the baby’s movements at 20-24 weeks.
Sometimes a little later. This is the average data. And a lot depends on the woman’s sensitivity, complexion and many other factors. Slender women and expectant mothers with developed abdominals feel movements earlier than plump ones.
Don't worry if you don't feel anything yet - for now, this is completely normal. It is likely that during your first pregnancy you will not immediately understand that it is the baby that is moving. The sensation is similar to the movement of air in the stomach. Only when they begin to repeat regularly do you realize that it is a baby tumbling!
As we have already said, this is due to the fact that all women are different, and the ability to sense movements within themselves is also different. Therefore, some expectant mothers hear movements earlier, others a little later. Everything is very individual!
We must warn you that when you first feel the baby’s movements, you don’t need to practice, since most of them are barely noticeable and only a special device can record them.
Some pregnant women say that they observe protrusion of the abdomen, which means they feel fetal movements literally from 8-10 weeks. We will have to disappoint you, all kinds of tremors, movements and “gurgling” that the expectant mother notices are nothing more than fermentation of gases in the intestines. Because under the influence of hormones, the body is rebuilt and a decrease in tone occurs in all the muscles of the female body. This also applies to intestinal loops, they increase in size and swell. The digestion process takes longer and is sometimes accompanied by similar “knocks” in the stomach.
The second reason why you may feel movement is incorrect. In the modern world, this happens extremely rarely.
Up to 16 weeks, the child weighs at most 100 grams, and reaches a length of approximately 10 cm. These sizes, as well as the baby’s strength, are simply not enough to physically exert any visible impact on the mother’s stomach. Of course, the baby touches its arms and legs, swims, frolics, tumbles and pushes off the walls of the uterus, but the mother does not feel this. This is also due to the fact that the child is reliably protected by the amniotic fluid, amniotic fluid, uterus and fat layer of the female body. Therefore, it is too early to listen to yourself and try to guess when the baby will make itself known.
When should you start listening to your feelings?
For your information, the fetus inside the uterus begins to move and move - swim in the amniotic fluid - as early as 8-9 weeks of pregnancy. “Then why doesn’t the expectant mother feel his movements at all?” - you will be surprised. The answer is very simple. The embryo at this stage is too small to be noticed.
But on the screen of an ultrasound machine, it is quite possible to observe how the baby moves and how its hand or foot touches the walls of the uterus.
Feeling the first movements of your child under your heart is a privilege only for the expectant mother. But very soon dad will be able to feel the baby pushing from inside
The twentieth week of pregnancy is considered the golden mean for detecting the first fetal movements. But already on the 16th it is quite possible to feel both the baby’s movements and his touch. And some women notice the first movements only at the 24th week. This is also considered the norm.
At the 20th week, the baby makes about 200 movements per day, and at 28-32 weeks the number of its movements reaches its maximum value - 600 in 24 hours.
At what stage of pregnancy you can first feel fetal movements depends on many factors. Among them:
- Weight and position of the fetus in the uterus. The greater the baby's body weight, the more noticeable his movements.
- Sensitivity of the mother's nerve endings. The so-called “sensitivity threshold”. Every woman has her own. Some pregnant women even claim that it was at 8-9 weeks that they began to feel some kind of tickling, slight feeling of movement in the uterus. This is quite real, although most expectant mothers are not so hypersensitive.
- The thickness of subcutaneous fat in a pregnant woman. Slender women can feel the first movements of their babies a little earlier than those who are inclined to be overweight.
- The activity of the expectant mother's intestines, which often makes it quite difficult to notice how the baby moves.
It is also believed that during the first pregnancy, a woman begins to feel fetal movements two and even three weeks later than the expectant mother who is pregnant with her second or third child.
Why is this happening?
During the first pregnancy, a woman feels fetal movements 2-3 weeks later than when she plans to become a mother again
During the first and subsequent pregnancies
Women who are preparing to become mothers for the second time (or third, or fifth) may indeed feel the first movements of the fetus a little earlier. But this is by no means because the baby in their womb begins to move earlier, or gains weight faster, or develops more intensely.
Regardless of how many times you have given birth before, the time limits for the onset of fetal movements are unchanged. This is the 16-24th week of pregnancy (depending on the physiological characteristics of your body and the characteristics of fetal development).
But experienced mothers, of course, are already well aware of what they should expect and what the sensations are like during the first movements of the fetus in their womb. Therefore, they do not confuse light stroking or barely noticeable shocks with intestinal peristalsis, but know for sure that it is their baby sending them greetings.
The expectant mother first feels the baby's movements when he is already sufficiently developed and strong. The baby itself begins to move inside the uterus much earlier
20-25 weeks of pregnancy, fetal movement
By 20 weeks, the baby’s brain and spinal cord are formed, they coordinate actions with each other, which allows the fetal movements to become regular, strong and active. It is these relatively ordered movements that the expectant mother feels.
It is important to remember that at 20-26 weeks the baby is still very tiny. Despite his height of 16-17 centimeters, he weighs about 300 grams. Of course, the baby is already more than actively tossing and turning and tumbling inside your tummy, but you still cannot control every movement of the fetus.
The baby may sleep for a long time, gaining strength, or scurry around near the back wall of the uterus. In addition, the baby still has very little strength to thoroughly push you from the inside, or turn around, touching the walls of the uterus.
The position of the child must also be taken into account. Active blows may not be so noticeable if the baby lies back forward, and her limbs are closer to the back wall of the uterus, as if “inside”.
Keep in mind the individual characteristics of the child. The innate temperament of a child is not much different from that of an adult. Look around: someone around you is a pronounced choleric person who needs to constantly move, sort out something, touch something, strive for somewhere, and someone is a thoughtful, dreamy contemplator who doesn’t want to move again. Children behave the same way.
Pregnant women describe the first movements of the fetus colorfully and unusually, like swimming fish, like fluttering butterflies, like the shimmering of water. Such sensations are remembered by expectant mothers almost forever. It is from this period that many women become fully aware of their future motherhood, and the movements of the fetus for them become a kind of signals of its well-being, tracking the rhythms of the baby and even its character by its movements.
By about five months, the baby moves “with a certain meaning”, his movements are orderly and clearly distinguishable. A fetus at 5 months moves approximately 20-50 times per hour. From this time on, movements may already depend on the time of day, external factors, the mother’s nutrition and many other conditions.
From 24 weeks of pregnancy, the movements of the fetus can be felt by others; from this period, the fetus can “inform” the mother’s well-being with its movements or react to her emotions. If the mother is excited, the fetus may freeze; if she is happy, it may move more actively and forcefully.
Fetal movements after 26 weeks of pregnancy
At this stage, the baby is still very small and still not strong enough. Therefore, when he moves closer to the back wall of the uterus, his movements can be almost imperceptible.
The size of his current home allows him to be not very close to the walls of the uterus, so if he tightly folds his arms and legs and snuggles up comfortably, you can only feel slight swaying inside. In addition, the child can sleep soundly for several hours, gaining strength, especially if you move a lot.
If the mother is tired or very nervous, the baby may also become overtired and rest for a long time.
Active fetal movement
Keep in mind that too strong, frequent fetal tremors, on the contrary, are not always a good sign. They may be a sign that the baby is not getting enough oxygen. In such situations, expectant mothers are advised to take more walks and breathe fresh air.
Expectant mothers should always dress according to the weather (not get too cold or overheat). For ease of walking, it’s worth looking at Mom’s Store. It’s important that your back doesn’t hurt during long walks, so it’s time to buy one.
Too strong, sharp and painful jolts or rare, weak movements will be dangerous. They may indicate that the child is suffering from acute or chronic hypoxia.
The nature and frequency of movements changes when the amount of amniotic fluid changes. With oligohydramnios, the fetus moves noticeably more, and its movements can cause pain. With polyhydramnios, fetal motor activity may become barely noticeable.
If the fetus moves for a long time and very actively, even to the point of pain, it is necessary without delay to inform the doctor about this fact.
Important! By the third trimester, pain may develop in the area of the liver and lower ribs; this is acceptable, since the fetus can rest its legs there.
Why does the baby move in the mother's tummy?
Already at 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, the nervous system of the embryo is mature enough to be able to conduct nerve impulses to the muscles. And the fetus in the uterus begins to move its limbs. These movements are still chaotic, and the movements are weak to be felt. But they do happen.
At 14-15 weeks, the fetus gains weight, its arms and legs take shape and acquire the familiar appearance for us, their movements become active and intense. But even now it is still quite difficult for the expectant mother to notice these movements.
But, starting from the 16-18th week, the baby is already growing and getting stronger enough for the pregnant woman to clearly begin to feel its movements. You don’t have to worry if your little one is late and in no hurry to express himself. This means that he has not yet gained the required body weight for his thrusts to become noticeable to you.
Why does the baby move in the mother's womb? Yes, because there he develops, swimming and moving in the only space available to him during this period. Why does his mother begin to feel his movements at a certain moment? Yes, because the fetus grows, its movements become more and more intense, and the little one has less and less space to move, due to the increase in his height and weight.
The baby's intrauterine life consists of periods of sleep and wakefulness, when he can study his own, albeit still very small, world and himself in it
In the second trimester of pregnancy, women can feel the baby's kicks in different parts of the abdomen. This will happen as long as the baby has enough space to swim in the amniotic fluid filling the uterine cavity, push off from the walls, turn over and rotate in all directions.
And only shortly before its birth - after the 34th week - the baby takes a cephalic presentation, thus preparing to pass through the birth canal.
But what, under the mother’s heart, can the baby do during his “free swimming”? It turns out that unborn babies have plenty to do.
They drink amniotic fluid and then hiccup. Turn the head. They play with the umbilical cord, fingering it with their hands. They twitch their legs, sleep, blink, suck their fingers. And today, thanks to the achievements of science and technology, all this can be seen with your own eyes - during a routine ultrasound of the fetus.
Just admire how rich and meaningful intrauterine life can be!
Video “What do babies do inside their mothers?”
Normal fetal movements
In this case, the word “norm” speaks of average indicators, so there is no need to worry too much if at some point you were distracted and did not notice the next movements.
So, the fruit:
- during the waking period in the mother's womb it constantly moves, it can freeze for a while if it is sleeping;
- at 20 weeks of age, moves about 200 times a day;
- at the age of 26 to 32 weeks, moves up to 600 times a day;
- after 32 weeks of pregnancy, it reduces physical activity due to its size; they amount to up to 400 per day.
It is worth remembering that the expectant mother will not feel the vast majority of these movements, but she will feel the main shocks and movements.
When purchasing from
us, we guarantee free delivery, replacement/return of products at our expense and, of course, pleasant and fast service .
The expectant mother is especially sensitive to the motor activity of the baby in her tummy. After all, with these movements the baby not only communicates that he is successfully growing and developing, but also seems to be communicating with his mother. When does fetal movement begin during pregnancy? And what should you keep in mind, what should you pay attention to when the baby starts to move? Let's figure it out.
Second and subsequent variations
Difficulties in determining the first movement during the second and subsequent pregnancies are rare. We can say that they do not exist at all. The woman already has experience and knows what to expect. The timing of the onset of movement remains the same - from 16 to 24 weeks, but a knowledgeable mother is able to feel movement 2-3 weeks earlier than the first time. Now the expectant mother will no longer confuse them with intestinal peristalsis, and will not mistake them for hungry stomach grumbling.
Mothers of many children claim that they feel the movement of their babies almost from the 12th week. Doctors are not inclined to trust these statements, but they cannot deny them either. Since the baby is already active at this time, the mother’s sensitivity may be exacerbated.
Regardless of whether it is a woman’s first pregnancy or her fifth, she worries about the development and health of her child. If the mother thinks that the baby is not moving enough or, on the contrary, is too active, then she needs to agree with the doctor on a method for counting daily movements. A significant deviation from the norm may indicate that the child is experiencing, for example, oxygen starvation.
Despite the fact that medicine knows everything about pregnancy, for a woman her condition remains a great mystery. A child meets his family while still in his mother’s womb. He distinguishes voices, perceives the intonations of conversations, understands when people are addressing him.
Tenderness, care and affection towards the expectant mother are perceived by the baby at his own expense. Remember the pleasant moments of pregnancy, spend as much time together as possible. All these touching memories can become the key to mutual understanding between parents and children in the future.
First fetal movement
Many pregnant women look forward to feeling their baby move. After all, then their connection with the child becomes stronger, since they already feel him physically. When does fetal movement begin? This question requires a fairly lengthy answer, since there are many nuances that we will try to understand.
The first movement of the fetus is observed approximately in the eighth week of pregnancy, when the baby acquires arms and legs. But the expectant mother does not feel these movements, they are still too weak, and the baby is so small that it does not reach the walls of the uterus. She will feel them much later. When depends on her “experience of the expectant mother.”
During the first pregnancy, a woman begins to notice fetal movements around the twentieth week. An expectant mother expecting her first baby is not always able to immediately understand that it is a baby moving. She may feel like it's rumbling in her stomach. But over time, she will learn to distinguish the baby’s movements and will not confuse them with anything. Mothers feel the first movements of the fetus during pregnancy in different ways. One feels like a kernel of popcorn is exploding inside her. Another is that she is being gently stroked from the inside. The third will compare the baby’s movements to the fluttering of a butterfly. The fourth will say that it’s like a small fish is swimming inside her. Fifth - that something is quietly rolling. The comparisons can be made endlessly.
During the second pregnancy, the expectant mother, who already has experience of bearing a child, feels the first movement of the fetus earlier than during the first. This happens around 18 weeks. But perhaps earlier.
Also, when a pregnant woman feels the fetus move is influenced by her complexion. Thin women feel the baby's kicks earlier and more clearly. The same applies to expectant mothers who lead an active lifestyle. If we talk about a certain average period in which a woman should feel the first movements of the baby, then this is the time from 16 to 24 weeks of pregnancy.
Be sure to record in your memory the date when you felt the baby’s first movements. You will need to tell your doctor. He will make the necessary calculations and determine the approximate.
Also, by the area of the baby’s most active movements, you can determine him in the future. For example, if the mother feels the strongest tremors in the lower abdomen, it means that the baby’s legs are there, and we are talking about breech presentation. And if active movements are observed in the diaphragm area, it means that the baby is positioned head down.
Active fetal movement - good or bad?
How active should the baby's movements be? When the baby is awake, he is constantly moving. The expectant mother feels the most frequent movements of the fetus, as a rule, in the evenings and at night, and also when she is at rest. This can be explained by the fact that when a woman moves, the baby sways inside her tummy, and it is pleasant for him. And when the expectant mother lies or sits, then the child is at rest. And he still wants to swing! And he begins to push his mother, telling her that she shouldn’t sit in one place. But over time, mutual understanding will be established between the baby and his mother, and the baby will rest with her. The child will even establish a certain routine. It will be useful for a woman to keep a diary in which she will write down when the baby moves and when she sleeps. After all, if any disruptions are noticeable in the regime, she will be able to consult a doctor in a timely manner, who will determine whether everything is in order.
On average, at 20 weeks, the baby moves about 200 times a day. The most active fetal movement is observed between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy. Then the baby moves about 600 times a day. Then the baby grows up and no longer moves so freely inside the mother, so the number of movements decreases. Of course, a woman does not feel all these movements. In general, it is normal if the expectant mother feels about 10-15 movements per hour. When the baby sleeps, he does not move. Therefore, if there is no activity for several hours (up to four), this is not a reason to panic. The baby is resting, and when he wakes up, he will start the heat again! But if the baby has not moved for about 6 hours or his overall activity has decreased significantly, you need to call an ambulance or go to an urgent appointment with a doctor. After all, this may indicate fetal hypoxia. If the baby moves very actively, you should consult a doctor. When performing somersaults inside the mother's tummy, the baby runs the risk of becoming entangled in the umbilical cord. An experienced doctor will definitely give advice, following which you can “persuad” your child to become calmer.
With his movements, the baby is also able to demonstrate his attitude to various events. For example, if his mother “treated” him to something tasty by eating lunch or a treat, the baby expresses his approval with strong kicks. But if a woman hasn’t eaten for a long time, and the baby also needs nutrients, he will also remind her that it’s time to eat by actively moving.
The baby may push hard if mommy has taken some position in which it is uncomfortable for him to be in her tummy. The baby is able to react to a stressed mother or loud noises around her either by completely stopping movements or, on the contrary, by actively moving.
Also, many babies begin to “dance” inside their mother’s tummy when she listens to music that they like. Most kids like classical calm music.
Riot in the stomach or why does the baby kick?
In some cases, excessive activity of the child may be due to the uncomfortable position of the mother’s body. If she is in a sitting position (especially when crossing and crossing her legs), compression of the uterine vessels occurs, which disrupts the flow of blood to the baby's place. The baby begins to experience a lack of oxygen and therefore moves actively. In this case, you need to change position, stand up or lie down. Such actions will help normalize blood supply. If you have taken a comfortable position, but the child still does not want to calm down, try patting the belly and talking to him. This will help him calm down.
A pregnant woman listens carefully to her feelings. She tries to remember every interesting moment of her condition. After all, a life is developing in her womb, which will very soon become an independent little person.
Some moments, such as the first guesses about pregnancy, two lines on the test, the first conversation with the future father, are more important for family history. But the first movement of the fetus must also be recognized because it is important for the most accurate determination of the date of birth. Especially during your first pregnancy.
Fetal movement begins much earlier than the woman’s body can detect it. The small embryo begins to move from the eighth week of development. However, no matter how much a woman listens to herself during pregnancy, she cannot feel this movement. The fact is that the length of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone at this time is no more than two centimeters, and its weight is only a few grams.
During the first pregnancy, the expectant mother should be attentive to her feelings, starting from the 16th week. It is at this time that you can feel the baby's first movements. The normal period for the first movement is up to 24 weeks of pregnancy.
Such a painful gap in timing can be explained as follows:
- People have different thresholds of sensitivity; during pregnancy, this affects the sensation of the first tremors of the fetus.
- A thin woman may feel movement earlier than a fat woman, but this does not mean that her baby is developing faster.
- Movement can be recognized only when the baby has gained a certain weight, and the intrauterine development of each fetus has individual characteristics.
- Women with an athletic build and strong abdominal muscles feel the baby's movements later.
- Sensitivity to movement may depend on the location of the placenta. When it is on the back wall of the uterus, the baby's movements can be felt quite early. The location of the placenta on the anterior wall of the uterus gives a pillow effect. The tremors become noticeable a little later.
During their first pregnancy, many women are prone to panic if they do not feel the first tremors at 16 weeks. But they have no reason for this. All questions of interest should be asked to the gynecologist during a scheduled visit to avoid unnecessary worries.